Emotional Eating in Adults: The Role of Sociodemographics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Self-Regulation—Findings from a U.S. National Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
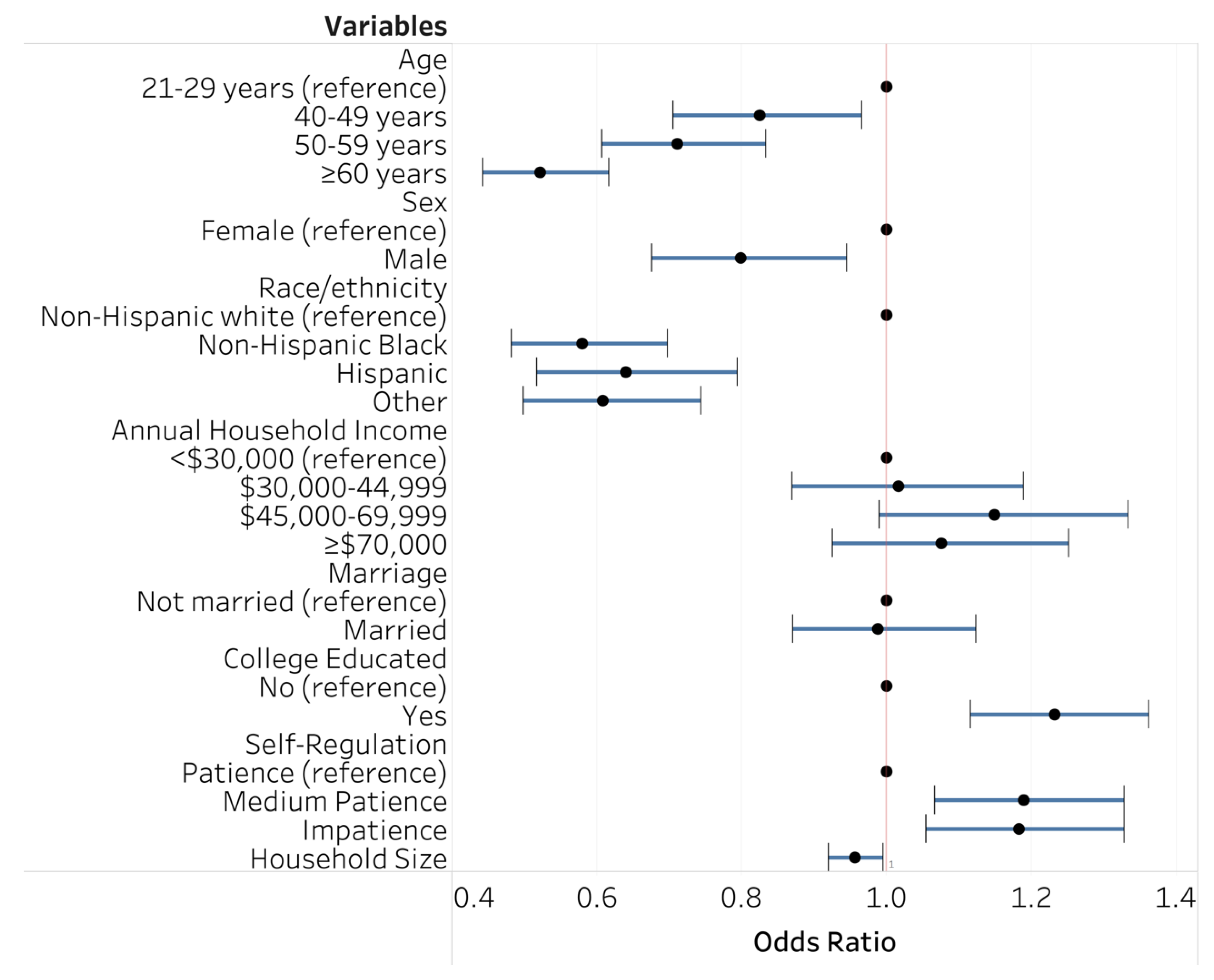
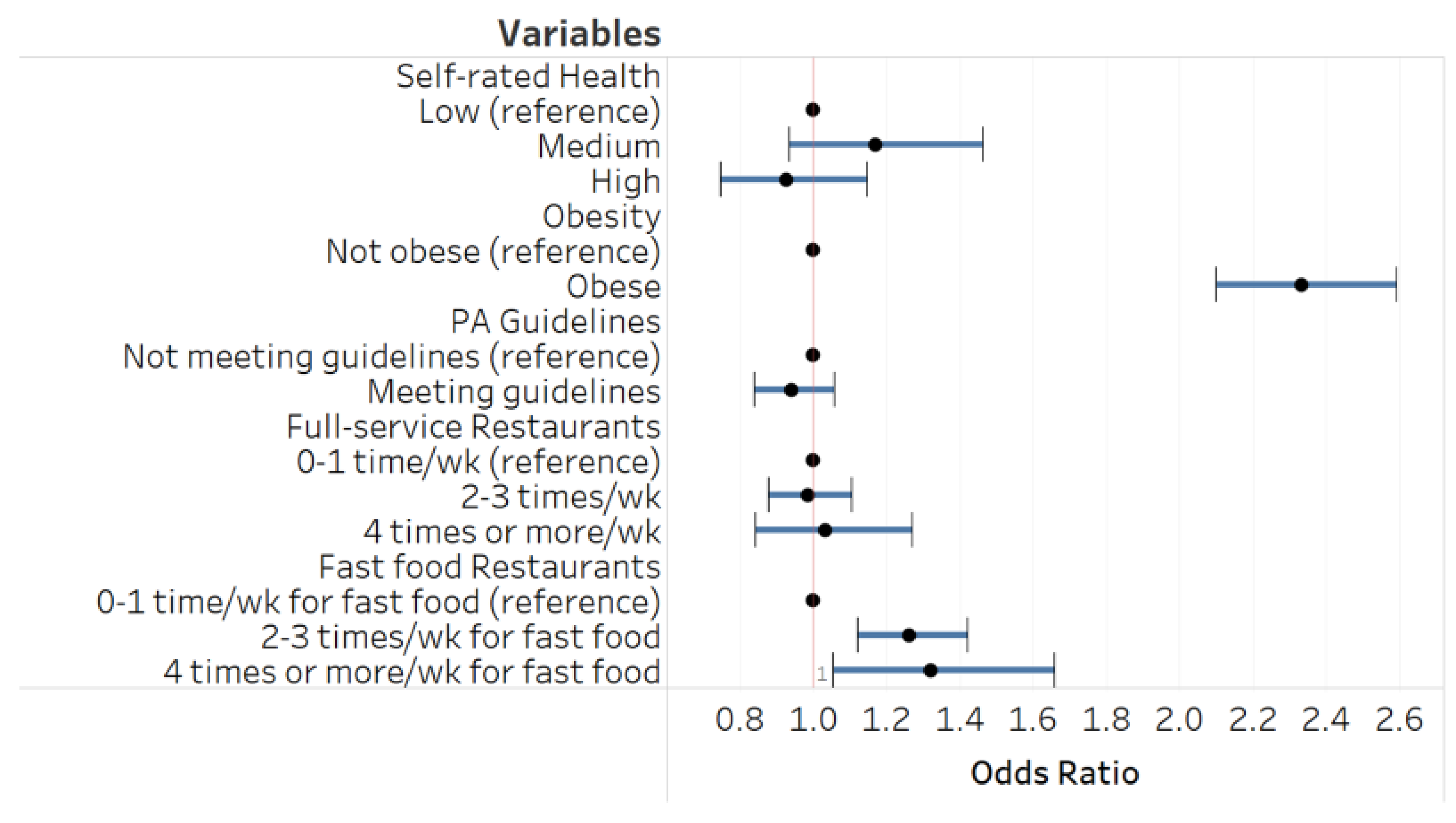
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Freedman, D.S.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in US Youth and Adults by Sex and Age, 2007–2008 to 2015–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 1723–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F. Global, Regional, and National Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Children and Adults during 1980–2013: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trogdon, J.; Finkelstein, E.A.; Hylands, T.; Dellea, P.S.; Kamal-Bahl, S. Indirect Costs of Obesity: A Review of the Current Literature. Obes. Rev. 2008, 9, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Overweight and Obesity. Available online: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/risk_factors/overweight_text/en/ (accessed on 26 February 2020).
