The Trend of HIV/AIDS Incidence and Risks Associated with Age, Period, and Birth Cohort in Four Central African Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
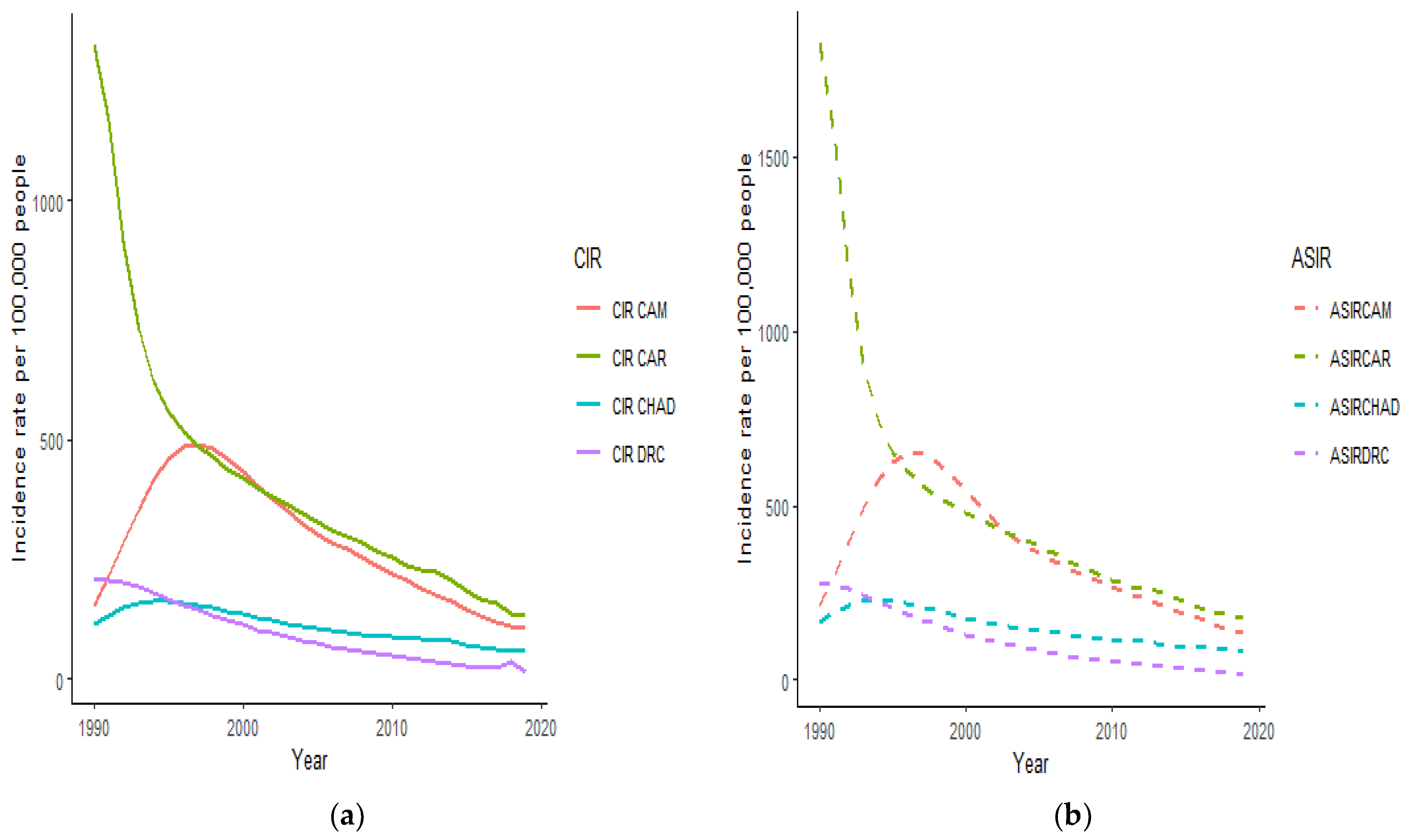
3.1. Trends of HIV/AIDS Incidence in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
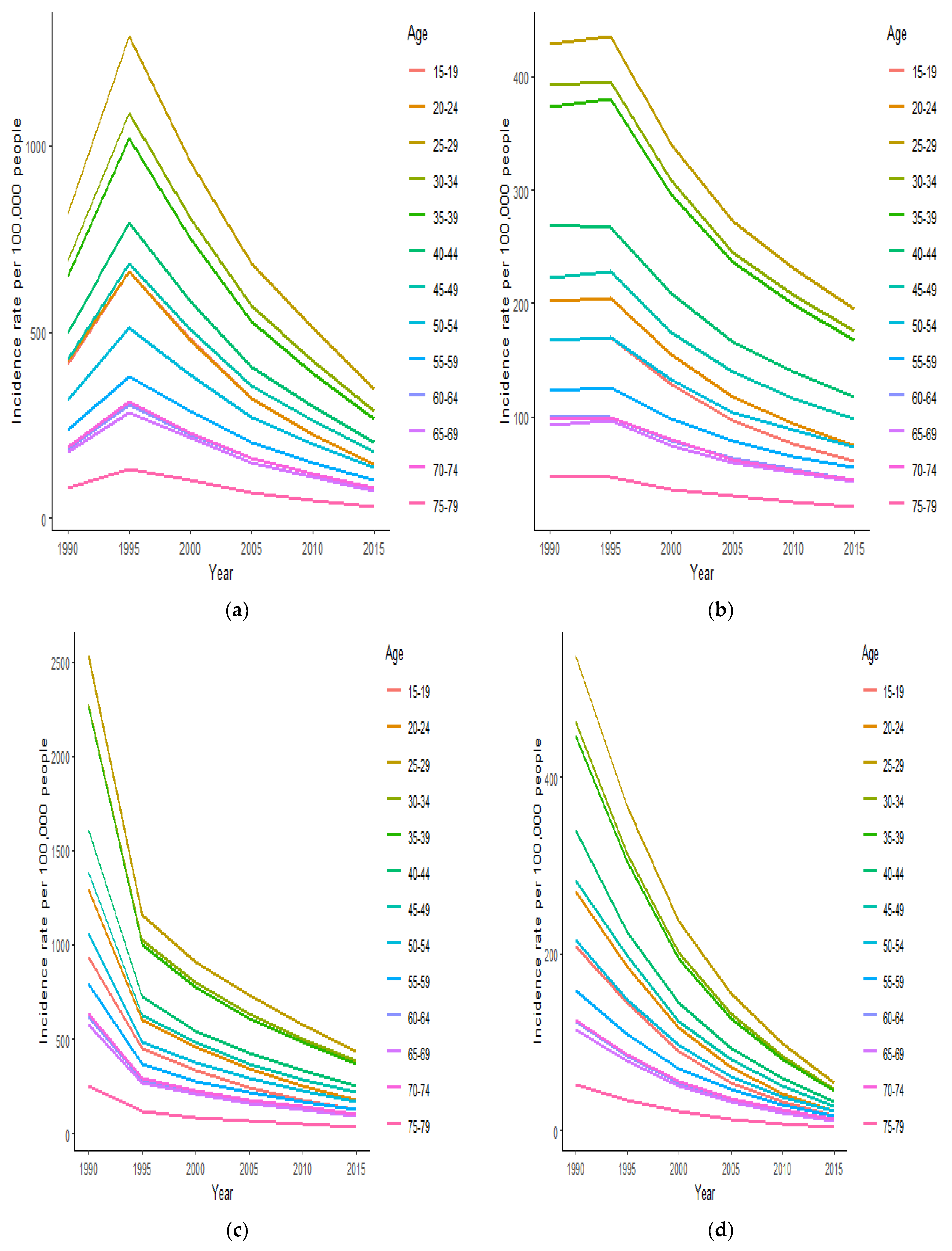
3.2. Net Drifts and Local Drifts of HIV/AIDS Incidence in Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
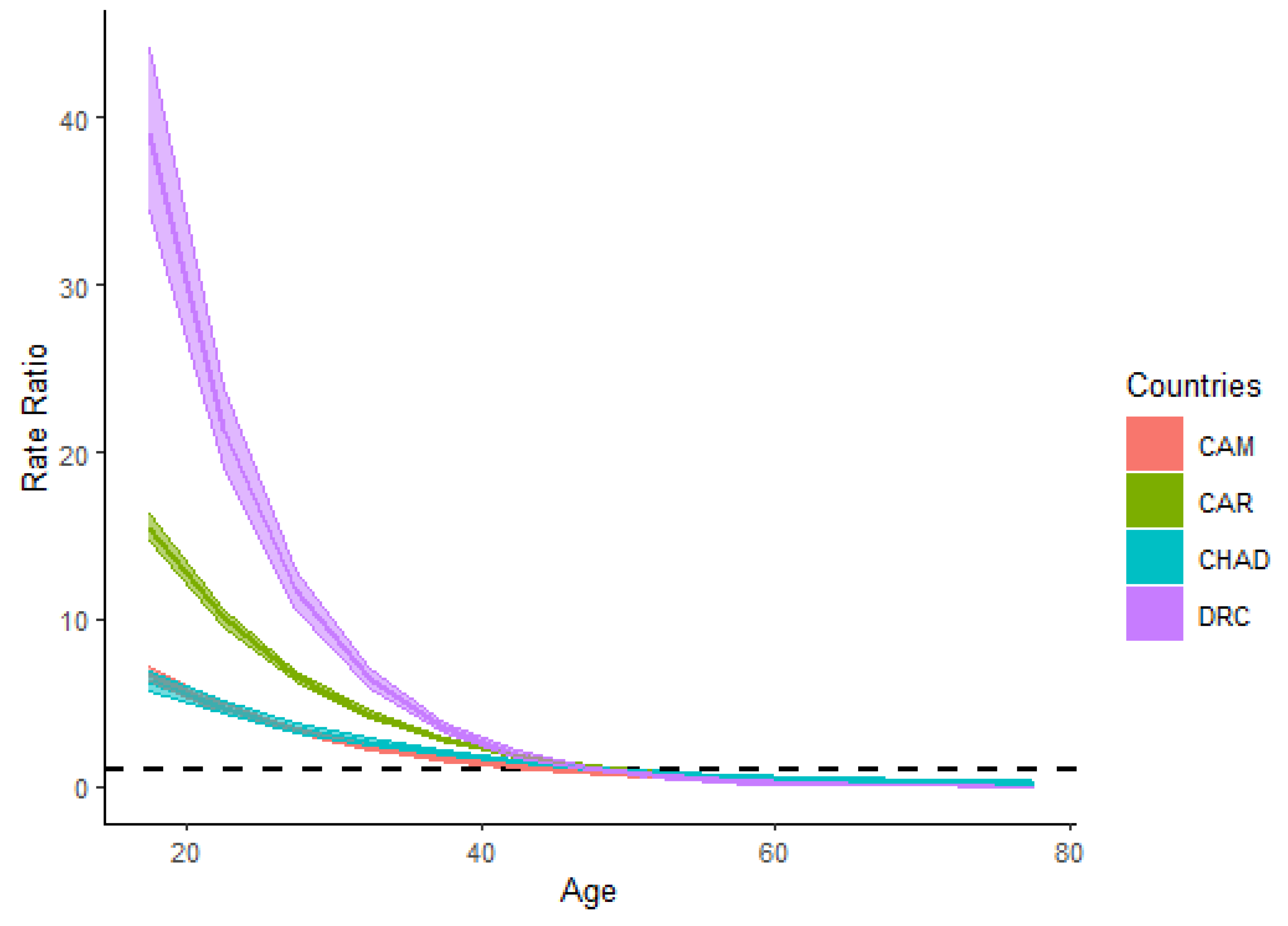
