An Application of a Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primary Headache Classification
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Early Literature Research
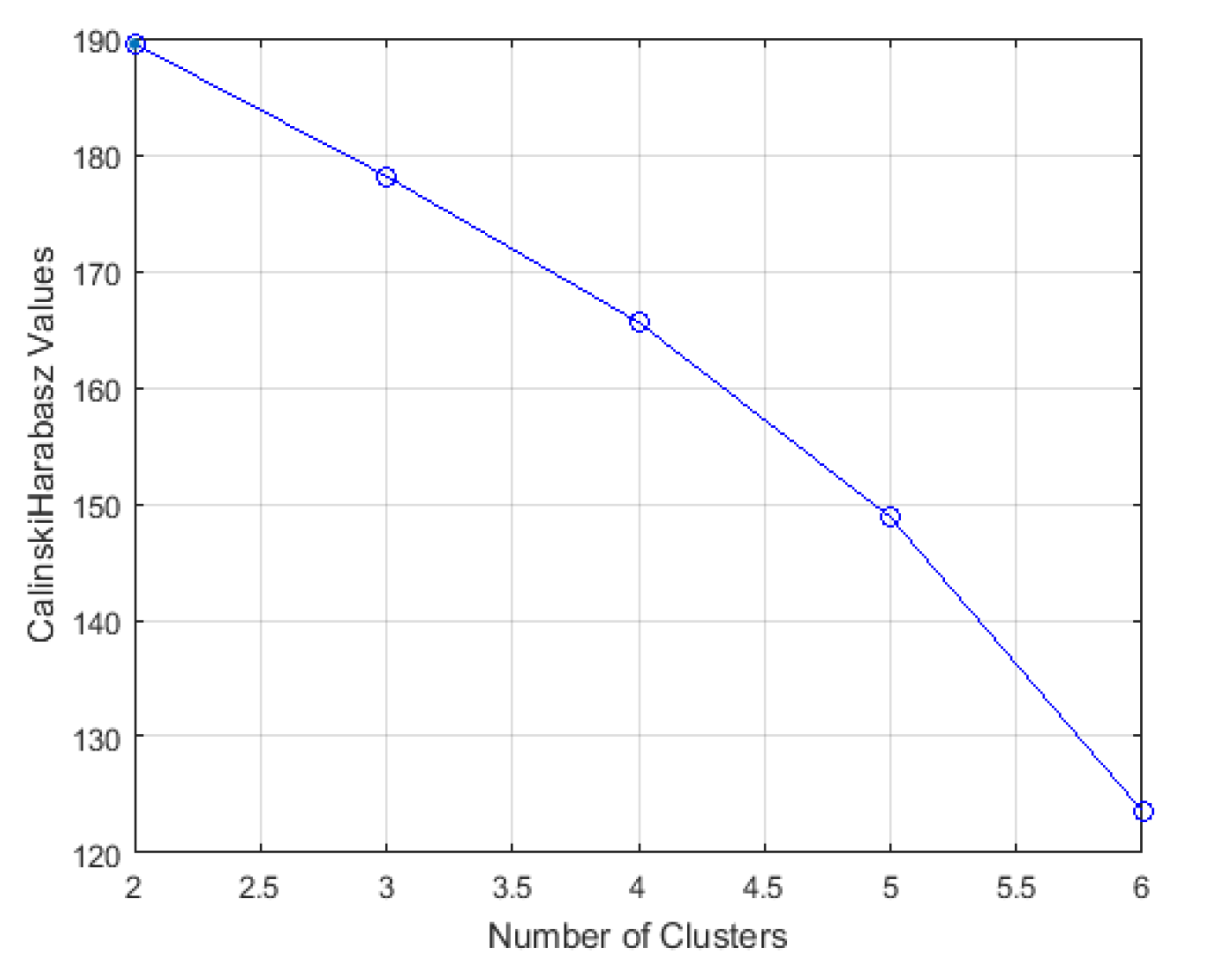
2.4. Optimal Number of Clusters
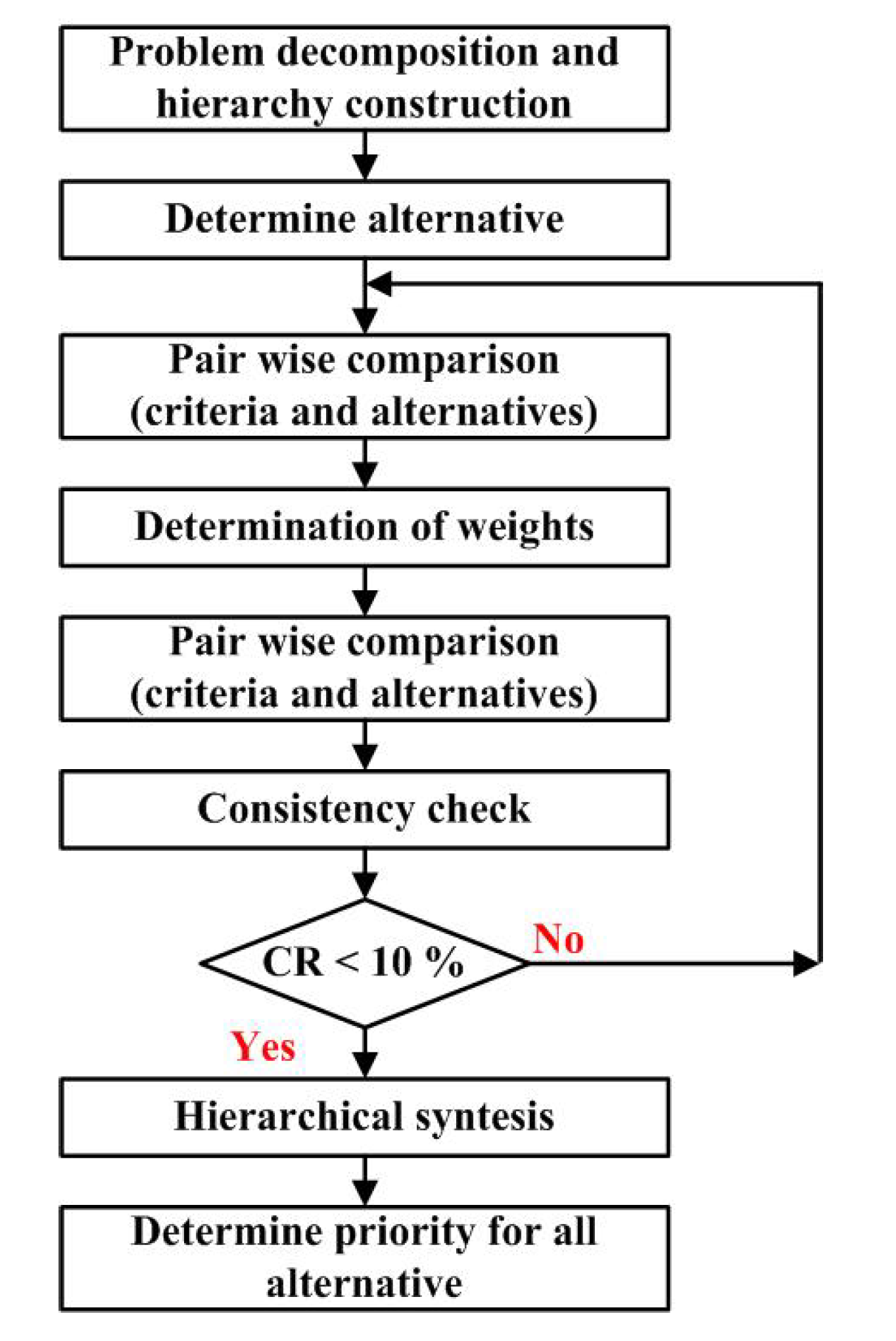
2.5. Analytical Hierarchy Process
2.6. Weighted Fuzzy C-means Clustering Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Weighted fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm |
| Begin Step 1: ---Initialization. X, c, ε > 0, W Step 2: ---Randomly select V cluster centers. 2 ≤ c ≤ N Step 3: ---Choose an appropriate level of cluster fuzzinessf. f [1, ∞], f > 1 Step 4: ---Choose an appropriate membership matrix U with size N × c × M Uijm ∈ [0, 1] and for a fixed value of m Step 5: ---Calculate the cluster centers. Repeat for jth cluster and its mth dimension Step 6: ---Calculate the Euclidean distance Step 7: ---Update fuzzy membership matrix U according to Dijm Step 8: Until U ≤ ε |
| End. |
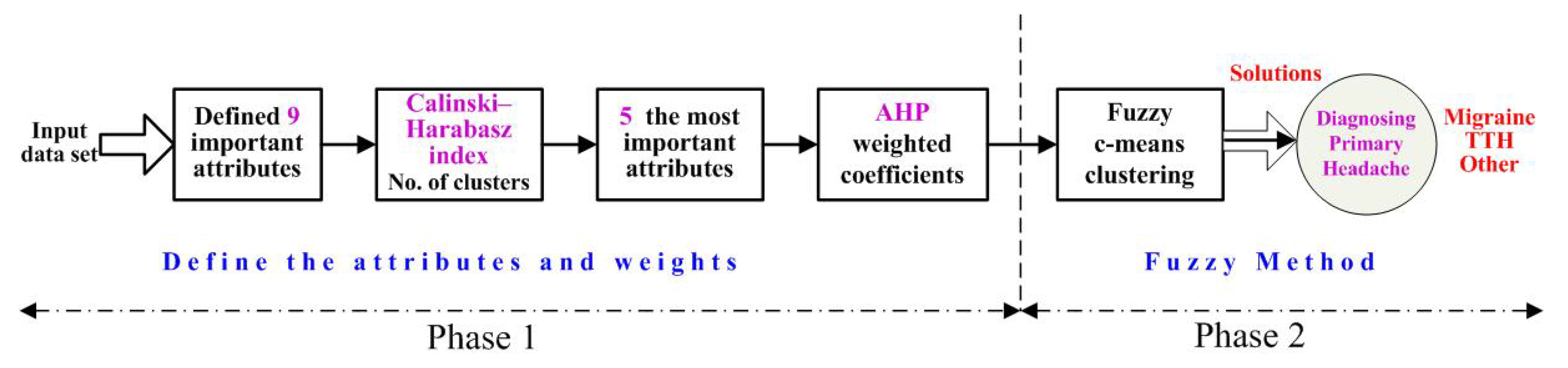
2.7. Implemented System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches
2.8. Metrics
3. Results
4. Discussion
- The application of the Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches and computational complexity calculation.
- Experimental evaluation of the application of the Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches and comparison with the selected state-of-the-art methods.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hagen, K.; Åsberg, N.A.; Uhlig, B.L.; Tronvik, E.; Brenner, E.; Stjern, M.; Helde, G.; Gravadahl, G.B.; Sand, T. The epidemiology of headache disorders: A face-to-face interview of participants in HUNT4. J. Headache Pain 2018, 19, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, B.S.; Stewart, W.F.; Simon, D.; Lipton, R.B. Epidemiology of tension-type headache. JAMA 1998, 279, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saylor, D.; Steiner, T.J. The global burden of headache. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burch, R.C.; Loder, S.; Loder, E.; Smitherman, T.A. The prevalence and burden of migraine and severe headache in the United States: Updated statistics from government health surveillance studies. Headache 2015, 55, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshima, T.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Komon, M.; Stretton, S.; Rajan, N.; Treuer, T.; Ueda, K. Prevalence, burden, and clinical management of migraine in China, Japan, and South Korea: A comprehensive review of the literature. J. Headache Pain 2019, 20, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mennini, F.S.; Gitto, L.; Martelletti, P. Improving care through health economics analyses: Cost of illness and headache. J. Headache Pain 2008, 9, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agosti, R. Migraine