Eustachian Tube Function Assessment after Radiofrequency Turbinate Reduction in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelikan, Z. Chronic otitis media (secretory) and nasal allergy. Scr. Med. 2006, 79, 177–178. [Google Scholar]
- Bentivegna, D.; Salvago, P.; Agrifoglio, M.; Ballacchino, A.; Ferrara, S.; Mucia, M.; Sireci, F.; Martines, F. The linkage between Upper Respiratory Tract Infections and Otitis Media: Evidence of the ‘United airways concept’. Acta Med. Medit. 2012, 28, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Tewfik, T.L.; Mazer, B. The links between allergy and otitis media with effusion. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 14, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martines, F.; Salvago, P.; Ferrara, S.; Messina, G.; Mucia, M.; Plescia, F.; Sireci, F. Factors influencing the development of otitis media among Sicilian children affected by upper respiratory tract infections. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 82, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casselbrant, M.L.; Mandel, E.M. Epidemiology. In Evidence-Based Otitis Media, 2nd ed.; Rosenfeld, R.M., Bluestone, C.D., Eds.; BC Decker: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2000; pp. 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Martines, F.; Bentivegna, D. Audiological investigation of Otitis Media in Children with Atopy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011, 11, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucia, M.; Salvago, P.; Brancato, A.; Cannizzaro, C.; Cannizzaro, E.; Gallina, S.; Ferrara, S.; La Mattina, E.; Mulè, A.; Plescia, F.; et al. Upper respiratory tract infections in children: From case history to management. Acta Med. Medit. 2015, 31, 419–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sade, J.; Ar, A. Middle ear and auditory tube: Middle ear clearance, gas exchange, and pressure regulation. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997, 116, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, G.G.; Gatehouse, S. The prevalence of middle ear disease in the adult British population. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1992, 17, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, S.; Di Marzo, M.; Martines, F.; Ferrara, P. Medical and surgical update on “atelectasic-Adhesive-Tympanosclerotic” otitis media. Otorinolaringologia 2011, 61, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bluestone, C.D. Eustachian Tube. Structure, Function, Role in Otitis Media; BC Decker Inc.: Hamilton, OH, USA; London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hillas, J.; Booth, R.J.; Somerfield, S.; Morton, R.; Avery, J.; Wilson, J.D. A comparative trial of intranasal beclomethasone dipionate and sodium chromoglycate in patients with chronic perennial rhinitis. Clin. Allergy 1980, 10, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, J.; Mygind, N.; Molgaard, F.; Grahne, B.; Holopainen, E.; Malmberget, H.; Brøondbo, K.; Røjne, T. Ordinary and high-dose ipratropium in perennial nonallergic rhinitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1987, 79, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, H. Antihistamines and decongestants. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1992, 6, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, G.; Gass, S.; Ophir, D. The histopathology of the hypertrophic inferior turbinate. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2006, 132, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willatt, D. The evidence for reducing inferior turbinates. Rhinology 2009, 47, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58 (Suppl. 29), 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harju, T.; Kivekäs, I.; Numminen, J.; Rautiainen, M. The effect of inferior turbinate surgery on ear symptoms. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 568–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.; Powell, N.B.; Riley, R.W.; Troell, R.J.; Guilleminault, C. Radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction for treatment of turbinate hypertrophy: A pilot study. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1998, 119, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elwany, S.; Gaimaee, R.; Fattah, H.A. Radiofrequency bipolar submucosal diathermy of the inferior turbinates. Am. J. Rhinol. 1999, 13, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, A.; Yona, L.; Blumen, M.; Louis, B.; Zerah, F.; Rugina, M.; Peynègre, R.; Harf, A.; Escudier, E. Radiofrequency is a safe and effective treatment of turbinate hypertrophy. Laryngoscope 2001, 111, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Society of Audiology. Tympanometry: Recommended Procedure; British Society of Audiology: Reading, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Seifert, M.W.; Seidemann, M.F.; Givens, G.D. An examination of variables involved in tympanometric assessment of Eustachian tube function in adults. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1979, 44, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, J.; Shelton, C. Basic principles and clinical applications of tympanometry. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 1991, 24, 299–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekelle, P.; Takata, G.; Chan, L.; Mangione-Smith, R.; Corley, P.M.; Morphew, T.; Morton, S. Diagnosis, Natural History, and Late Effects of Otitis Media with Effusion. Evid. Rep./Technol. Assess. 