3.3. HIV/AIDS Incidence and Age Relative Risks
3.4. HIV/AIDS Incidence and Period Relative Risks
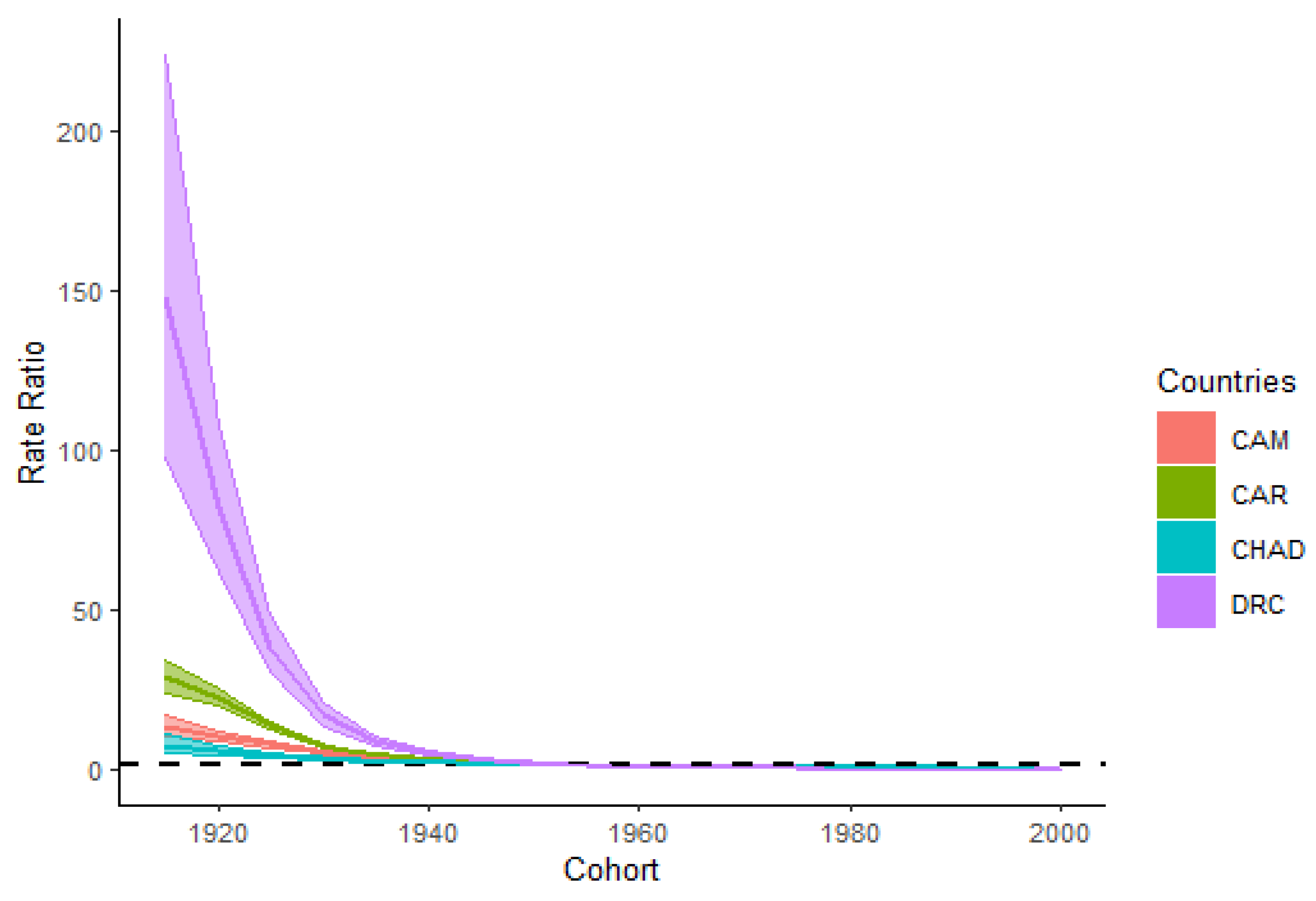
3.5. HIV/AIDS Incidence and Cohort Relative Risks
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. HIV/AIDS Basics. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/HIV/AIDS/basics/whatisHIV/AIDS.html (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Avert. Global HIV/AIDS and AIDS Statistics. 2020. Available online: https://www.avert.org/global-HIV/AIDS-and-aids-statistics (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- World Health Organization Regional Office for Africa. HIV/AIDS/AIDS. Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/HIV/AIDSaids (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Avert. HIV/AIDS and AIDS in West and Central Africa Overview. 2019. Available online: https://www.avert.org/HIV/AIDS-and-aids-west-and-central-africa-overview (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- University of Pittsburgh. Central African Countries. Available online: https://pitt.libguides.com/c.php?g=12378&p=65816 (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- UNAIDS. Cameroon. Country. 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/cameroon (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- UNAIDS. Chad. Country. 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/chad (accessed on 10 November 2020).