burden of disease: From the patient’s experience to a socio-economic view. Headache 2018, 58, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, L.A.; Cainazzo, M.M.; Brovia, D. Risk–Benefit and cost–benefit ratio in headache treatment. J. Headache Pain 2005, 6, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Andlin-Sobocki, P.; Jonsson, B.; Wittchen, H.U.; Olsen, J. Cost of disorder of the brain in Europe. J. Eur. Neurol. 2005, 12 (Suppl. 1), 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.H.; Makson, L.E.; Lipton, R.B.; Stewart, W.F.; Berger, M.L. Burden of migraine in the United States: Disability and economic cost. Arch. Intern. Med. 1999, 159, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kernick, D.P. An introduction to the basic principles of health economics for those involved in the development and delivery of headache care. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.; Di Tanna, G.L.; Lipton, R.B.; Sapra, S.; Villa, G. Costs of acute headache medication use and productivity losses among patients with migraine: Insights from three randomized controlled trials. Pharm. Open 2019, 3, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.J.; Findlay, T.; Moga, C.; Scott, N.A.; Harstall, C.; Taenzer, P. Guideline for primary care management of headache in adults. Can. Fam. Physician 2015, 8, 670–679. [Google Scholar]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 629–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simić, S.; Rabi-Žikić, T.; Villar, J.R.; Calvo-Rolle, J.L.; Simić, D.; Simić, S.D. Impact of individual headache types on the work and work efficiency of headache sufferers. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Simić, D.; Slankamenac, P.; Simić-Ivkov, M. Computer-Assisted diagnosis of primary headaches. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5271, pp. 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Simić, D.; Slankamenac, P.; Simić-Ivkov, M. Rule-Based Fuzzy Logic System for Diagnosing Migraine. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 5138, pp. 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Banković, Z.; Simić, D.; Simić, S.D. A hybrid clustering approach for diagnosing medical diseases. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10870, pp. 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, D.; Ilin, V.; Tanackov, I.; Svirčević, V.; Simić, S. A Hybrid Analytic Hierarchy process for clustering and ranking best location for logistics distribution center. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 9121, pp. 