Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them
Abstract
1. Introduction
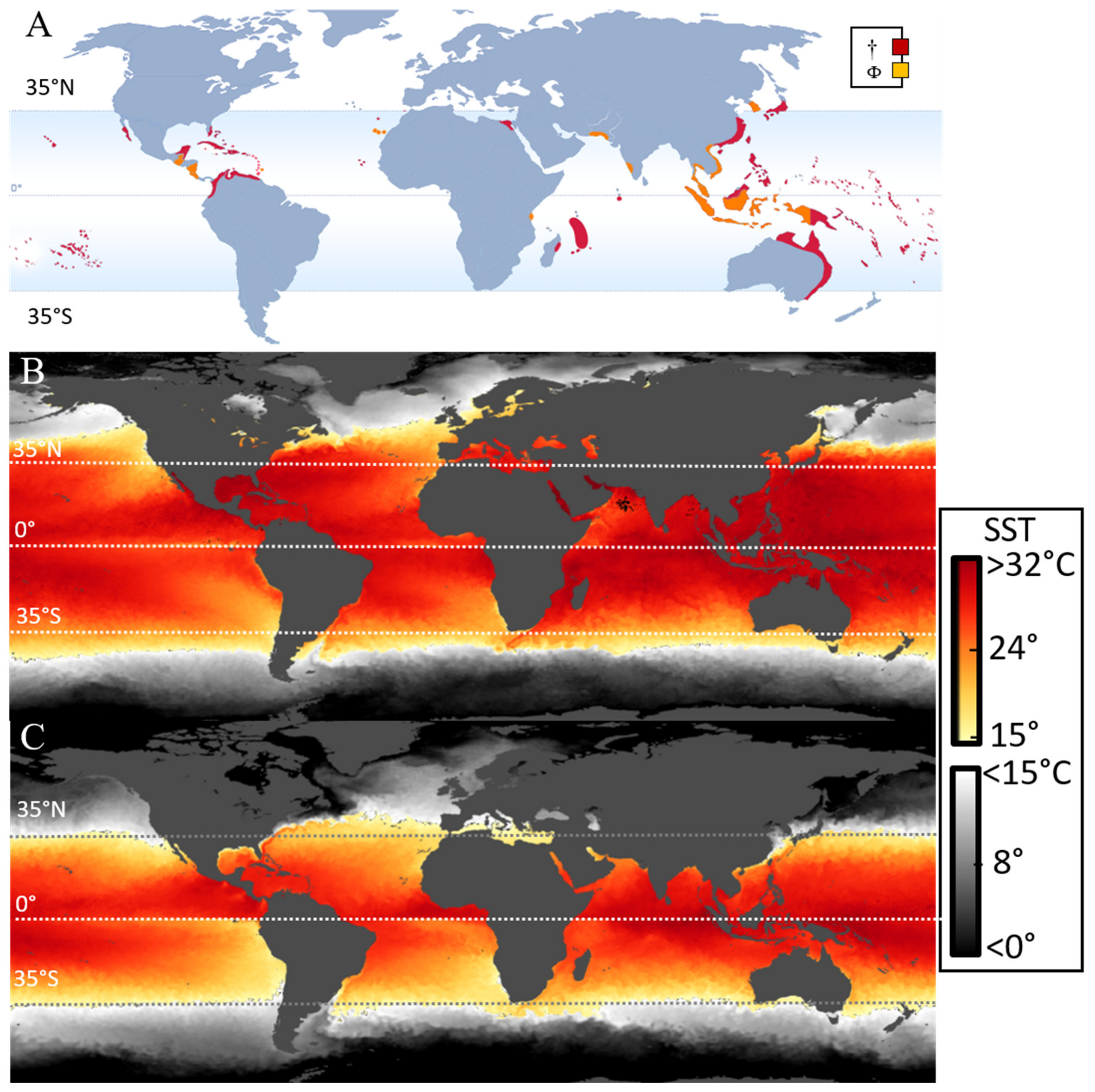
1.1. Toxin Production
1.2. CTX Vectors
1.3. Human Health: Ciguatera Diagnosis, Epidemiology, and Traceback Investigation
1.4. Modern Testing and Investigation Capabilities
1.5. Anthropogenic Impacts
1.6. Outlook- Risks and Opportunities
2. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Economic Forum. The Global Risks Report 2020. In World Economic Forum, Geneva, Switzerland, Insight Report; World Economic Forum: Cologny/Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Glibert, P.M.; Burford, M.A. Globally changing nutrient loads and harmful algal blooms: Recent advances, new paradigms, and continuing challenges. Oceanography 2017, 30, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Global Warming of 1.5 °C. An IPCC Special Report on the Impacts of Global Warming of 1.5 °C Above Pre-Industrial Levels and Related Global Greenhouse Gas Emission Pathways, in the Context of Strengthening the Global Response to the Threat of Climate Change, Sustainable Development, and Efforts to Eradicate Poverty; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bindoff, N.; Cheung, W.W.; Kairo, J.; Arstegui, J.; Guinder, V.; Hallberg, R.; Hilmi, N.; Jiao, N.; Karim, M.; Levin, L.; et al. Changing ocean, marine ecosystems, and dependent communities. In IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Pörtner, D.C.R.H.-O., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Nicolai, A.O.M., Petzold, J., Rama, B., et al., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; in press. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; Fisheries Department Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Connell, J.; Lowitt, K. Food Security in Small Island States; Springer: Singapore, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, J. Dangerous climate change in the Pacific Islands: Food production and food security. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, C.; Macfadyen, G.; Allison, E.H. Increasing the Contribution of Small-Scale Fisheries to Poverty Alleviation and Food Security; Food & Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ghina, F. Sustainable Development in Small Island Developing States. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2003, 5, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food Drug Administration. Guidance for Industry: Purchasing Reef Fish Species Associated with the Hazard of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/guidance-industry-purchasing-reef-fish-species-associated-hazard-ciguatera-fish-poisoning (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; et al. An Updated Review of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Clinical, Epidemiological, Environmental, and Public Health Management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydney Fish Market. Sydney Fish Market Seafood Handing Guidelines. Available online: https://www.sydneyfishmarket.com.au/Seafood-Trading/Quality/Food-Safety (accessed on 6 October 2020).
- Skinner, M.P.; Brewer, T.D.; Johnstone, R.; Fleming, L.E.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in the Pacific Islands (1998 to 2008). PloS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Socioeconomic impacts and management ciguatera in the Pacific. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- McCubbin, S.G.; Pearce, T.; Ford, J.D.; Smit, B. Social-ecological change and implications for food security in Funafuti, Tuvalu. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO; WHO. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning; Food Safety and Quality: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, S.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Vandersea, M.W.; Tester, P.A. Growth of eight Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae) species: Effects of temperature, salinity and irradiance. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Liefer, J.D.; Robertson, A.; Kulis, D.; Smith, T.B.; Parsons, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Influence of Environmental Variables on Gambierdiscus spp.(Dinophyceae) Growth and Distribution. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure of CTX3C, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1975–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Wang, Z.; Ponton, D.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Growth and toxin production in the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) in culture. Toxicon 2010, 56, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. Gambierol: A new toxic polyether compound isolated from the marine dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Suzuki, T.; Matsushima, R.; Nagae, M.; Toyohara, Y.; Satake, M.; Oshima, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yasumoto, T. Gambieroxide, a novel epoxy polyether compound from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus GTP2 strain. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 10299–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morohashi, A.; Satake, M.; Nagai, H.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. The Absolute Configuration of Gambieric Acids A–D, Potent Antifungal Polyethers, Isolated from the Marine Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 8995–9001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, I.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Alfonso, C.; Calabro, K.; Alonso, E.; Sánchez, J.A.; Alfonso, A.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Gambierone, a Ladder-Shaped Polyether from the Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2392–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C.; Rhodes, L.L.; Puddick, J.; Harwood, D.T.; Larsson, M.E.; Doblin, M.A.; Leung, P.; Yan, M.; et al. The role of 44-methylgambierone in ciguatera fish poisoning: Acute toxicity, production by marine microalgae and its potential as a biomarker for Gambierdiscus spp. Harmful Algae 2020, 97, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J. Purification and characterisation of large and small maitotoxins from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Nat. Toxins 1994, 2, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boente-Juncal, A.; Álvarez, M.; Antelo, Á.; Rodríguez, I.; Calabro, K.; Vale, C.; Thomas, O.P.; Botana, L.M. Structure Elucidation and Biological Evaluation of Maitotoxin-3, a Homologue of Gambierone, from Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2019, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Naoki, H.; Iwashita, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Sasaki, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Yasumoto, T. Structure of maitotoxin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 2060–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisapia, F.; Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Lhaute, K.; Gaiani, G.; Ferron, P.-J.; Fessard, V.; Fraga, S.; Nascimento, S.M.; Litaker, R.W.; et al. Maitotoxin-4, a novel MTX analog produced by Gambierdiscus excentricus. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Naoki, H.; Matsunaga, S.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structure and Partial Stereochemical Assignments for Maitotoxin, the Most Toxic and Largest Natural Non-Biopolymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 7098–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Murata, M.; Oshima, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Yasumoto, T. Some chemical properties of maitotoxin, a putative calcium channel agonist isolated from a marine dinoflagellate. J. Biochem. 1988, 104, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Gillespie, N.C. Toxicity of Australian and French Polynesian strains of Gambierdiscus Toxicus (Dinophyceae) grown in culture: Characterization of a new type of maitotoxin. Toxicon 1990, 28, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, G.; Papiol, G.; Rhodes, L.; Harwood, D.; Selwood, A.; Jerrett, A. A feeding study to probe the uptake of Maitotoxin by snapper (Pagrus auratus). Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.M.; Fukui, M.; Cruchet, P.; Yasumoto, T. Progress on chemical knowledge of ciguatoxins. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yogi, K.; Sakugawa, S.; Oshiro, N.; Ikehara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of Toxins Involved in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in the Pacific by LC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing Distinct Regional and Species Characteristics in Fish and Causative Alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, Y.L.; Wai, T.-C.; Murphy, M.B.; Chan, W.H.; Wu, J.J.; Lam, J.C.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K. Pacific Ciguatoxins in Food Web Components of Coral Reef Systems in the Republic of Kiribati. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 14070–14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.H.; Mak, Y.L.; Wu, J.J.; Jin, L.; Sit, W.H.; Lam, J.C.W.; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Spatial distribution of ciguateric fish in the Republic of Kiribati. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.P.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean islands and western Atlantic. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 168, 99–141. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikehara, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Yasumoto, T. Biooxidation of Ciguatoxins Leads to Species-Specific Toxin Profiles. Toxins 2017, 9, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusetani, N. Marine toxins: An overview. In Marine Toxins as Research Tools; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.i.; Darius, H.T.; Quod, J.P.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatera poisonings: A global review of occurrences and trends. Harmful Algae 2020, 101873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.i.; Ung, A.; Cruchet, P.; Revel, T.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Varney, P.; Laurent, V.; Hess, P.; et al. Evidence for the Range Expansion of Ciguatera in French Polynesia: A Revisit of the 2009 Mass-Poisoning Outbreak in Rapa Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxins 2020, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanna, L.; Khatiwala, S.; Gregory, J.M.; Ison, J.; Heimbach, P. Global reconstruction of historical ocean heat storage and transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffoley, D.; Baxter, J.M. Explaining Ocean Warming: Causes, Scale, Effects and Consequences; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2016; p. 