- Evers, C.; Marijn Stok, F.; de Ridder, D.T.D. Feeding Your Feelings: Emotion Regulation Strategies and Emotional Eating. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2010, 36, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geliebter, A.; Aversa, A. Emotional Eating in Overweight, Normal Weight, and Underweight Individuals. Eat. Behav. 2003, 3, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J.K.; Van Strien, T.; Eisinga, R.; Engels, R.C.M.E. Gender Differences in the Association between Alexithymia and Emotional Eating in Obese Individuals. J. Psychosom. Res. 2006, 60, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masheb, R.M.; Grilo, C.M. Emotional Overeating and Its Associations with Eating Disorder Psychopathology among Overweight Patients with Binge Eating Disorder. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2006, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianini, L.M.; White, M.A.; Masheb, R.M. Eating Pathology, Emotion Regulation, and Emotional Overeating in Obese Adults with Binge Eating Disorder. Eat. Behav. 2013, 14, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayn, M.; Knäuper, B. Emotional Eating and Weight in Adults: A Review. Curr. Psychol. 2018, 37, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, J.L.; Touyz, S.; Hill, A.J. Negative Mood-Induced Overeating in Obese Binge Eaters: An Experimental Study. Int. J. Obes. 2004, 28, 606–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haedt-Matt, A.A.; Keel, P.K. Revisiting the Affect Regulation Model of Binge Eating: A Meta-Analysis of Studies Using Ecological Momentary Assessment. Psychol. Bull. 2011, 137, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.I.; Kaplan, H.S. The Psychosomatic Concept of Obesity. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 1957, 125, 181–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenders, P.G.; van Strien, T. Emotional Eating, Rather than Lifestyle Behavior, Drives Weight Gain in a Prospective Study in 1562 Employees. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 53, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Strien, T. Causes of Emotional Eating and Matched Treatment of Obesity. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2018, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarevich, I.; Camacho, M.E.I.; del Consuelo Velázquez-Alva, M.; Zepeda, M.Z. Relationship among Obesity, Depression, and Emotional Eating in Young Adults. Appetite 2016, 107, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkavi, A.Z.; Eisenberg, I.W.; Bissett, P.G.; Mazza, G.L.; MacKinnon, D.P.; Marsch, L.A.; Poldrack, R.A. Large-Scale Analysis of Test–Retest Reliabilities of Self-Regulation Measures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5472–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachucki, M.C.; Lovenheim, M.F.; Harding, M. Within-Family Obesity Associations: Evaluation of Parent, Child, and Sibling Relationships. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 47, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuval, K.; Stoklosa, M.; Pachucki, M.C.; Yaroch, A.L.; Drope, J.; Harding, M. Economic Preferences and Fast Food Consumption in US Adults: Insights from Behavioral Economics. Prev. Med. 2016, 93, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, J.L.; Graham, J.W. Missing Data: Our View of the State of the Art. Psychol. Methods 2002, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuval, K.; Drope, J.; Stoklosa, M.; Yaroch, A.L.; Pachucki, M.C.; Harding, M. Time Preferences and Physical Activity: Insights from Behavioral Economics. Health Behav. Policy Rev. 2017, 4, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.L.F.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F. International Physical Activity Questionnaire: 12-Country Reliability and Validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piercy, K.L.; Troiano, R.P.; Ballard, R.M.; Carlson, S.A.; Fulton, J.E.; Galuska, D.A.; George, S.M.; Olson, R.D. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans. JAMA 2018, 320, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.A.; Vinyard, B.T. Fast Food Consumption of US Adults: Impact on Energy and Nutrient Intakes and Overweight Status. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, A.L. Delay Discounting: I’m a k, You’re a k. J. Exp. Anal. Behav. 2011, 96, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.C.; Leonard, T.C.; Shuval, K.; Skinner, C.S.; Eckel, C.; Murdoch, J.C. Economic Preferences and Obesity among a Low-Income African American Community. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2016, 131, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, T.; Shuval, K.; de Oliveira, A.; Skinner, C.S.; Eckel, C.; Murdoch, J.C. Health Behavior and Behavioral Economics: Economic Preferences and Physical Activity Stages of Change in a Low-Income African-American Community. Am. J. Health Promot. 2013, 27, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelson, P.A. A Note on Measurement of Utility. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1937, 4, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoklosa, M.; Shuval, K.; Drope, J.; Tchernis, R.; Pachucki, M.; Yaroch, A.; Harding, M. The Intergenerational Transmission of Obesity: The Role of Time Preferences and Self-Control. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2018, 28, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Strien, T.; Frijters, J.E.R.; Bergers, G.P.A.; Defares, P.B. The Dutch Eating Behavior Questionnaire (DEBQ) for Assessment of Restrained, Emotional, and External Eating Behavior. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1986, 5, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocklisch, F.; Bocklisch, S.F.; Krems, J.F. Sometimes, Often, and Always: Exploring the Vague Meanings of Frequency Expressions. Behav. Res. Methods 2012, 44, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicks, M.; Degeneffe, D.; Rendahl, A.; Edge, M.S.; Meara, B.O.; Blevins, G.; Reicks, M.; Degeneffe, D.; Rendahl, A.; Edge, M.S.; et al. Associations Between Eating Occasion Characteristics and Age, Gender, Presence of Children and BMI Among US Adults. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airburn, C.G.; Harrison, P.J. Eating Disorders. Lancet 2003, 361, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Obesity Is a Common, Serious, and Costly Disease. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/adult.html (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Elran-Barak, R. Self-Esteem, Weight Status, and Trying to Lose Weight during Young Adulthood: The Roles of Sex and Ethnicity/Race. Ethn. Dis. 2019, 29, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Ohrt, T.K.; Hoek, H.W. Prevalence and Treatment of Eating Disorders among Hispanics/Latino Americans in the United States. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2016, 29, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quick, V.M.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C. Disordered Eating, Socio-Cultural Media Influencers, Body Image, and Psychological Factors among a Racially/Ethnically Diverse Population of College Women. Eat. Behav. 2014, 15, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diggins, A.; Woods-Giscombe, C.; Waters, S. The Association of Perceived Stress, Contextualized Stress, and Emotional Eating with Body Mass Index in College-Aged Black Women. Eat. Behav. 2015, 19, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibald, P. Explaining the Minority Status Hypothesis: Development of the Cultural Resilience Life Stress Paradigm. Int. J. Psychol. Psychoanal. 2018, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A.T.; Fought, A. Beyond Alcohol and Drug Addiction. Does the Negative Trait of Low Distress Tolerance Have an Association with Overeating? Appetite 2011, 57, 578–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lluch, A.; Herbeth, B.; Mejean, L.; Siest, G. Dietary Intakes, Eating Style and Overweight in the Stanislas Family Study. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Michel, S.T.; Unger, J.B.; Spruijt-Metz, D. Dietary Correlates of Emotional Eating in Adolescence. Appetite 2007, 49, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Physical Activity for a Healthy Weight. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/physical_activity/index.html (accessed on 6 June 2020).