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, D.; Ilin, V.; Svirčević, V.; Simić, S. A hybrid clustering and ranking method for best positioned logistics distribution centre in Balkan Peninsula. Log. J. IGPL 2017, 25, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society. The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, B.; Simić, D.; Simić, S.; Wozniak, M. Automatic diagnosis of primary headaches by machine learning methods. Open Med. 2013, 8, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallon-Ballesteros, A.J.; Correia, L.; Cho, S.-B. Stochastic and non-stochastic feature selection. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10585, pp. 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehr, P.; Diehr, G.; Koepsell, T.; Wood, R.; Beach, K.; Wolcott, B.; Tompkins, R.K. Cluster analysis to determine headache types. J. Chronic Dis. 1982, 35, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, G. Machine Learning Algorithms, 2nd ed.; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Babuška, R.; van der Veen, P.J.; Kaymak, U. Improved covariance estimation for Gustafson-Kessel clustering. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures. J. Math. Psychol. 1977, 15, 123–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, T.L. Analytic Hierarchy Process, Planning, Priority Setting, Resource Allocation; McGraw Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Everitt, B.S.; Landau, S.; Leese, M.; Stahl, D. ClusterAnalysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, J.C. A Fuzzy relative of the ISODATA Process and its use in detecting compact well-separated clusters. J. Cybern. 1973, 3, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdek, J.C. Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective Function Algorithms; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Norwell, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, M. The headache scale: A new approach to the assessment of headache pain based on pain descriptions. Pain 1983, 16, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, A.; Akben, S.B. Use of k-means clustering in migraine detection by using EEG records under flash stimulation. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2011, 6, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, U.; Yurtay, N. An ant colony optimization algorithm-based classification for the diagnosis of primary headaches using a website questionnaire expert system. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 25, 4200–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, U.; Yurtay, N.; Koc, E.R.; Tepe, N.; Gulluoglu, H.; Ertas, M. Diagnostic accuracy comparison of artificial immune algorithms for primary headaches. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2015, 465192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, S.; Banković, Z.; Villar, J.R.; Simić, D.; Simić, S.D. A hybrid fuzzy clustering approach for diagnosing primary headache disorder. Log. J. IGPL 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseleno, A.; Tang, A.Y.C.