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobler, C.J. Climate Change and Harmful Algal Blooms: Insights and perspective. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tester, P.A.; Litaker, R.W.; Berdalet, E. Climate change and harmful benthic microalgae. Harmful Algae 2020, 91, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallegraeff, G.M.; Anderson, D.M.; Cembella, A.D. Manual on Harmful Marine Algae; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003; p. 794. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Arellano, J.L.; Luzardo, O.P.; Brito, A.P.; Cabrera, M.H.; Zumbado, M.; Carranza, C.; Angel-Moreno, A.; Dickey, R.W.; Boada, L.D. Ciguatera fish poisoning, Canary Islands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1981–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.A.; Feldman, R.L.; Nau, A.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Wayne Litaker, R. Ciguatera fish poisoning and sea surface temperatures in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. Toxicon 2010, 56, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Global impact of ciguatoxins and ciguatera fish poisoning on fish, fisheries and consumers. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goater, S.; Derne, B.; Weinstein, P. Critical Issues in the Development of Health Information Systems in Supporting Environmental Health: A Case Study of Ciguatera. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A.; Kunkel, K.E.; Moore, S.K.; Litaker, R.W. Effects of ocean warming on growth and distribution of dinoflagellates associated with ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean. Ecol. Model. 2015, 316, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalachkov, Y.; Hildner, M.; Polomac, N.; Jahnke, K.; Wagner, M.; Baudrexel, S. Cytotoxic edema affecting distinct fiber tracts in ciguatera fish poisoning. Neurology 2019, 92, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Biology Processing Group. MODIS Terra Level 3 SST Thermal IR Monthly 4km Daytime v2014; NASA Physical Oceanography DAAC: OBPG, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Ocean Biology Processing Group. MODIS Aqua Level 3 SST Thermal IR Monthly 4km Daytime v2014. NASA Physical Oceanography DAAC: OBPG, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocean Biology Processing Group. MODIS Aqua Level 3 SST Thermal IR Monthly 9km Daytime v2014. NASA Physical Oceanography DAAC: OBPG, Goddard Space Flight Center: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau Of Meteorology. GHRSST Level 4 GAMSSA_28km Global Foundation Sea Surface Temperature Analysis v1.0 dataset (GDS2); NASA Physical Oceanography DAAC, Australian Bureau of Meteorology: Melbourne, Australia, 2019. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food Drug Administration. Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance Fourth Edition. March 2020; p. 498. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/80637/download (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T.; Ung, A.; Fouc, M.T.; Revel, T.; Cruchet, P.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ciguatera risk management in French Polynesia: The case study of Raivavae Island (Australes Archipelago). Toxicon 2010, 56, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, H.; Murray, S.; Zammit, A.; Edwards, A. Management of Ciguatoxin Risk in Eastern Australia. Toxins 2017, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.K. Ciguatoxic potential of Brown-Marbled Grouper in relation to fish size and geographical origin. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quod, J.P.; Turquet, J. Ciguatera in Reunion Island (SW Indian Ocean): Epidemiology and clinical patterns. Toxicon 1996, 34, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Vandersea, M.; Chamero-Lago, D.; Gómez-Batista, M.; Hernández-Albernas, J.I.; Chomérat, N.; Rojas-Abrahantes, G.; Litaker, R.W.; Tester, P.; et al. Ciguatoxin Occurrence in Food-Web Components of a Cuban Coral Reef Ecosystem: Risk-Assessment Implications. Toxins 2019, 11, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Anglada, L.; Gould, C.; Thur, S.; Lape, J.; Backer, L.; Bricker, S.; Clyde, T.; Davis, T.; Dortch, Q.; Duriancik, L.; et al. Harmful Algal Blooms and Hypoxia in the United States: A Report on Interagency Progress and Implementation; National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration; Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- BfR. Feed and Food Safety in Times of Global Production and Trade; German Federal Institute for Risk Assessment: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Banas, N.; Bresnan, E.; Burford, M.A.; Davidson, K.; Gobler, C.J.; Karlson, B.; Kudela, R.; Lim, P.; Mackenzie, L. GlobalHAB (IOC-UNESCO and SCOR): International Coordination for Sound Knowledge of HABs to Manage their Impacts; Oceanography Soc. Inc.: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Berdalet, E.; Tester, P.A.; Chinain, M.; Fraga, S.; Lemée, R.; Litaker, W.; Penna, A.; Usup, G.; Vila, M.; Zingone, A. Harmful algal blooms in benthic systems: Recent progress and future research. Oceanography 2017, 30, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, D. The Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms (ECOHAB): A National Research Agenda; Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution: Woods Hole, MA, USA, 1995; p. 66. [Google Scholar]
- Kudela, R.M.; Raine, R.; Pitcher, G.C.; Gentien, P.; Berdalet, E.; Enevoldsen, H.; Urban, E. Establishment, Goals, and Legacy of the Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms (GEOHAB) Programme. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 27–49. [Google Scholar]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G. AlgaeBase. Available online: http://www.algaebase.org/search/genus/detail/?genus_id=45535 (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Pisapia, F.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Litaker, R.W.; Fraga, S.; Nishimura, T.; Adachi, M.; Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; et al. Toxicity screening of 13 Gambierdiscus strains using neuro-2a and erythrocyte lysis bioassays. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaker, R.W.; Holland, W.C.; Hardison, D.R.; Pisapia, F.; Hess, P.; Kibler, S.R.; Tester, P.A. Ciguatoxicity of Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa species from the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudó, À.; Toldrà, A.; Rey, M.; Todolí, I.; Andree, K.B.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Campàs, M.; Sureda, F.X.; Diogène, J. Gambierdiscus and fukuyoa as potential indicators of ciguatera risk in the balearic islands. Harmful Algae 2020, 99, 101913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudó, À.; Gaiani, G.; Varela, M.R.; Tsumuraya, T.; Andree, K.B.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Campàs, M.; Diogène, J. Further advance of Gambierdiscus Species in the Canary Islands, with the First Report of Gambierdiscus belizeanus. Toxins 2020, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, M.; Laczka, O.; Harwood, D.; Lewis, R.; Himaya, S.; Murray, S.; Doblin, M. Toxicology of Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) from Tropical and Temperate Australian Waters. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, R.; Murray, S.; Rhodes, L.L.; Larsson, M.E.; Harwood, D.T. Ciguatoxins and Maitotoxins in Extracts of Sixteen Gambierdiscus Isolates and One Fukuyoa Isolate from the South Pacific and Their Toxicity to Mice by Intraperitoneal and Oral Administration. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Faust, M.A.; Pauillac, S. Morphology and molecular analyses of three toxic species of Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae): G. pacificus, sp. nov., G. australes, sp. nov., and G. polynesiensis, sp. nov. J. Phycol. 1999, 35, 1282–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinain, M.; Gatti, C.M.; Roué, M.; Darius, H.T. Ciguatera-causing dinoflagellates in the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa: Distribution, ecophysiology and toxicology. In Dinoflagellates: Morphology, Life History and Ecological Significance; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Longo, S.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Darius, H.T.; Hess, P.; Chinain, M. Intraspecific Variability in the Toxin Production and Toxin Profiles of In Vitro Cultures of Gambierdiscus polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) from French Polynesia. Toxins 2019, 11, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laza-Martinez, A.; David, H.; Riobo, P.; Miguel, I.; Orive, E. Characterization of a Strain of Fukuyoa paulensis (Dinophyceae) from the Western Mediterranean Sea. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeder, K.; Erler, K.; Kibler, S.; Tester, P.; Ho, V.T.; Lam, N.N.; Gerdts, G.; Luckas, B. Characteristic profiles of Ciguatera toxins in different strains of Gambierdiscus spp. Toxicon 2010, 56, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and Structure of Ciguatoxin-4A, a New Ciguatoxin Precursor, from Cultures of Dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and Parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibat, M.; Herrenknecht, C.; Darius, H.T.; Roue, M.; Chinain, M.; Hess, P. Detection of pacific ciguatoxins using liquid chromatography coupled to either low or high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J. Chromatogr. A 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, A.L.; Verma, A.; Kohli, G.; Murray, S. Development of a quantitative PCR assay for the detection and enumeration of a potentially ciguatoxin-producing dinoflagellate, Gambierdiscus lapillus (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretzschmar, A.L.; Verma, A.; Harwood, T.; Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S. Characterization of Gambierdiscus lapillus sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae): A new toxic dinoflagellate from the Great Barrier Reef (Australia). J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.F.; Biessy, L.; Argyle, P.A.; Trnski, T.; Halafihi, T.; Rhodes, L.L. Molecular Identification of Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa (Dinophyceae) from Environmental Samples. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Sehein, T.R.; Chinain, M.; Adachi, M.; Nishimura, T.; Xu, Y.; Parsons, M.L.; Smith, T.B.; Zheng, T.; et al. LSU rDNA based RFLP assays for the routine identification of Gambierdiscus species. Harmful Algae 2017, 66, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassenhagen, I.; Erdner, D.L. Microsatellite markers for the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus caribaeus from high-throughput sequencing data. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Hariganeya, N.; Tawong, W.; Sakanari, H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Adachi, M. Quantitative PCR assay for detection and enumeration of ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Gonyaulacales) in coastal areas of Japan. Harmful Algae 2016, 52, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Sato, S.; Tawong, W.; Sakanari, H.; Uehara, K.; Shah, M.M.R.; Suda, S.; Yasumoto, T.; Taira, Y.; Yamaguchi, H.; et al. Genetic diversity and distribution of the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae) in coastal areas of Japan. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.T.Y.; Yan, M.; Lam, V.T.T.; Yiu, S.K.F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Murray, J.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Rhodes, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wai, T.-C. Phylogeny, morphology and toxicity of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Fukuyoa (Goniodomataceae, Dinophyceae) from a subtropical reef ecosystem in the South China Sea. Harmful Algae 2018, 74, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Qiu, D.; Lopes, R.M.; Lin, S. Fukuyoa paulensis gen. et sp. nov., a new genus for the globular species of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus (Dinophyceae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Holland, W.C.; Tester, P.A.; Schultz, T.F.; Faust, M.A.; Holmes, M.J.; Chinain, M.; Wayne Litaker, R. Development of semi-quantitative pcr assays for the detection and enumeration of gambierdiscus species (gonyaulacales, dinophyceae) 1. J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F. Genus Gambierdiscus in the Canary Islands (NE Atlantic Ocean) with Description of Gambierdiscus silvae sp. nov., a New Potentially Toxic Epiphytic Benthic Dinoflagellate. Protist 2014, 165, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.L.; Barber, P.H. A technique for the rapid extraction of microalgal DNA from single live and preserved cells. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Richlen, M.L.; Brandt, M.E.; Smith, T.B. Effects of grazing, nutrients, and depth on the ciguatera-causing dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus in the US Virgin Islands. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 531, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumoto, T.; Inoue, A.; Ochi, T.; Fujimoto, K.; Oshima, Y.; Fukuyo, Y.; Adachi, R.; Bagnis, R. Environmental-studies on a toxic dinoflagellate responsible for ciguatera. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 1980, 46, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Settlemier, C.J.; Bienfang, P.K. A simple model capable of simulating the population dynamics of Gambierdiscus, the benthic dinoflagellate responsible for ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 2010, 10, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chateau-Degat, M.L.; Chinain, M.; Cerf, N.; Gingras, S.; Hubert, B.; Dewailly, E. Seawater temperature, Gambierdiscus spp. variability and incidence of ciguatera poisoning in French Polynesia. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.L.; Lobel, P.S. Effects of depth, habitat, and water motion on the abundance and distribution of ciguatera dinoflagellates at Johnston Atoll, Pacific Ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 421, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedding, L.M.; Lecky, J.; Gove, J.M.; Walecka, H.R.; Donovan, M.K.; Williams, G.J.; Jouffray, J.-B.; Crowder, L.B.; Erickson, A.; Falinski, K. Advancing the integration of spatial data to map human and natural drivers on coral reefs. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverté, L.; Toldrà, A.; Andree, K.B.; Fraga, S.; de Falco, G.; Campàs, M.; Diogène, J. Assessment of cytotoxicity in ten strains of Gambierdiscus australes from Macaronesian Islands by neuro-2a cell-based assays. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2447–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Luo, H.; Yu, L.; Lee, W.H.; Li, L.; Mak, Y.L.; Lin, S.; Lam, P.K. Characterizing ciguatoxin (CTX)-and Non-CTX-producing strains of Gambierdiscus balechii using comparative transcriptomics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Tudó, A.; Bravo, I.; Díaz, P.A.; Diogène, J.; Riobó, P. Toxicity Characterisation of Gambierdiscus Species from the Canary Islands. Toxins 2020, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, L.; Harwood, T.; Smith, K.; Argyle, P.; Munday, R. Production of ciguatoxin and maitotoxin by strains of Gambierdiscus australes, G. pacificus and G. polynesiensis (Dinophyceae) isolated from Rarotonga, Cook Islands. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Tudó, A.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Aligizaki, K.; Diogène, J.; Gago-Martinez, A.; Hess, P. Use of Mass Spectrometry to Determine the Diversity of Toxins Produced by Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa Species from Balearic Islands and Crete (Mediterranean Sea) and the Canary Islands (Northeast Atlantic). Toxins 2020, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambo, I.M.; Dombrowski, N.; Constant, L.; Erdner, D.; Baker, B.J. Metabolic relationships of uncultured bacteria associated with the microalgae. Gambierdiscus. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1764–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakami, T.; Nakahara, H.; Chinain, M.; Ishida, Y. Effects of epiphytic bacteria on the growth of the toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1999, 233, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Zhou, J.; Tan, S.; Jin, H.; Zhang, F.; Mak, Y.L.; Wu, J.; Lai Chan, L.; Cai, Z. Growth and toxin production of Gambierdiscus spp. can be regulated by quorum-sensing bacteria. Toxins 2018, 10, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Differential toxin profiles of ciguatoxins in marine organisms: Chemistry, fate and global distribution. Toxicon 2018, 150, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J.P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterisation of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogène, J.; Reverté, L.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; del Río, V.; de la Iglesia, P.; Campàs, M.; Palacios, O.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Ralijaona, C.; et al. Identification of ciguatoxins in a shark involved in a fatal food poisoning in the Indian Ocean. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuer, P.J.; Takahashi, W.; Tsutsumi, J.; Yoshida, T. Ciguatoxin: Isolation and chemical nature. Science 1967, 155, 1267–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, J.E. A review of ciguatera, tropical fish poisoning, with a tentative explanation of its cause. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1958, 8, 236–267. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, A.H.; Scheuer, P.J.; Sasaki, S.; Helfrich, P.; Alender, C.B. Observations on Ciguatera-Type Toxin in Fish. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1960, 90, 770–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Holmes, M.J. Origin and Transfer of Toxins Involved in Ciguatera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1993, 106, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.; Roué, M.; Sibat, M.; Viallon, J.; Gatti, C.; Vandersea, M.; Tester, P.; Litaker, R.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P.; et al. Tectus niloticus (Tegulidae, Gastropod) as a Novel Vector of Ciguatera Poisoning: Detection of Pacific Ciguatoxins in Toxic Samples from Nuku Hiva Island (French Polynesia). Toxins 2018, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munsterman, K.S.; Allgeier, J.E.; Peters, J.R.; Burkepile, D.E. A View From Both Ends: Shifts in Herbivore Assemblages Impact Top-Down and Bottom-Up Processes on Coral Reefs. Ecosystems 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.B.; Motta, P.J. A kinematic investigation into the feeding behavior of the Goliath grouper Epinephelus itajara. Environ. Biol. Fish. 2017, 100, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szedlmayer, S.T.; Lee, J.D. Diet shifts of juvenile red snapper (Lutjanus campechanus) with changes in habitat and fish size. Fish. Bull. 2004, 102, 366–375. [Google Scholar]
- Zamora-Terol, S.; Novotny, A.; Winder, M. Reconstructing marine plankton food web interactions using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 3380–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, K.E. Asynchronous food availability on neighboring Caribbean coral reefs determines seasonal patterns of growth and reproduction for the herbivorous parrotfish Scarus iserti. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 116, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.M.; Smith, J.A.; Everett, J.D.; Vergés, A.; Suthers, I.M. Latitudinal patterns in trophic structure of temperate reef-associated fishes and predicted consequences of climate change. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 1092–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, J.E. Food Habits of Reef Fishes of the West Indies; Institute of Marine Sciences, University of Miami: Coral Gables, FL, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, S.J.; Monaco, M.E.; Friedlander, A.M.; Legare, B.; Nemeth, R.S.; Kendall, M.S.; Poti, M.; Clark, R.D.; Wedding, L.M.; Caldow, C. Fish with Chips: Tracking Reef Fish Movements to Evaluate Size and Connectivity of Caribbean Marine Protected Areas. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, R.S. Population characteristics of a recovering US Virgin Islands red hind spawning aggregation following protection. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2005, 286, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlander, A.M.; Monaco, M.E.; Clark, R.; Pittman, S.J.; Beets, J.; Boulon, R.; Callender, R.; Christensen, J.; Hile, S.D.; Kendall, M.S. Fish Movement Patterns in Virgin Islands National Park, Virgin Islands Coral Reef National Monument and Adjacent Waters. NOAA Technical Memorandum NOS NCCOS; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2013; p. 172. [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth, R.S. Ecosystem Aspects of Species That Aggregate to Spawn. In Reef Fish Spawning Aggregations: Biology, Research and Management; Sadovy de Mitcheson, Y., Colin, P.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, N.; Tomikawa, T.; Kuniyoshi, K.; Ishikawa, A.; Toyofuku, H.; Kojima, T.; Asakura, H. LC–MS/MS Analysis of Ciguatoxins Revealing the Regional and Species Distinction of Fish in the Tropical Western Pacific. