Engagement of Government Social Media on Facebook during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Macao
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background: The COVID-19 Outbreak in Macao
3. Literature Review
3.1. Crisis Management and COVID-19
3.2. Government Social Media and COVID-19
- RQ1: How does public’s engagement of government social media change over the course of the COVID-19 pandemic?
- RQ2: How do the categories of the content posted by a government affect the level of such engagement?
- RQ3: What are the implications for governments to use social media to engage with the public in pandemics?
4. Methods and Data Collection
4.1. Data Collection
4.2. Methods
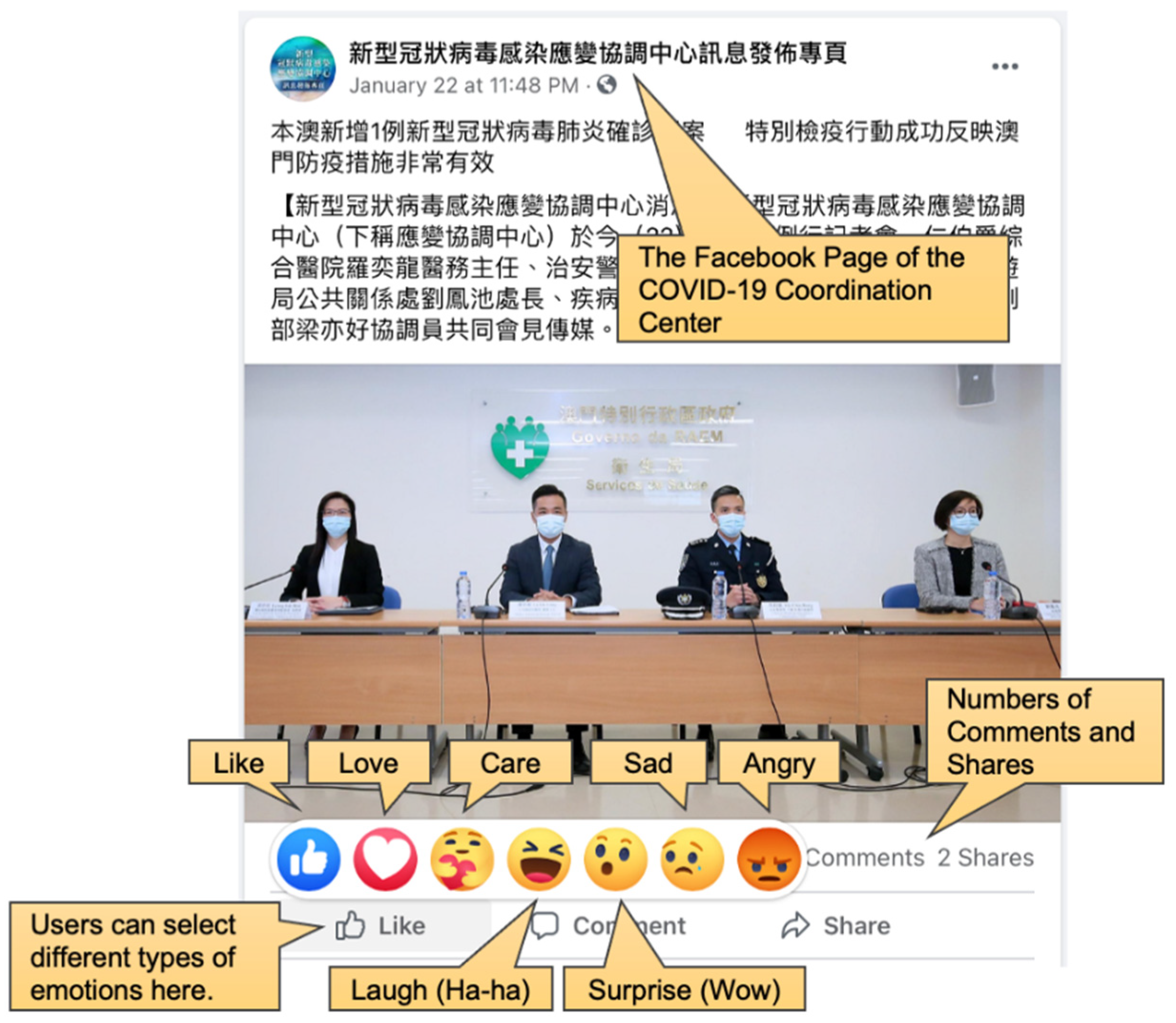
- Positive emotions: The sum of likes, love, laugh and care emotions
- Negative emotions: The sum of angry and sad emotions
- Numbers of comments
- Numbers of shares
5. Results
5.1. Data Overview
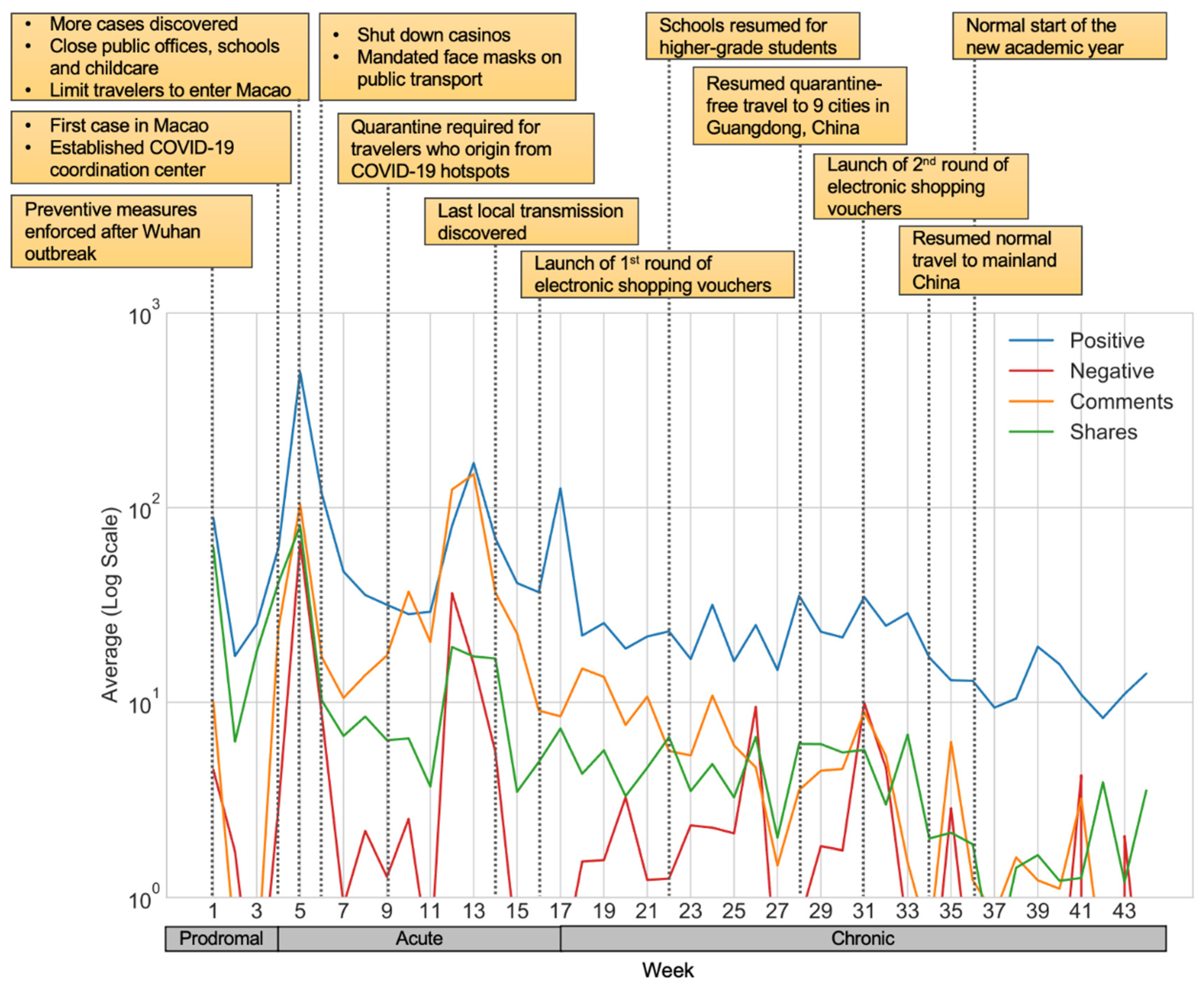