- UNAIDS. Central African Republic. Country. 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/centralafricanrepublic (accessed on 1 November 2020).
- UNAIDS. Democratic Republic of the Congo. Country. 2019. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/regionscountries/countries/democraticrepublicofthecongo (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Africanews. Death. HIV/AIDS/AIDS Is No More the Leading Cause of Death in Africa. 2017. Available online: https://www.africanews.com/2017/08/15/HIV/AIDSaids-is-no-more-the-leading-cause-of-death-in-africa// (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- IndexMundi. VIH/SIDA—Taux D’incidence Du Sida (Adultes) (%). Diagrammes Historiques de Données Par Année>Cameroun. 2020. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/g/g.aspx?v=32&c=cm&l=fr (accessed on 4 November 2020).
- IndexMundi. VIH/SIDA—Taux D’incidence Du Sida (Adultes) (%). Diagrammes Historiques de Données Par Année>République Centrafricaine. 2019. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/g/g.aspx?v=32&c=ct&l=fr (accessed on 19 November 2020).
- IndexMundi. VIH/SIDA—Taux D’incidence Du Sida (Adultes) (%). Diagrammes Historiques de Données Par Année>Tchad. 2019. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/g/g.aspx?v=32&c=cd&l=fr (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- IndexMundi. VIH/SIDA—Taux D’incidence Du Sida (Adultes) (%). Diagrammes Historiques de Données Par Année>République Démocratique Du Congo. 2019. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/g/g.aspx?v=32&c=cg&l=fr (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network. Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results; Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME): Seattle, WA, USA, 2020; Available online: http://ghdx.healthdata.org/gbd-results-tool (accessed on 17 November 2020).
- Zou, Z.; Cini, K.; Dong, B.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J.; Burgner, D.P.; Patton, G.C. Time Trends in Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Across the BRICS: An Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of Key Nations with Emerging Economies Using the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Circulation 2020, 141, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holford, T.R. The estimation of age, period and cohort effects for vital rates. Biometrics 1983, 39, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.; Gandini, S.; Boyle, P. Age-period-cohort models: A comparative study of available methodologies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1999, 52, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, P.S.; Anderson, W.F. Age-Period-Cohort Models in Cancer Surveillance Research: Ready for Prime Time? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 20, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Holford, T. Age-period-cohort analysis. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanya, D.; Sama, M.; Tchounwou, P. Current status of HIV/AIDS/AIDS in Cameroon: How effective are control strategies? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSNL/VIH SIDACameroun. Plan Stratégique National De Lutte Contre Le Vih/Sida 2006–2010. MINSANTE. 2006, p. 89. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/---ed_protect/---protrav/---ilo_aids/documents/legaldocument/wcms_126706.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- CSNL/VIH SIDA République Centrafricaine. Cadre Stratégique National de Lutte Contre le VIH et le Sida. 2013, pp. 1–76. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/docs/ELECTRONIC/93910/116674/F2022362440/CAF-93910.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- CSNL/VIH SIDA Tchad. Cadre stratégique national de lutte contre le VIH, le SIDA et les IST, 2011–2015. Noûs 2011, 25. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/docs/MONOGRAPH/97360/115482/F1606408110/TCD-97360.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- PSL/VIH SIDA République Démocratique du Congo. Plan Strategique de Lutte contre le VIH et le SIDA du secteur de la santé. 2008-2012. Available online: https://www.ilo.org/dyn/natlex/docs/ELECTRONIC/91499/106134/F-413555495/COD-91499.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- World Population Review. Most Promiscuous Countries. 2020. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/most-promiscuous-countries (accessed on 19 December 2020).
- STEPHANIE KRAMER. Polygamy is Rare Around the World and Mostly Confined to A Few Regions. Pew Research Center. 2020. Available online: https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2020/12/07/polygamy-is-rare-around-the-world-and-mostly-confined-to-a-few-regions/ (accessed on 26 December 2020).
- World Population Review. Countries Where Polygamy Is Legal. 2021. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/countries-where-polygamy-is-legal (accessed on 3 February 2021).
- Koenig, L.J.; Hoyer, D.; Purcell, D.W.; Zaza, S.; Mermin, J. Young People and HIV/AIDS: A Call to Action. Am. J. Public Health 2016, 106, 402–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Max Roser and Hannah Ritchie (2018)—“HIV/AIDS/AIDS”. Published online at OurWorldInData.org. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/HIV/AIDS-aids (accessed on 26 December 2020).