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Robertson, A.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Silander, M.C.; Smith, T.B.; Olsen, D. Ciguatoxin prevalence in 4 commercial fish species along an oceanic exposure gradient in the US Virgin Islands. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, D.A.; Nellis, D.W.; Wood, R.S. Ciguatera in the Eastern Caribbean. Mar. Fish. Rev. 1984, 46, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mak, Y.L.; Chang, Y.-H.; Xiao, C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Shen, J.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Lam, P.K.S. Uptake and Depuration Kinetics of Pacific Ciguatoxins in Orange-Spotted Grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausing, R.J.; Losen, B.; Oberhaensli, F.R.; Darius, H.T.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Chinain, M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. Experimental evidence of dietary ciguatoxin accumulation in an herbivorous coral reef fish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 200, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roué, M.; Darius, H.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Sibat, M.; Hess, P.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Tissue Distribution and Elimination of Ciguatoxins in Tridacna maxima (Tridacnidae, Bivalvia) Fed Gambierdiscus polynesiensis. Toxins 2018, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledreux, A.; Brand, H.; Chinain, M.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Ramsdell, J.S. Dynamics of ciguatoxins from Gambierdiscus polynesiensis in the benthic herbivore Mugil cephalus: Trophic transfer implications. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehinto, A.; Martyniuk, C.; Spade, D.; Denslow, N. Applications for next-generation sequencing in fish ecotoxicogenomics. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miracle, A.L.; Ankley, G.T. Ecotoxicogenomics: Linkages between exposure and effects in assessing risks of aquatic contaminants to fish. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 19, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malpica-Cruz, L.; Green, S.J.; Côté, I.M. Temporal and ontogenetic changes in the trophic signature of an invasive marine predator. Hydrobiologia 2019, 839, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. FishBase. Available online: www.fishbase.org (accessed on 20 November 2020).
- Taylor, J.C.; Karnauskas, M.; Cherubin, L.; Schärer-Umpierre, M.; Michaels, W.L.; Caillouet, R.; Campbell, M.; Demer, D.; Erisman, B.; Fulton, S.; et al. Emerging Science and Technology to Improve Monitoring and Assessments of Fish Spawning Aggregations. Report from the 2019 Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute Workshop. Gulf and Caribbean Fisheries Institute: Overseas Hwy Marathon, FL, USA, 2020; p. 74, NOAA Tech. Memo. NMFS-F/SPO-207. [Google Scholar]
- de Haro, L.; Schmitt, C.; Sinno-Tellier, S.; Paret, N.; Boels, D.; Le Roux, G.; Langrand, J.; Delcourt, N.; Labadie, M.; Simon, N. Ciguatera fish poisoning in France: Experience of the French Poison Control Centre Network from 2012 to 2019. Clin. Toxicol. 2020; 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedemann, M. Ciguatera fish poisoning outbreaks from 2012 to 2017 in Germany caused by snappers from India, Indonesia, and Vietnam. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2019, 14, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Handy, S.M.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Deeds, J.R. Fish hybridization leads to uncertainty regarding ciguatera fish poisoning risk: Confirmation of hybridization and ciguatoxin accumulation with implications for stakeholders. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusche, H.; Hanel, R. Consumers of mislabeled tropical fish exhibit increased risks of ciguatera intoxication: A report on substitution patterns in fish imported at Frankfurt Airport, Germany. Food Control 2021, 121, 107647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappel, K.; Schröder, U. Difficulties in DNA barcoding-based authentication of snapper products due to ambiguous nucleotide sequences in public databases. Food Control 2020, 118, 107348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, M.A.; Schunter, C.; Lehmann, R.; Lightfoot, D.J.; Allan, B.J.M.; Veilleux, H.D.; Rummer, J.L.; Munday, P.L.; Ravasi, T. Species-specific molecular responses of wild coral reef fishes during a marine heatwave. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, J.M.; Pecl, G.T.; Frusher, S.; Hobday, A.J.; Hill, N.; Holbrook, N.J.; Edgar, G.J.; Stuart-Smith, R.; Barrett, N.; Wernberg, T. Species traits and climate velocity explain geographic range shifts in an ocean-warming hotspot. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitgas, P.; Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Dickey-Collas, M.; Engelhard, G.H.; Peck, M.A.; Pinnegar, J.K.; Drinkwater, K.; Huret, M.; Nash, R.D.M. Impacts of climate change on the complex life cycles of fish. Fish. Oceanogr. 2013, 22, 121–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, E.C.; Donat, M.G.; Burrows, M.T.; Moore, P.J.; Smale, D.A.; Alexander, L.V.; Benthuysen, J.A.; Feng, M.; Gupta, A.S.; Hobday, A.J. Longer and more frequent marine heatwaves over the past century. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, R.E.; Jørgensen, C. Climate change in fish: Effects of respiratory constraints on optimal life history and behaviour. Biol. Lett. 2015, 11, 20141032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alva-Basurto, J.C.; Arias-González, J.E. Modelling the effects of climate change on a Caribbean coral reef food web. Ecol. Model. 2014, 289, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.E.; Östlund-Nilsson, S.; Munday, P.L. Effects of elevated temperature on coral reef fishes: Loss of hypoxia tolerance and inability to acclimate. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 156, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rummer, J.L.; Couturier, C.S.; Stecyk, J.A.W.; Gardiner, N.M.; Kinch, J.P.; Nilsson, G.E.; Munday, P.L. Life on the edge: Thermal optima for aerobic scope of equatorial reef fishes are close to current day temperatures. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, J.A.; Bickford, D. Shrinking body size as an ecological response to climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2011, 1, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.W.L.; Sarmiento, J.L.; Dunne, J.; Frolicher, T.L.; Lam, V.W.Y.; Deng Palomares, M.L.; Watson, R.; Pauly, D. Shrinking of fishes exacerbates impacts of global ocean changes on marine ecosystems. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doney, S.C.; Ruckelshaus, M.; Duffy, J.E.; Barry, J.P.; Chan, F.; English, C.A.; Galindo, H.M.; Grebmeier, J.M.; Hollowed, A.B.; Knowlton, N.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Marine Ecosystems. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 11–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, R.C. Partitioning herbivory and its effects on coral reef algal communities. Ecol. Monogr. 1986, 56, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Nau, A.W.; Holland, W.C.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Tester, P.A. Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.C.; Bohrer, G.; Gurarie, E.; LaPoint, S.; Mahoney, P.J.; Boelman, N.T.; Eitel, J.U.H.; Prugh, L.R.; Vierling, L.A.; Jennewein, J.; et al. Ecological insights from three decades of animal movement tracking across a changing Arctic. Science 2020, 370, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.-C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dor, R.K.; Stokesbury, M.J.W. The Ocean Tracking Network—Adding Marine Animal Movements to the Global Ocean Observing System. In Tagging and Tracking of Marine Animals with Electronic Devices; Nielsen, J.L., Arrizabalaga, H., Fragoso, N., Hobday, A., Lutcavage, M., Sibert, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, E.; Grattan, L.; Roberts, S.; Abbott, M.; Morris, J.G. Incidence and Awareness of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in St. Thomas, Us Virgin Islands. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, S224. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, E.G.; Grattan, L.M.; Cook, R.L.; Smith, T.B.; Anderson, D.M.; Morris, J.G. Ciguatera Incidence in the US Virgin Islands Has Not Increased over a 30-Year Time Period Despite Rising Seawater Temperatures. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 88, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedemann, M. Tropical fish poisonings in Germany 2012–2017–What is ciguatera? Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 79, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, J.Y.; Brown, A.F. Ciguatera poisoning: A global issue with common management problems. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaich, C.; Hagelstein, J.G.; Burchard, G.D.; Schmiedel, S. Outbreak of ciguatera fish poisoning on a cargo ship in the port of Hamburg. J. Travel Med. 2012, 19, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, N.P.B.; Kumar, G.; Asthana, P.; Tin, C.; Mak, Y.L.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ma, C.H.E. Ciguatoxin reduces regenerative capacity of axotomized peripheral neurons and delays functional recovery in pre-exposed mice after peripheral nerve injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Chan, L.L.; Li, Y. Chronic ciguatoxin poisoning causes emotional and cognitive dysfunctions in rats. Toxicol. Res. 2016, 6, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.C.; Wu, Q.; Shoemaker, R.C. Transcriptomic signatures in whole blood of patients who acquire a chronic inflammatory response syndrome (CIRS) following an exposure to the marine toxin ciguatoxin. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbao-Sieyro, A.; Pérez-González, Y.; Pavón-Salas, N.; De La Cruz-Modino, R.; Chinea-Mederos, I.; Tabares-Santos, J.L.; Cabrera-Suárez, F. Acquired knowledge about ciguatera fish poisoning in the Canary Islands population. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fuquay, J.M.; Ledreux, A.; Barbieri, M.; Ramsdell, J.S. Sample preparation and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of selected Pacific ciguatoxins in blood samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 461050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Optimization of ciguatoxin extraction method from blood for Pacific ciguatoxin (P-CTX-1). Toxicon 2007, 49, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, B.; Voglhuber-Slavinsky, A.; Dönitz, E.; Rosa, A. 50 Trends Influencing Europe’s Food Sector by 2035; Fraunhofer Institute for Systems and Innovations Research ISI: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Saari, U.A.; Herstatt, C.; Tiwari, R.; Dedehayir, O.; Mäkinen, S.J. The vegan trend and the microfoundations of institutional change: A commentary on food producers’ sustainable innovation journeys in Europe. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvion, L. Generation V: Millennial Vegans in Israel. J. Contemp. Ethnogr. 2020, 49, 564–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopwood, C.J.; Bleidorn, W.; Schwaba, T.; Chen, S. Health, environmental, and animal rights motives for vegetarian eating. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, E.G.; Reich, A.; Morris, J.G. Epidemiology of Ciguatera in Florida. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUMOFA. The EU Fish Market; European Market Observatory for Fisheries and Aquaculture Products; European Union: Luxembourg, 2019; p. 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain; Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Emerging toxins: Ciguatoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienfang, P.; DeFelice, S.; Dowling, A. Quantitative evaluation of commercially available test kit for ciguatera in fish. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 6617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, R.W.; Plakas, S.M. Ciguatera: A public health perspective. Toxicon 2010, 56, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botana, L.M. Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection, 3rd ed.; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 33487–33742. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Rhodes, L.L. Ciguatera fish poisoning event in New Zealand from imported tropical reef fish and confirmation of Pacific ciguatoxins by LC-MS/MS. Harmful Algae News 2020, 66, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, A.; Jester, E.L.E.; Granade, H.R.; Plakas, S.M.; Dickey, R.W. Caribbean ciguatoxin profile in raw and cooked fish implicated in ciguatera. Food Chem. 2012, 131, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.J.; Deeds, J.R.; Wong, E.S.; Hanner, R.H.; Yancy, H.F.; White, K.D.; Thompson, T.M.; Wahl, M.; Pham, T.D.; Guichard, F.M.; et al. Public health response to puffer fish (Tetrodotoxin) poisoning from mislabeled product. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Heegaard, W.G.; Deeds, J.R.; McGrath, S.C.; Handy, S.M. Tetrodotoxin poisoning outbreak from imported dried puffer fish-Minneapolis, Minnesota, 2014. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2015, 63, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Willette, D.A.; Simmonds, S.E.; Cheng, S.H.; Esteves, S.; Kane, T.L.; Nuetzel, H.; Pilaud, N.; Rachmawati, R.; Barber, P.H. Using DNA barcoding to track seafood mislabeling in Los Angeles restaurants. Conserv. Biol. 2017, 31, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeds, J.R.; Handy, S.M.; Fry, J.F.; Granade, H.; Williams, J.T.; Powers, M.; Shipp, R.; Weigt, L.A. Protocol for building a reference standard sequence library for DNA-based seafood identification. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eischeid, A.C.; Stadig, S.R.; Handy, S.M.; Fry, F.S.; Deeds, J. Optimization and evaluation of a method for the generation of DNA barcodes for the identification of crustaceans. LWT 2016, 73, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, L.L.; Peatman, E.; Lu, J.; Kucuktas, H.; He, S.; Zhou, C.; Na-nakorn, U.; Liu, Z. DNA Barcoding of Catfish: Species Authentication and Phylogenetic Assessment. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handy, S.M.; Deeds, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hanner, R.H.; Ormos, A.; Weigt, L.A.; Moore, M.M.; Yancy, H.F. A single-laboratory validated method for the generation of DNA barcodes for the identification of fish for regulatory compliance. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoelinck, C.; Hinsinger, D.D.; Dettaï, A.; Cruaud, C.; Justine, J.-L. A Phylogenetic Re-Analysis of Groupers with Applications for Ciguatera Fish Poisoning. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.V.; Uesugi, A.; Uchida, H.; Ky, P.X.; Minh, D.Q.; Watanabe, R.; Matsushima, R.; Oikawa, H.; Nagai, S.; Iwataki, M.; et al. Identification of Causative Ciguatoxins in Red Snappers Lutjanus bohar Implicated in Ciguatera Fish Poisonings in Vietnam. Toxins 2018, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magras, J.; Olsen, D. St. Thomas Fishermen’s Association: Involving Fishermen in Fishery Management. Proc. Sixty Fifth Annu. Gulf Caribb. Fish. Inst. 2012, 65, 48–51. [Google Scholar]
- Howson, P. Building trust and equity in marine conservation and fisheries supply chain management with blockchain. Mar. Policy 2020, 115, 103873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownscombe, J.W.; Griffin, L.P.; Morley, D.; Acosta, A.; Hunt, J.; Lowerre-Barbieri, S.K.; Adams, A.J.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Cooke, S.J. Application of machine learning algorithms to identify cryptic reproductive habitats using diverse information sources. Oecologia 2020, 194, 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst, W.N. How emerging data technologies can increase trust and transparency in fisheries. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 77, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B. Blockchain: Transforming the seafood supply chain. In World Wide Fund for Nature; World Wide Fund for Nature, WWF: Gland, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gopi, K.; Mazumder, D.; Sammut, J.; Saintilan, N. Determining the provenance and authenticity of seafood: A review of current methodologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, N.; Niedenzu, D.; Simonetto, M.; Dora, M.; Kumar, M. Supply network design to address United Nations Sustainable Development Goals: A case study of blockchain implementation in Thai fish industry. J. Bus. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, A.; de la Iglesia, P.; Darius, H.T.; Pauillac, S.; Aligizaki, K.; Fraga, S.; Chinain, M.; Diogene, J. Update on methodologies available for ciguatoxin determination: Perspectives to confront the onset of ciguatera fish poisoning in Europe. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1838–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estevez, P.; Castro, D.; Manuel Leao, J.; Yasumoto, T.; Dickey, R.; Gago-Martinez, A. Implementation of liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of ciguatera fish poisoning in contaminated fish samples from Atlantic coasts. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Selwood, A.I.; Harwood, D.T. Development of an LC–MS/MS method to simultaneously monitor maitotoxins and selected ciguatoxins in algal cultures and P-CTX-1B in fish. Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, D.T.; Murray, S.; Boundy, M.J. Sample preparation prior to marine toxin analysis. In Recent Advances in the Analysis of Marine Toxins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; McCall, J.R.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; et al. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay for Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowiez, R.; Darius, H.T.; Cruchet, P.; Rossi, F.; Caillaud, A.; Laurent, D.; Chinain, M. Evaluation of seafood toxicity in the Australes archipelago (French Polynesia) using the neuroblastoma cell-based assay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. Marine Biotoxins FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 80; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dickey, R.W. Ciguatera Toxins: Chemistry, Toxicology, and Detection, 2nd ed.; CRC Press/Taylor & Franci: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 173, p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Viallon, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, H.T. Revisiting the Neuroblastoma Cell-Based Assay (CBA-N2a) for the Improved Detection of Marine Toxins Active on Voltage Gated Sodium Channels (VGSCs). Toxins 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manger, R.L.; Leja, L.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Hungerford, J.M.; Hokama, Y.; Dickey, R.W.; Granade, H.R.; Lewis, R.; Yasumoto, T.; Wekell, M.M. Detection of sodium channel toxins: Directed cytotoxicity assays of purified ciguatoxins, brevetoxins, saxitoxins, and seafood extracts. J. AOAC Int. 1995, 78, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillaud, A.; Cañete, E.; de la Iglesia, P.; Giménez, G.; Diogène, J. Cell-based assay coupled with chromatographic fractioning: A strategy for marine toxins detection in natural samples. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campora, C.E.; Dierking, J.; Tamaru, C.S.; Hokama, Y.; Vincent, D. Detection of ciguatoxin in fish tissue using sandwich ELISA and neuroblastoma cell bioassay. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Sato, T.; Hirama, M.; Fujii, I. Highly Sensitive and Practical Fluorescent Sandwich ELISA for Ciguatoxins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7318–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardo, S.; Gaiani, G.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Turquet, J.; Sagristà, N.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Flores, C.; Caixach, J.; Diogene, J.; et al. Addressing the analytical challenges for the detection of ciguatoxins using an electrochemical biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Asencio, L.; Clausing, R.J.; Rañada, M.L.; Alonso-Hernández, C.M.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y. A radioligand receptor binding assay for ciguatoxin monitoring in environmental samples: Method development and determination of quality control criteria. J. Environ. Radioact. 2018, 192, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Clausing, R.J. Chapter Eight—Receptor-Binding Assay for the Analysis of Marine Toxins: Detection and Mode of Action. In Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry; Diogène, J., Campàs, M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 78, pp. 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Loeffler, C.R.; Bodi, D.; Tartaglione, L.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Preiss-Weigert, A. Improving in vitro ciguatoxin and brevetoxin detection: Selecting neuroblastoma (Neuro-2a) cells with lower sensitivity to ouabain and veratridine (OV-LS). Harmful Algae 2021, 103, 101994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Reis Costa, P.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Hess, P. Liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry for the confirmation of Caribbean ciguatoxin-1 as the main toxin responsible for ciguatera poisoning caused by fish from European Atlantic coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A.; Vernoux, J.