5.2. Overall Trends
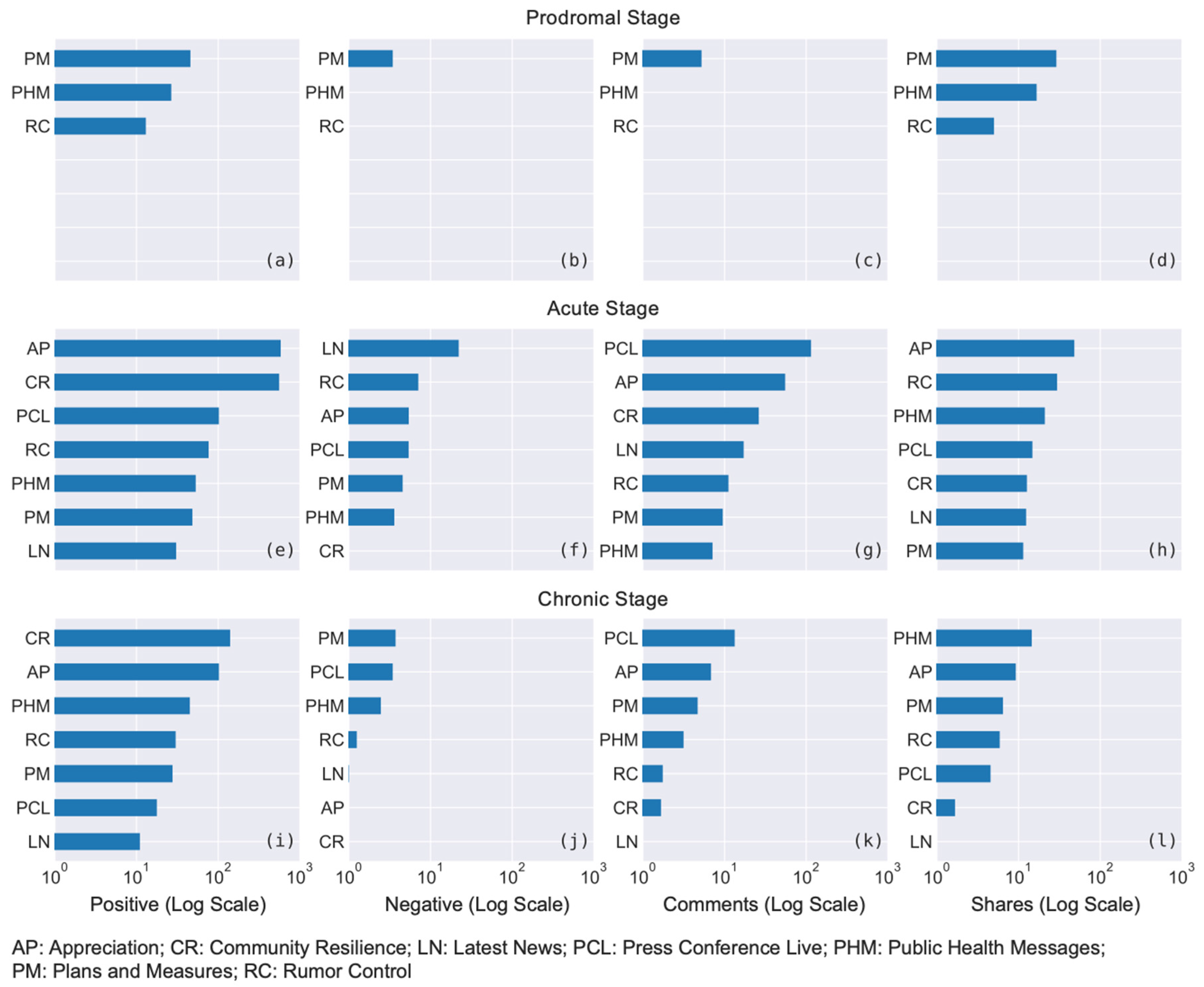
5.3. Post Categories
5.4. Trends of Post Categories
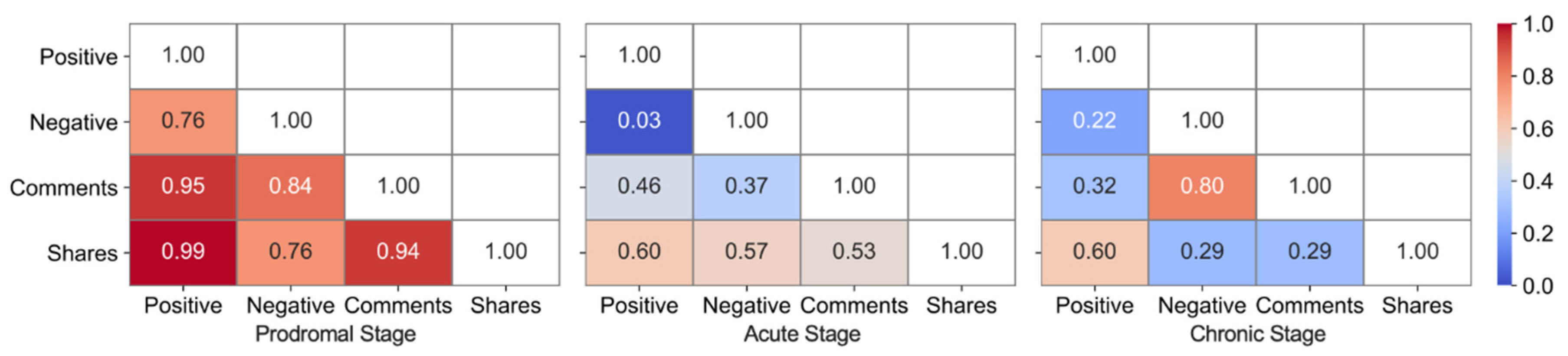
5.5. Content Analysis of Three Crisis Stages
5.5.1. Prodromal Stage
“In response to clusters of pneumonia cases of unknown cause in Wuhan, the Health Bureau started today to screen passengers on flights from Wuhan at the Macao Airport. No abnormalities were found for the time being… [Link]”(Category: Plans and Measures; posted on 1 January 2020).