- The U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Data & Trends: Surveillance People with HIV/AIDS. U.S. Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://www.HIV/AIDS.gov/HIV/AIDS-basics/overview/data-and-trends/statistics (accessed on 26 December 2020).
- World Health Organization. Prevalence of HIV/AIDS Among Adults Aged 15–49 (%). Global Health Observatory (GHO) Data. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/gho/HIV/AIDS/epidemic_status/prevalence/en/ (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- The World Bank. Prevalence of HIV/AIDS, Total (% of Population Ages 15–49)—Cameroon, Chad, Central African Republic, Congo, Dem. Rep. 2019. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.DYN.AIDS.ZS?locations=CM-TD-CF-CD (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- Gao, D.; Zou, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, T.; Cui, W.; Ma, Y. Age-Period-Cohort Analysis of HIV/AIDS Mortality in China: Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosie Perper. The 29 Countries Around the World Where Same-Sex Marriage is Legal. 2020. Available online: https://www.businessinsider.com/where-is-same-sex-marriage-legal-world-2017-11 (accessed on 28 December 2020).
- McCabe, J.; Brewster, K.L.; Tillman, K.H. Patterns and Correlates of Same-Sex Sexual Activity Among U.S. Teenagers and Young Adults. Perspect. Sex. Reprod. Health 2011, 43, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) United States of America (USA). HIV/AIDS and Young Men Who Have Sex With Men; National Center for HIV/AIDS/AIDS, VIral Hepatitis, STD and TB Prevention; 2014; pp. 1–4. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/sexualbehaviors/pdf/HIV/AIDS_factsheet_ymsm.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2020).
- Beyrer, C.; Wirtz, A.L.; Walker, D.; Johns, B.; Sifakis, F.; Baral, S.D. The Global HIV Epidemics among Men Who Have Sex with Men. Available online: https://www.jhsph.edu/research/centers-and-institutes/center-for-public-health-and-human-rights/_pdf/MSMReport_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Gökengin, D.; Oprea, C.; Uysal, S.; Begovac, J. The growing HIV epidemic in Central Europe: A neglected issue? J. Virus Erad. 2016, 2, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumtaz, G.R.; Riedner, G.; Abu-Raddad, L.J. The emerging face of the HIV epidemic in the Middle East and North Africa. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2014, 9, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Population Review. Most Christian Countries. 2020. Available online: https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/most-christian-countries (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- The Religious Institute. To Encourage Responsible Christian Sexual Behavior. RESOLUTION 7-11a. Available online: http://religiousinstitute.org/denom_statements/to-encourage-responsible-christian-sexual-behavior/ (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Abbott, D.M.; Harris, J.E.; Mollen, D. The Impact of Religious Commitment on Women’s Sexual Self-Esteem. Sex. Cult. 2016, 20, 1063–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME. Human Development Index (HDI). Human Development Reports. Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/human-development-index-hdi (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- UNITED NATIONS DEVELOPMENT PROGRAMME. (n.d.) Human Development Index (HDI) Ranking. 2020 Human Development Report. Available online: http://hdr.undp.org/en/content/latest-human-development-index-ranking (accessed on 30 December 2020).