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Othman, M.; Saputra, S.; Muslihudin, M. Fuzzy AHP method to determine headache types based on symptoms. Investig. Clin. 2017, 58, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gallai, V.; Sarchielli, P.; Alberti, A.; Pedini, M.; Gallai, B.; Rossi, C.; Cittadini, E. Application of the 1988 International Headache Society diagnostic criteria in nine Italian headache centers using a computerized structured record. Headache 2002, 42, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarchielli, P.; Pedini, M.; Alberti, A.; Rossi, C.; Baldi, A.; Corbelli, I.; Calabresi, P. Application of ICHD 2nd edition criteria for primary headaches with the aid of a computerised, structured medical record for the specialist. J. Headache Pain 2005, 6, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Eslami, V.; Rouhani-Esfahani, S.; Hafezi-Nejad, N.; Refaeian, F.; Abdi, S.; Togha, M. A computerized expert system for diagnosing primary headache based on International Classification of Headache Disorder (ICHD-II). Springer Plus 2013, 2, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.-G.; Kim, K.T.; Moon, H.-J.; Do, J.K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Park, S.-P. Suicidality and its risk factors in tension-type headache patients: A multicenter case-control study. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.; Leaver, A.; Sibbritt, D.; Adams, J. The features and burden of headaches within a chiropractic clinical population: A cross-sectional analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 48, 102276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Tseng, W.-T.; Chiang, C.-Y.; Zhang, E.-W.; Wu, C.-H.; Cheng, F.-J. The effect of peer influence on the use of CT by emergency physicians for patients with headaches. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskar, S.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K. Comparison of chronic daily headache with and without medication overuse headache using ICHD II R and ICHD 3 beta criteria. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 183, 105382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, W.F.; Ricci, J.A.; Chee, E.; Morganstein, D.; Lipton, R. Lost productive time and cost due to common pain conditions in the US workforce. JAMA 2003, 290, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duru, G.; Auray, J.P.; Gaudin, A.F.; Dartigues, J.F.; Henry, P.; Lanteri-Minet, M.; Lucas, C.; Pradalier, A.; Chazot, G.; El Hasnaoui, A. Impact of headache on quality of life in general population survey in France (GRIM 2000 Study). Headache 2004, 44, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hasnaoui, A.; Vray, M.; Blin, P.; Nachit-Ouinekh, F.; Boureau, F.; HEMISFERE study group. Assessment of migraine severity using the MIGSEV scale: Relationship to migraine features and quality of life. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrell, J.; Gaskin, D.J.; Richard, P. The economic costs of pain in the United States. J. Pain 2012, 13, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampl, C.; Buzath, A.; Baumhackl, U.; Klingler, D. One-Year prevalence of migraine in Austria: A nation-wide survey. Cephalalgia 2003, 23, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moens, G.; Johannik, K.; Verbeek, C.; Bulterys, S. The prevalence and characteristics of migraine among the Belgian working population. ActaNeurol. Belg. 2007, 107, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Steiner, T.J.; Scher, A.I.; Stewart, W.F.; Kolodner, K.; Liberman, J.; Lipton, R.B. The prevalence and disability burden of adult migraine in England and their relationships to age, gender and ethnicity. Cephalalgia 2003, 23, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ICHD-3 Code | Diagnosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Primary Headache Disorders | ||
| 1. | Migraine | ||
| 1.1 | Migraine without aura (MWoA) | ||
| 1.2 | Migraine with aura (MWA) | ||
| ¦ | ¦ | ||
| 1.6 | Episodic syndromes that may be associated with migraine | ||
| 2. | Tension-type headache (TTH) | ||
| 2.1 | Infrequent episodic tension-type headache | ||
| ¦ | ¦ | ||
| 2.4 | Probable tension-type headache | ||
| 3. | Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias (TACs) | ||
| 4. | Other primary headache disorders | ||
| B | 5. | Secondary headache disorders | |
| ¦ | |||
| 12. | |||
| Attributes | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | RES | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sex | ||||||||
| 2 | How old were you when the headache occurred for the first time? | ||||||||
| 3 | How often do you have headache attacks? | ||||||||
| 4 | How long do the headache attacks last? | ||||||||
| 5 | Where is the headache located? | ||||||||
| 6 | How intense is the pain? | ||||||||
| 7 | What is the quality of the pain you experience? | ||||||||
| 8 | Do your headaches worsen after physical activities such as walking? | ||||||||
| 9 | Do you avoid routine physical activities because you fear they might trigger your headache? | ||||||||
| 10 | Are the headaches accompanied by? a) Nausea | ||||||||
| 11 | Are the headaches accompanied by? b) Vomiting | ||||||||
| 12 | Are the headaches accompanied by? c) Photophobia | ||||||||
| 13 | Are the headaches accompanied by? d) Phonophobia | ||||||||
| 14 | Do you have temporary visual, sensory or speech disturbance? | ||||||||
| 15 | Do you, during a headache attack, have tension and/or heightened tenderness of head or neck muscles? | TTH | |||||||
| 16 | Do you have any body numbness or weakness? | ||||||||
| 17 | Do you have any indications of oncoming headache? | ||||||||