“To prevent the pneumonia of unknown cause in Wuhan, everyone should pay attention to personal hygiene. When coughing or sneezing, cover your mouth and nose with a tissue. If you don’t have a tissue, you can cover your mouth and nose with your elbow or upper sleeve… [Infographic]”(Category: Public Health Messages; posted on 16 January 2020).
5.5.2. Acute Stage
“Thanks to our medical staff—In the difficult time of epidemic prevention and control, not only in hospitals, but also in health centers, blood donation centers and other locations, medical staff are doing their best to continue providing services to Macao residents. We would like to say thank you! … [Photos]”(Category: Appreciation; posted on 31 January 2020).
“In the afternoon on 4 February, [an entrepreneur] donated 100,000 surgical masks to the Macao SAR government to help prevent and control the epidemic and reduce the risk of virus transmission. [Photos]”(Category: Community Resilience; posted on 5 February 2020).
“There is a rumor that the Health Bureau will distribute face masks to Macao residents free of charge. The Coordination Center clarified again today that masks need to be purchased at their own expense… Meanwhile, we urge not to spread false information.”(Category: Rumor Control; posted on 23 January 2020).
5.5.3. Chronic Stage
“The Public Security Police Force continues to assist customs clearance and help travelers to create their health QR codes at various ports... [Photos]”(Category: Appreciation; posted on 11 July 2020).
“The Education and Youth Affairs Bureau collects epidemic prevention materials for schools donated by enterprises to schools — [a business] donated 10,000 masks, 54 disinfection supplies and 1200 chlorine disinfection tablets to Macao schools on August 10... [Photos]”(Category: Community Resilience; posted on 13 August 2020).
“In response to the epidemic, the Department of Social Work of the Macao Polytechnic Institute used their professional strengths and launched the [course name] online lecture free of charge. They, hope to provide assistance to residents who need physical and mental support... [Link]”(Category: Public Health Messages; posted on 4 May 2020).
“The Macao SAR Government appeals for washing hands, wearing masks, keep social distancing and not gathering... [Infographic]”(Category: Public Health Messages; posted on 30 July 2020).
“A person who was under quarantine in a designated hotel room left the room to another one on the same floor without authorization. The Macao Government Tourism Office has condemned the behavior and instructed hotels to strengthen the security. [Other measures…] Residents are reminded that they must abide by the relevant laws...”(Category: Plans and Measures; posted on 29 July 2020).
“New Coronavirus Infection Response Coordination Center Press Conference (27/08) [about the arrangements of backing to school] [Video]”(Category: Press Conference Live; posted on 27 August 2020).
5.6. Word Frequency Analysis of Comments
6. Discussion
6.1. Principal Results
6.2. Rumor Control
6.3. Regular Updates
6.4. Community Cohesion
6.5. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spence, P.R.; Lachlan, K.A.; Edwards, A.; Edwards, C. Tweeting Fast Matters, But Only If I Think About It: Information Updates on Social Media. Commun. Q. 2016, 64, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarocostas, J. How to Fight an Infodemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depoux, A.; Martin, S.; Karafillakis, E.; Preet, R.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Larson, H. The Pandemic of Social Media Panic Travels Faster than the COVID-19 Outbreak. J. Travel Med. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, A.; Khan, S. Coronavirus: The Spread of Misinformation. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, R.M.; Lurie, N. Social Media and Emergency Preparedness in Response to Novel Coronavirus. JAMA 2020, 323, 2011–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Miller, A.S.; Zhou, Z.; Warkentin, M. Does Government Social Media Promote Users’ Information Security Behavior towards COVID-19 Scams? Cultivation Effects and Protective Motivations. Gov. Inf. Q. 2021, 101572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dmour, H.; Masa’deh, R.; Salman, A.; Abuhashesh, M.; Al-Dmour, R. Influence of Social Media Platforms on Public Health Protection Against the COVID-19 Pandemic via the Mediating Effects of Public Health Awareness and Behavioral Changes: Integrated Model. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e19996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raamkumar, A.S.; Tan, S.G.; Wee, H.L. Measuring the Outreach Efforts of Public Health Authorities and the Public Response on Facebook During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Early 2020: Cross-Country Comparison. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e19334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Min, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Ma, X.; Evans, R. Unpacking the Black Box: How to Promote Citizen Engagement through Government Social Media during the COVID-19 Crisis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 110, 106380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernicova-Buca, M.; Palea, A. An Appraisal of Communication Practices Demonstrated by Romanian District Public Health Authorities at the Outbreak of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, M.; Lauren, E.; Hon, E.S.; Birmingham, W.C.; Xu, J.; Su, S.; Hon, S.D.; Park, J.; Dang, P.; Lipsky, M.S. Social Network Analysis of COVID-19 Sentiments: Application of Artificial Intelligence. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e22590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Mehta, V.; Valkunde, T.; Moustakas, E. Topics, Trends, and Sentiments of Tweets About the COVID-19 Pandemic: Temporal Infoveillance Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e22624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Vidal-Alaball, J.; Downing, J.; López Seguí, F. COVID-19 and the 5G Conspiracy Theory: Social Network Analysis of Twitter Data. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Fan, J.; Basnyat, I.; Hu, B. Online Health Information Seeking Using “#COVID-19 Patient Seeking Help” on Weibo in Wuhan, China: Descriptive Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e22910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Cheng, S.; Yu, X.; Xu, H. Chinese Public’s Attention to the COVID-19 Epidemic on Social Media: Observational Descriptive Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e18825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngai, C.S.B.; Singh, R.G.; Lu, W.; Koon, A.C. Grappling With the COVID-19 Health Crisis: Content Analysis of Communication Strategies and Their Effects on Public Engagement on Social Media. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e21360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Q.; Yuan, J.; Dong, M.; Yang, L.; Fielding, R.; Lam, W.W.T. Public Engagement and Government Responsiveness in the Communications About COVID-19 During the Early Epidemic Stage in China: Infodemiology Study on Social Media Data. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e18796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.-M.; Shieh, G.-J.; Wu, S.-L.; Sheu, W.H.-H. Use of Facebook by Academic Medical Centers in Taiwan During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Observational Study. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2020, 22, e21501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Sohn, D.; Choi, S.M. Cultural Difference in Motivations for Using Social Network Sites: A Comparative Study of American and Korean College Students. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Pang, P.C.-I.; Si, Y.-W. Roles of Information Propagation of Chinese Microblogging Users in Epidemics: A Crisis Management Perspective. Internet. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.-L.; Meng, J. Media Frames across Stages of Health Crisis: A Crisis Management Approach to News Coverage of Flu Pandemic. J. Contingencies Crisis Manag. 2016, 24, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, S. Crisis Management: Planning for the Inevitable; American Management Association: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Loi, K.I.; Lei, W.S.; Lourenço, F. Understanding the Reactions of Government and Gaming Concessionaires on COVID-19 through the Neo-Institutional Theory – The Case of Macao. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieng, S.M.; Cheong, I.H. An Overview of Epidemiology of COVID-19 in Macau S.A.R. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.-S.; Zheng, Z.; Gong, R. A Study on Crisis Management of Typhoon Hato in Macau. Journal. Mass Commun. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Pneumonia of Unknown Cause—China. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/ (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Macao SAR Government Health Bureau. Information about Confirmed Diagnosed Patients with Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) in Macau SAR. Available online: https://www.ssm.gov.mo/apps1/PreventCOVID-19/en.aspx#clg17046 (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Lo, I.L.; Lio, C.F.; Cheong, H.H.; Lei, C.I.; Cheong, T.H.; Zhong, X.; Tian, Y.; Sin, N.N. Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Shedding in Clinical Specimens and Clinical Characteristics of 10 Patients with COVID-19 in Macau. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, G. The Impact of the Coronavirus Outbreak on Macao. From Tourism Lockdown to Tourism Recovery. Curr. Issues Tour. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macao SAR Government Health Bureau. Special Webpage against Epidemics. Available online: https://www.ssm.gov.mo/apps1/PreventCOVID-19/en.aspx#clg17458 (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Seeger, M.W.; Sellnow, T.L.; Ulmer, R.R. Communication, Organization, and Crisis. Ann. Int. Commun. Assoc. 1998, 21, 231–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.; Pfarrer, M.D.; Short, C.E.; Coombs, W.T. Crises and Crisis Management: Integration, Interpretation, and Research Development. J. Manag. 2016, 43, 1661–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crandall, W.; Parnell, J.A.; Spillan, J.E. Crisis Management: Leading in the New Strategy Landscape, 2nd ed.; SAGE: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-4129-9168-1. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.; Zhong, K. Classification of Types, Levels and Stages for Emergencies: Managerial Foundation of Government Emergency Response System. Chin. Public Adm. 2005, 2, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, H.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Osman, S.; Farooq, Z.; Rocklöv, J. Only Strict Quarantine Measures Can Curb the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak in Italy, 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Criteria for Declaring the End of the Ebola Outbreak in Guinea, Liberia or Sierra Leone. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/disease/ebola/declaration-ebola-end/en/ (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Wirtz, B.W.; Daiser, P.; Mermann, M. Social Media as a Leverage Strategy for Open Government: An Exploratory Study. Int. J. Public Adm. 2018, 41, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.-J.; Hwang, H.; Kim, J.H. Can Social Media Increase Government Responsiveness? A Case Study of Seoul, Korea. Gov. Inf. Q. 2018, 35, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, E.; Kleinhans, R. Beyond Technology: Identifying Local Government Challenges for Using Digital Platforms for Citizen Engagement. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 40, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro-de-Rosario, A.; Sáez-Martín, A.; del Carmen Caba-Pérez, M. Using Social Media to Enhance Citizen Engagement with Local Government: Twitter or Facebook? New Media Soc. 2016, 20, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, N.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C. Why Do Citizens Participate on Government Social Media Accounts during Crises? A Civic Voluntarism Perspective. Inf. Manag. 2021, 58, 103286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Online Engagement in Social Media: A Cross-Cultural Comparison. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2019, 97, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Menendez, A.; Saura, J.R.; Filipe, F. The Importance of Behavioral Data to Identify Online Fake Reviews for Tourism Businesses: A Systematic Review. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2019, 5, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Menendez, A.; Correia, M.B.; Matos, N.; Adap, C. Understanding Online Consumer Behavior and EWOM Strategies for Sustainable Business Management in the Tourism Industry. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.C.-I.; Liu, L. Why Do Consumers Review Doctors Online? Topic Modeling Analysis of Positive and Negative Reviews on an Online Health Community in China. In Proceedings of the 53rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 7 January 2020; pp. 705–714. [Google Scholar]
- Limaye, R.J.; Sauer, M.; Ali, J.; Bernstein, J.; Wahl, B.; Barnhill, A.; Labrique, A. Building Trust While Influencing Online COVID-19 Content in the Social Media World. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e277–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.C.-I.; Chang, S.; Verspoor, K.; Clavisi, O. The Use of Web-Based Technologies in Health Research Participation: Qualitative Study of Consumer and Researcher Experiences. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Qiao, R.; Shao, G.; Chen, H. Research on Chinese Social Media Users’ Communication Behaviors during Public Emergency Events. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X. Using Social Media to Mine and Analyze Public Opinion Related to COVID-19 in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Gao, T.-L.; Duan, W.; Tsoi, K.K.; Wang, F.-Y. Characterizing the Propagation of Situational Information in Social Media During COVID-19 Epidemic: A Case Study on Weibo. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2020, 7, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Sarkar, T.; Khan, S.H.; Mostofa Kamal, A.-H.; Hasan, S.M.M.; Kabir, A.; Yeasmin, D.; Islam, M.A.; Amin Chowdhury, K.I.; Anwar, K.S.; et al. COVID-19–Related Infodemic and Its Impact on Public Health: A Global Social Media Analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macao Association for Internet Research. Internet Usage Trends in Macao 2020; MAIR: Macao, China, 2020; ISBN 978-99965-852-3-4. [Google Scholar]
- Government Information Bureau. Government Information Bureau to Launch a Facebook Page. Available online: https://www.gov.mo/en/news/66291/ (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Erlingsson, C.; Brysiewicz, P. A Hands-on Guide to Doing Content Analysis. Afr. J. Emerg. Med. 2017, 7, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Vidal-Alaball, J.; Lopez Segui, F.; Moreno-Sánchez, P.A. A Social Network Analysis of Tweets Related to Masks during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Method Approaches, 4th ed.; International Student Edition; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4522-7461-4. [Google Scholar]
- Strauss, A.; Corbin, J. Basics of Qualitative Research Techniques; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, K.; Dowell, A.; Nie, J.-B. Attempting Rigour and Replicability in Thematic Analysis of Qualitative Research Data; a Case Study of Codebook Development. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2019, 19, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, X.; Sun, X. PKUSEG: A Toolkit for Multi-Domain Chinese Word Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.11455. [Google Scholar]
- Bird, S.; Klein, E.; Loper, E. Natural Language Processing with Python; O’Reilly Media Inc.: Newton, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, P.C.-I.; McKay, D.; Chang, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L. Privacy Concerns of the Australian My Health Record: Implications for Other Large-Scale Opt-out Personal Health Records. Inf. Process. Manag. 2020, 57, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krippendorff, K. Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Salkind, N. Encyclopedia of Research Design; SAGE Publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2010; ISBN 978-1-4129-6128-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, P.C.-I.; Chang, S.; Pearce, J.; Verspoor, K. Online Health Information Seeking Behaviour: Understanding Different Search Approaches. In Proceedings of the Pacific Asia Conference on Information Systems 2014 (PACIS 2014), Chengdu, China, 24 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, N.H.L.; Chu, D.K.W.; Shiu, E.Y.C.; Chan, K.