- Ebneter, D.; Latner, J.; Rosewall, J.; Chisholm, A. Impulsivity in Restrained Eaters: Emotional and External Eating Are Associated with Attentional and Motor Impulsivity. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2012, 17, e62–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konttinen, H.; Haukkala, A.; Sarlio-Lähteenkorva, S.; Silventoinen, K.; Jousilahti, P. Eating Styles, Self-Control and Obesity Indicators. The Moderating Role of Obesity Status and Dieting History on Restrained Eating. Appetite 2009, 53, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, J.P.; Baumeister, R.F.; Boone, A.L. High Self-control Predicts Good Adjustment, Less Pathology, Better Grades, and Interpersonal Success. J. Personal. 2004, 72, 271–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, S.J.; Fennis, B.M.; de Ridder, D.T.; Adriaanse, M.A.; De Vet, E. Health on Impulse: When Low Self-Control Promotes Healthy Food Choices. Health Psychol. 2014, 33, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardisty, D.J.; Thompson, K.F.; Krantz, D.H.; Weber, E.U. How to Measure Time Preferences: An Experimental Comparison of Three Methods. Judgm. Decis. Mak. 2013, 8, 236–249. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, G.W.; Lau, M.I.; Williams, M.B. Estimating Individual Discount Rates in Denmark: A Field Experiment. Am. Econ. Rev. 2002, 92, 1606–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.A.; Matthews, C.E.; Ebbeling, C.B.; Moore, C.G.; Cunningham, J.E.; Fulton, J.; Hebert, J.R. The Effect of Social Desirability and Social Approval on Self-Reports of Physical Activity. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 161, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.H.; Abramson, Z. Making Sense of Data: A Self-Instruction Manual on the Interpretation of Epidemiological Data; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001; ISBN 0-19-975976-6. [Google Scholar]
| Characteristic | n | Percentage * |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| 21–39 | 786 | 13.41% |
| 40–49 | 1605 | 27.38% |
| 50–59 | 1796 | 30.63% |
| 60+ | 1676 | 28.59% |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 454 | 29.67% |
| Female | 1076 | 70.33% |
| Race and ethnicity | ||
| Non-Hispanic White | 4785 | 81.61% |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 426 | 7.27% |
| Hispanic | 308 | 5.25% |
| Other | 344 | 5.87% |
| Annual household income | ||
| <$30,000 | 1087 | 18.54% |
| $30,000–44,999 | 1030 | 17.57% |
| $45,000–69,999 | 1559 | 26.59% |
| ≥$70,000 | 2187 | 37.30% |
| Married | ||
| No | 4113 | 70.15% |
| Yes | 1750 | 29.85% |
| College Graduate | ||
| No | 3187 | 54.36% |
| Yes | 2676 | 45.64% |
| Household Size- Mean (SD) | 5863 | 2.84 (1.43) |
| Self-rated Health | ||
| Low | 331 | 5.65% |
| Medium | 1356 | 23.13% |
| High | 4176 | 71.23% |
| Self-Regulation | ||
| Patience | 2434 | 41.52% |
| Medium patience | 1837 | 31.33% |
| Impatience | 1592 | 27.15% |
| Obese | ||
| No | 3892 | 66.38% |
| Yes | 1971 | 33.62% |
| Meeting PA Guidelines | ||
| No | 4603 | 78.51% |
| Yes | 1260 | 21.49% |
| Fast-food restaurants | ||
| 0–1 times/week | 4344 | 74.09% |
| 2–3 times/week | 1240 | 21.15% |
| ≥4 times per week | 279 | 4.76% |
| Full-service Restaurants | ||
| 0–1 times/week | 4171 | 71.14% |
| 2–3 times/week | 1332 | 22.72% |
| ≥4 times per week | 360 | 6.14% |
| Emotional Eating | ||
| Never | 1047 | 17.86% |
| Rarely | 1744 | 29.75% |
| Sometimes | 1868 | 31.86% |
| Often | 680 | 11.60% |
| Very often | 524 | 8.94% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elran Barak, R.; Shuval, K.; Li, Q.; Oetjen, R.; Drope, J.; Yaroch, A.L.; Fennis, B.M.; Harding, M. Emotional Eating in Adults: The Role of Sociodemographics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Self-Regulation—Findings from a U.S. National Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041744
Elran Barak R, Shuval K, Li Q, Oetjen R, Drope J, Yaroch AL, Fennis BM, Harding M. Emotional Eating in Adults: The Role of Sociodemographics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Self-Regulation—Findings from a U.S. National Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(4):1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041744
Chicago/Turabian StyleElran Barak, Roni, Kerem Shuval, Qing Li, Reid Oetjen, Jeffrey Drope, Amy L. Yaroch, Bob M. Fennis, and Matthew Harding. 2021. "Emotional Eating in Adults: The Role of Sociodemographics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Self-Regulation—Findings from a U.S. National Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 4: 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041744
APA StyleElran Barak, R., Shuval, K., Li, Q., Oetjen, R., Drope, J., Yaroch, A. L., Fennis, B. M., & Harding, M. (2021). Emotional Eating in Adults: The Role of Sociodemographics, Lifestyle Behaviors, and Self-Regulation—Findings from a U.S. National Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(4), 1744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18041744