| 18 | Headache is usually triggered by: Menstrual periods | ||||||||
| 19 | In the half or my visual field, lasting 5 minutes to an hour, along with the headache attack or an hour before. | ||||||||
| 20 | Along with the headache attack or an hour before one I have sensory symptoms. |
| Actual Class | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted class | Migraine | TTH | Other | |
| Migraine | TPM | ETM | EOM | |
| TTH | EMT | TPT | EOT | |
| Other | EMO | ETO | TPO | |
| Classes | Attributes | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (4) | (5) | (6) | (7) | (8) | (10) | (12) | (13) | (15) | |
| Migraine | 2.0 ± 0.2 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 2.8 ± 0.6 | 1.3 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| TTHs | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 2.7 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 0.6 | 1.8 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.4 |
| Other | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.7 | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 |
| Attribute (4) | Attribute (6) | Attribute (7) | Attribute (8) | Attribute (15) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attribute (4) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Attribute (6) | ½ | 1 | ½ | 1 | 1 |
| Attribute (7) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Attribute (8) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Attribute (15) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Actual Classes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Migraine | TTHs | Other | Σ | ||
| Predicted classes | Migraine | 146 | 44 | 27 | 217 |
| TTH | 21 | 163 | 34 | 218 | |
| Other | 2 | 17 | 125 | 144 | |
| Total | 169 | 224 | 186 | 579 | |
| Migraine | TTHs | Other | Average | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision % | 67.3 | 74.8 | 86.8 | 76.3 |
| Recall % | 86.4 | 72.7 | 67.2 | 75.4 |
| F1score % | 75.6 | 73.7 | 75.7 | 75.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simić, S.; Villar, J.R.; Calvo-Rolle, J.L.; Sekulić, S.R.; Simić, S.D.; Simić, D. An Application of a Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041890
Simić S, Villar JR, Calvo-Rolle JL, Sekulić SR, Simić SD, Simić D. An Application of a Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041890
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimić, Svetlana, José R. Villar, José Luis Calvo-Rolle, Slobodan R. Sekulić, Svetislav D. Simić, and Dragan Simić. 2021. "An Application of a Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041890
APA StyleSimić, S., Villar, J. R., Calvo-Rolle, J. L., Sekulić, S. R., Simić, S. D., & Simić, D. (2021). An Application of a Hybrid Intelligent System for Diagnosing Primary Headaches. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041890