-H.; McDevitt, J.J.; Hau, B.J.P.; Yen, H.-L.; Li, Y.; Ip, D.K.M.; Peiris, J.S.M.; et al. Respiratory Virus Shedding in Exhaled Breath and Efficacy of Face Masks. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, C.J.; Li, Y.-C.; Malwade, S.; Syed-Abdul, S. COVID-19 Preventive Measures Showing an Unintended Decline in Infectious Diseases in Taiwan. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.P.T.; Hoang, T.D.; Tran, V.T.; Vu, C.T.; Siewe Fodjo, J.N.; Colebunders, R.; Dunne, M.P.; Vo, T.V. Preventive Behavior of Vietnamese People in Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, P.; Barnett, J.; Bigdeli, A.Z.; Sams, S. Social Media in Emergency Management: Twitter as a Tool for Communicating Risks to the Public. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2016, 111, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.-W. COVID-19 Pandemic: Impact and Implications for Macau Casinos. Gaming Law Rev. 2020, 24, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, I.K.W.; Wong, J.W.C. Comparing Crisis Management Practices in the Hotel Industry between Initial and Pandemic Stages of COVID-19. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2020, 32, 3135–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Torres, M.J.; Almansa-Martínez, A.; Chamizo-Sánchez, R. Infodemic and Fake News in Spain during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ABC News Daniel Andrews Is Finally Taking a Day off. Is This a Sign Things Are Looking up for Victoria? Available online: https://www.abc.net.au/news/2020-10-30/daniel-andrews-takes-day-off-after-120-covid-media-briefings/12831460 (accessed on 12 June 2020).
- Lai, C.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Wang, Y.-H.; Hsueh, S.-C.; Ko, W.-C.; Hsueh, P.-R. Global Epidemiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Disease Incidence, Daily Cumulative Index, Mortality, and Their Association with Country Healthcare Resources and Economic Status. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, P.C.-I.; Chang, S.; Verspoor, K.; Pearce, J. Designing Health Websites Based on Users’ Online Information Seeking Behaviours: A Mixed-Method Observational Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2016, 18, e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, V.-P.; Pham, T.-H.; Ho, M.-T.; Nguyen, M.-H.; P Nguyen, K.-L.; Vuong, T.-T.; Nguyen, H.-K.T.; Tran, T.; Khuc, Q.; Ho, M.-T.; et al. Policy Response, Social Media and Science Journalism for the Sustainability of the Public Health System Amid the COVID-19 Outbreak: The Vietnam Lessons. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, S. Analysis of Macao Community Legal System: Centers on Relationship of Government and Community. J. China Natl. Sch. Adm. 2006, 6, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, Y. Public Voice via Social Media: Role in Cooperative Governance during Public Health Emergency. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Policy Category | Measures and Actions |
|---|---|
| Disposition of government | Established the COVID-19 Coordination Center Increased the alert level of public emergencies Improved public education about the virus Global procurement of face masks |
| Prevention and control | Strengthened health screening and quarantine Reduced social gatherings Shut down casinos, businesses and entertainment premises Suspended classes in schools and universities Mandated the use of face masks on public transport Set up an online personal health declaration system (Health QR Code) |
| Medical support | Suspended non-critical medical services Provided support to front-line medical staff Provided mental health assistance |
| Border control and immigration | Limited travelers’ entry to Macao Suspended self-service customs clearance Shortened customs clearance time to avoid queues and allow social distancing |
| Business support | Established a special anti-epidemic assistance fund Launched economic assistance measures Tax reduction and exemption Provided subsidized employee training |
| Livelihood support | Issued electronic shopping vouchers Subsidized water and electricity bills Monitored the prices of food and other daily necessities |
| Crisis Stage | Definition | Start of Stage | End of Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prodromal | This comes before the actual crisis, and its main focus is to prevent or delay the crisis from happening. | The start of the current analysis | The first confirmed COVID-19 case |
| Acute | This stage follows the prodromal stage. It is signaled by the sudden onset of the event, and the event often develops rapidly. The main goals lie in controlling the crisis and avoiding its deterioration. | The first confirmed case | 28 days after the last case of local transmissions a |
| Chronic | The crisis situation begins to ease in this stage and its appearance is less dramatic in appearance. As such, the focuses should be on relieving controlling measures, reducing damage and initiating the steps towards recovery. | The first day after the acute period | The end of the current analysis |
| Crisis Resolution | The crisis is over in this stage. Learnings should be synthesized for preparing the responses to future crises and the society/organization is returning to normal. | Not applicable (since the world is still in the middle of the pandemic at the time of writing, this stage is not applicable). | |
| Category | Concepts and Related Literature |
|---|---|