-P. HPLC/Tandem Electrospray Mass Spectrometry for the Determination of Sub-ppb Levels of Pacific and Caribbean Ciguatoxins in Crude Extracts of Fish. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-K.; Hung, P.; Lo, J.Y. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Hong Kong–A 10-year perspective on the class of ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2014, 86, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Yang, A.; Jones, A. Rapid extraction combined with LC-tandem mass spectrometry (CREM-LC/MS/MS) for the determination of ciguatoxins in ciguateric fish flesh. Toxicon 2009, 54, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darius, H.T.; Drescher, O.; Ponton, D.; Pawlowiez, R.; Laurent, D.; Dewailly, E.; Chinain, M. Use of folk tests to detect ciguateric fish: A scientific evaluation of their effectiveness in Raivavae Island (Australes, French Polynesia). Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 30, 550–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasinszki, T.; Lako, J.; Dennis, T.E. Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins 2020, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodero, M.; Gerssen, A.; Portier, L.; Klijnstra, M.; Hoogenboom, R.; Guzmán, L.; Hendriksen, P.; Bovee, T. A Strategy to Replace the Mouse Bioassay for Detecting and Identifying Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins by Combining the Neuro-2a Bioassay and LC-MS/MS Analysis. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Herondelle, K.; Talagas, M.; Mignen, O.; Misery, L.; Le Garrec, R. Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis. Cells 2020, 9, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshney, R.I. Serum-Free Media. In Culture of Animal Cells; Freshney, R.I., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrée, B.; Ichanti, H.; Kalies, S.; Heisterkamp, A.; Strauß, S.; Vogt, P.-M.; Haverich, A.; Hilfiker, A. Formation of three-dimensional tubular endothelial cell networks under defined serum-free cell culture conditions in human collagen hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, D.; Frank, J.; Appl, H.; Schöffl, H.; Pfaller, W.; Gstraunthaler, G. The serum-free media interactive online database. ALTEX-Altern. Anim. Exp. 2010, 27, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Bodero, M.; Bovee, T.F.H.; Wang, S.; Hoogenboom, R.L.A.P.; Klijnstra, M.D.; Portier, L.; Hendriksen, P.J.M.; Gerssen, A. Screening for the presence of lipophilic marine biotoxins in shellfish samples using the neuro-2a bioassay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2018, 35, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gstraunthaler, G. Alternatives to the use of fetal bovine serum: Serum-free cell culture. ALTEX-Altern. Anim. Exp. 2003, 20, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, L.; Ran, F.A.; Cox, D.; Lin, S.; Barretto, R.; Habib, N.; Hsu, P.D.; Wu, X.; Jiang, W.; Marraffini, L.A. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 2013, 339, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, P.; Yang, L.; Esvelt, K.M.; Aach, J.; Guell, M.; DiCarlo, J.E.; Norville, J.E.; Church, G.M. RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 2013, 339, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Oost, J.; Westra, E.R.; Jackson, R.N.; Wiedenheft, B. Unravelling the structural and mechanistic basis of CRISPR–Cas systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalem, O.; Sanjana, N.E.; Hartenian, E.; Shi, X.; Scott, D.A.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Heckl, D.; Ebert, B.L.; Root, D.E.; Doench, J.G. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screening in human cells. Science 2014, 343, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratovič, M.; Fonfara, I.; Chylinski, K.; Gálvez, E.J.C.; Sullivan, T.J.; Boerno, S.; Timmermann, B.; Boettcher, M.; Charpentier, E. Bridge helix arginines play a critical role in Cas9 sensitivity to mismatches. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.D.; Lander, E.S.; Zhang, F. Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 2014, 157, 1262–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Rush, A.M.; Cummins, T.R.; Hisama, F.M.; Novella, S.; Tyrrell, L.; Marshall, L.; Waxman, S.G. Gain-of-function mutation in Nav1.7 in familial erythromelalgia induces bursting of sensory neurons. Brain 2005, 128, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yang, Y.; de Greef, B.T.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.; Gerrits, M.M.; Verhamme, C.; Qu, J.; Lauria, G.; Merkies, I.S.; Faber, C.G.; et al. The Domain II S4-S5 Linker in Nav1.9: A Missense Mutation Enhances Activation, Impairs Fast Inactivation, and Produces Human Painful Neuropathy. Neuromol. Med. 2015, 17, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipold, E.; Liebmann, L.; Korenke, G.C.; Heinrich, T.; Giesselmann, S.; Baets, J.; Ebbinghaus, M.; Goral, R.O.; Stödberg, T.; Hennings, J.C.; et al. A de novo gain-of-function mutation in SCN11A causes loss of pain perception. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipold, E.; Hanson-Kahn, A.; Frick, M.; Gong, P.; Bernstein, J.A.; Voigt, M.; Katona, I.; Oliver Goral, R.; Altmüller, J.; Nürnberg, P.; et al. Cold-aggravated pain in humans caused by a hyperactive NaV1.9 channel mutant. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, C.G.; Lauria, G.; Merkies, I.S.; Cheng, X.; Han, C.; Ahn, H.S.; Persson, A.K.; Hoeijmakers, J.G.; Gerrits, M.M.; Pierro, T.; et al. Gain-of-function Nav1.8 mutations in painful neuropathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19444–19449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lutz, B.M.; Tao, Y.-X. The CRISPR/Cas9 system for gene editing and its potential application in pain research. Transl. Perioper. Pain Med. 2016, 1, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Sabi, A.; McArthur, J.; Ostroumov, V.; French, R.J. Marine Toxins That Target Voltage-gated Sodium Channels. Mar. Drugs 2006, 4, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergholz, T.M.; Moreno Switt, A.I.; Wiedmann, M. Omics approaches in food safety: Fulfilling the promise? Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, A.; Freitas, M.; de Almeida, A.M.; Martins, J.C.; Domínguez-Pérez, D.; Osório, H.; Vasconcelos, V.; Reis Costa, P. OMICs Approaches in Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins Research. Toxins 2020, 12, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Petschnigg, J.; Ketteler, R.; Stagljar, I. Application guide for omics approaches to cell signaling. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapcariu, S.C.; Kanashova, T.; Weindl, D.; Ghelfi, J.; Dittmar, G.; Hiller, K. Simultaneous extraction of proteins and metabolites from cells in culture. MethodsX 2014, 1, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Hiyama, T.Y.; Kuboyama, K.; Suzuki, R.; Fujikawa, A.; Noda, M. Channel Properties of Nax Expressed in Neurons. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for sandwich immunoassay detection of Pacific ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2010, 56, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Inoue, M.; Tatami, A.; Miyazaki, K.; Hirama, M. Production of monoclonal antibodies for sandwich immunoassay detection of ciguatoxin 51-hydroxyCTX3C. Toxicon 2006, 48, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Preparation of anti-ciguatoxin monoclonal antibodies using synthetic haptens: Sandwich ELISA detection of ciguatoxins. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M. Rationally Designed Synthetic Haptens to Generate Anti-Ciguatoxin Monoclonal Antibodies, and Development of a Practical Sandwich ELISA to Detect Ciguatoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Yamashita, S.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Development of a monoclonal antibody against the left wing of ciguatoxin CTX1B: Thiol strategy and detection using a sandwich ELISA. Toxicon 2012, 60, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campora, C.E.; Hokama, Y.; Yabusaki, K.; Isobe, M. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of ciguatoxin in fish tissue using chicken immunoglobulin Y. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2008, 22, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaiani, G.; Leonardo, S.; Tudó, À.; Toldrà, A.; Rey, M.; Andree, K.B.; Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M.; Diogène, J.; O’Sullivan, C.K.; et al. Rapid detection of ciguatoxins in Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa with immunosensing tools. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 204, 111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luan, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Ultrasensitive and accelerated detection of ciguatoxin by capillary electrophoresis via on-line sandwich immunoassay with rotating magnetic field and nanoparticles signal enhancement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Hua, X.; Yang, C.; Chen, C.; Yan, F.; Zhu, S.; Li, T. Metalens-integrated compact imaging devices for wide-field microscopy. Adv. Photon. 2020, 2, 66004. [Google Scholar]