- Ortblad, K.F.; Baeten, J.M.; Cherutich, P.; Wamicwe, J.N.; Wasserheit, J.N. The arc of HIV/AIDS epidemics in sub-Saharan Africa: New challenges with concentrating epidemics in the era of 90-90-90. Curr. Opin. HIV/AIDS 2019, 14, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hu, S.; Sang, S.; Luo, L.; Yu, C. Age–Period–Cohort Analysis of Stroke Mortality in China Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Stroke 2017, 48, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, E.K.; Oh, C.M.; Won, Y.J.; Lee, J.K.; Jung, K.W.; Cho, H.; Jun, J.K.; Lim, M.C.; Ki, M. Trends and Age-Period-Cohort Effects on the Incidence and Mortality Rate of Cervical Cancer in Korea. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 49, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Age | CAR | CAM | CHAD | DRC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local Drift (%) | 95% CI | Local Drift (%) | 95% CI | Local Drift (%) | 95% CI | Local Drift (%) | 95% CI | |
| 15–19 | −9.47 | −9.99; −8.95 | −8.44 | −8.94; −7.93 | −7.23 | −8.02; −6.42 | −11.96 | −13.28; −10.63 |
| 20–24 | −9.14 ꜜ | −9.46; −8.82 | −8.05 ꜜ | −8.39; −7.72 | −6.76 ꜜ | −7.29; −6.24 | −11.70 ꜜ | −12.47; −10.92 |
| 25–29 | −8.93 ꜜ | −9.15; −8.71 | −7.64 ꜜ | −7.89; −7.39 | −6.36 ꜜ | −6.73; −5.99 | −11.75 ꜛ | −12.28; −11.23 |
| 30–34 | −8.83 ꜜ | −9.03; −8.64 | −7.30 ꜜ | −7.54; −7.07 | −6.24 ꜜ | −6.57; −5.90 | −11.94 ꜛ | −12.40; −11.47 |
| 35–39 | −8.57ꜜ | −8.77; −8.37 | −6.94 ꜜ | −7.18; −6.71 | −6.2 ꜜ | −6.54; −5.85 | −11.85 ꜜ | −12.31; −11.39 |
| 40–44 | −8.03 ꜜ | −8.24; −7.82 | −6.52 ꜜ | −6.78; −6.26 | −6.08 ꜜ | −6.45; −5.71 | −11.45 ꜜ | −11.93; −10.97 |
| 45–49 | −7.41 ꜜ | −7.65; −7.19 | −6.11 ꜜ | −6.39; −5.83 | −5.86 ꜜ | −6.27; −5.45 | −10.79 ꜜ | −11.31; −10.26 |
| 50–54 | −7.02 ꜜ | −7.27; −6.77 | −5.95 ꜜ | −6.26; −5.64 | −5.45 ꜜ | −5.91; −4.99 | −10.21 ꜜ | −10.79; −9.64 |
| 55–59 | −7.00 ꜜ | −7.28; −6.72 | −6.15 ꜛ | −6.50; −5.80 | −4.87 ꜜ | −5.39; −4.35 | −10.13 ꜜ | −10.77; −9.49 |
| 60–64 | −7.37 ꜛ | −7.67; −7.06 | −6.45 ꜛ | −6.83; −6.07 | −4.50 ꜜ | −5.07; −3.92 | −10.55 ꜛ | −11.24; −9.85 |
| 65–69 | −8.48 ꜛ | −8.81; −8.15 | −6.75 ꜛ | −7.17; −6.34 | −4.33 ꜜ | −4.96; −3.70 | −11.57 ꜛ | −12.32; −10.81 |
| 70–74 | −9.35 ꜛ | −9.71; −8.99 | −6.67 ꜜ | −7.16; −6.18 | −4.49 ꜛ | −5.22; −3.76 | −12.66 ꜛ | −13.48; −11.83 |
| 75–79 | −9.29 ꜜ | −9.82; −8.77 | −6.37 ꜜ | −7.14; −5.60 | −4.88 ꜛ | −5.95; −3.80 | −13.11 ꜛ | −14.25; −11.95 |
| Net drift (%) | −8.16 | −8.02; −8.30 | −6.74 | −6.57; −6.91 | −5.63 | −5.38; −5.87 | −11.33 | −10.98; −11.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martial, N.T.; Mubarik, S.; Yu, C. The Trend of HIV/AIDS Incidence and Risks Associated with Age, Period, and Birth Cohort in Four Central African Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052564
Martial NT, Mubarik S, Yu C. The Trend of HIV/AIDS Incidence and Risks Associated with Age, Period, and Birth Cohort in Four Central African Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(5):2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052564
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartial, Nodjimadji Tamlengar, Sumaira Mubarik, and Chuanhua Yu. 2021. "The Trend of HIV/AIDS Incidence and Risks Associated with Age, Period, and Birth Cohort in Four Central African Countries" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 5: 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052564
APA StyleMartial, N. T., Mubarik, S., & Yu, C. (2021). The Trend of HIV/AIDS Incidence and Risks Associated with Age, Period, and Birth Cohort in Four Central African Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(5), 2564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052564