| Plans and Measures | Disposition of government [48] Government’s handling of crisis [9] Preventive measures [8] Government response [12,49] Policies, guidelines and official actions [17] Notifications and measures been taken [50] Control measures [51] |
| Public Health Messages | Civic skills [41] Caring of self-interest [48] Education [18] Disease prevention [16] Popularization of prevention and treatment [49] |
| Rumor Control | Rumor Control [41] Falsehood correction [8] Counter-rumor [50] |
| Latest News | Latest news [9] New cases of COVID-19 [15] |
| Appreciation | Appreciation of front-line workers [9] Appreciation [8] |
| Community Resilience | Donations of money, goods or services [50] Making donations [49] |
| Crisis Stage | Date Range | Week Range (of Calendar Year 2020) |
|---|---|---|
| Prodromal | 1 January 2020–21 January 2020 | Week 1–4 |
| Acute | 22 January 2020–25 April 2020 | Week 4–17 |
| Chronic | 26 April 2020–31 October 2020 | Week 18–44 |
| Prodromal (N = 18) | Acute (N = 481) | Chronic (N = 1165) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metrics | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max | Mean | SD | Min | Max |
| Positive Emotion | 35.39 | 60.56 | 5 | 262 | 99.59 | 372.89 | 0 | 4504 | 20.29 | 42.48 | 0 | 471 |
| Negative Emotion | 1.72 | 4.40 | 0 | 16 | 9.64 | 66.54 | 0 | 1267 | 2.24 | 23.01 | 0 | 667 |
| Comments | 2.72 | 9.36 | 0 | 40 | 34.83 | 124.30 | 0 | 2000 | 3.80 | 20.18 | 0 | 459 |
| Shares | 22.17 | 50.21 | 0 | 208 | 15.91 | 47.01 | 0 | 577 | 3.82 | 14.28 | 0 | 246 |
| Name | Definition | Count | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plans and Measures | Government’s plans and measures to combat the pandemic | 542 | “Starting from 0:00 h on 19 March all foreign worker ID card holders will be prohibited from entering Macau, except for those with a resident status of Mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan… [Infographic]” |
| Public Health Messages | Messages for educating the public, persuading them to change behavior and preventing COVID-19 infection | 99 | “The representative of the Health Bureau explained that aerosol transmission is not equivalent to air transmission; aerosols are small droplets formed when patients cough, sneeze or talk to people…” |
| Rumor Control | Posts for rumor control or clarifying untrue information | 22 | “Regarding rumors on the internet that influenza vaccination can prevent COVID-19, the Health Bureau emphasized that the rumors are not true and appealed the public not to believe or spread false information…” |
| Latest News | Latest update about the pandemic, including regular updates of numbers | 709 | “In the past 24 h, there have been no new confirmed cases of COVID-19 infection in Macao, and a total of 10 confirmed cases have been maintained. All of which are in a mild condition. As of 3 pm, there are a total of 316 suspected cases in Macao...” |
| Appreciation | Appreciation message to front-line workers and public staff for controlling the pandemic | 44 | “In response to the anticipated increase in tourists, all relevant departments in Macao have made specific arrangements, strengthened epidemic preventive work and passenger management. Let’s have a look at what they do and thank them for their efforts.” |
| Community Resilience | Actions (e.g., donations of resources) taken by communities (e.g., non-government organizations and individuals) to combat the pandemic | 17 | “ [The name of an enterprise] donated 4000 L of disinfectant alcohol to the SAR government…” |
| Press Conference Live | Live video of the government’s press conferences about the pandemic and its latest development | 231 | “Press conference on the latest outbreak of COVID-19 and announcements of various prevention and control measures in Macao [Date] [Video]” |
| Rank | Prodromal Stage | Acute Stage | Chronic Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | achieve (3) | question (379) | resident (109) |
| 2 | good (2) | Hong Kong (340) | Hong Kong (88) |
| 3 | prevent (2) | border closure (338) | children (79) |
| 4 | measure (2) | Macanese (295) | student (63) |
| 5 | border entry (2) | border entry (279) | quarantine (59) |
| 6 | well (2) | quarantine (276) | why (59) |
| 7 | quarantine (2) | cheer up (265) | question (55) |
| 8 | Gongbei (2) | appreciate (257) | teacher (45) |
| 9 | check (2) | Portuguese reporter (252) | face mask (43) |
| 10 | not bad (2) | reporter (249) | bus (40) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, P.C.-I.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, W.; Chan, K.S. Engagement of Government Social Media on Facebook during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Macao. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073508
Pang PC-I, Cai Q, Jiang W, Chan KS. Engagement of Government Social Media on Facebook during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Macao. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(7):3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073508
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Patrick Cheong-Iao, Qixin Cai, Wenjing Jiang, and Kin Sun Chan. 2021. "Engagement of Government Social Media on Facebook during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Macao" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 7: 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073508
APA StylePang, P. C.-I., Cai, Q., Jiang, W., & Chan, K. S. (2021). Engagement of Government Social Media on Facebook during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Macao. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(7), 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18073508