- Parolo, C.; Sena-Torralba, A.; Bergua, J.F.; Calucho, E.; Fuentes-Chust, C.; Hu, L.; Rivas, L.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Nguyen, E.P.; Cinti, S.; et al. Tutorial: Design and fabrication of nanoparticle-based lateral-flow immunoassays. Nat. Protoc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, Y.M.; Zhou, R.; Zhuang, X. Visualizing and discovering cellular structures with super-resolution microscopy. Science 2018, 361, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Sirinakis, G.; Allgeyer, E.S.; Schroeder, L.K.; Duim, W.C.; Kromann, E.B.; Phan, T.; Rivera-Molina, F.E.; Myers, J.R.; Irnov, I.; et al. Ultra-High Resolution 3D Imaging of Whole Cells. Cell 2016, 166, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.W.; So, P.T.C.; Dasari, R.R.; Lim, D.-K. High Resolution Live Cell Raman Imaging Using Subcellular Organelle-Targeting SERS-Sensitive Gold Nanoparticles with Highly Narrow Intra-Nanogap. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Wright, K.L.; Ashton, L. Raman spectroscopy: An evolving technique for live cell studies. Analyst 2016, 141, 3590–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, J.; Gerssen, A.; Pawliszyn, J.; Sterk, S.S.; Nielen, M.W.F.; Blokland, M.H. USB-Powered Coated Blade Spray Ion Source for On-Site Testing Using Transportable Mass Spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 31, 2243–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielczarek, P.; Silberring, J.; Smoluch, M. Minaturization in mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2020, 39, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokland, M.H.; Gerssen, A.; Zoontjes, P.W.; Pawliszyn, J.; Nielen, M.W.F. Potential of recent ambient ionization techniques for future food contaminant analysis using (trans)portable mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, M.; Hirama, M. Total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C, a causative toxin of ciguatera seafood poisoning. Synlett 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, M.; Oishi, T.; Uehara, H.; Inoue, M.; Maruyama, M.; Oguri, H.; Satake, M. Total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C. Science 2001, 294, 1904–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain; Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Emerging toxins: Brevetoxin group. EFSA J. 2010, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, R.A.; Rutterford, L.A.; Freer, J.J.; Collins, R.A.; Simpson, S.D.; Genner, M.J. Climate change drives poleward increases and equatorward declines in marine species. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea-Level Rise and Its Impact on Coastal Zones. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J. Sea-Level Rise from the Late 19th to the Early 21st Century. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, S.; Weinstein, P.; Woodward, A. Ciguatera (Fish Poisoning), El Niño, and Pacific Sea Surface Temperatures. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 5, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: The Risk from an Aotearoa/New Zealand Perspective. Toxins 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bove, G.; Becker, A.; Sweeney, B.; Vousdoukas, M.; Kulp, S. A method for regional estimation of climate change exposure of coastal infrastructure: Case of USVI and the influence of digital elevation models on assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heron, S.; van Hooidonk, R.; Maynard, J.; Anderson, K.; Day, J.; Geiger, E.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Hughes, T.; Marshall, P.; Obura, D. Impacts of Climate Change on World Heritage coral Reefs: Update to the First Global Scientific Assessment; UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel, A.; Bode, M.; Connolly, S.R.; Hughes, T.P. Long-term shifts in the colony size structure of coral populations along the Great Barrier Reef. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2020, 287, 20201432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, K.K.; Zawada, D.G.; Smiley, N.A.; Tiling-Range, G. Divergence of seafloor elevation and sea level rise in coral reef ecosystems. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciro Aucelli, P.P.; Di Paola, G.; Incontri, P.; Rizzo, A.; Vilardo, G.; Benassai, G.; Buonocore, B.; Pappone, G. Coastal inundation risk assessment due to subsidence and sea level rise in a Mediterranean alluvial plain (Volturno coastal plain—southern Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 198, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, M.W.; Losada, I.J.; Menéndez, P.; Reguero, B.G.; Díaz-Simal, P.; Fernández, F. The global flood protection savings provided by coral reefs. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherman, S.P.; Beller-Simms, N. Sea-level rise and small island states: An overview. J. Coast. Res. 1997, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, T.P. Catastrophes, phase shifts, and large-scale degradation of a Caribbean coral reef. Science 1994, 265, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, J.W.; Meñez, L.A.B.; Kesner-Reyes, K.N.; Vergara, S.G.; Ablan, M.C. Coral reef fishing and coral-algal phase shifts: Implications for global reef status. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, J.W.; Polsenberg, J.F. Coral–algal phase shifts on coral reefs: Ecological and environmental aspects. Prog. Oceanogr. 2004, 60, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, S.; Kohler, C. Dead bleached coral provides new surfaces for dinoflagellates implicated in ciguatera fish poisonings. Environ. Biol. Fish 1992, 35, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahara, H.; Sakami, T.; Chinain, M.; Ishida, Y. The role of macroalgae in epiphytism of the toxic dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae). Phycol. Res. 1996, 44, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, M.L.; Settlemier, C.J.; Ballauer, J.M. An examination of the epiphytic nature of Gambierdiscus toxicus, a dinoflagellate involved in ciguatera fish poisoning. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, M.P.; Lewis, R.J.; Morton, S. Ecology of the ciguatera causing dinoflagellates from the Northern Great Barrier Reef: Changes in community distribution and coastal eutrophication. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Rivera, E.; Villareal, T.A. Macroalgal palatability and the flux of ciguatera toxins through marine food webs. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 497–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.; Ranelletti, M.; Kaushik, S. Invasive marine algae: An ecological perspective. Bot. Rev. 2006, 72, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, P.; Wickliffe, L.; Jossart, J.; Rhodes, L.; Enevoldsen, H.; Adachi, M.; Nishimura, T.; Rodriguez, F.; Chinain, M.; Litaker, W. Global distribution of the genera Gambierdiscus and Fukuyoa. Harmful Algae 2018–From Ecosystems to Socio-Ecosystems. In Proceedings of the 18th Internationalconference on Harmful Algae, Nantes, France, 21–26 October 2018; p. 138. [Google Scholar]
- Masó, M.; Garcés, E.; Pagès, F.; Camp, J. Drifting plastic debris as a potential vector for dispersing Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB) species. Sci. Mar. 2003, 67, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, M.E.; Laczka, O.F.; Suthers, I.M.; Ajani, P.A.; Doblin, M.A. Hitchhiking in the east Australian current: Rafting as a dispersal mechanism for harmful epibenthic dinoflagellates. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 596, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallegraeff, G.M. Transport of harmful marine microalgae via ship’s ballast water: Management and mitigation with special reference to the Arabian Gulf region. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2015, 18, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. The changing face of ciguatera. Toxicon 2001, 39, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera management. SPC Live Reef Fish Inf. Bull. 2000, 7, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the moray eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Brereton, I.M. Structure of Caribbean Ciguatoxin Isolated from Caranx latus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 5914–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; López-Cortés, D.J.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Hernández-Sandoval, F.E.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Bustillos-Guzmán, J.J.; Gárate-Lizárraga, I.; García-Mendoza, E.; Salinas-Zavala, C.A.; et al. Ciguatera in Mexico (1984–2013). Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Quiroz, R.; Herrera-Usuga, J.C.; Osorio-Ospina, L.M.; Garcia-Pertuz, K.M.; Navarro Quiroz, E. Epidemiology and Toxicology of Ciguatera Poisoning in the Colombian Caribbean. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.M. Dinoflagellate Toxins Responsible for Ciguatera Food Poisoning. Southern Illinois University at Carbondale Department of Physiology: Carbondale, IL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Bomber, J.W.; Tindall, D.R.; Miller, D.M. Genetic variability in toxin protencies among seventeen clones of Gambierdiscus toxicus (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 1989, 25, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, K.-T.; Hsieh, C.-h. Fishing and temperature effects on the size structure of exploited fish stocks. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, M.J.; Latijnhouwers, K.R.; Dilrosun, F.; Chamberland, V.F.; Dubé, C.E.; Van Buurt, G.; Debrot, A.O. Historical changes (1905-present) in catch size and composition reflect altering fisheries practices on a small Caribbean island. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audzijonyte, A.; Kuparinen, A.; Gorton, R.; Fulton, E.A. Ecological consequences of body size decline in harvested fish species: Positive feedback loops in trophic interactions amplify human impact. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20121103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, J. Effects of the Introduced Predatory Fish Cephalopholis Argus on Native Reef Fish Populations in Hawaii. University of Hawaii at Manoa, Dept. of Zoology: Manoa, HI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Trehern, R.H.; Raguse, C.; Bigelow, W.F.; Garg, A.; Hauptman, H.; Brooks, A.; Van Leeuwen, T.E.; Hawkes, L.A. The effect of salinity on behavioural interactions between native Schoolmaster snapper (Lutjanus apodus) and invasive lionfish (Pterois spp.). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 530–531, 151414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierking, J.; Williams, I.D.; Walsh, W.J. Diet composition and prey selection of the introduced grouper species peacock hind (Cephalopholis argus) in Hawaii. Fish. Bull. 2009, 107, 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Birrell, C.L.; McCook, L.J.; Willis, B.L. Effects of algal turfs and sediment on coral settlement. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 51, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Bogdanoff, A.K.; Morris, J.A., Jr.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; Loeffler, C.R.; et al. Investigation of ciguatoxins in invasive lionfish from the greater Caribbean region: Implications for fishery development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Widgy, S.; Pautonnier, A.; Turquet, J.; Loeffler, C.R.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Diogène, J. Prevalence of ciguatoxins in lionfish (Pterois spp.) from Guadeloupe, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthélmy Islands (Caribbean). Toxicon 2015, 102, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.; Garcia, A.C.; Quintana, H.A.F.; Smith, T.B.; Castillo, B.F., II; Reale-Munroe, K.; Gulli, J.A.; Olsen, D.A.; Hooe-Rollman, J.I.; Jester, E.L. Invasive lionfish (Pterois volitans): A potential human health threat for ciguatera fish poisoning in tropical waters. Mar. Drugs 2013, 12, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierking, J.; Campora, C.E. Ciguatera in the introduced fish Cephalopholis argus (Serranidae) in Hawai‘i and implications for fishery management. Pac. Sci. 2009, 63, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, S.E.; Halpern, B.S.; Grorud-Colvert, K.; Lubchenco, J.; Ruttenberg, B.I.; Gaines, S.D.; Airamé, S.; Warner, R.R. Biological effects within no-take marine reserves: A global synthesis. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 384, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyrenbach, K.D.; Forney, K.A.; Dayton, P.K. Marine protected areas and ocean basin management. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2000, 10, 437–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinner, J.E.; Zamborain-Mason, J.; Gurney, G.G.; Graham, N.A.J.; MacNeil, M.A.; Hoey, A.S.; Mora, C.; Villéger, S.; Maire, E.; McClanahan, T.R.; et al. Meeting fisheries, ecosystem function, and biodiversity goals in a human-dominated world. Science 2020, 368, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, R.B.; Bradley, D.; Mayorga, J.; Goodell, W.; Friedlander, A.M.; Sala, E.; Costello, C.; Gaines, S.D. A global network of marine protected areas for food. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goñi, R.; Adlerstein, S.; Alvarez-Berastegui, D.; Forcada, A.; Reñones, O.; Criquet, G.; Polti, S.; Cadiou, G.; Valle, C.; Lenfant, P.; et al. Spillover from six western Mediterranean marine protected areas: Evidence from artisanal fisheries. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 366, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC. Adoption of the Paris Agreement. Available online: http://unfccc.int/resource/docs/2015/cop21/eng/l09r01.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Villareal, T.A.; Hanson, S.; Qualia, S.; Jester, E.L.E.; Granade, H.R.; Dickey, R.W. Petroleum production platforms as sites for the expansion of ciguatera in the northwestern Gulf of Mexico. Harmful Algae 2007, 6, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubens, J.T.; Braeckman, U.; Vanaverbeke, J.; Van Colen, C.; Degraer, S.; Vincx, M. Aggregation at windmill artificial reefs: CPUE of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) and pouting (Trisopterus luscus) at different habitats in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Fish. Res. 2013, 139, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glarou, M.; Zrust, M.; Svendsen, J.C. Using artificial-reef knowledge to enhance the ecological function of offshore wind turbine foundations: Implications for fish abundance and diversity. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, F.R. Structures That Protect Coastal Populations, Assets, and GDPs: Sea Dikes, Breakwaters, Seawalls. In Adaptations of Coastal Cities to Global Warming, Sea Level Rise, Climate Change and Endemic Hazards; Siegel, F.R., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, N. Physical Model Study of Living Breakwaters: Stability and Ecological Analysis of Green-Grey Hybrid Structure Concept for Climate Change Adaptation. Master’s Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Danladi, I.B.; Kore, B.M.; Gül, M. Vulnerability of the Nigerian coast: An insight into sea level rise owing to climate change and anthropogenic activities. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2017, 134, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Kyoto Conference Outcome and Papers Presented. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/AC442e/AC442e00.htm (accessed on 6 November 2020).
- UNEP. Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefi ts Arising from their Utilization to the Convention on Biological Diversity; United Nations Environmental Programme; Secretariat of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2010; ISBN 92-9225-306-9. [Google Scholar]
- McCluskey, K.; Barker, K.B.; Barton, H.A.; Boundy-Mills, K.; Brown, D.R.; Coddington, J.A.; Cook, K.; Desmeth, P.; Geiser, D.; Glaeser, J.A.; et al. The U.S. Culture Collection Network Responding to the Requirements of the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit Sharing. mBio 2017, 8, e00982-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filous, A.; Lennox, R.J.; Beaury, J.P.; Bagnis, H.; McHugh, M.; Friedlander, A.M.; Clua, E.E.G.; Cooke, S.J.; Fuller, T.K.; Danylchuk, A.J. Fisheries science and marine education catalyze the renaissance of traditional management (rahui) to improve an artisanal fishery in French Polynesia. Mar. Policy 2021, 123, 104291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.C.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Suski, C.D.; Cooke, S.J. Consequences of catch-and-release angling on the physiological status, injury, and immediate mortality of great barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) in The Bahamas. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Cons. 2010, 67, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, A.C.; Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Danylchuk, A.J.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Cooke, S.J. Linking ciguatera poisoning to spatial ecology of fish: A novel approach to examining the distribution of biotoxin levels in the great barracuda by combining non-lethal blood sampling and biotelemetry. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Eros, C.M. Ethics of field research: Do journals set the standard? Sci. Eng. Ethics 1999, 5, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangialajo, L.; Fricke, A.; Perez-Gutierrez, G.; Catania, D.; Jauzein, C.; Lemee, R. Benthic Dinoflagellate Integrator (BEDI): A new method for the quantification of Benthic Harmful Algal Blooms. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Richlen, M.L.; Morton, S.L.; Mak, Y.L.; Chan, L.L.; Tekiau, A.; Anderson, D.M. Distribution, abundance and diversity of Gambierdiscus spp. from a ciguatera-endemic area in Marakei, Republic of Kiribati. Harmful Algae 2014, 34, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.R.; Berdalet, E.; Kudela, R.M.; Cusack, C.K.; Silke, J.; O’Rourke, E.; Dugan, D.; McCammon, M.; Newton, J.A.; Moore, S.K.; et al. Scaling up from regional case studies to a global harmful algal bloom observing system. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, B.A.; Bowers, H.A.; Buckley, E.; Davis, T.W.; Johengen, T.H.; Kudela, R.; McManus, M.A.; Purcell, H.; Smith, G.J.; Vander Woude, A.; et al. Considerations in Harmful Algal Bloom Research and Monitoring: Perspectives From a Consensus-Building Workshop and Technology Testing. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdalet, E.; Bravo, I.; Evans, J.; Fraga, S.; Kibler, S.; Kudela, M.; Larsen, J.; Litaker, W.; Penna, A.; Tester, P.; et al. Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms, GEOHAB Core Research Project: HABs in Benthic Systems; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission. Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research (SCOR); Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Brunson, J.K.; McKinnie, S.M.K.; Chekan, J.R.; McCrow, J.P.; Miles, Z.D.; Bertrand, E.M.; Bielinski, V.A.; Luhavaya, H.; Obornik, M.; Smith, G.J. Biosynthesis of the neurotoxin domoic acid in a bloom-forming diatom. Science 2018, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, M. Total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C: A venture into the problems of ciguatera seafood poisoning. Chem. Rec. 2005, 5, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Uehara, H.; Maruyama, M.; Hirama, M. First- and second-generation total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12013–12018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Ishihara, Y.; Tatami, A.; Ohnuma, Y.; Kawada, Y.; Komano, K.; Yamashita, S.; Lee, N.; Hirama, M. Total Synthesis of Ciguatoxin and 51-HydroxyCTX3C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 9352–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamajima, A.; Isobe, M. Total Synthesis of Ciguatoxin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 2941–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Mori, Y. Total Synthesis of Gambierol. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 4382–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuwa, H.; Noji, S.; Sasaki, M. Studies toward the Total Synthesis of Gambieric Acids: Stereocontrolled Synthesis of a DEFG-Ring Model Compound. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 75, 5072–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuwa, H.; Ishigai, K.; Hashizume, K.; Sasaki, M. Total Synthesis and Complete Stereostructure of Gambieric Acid A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11984–11987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.; Aversa, R.J. Maitotoxin: An inspiration for synthesis. Isr. J. Chem. 2011, 51, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, C.; Antero, A.; Martín, V. Pharmacology of ciguatoxins. In Phycotoxins, Chemistry and Biochemistry; Alfonso, L.B.A.A., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 23–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, K.; Zimmermann, K.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J. Therapeutic opportunities for targeting cold pain pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, J.G.; Sánchez-Cárdenas, C.; Acevedo-Castillo, W.; Leyton, P.; López-González, I.; Felix, R.; Gandini, M.A.; Treviño, M.B.; Treviño, C.L. Maitotoxin: An enigmatic toxic molecule with useful applications in the biomedical sciences. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 677–694. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure elucidation and biological activities of high molecular weight algal toxins: Maitotoxin, prymnesins and zooxanthellatoxins. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2000, 17, 293–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loeffler, C.R.; Tartaglione, L.; Friedemann, M.; Spielmeyer, A.; Kappenstein, O.; Bodi, D. Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063027
Loeffler CR, Tartaglione L, Friedemann M, Spielmeyer A, Kappenstein O, Bodi D. Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(6):3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoeffler, Christopher R., Luciana Tartaglione, Miriam Friedemann, Astrid Spielmeyer, Oliver Kappenstein, and Dorina Bodi. 2021. "Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 6: 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063027
APA StyleLoeffler, C. R., Tartaglione, L., Friedemann, M., Spielmeyer, A., Kappenstein, O., & Bodi, D. (2021). Ciguatera Mini Review: 21st Century Environmental Challenges and the Interdisciplinary Research Efforts Rising to Meet Them. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(6), 3027. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18063027