2002, 55, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, W.J.; Swarts, J.D.; Banks, J.; Casselbrant, M.L.; Mandel, E.M.; Alper, C.M. Sensitivity andspecificity of eustachian tube function tests in adults. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.E.; Tysome, J.R. Tests of Eustachian tube function: A review. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2015, 40, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Su, K.; Zhu, B.; Wu, Y.; Shi, H.; Yin, S. Detection of Eustachian tube openings by tubomanometry in adult otitis media with effusion. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 3109–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Avoort, S.J.; van Heerbeek, N.; Zielhuis, G.A.; Cremers, C.W. Sonotubometry: Eustachian tube ventilatory function test: A state-of-the-art review. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoul, E.D.; Anand, V.K.; Christos, P.J. Validating the clinical assessment of eustachian tube dysfunction: The Eustachian Tube Dysfunction Questionnaire (ETDQ-7). Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.S.; Swarts, J.D.; Alper, C.M. Accuracy of the ETDQ-7 Questionnaire for Identifying Persons with Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 158, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, W.K.; Willatt, D.J. The relationship between middle ear pressure and deviated nasal septum. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1993, 8, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanda, M.S.; Kaur, M.; Bhatia, S. Impact of septoplasty on hearing and middle ear function. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şereflican, M.; Yurttaş, V.; Oral, M.; Yılmaz, B.; Dağlı, M. Is middle ear pressure affected by nasal packings after septoplasty? J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2015, 11, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, M.; Dağlı, E.; Kırat, S. Does Nasal Septal Deviation Affect the Eustachian Tube Function and Middle Ear Ventilation? Turk. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 56, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvinelli, F.; Casale, M.; Greco, F.; D’Ascanio, L.; Petitti, T.; Di Peco, V. Nasal surgery and Eustachian tube function: Effects on middle ear ventilation. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2005, 30, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyildiz, M.Y.; Özmen, Ö.A.; Demir, U.L.; Kasapoğlu, F.; Coşkun, H.H.; Basut, O.I.; Siğirli, D. Impact of septoplasty on Eustachian tube functions. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 1929–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo-Sáenz, J.G.; Galván-Aguilera, A.A.; Martínez-Ordaz, V.A.; Velasco-Rodríguez, V.M.; Nieves-Rentería, A.; Rincón-Castañeda, C. Eustachian tube dysfunction in allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 32, 626–629. [Google Scholar]
- Doğan, R. The Effect of Types of Nasal Septum Deviation on the Eustachian Tube Function. Bezmialem Sci. 2019, 7, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ETDQ-7 | Atopic + Non-Atopic G1 + G2 | Atopic G1 | Non-Atopic G2 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Items | Pre-Surgery Mean (SD) | Post-Surgery Mean (SD) | T-Test (p-Value) | Pre-Surgery Mean (SD) | Post-Surgery Mean (SD) | T-Test (p-Value) | Pre-Surgery Mean (SD) | Post-Surgery Mean (SD) | T-Test (p-Value) |
| Pressure in the ears? | 1.75 ± 0.81 | 1.55 ± 0.79 | 0.09 | 1.87 ± 0.87 | 1.72 ± 0.89 | 0.41 | 1.63 ± 0.75 | 1.38 ± 0.63 | 0.08 |
| Pain in the ears? | 1.87 ± 1.37 | 1.64 ± 1.10 | 0.21 | 2.12 ± 1.52 | 1.89 ± 1.29 | 0.43 | 1.63 ± 1.18 | 1.41 ± 0.83 | 0.28 |
| A feeling that your ears are clogged or “under water”? | 1.94 ± 0.96 | 1.69 ± 0.89 | 0.05 | 2.25 ± 0.88 | 1.87 ± 0.95 | 0.04 | 1.65 ± 0.95 | 1.51 ± 0.79 | 0.42 |
| Ear symptoms when you have a cold or sinusitis? | 2.21 ± 1.20 | 1.97 ± 1.01 | 0.14 | 2.41 ± 1.25 | 2.23 ± 1.03 | 0.42 | 2.02 ± 1.14 | 1.73 ± 0.93 | 0.18 |
| Crackling or popping sounds in the ears? | 1.61 ± 0.99 | 1.47 ± 0.84 | 0.31 | 1.73 ± 1.04 | 1.58 ± 0.91 | 0.47 | 1.49 ± 0.93 | 1.36 ± 0.75 | 0.48 |
| Ringing in the ears? | 1.27 ± 0.55 | 1.26 ± 0.54 | 0.89 | 1.29 ± 0.50 | 1.27 ± 0.49 | 0.84 | 1.26+0.60 | 1.26 ± 0.60 | 1 |
| A feeling that your hearing is muffled? | 1.78 ± 0.89 | 1.64 ± 0.75 | 0.25 | 1.83 ± 0.86 | 1.68 ± 0.77 | 0.38 | 1.73 ± 0.93 | 1.61 ± 0.73 | 0.47 |
| Mean Total Score (Min–Max) | 12.46 ± 5.77 (8–26) | 11.26 ± 5.04 (7–26) | 0.12 | 13.52 ± 6.11 (8–26) | 12.27 ± 5.61 (7–26) | 0.29 | 11.42 ± 5.28 (8–25) | 10.28 ± 4.25 (7–21) | 0.24 |
| Mean Item Score (Min–Max) | 1.8 ± 0.8 (1.1–3.7) | 1.6 ± 0.7 (1.0–3.7) | 0.12 | 1.9 ± 0.9 (1.1–3.7) | 1.7 ± 0.8 (1.0–3.7) | 0.29 | 1.6 ± 0.7 (1.1–3.5) | 1.5 ± 0.6 (1.0–3.0) | 0.24 |
| William’s Test | Atopic + Non-Atopic | Atopic | Non-Atopic | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G1 + G2 | G1 | G2 | |||||||
| Ears (194) | Ears (96) | Ears (98) | |||||||
| Pre-surgery | Post-surgery | χ2 | Pre-surgery | Post-surgery | χ2 | Pre-surgery | Post-surgery | χ2 | |
| n (%) | n (%) | (p-value) | n (%) | n (%) | (p-value) | n (%) | n (%) | (p-value) | |
| Normal | 141 (72.68) | 140 (72.16) | (0.0001) | 63 (65.62) | 63 (65.62) | (0.0001) | 78 (79.59) | 77 (78.57) | |
| Partially Impaired | 15 (7.73) | 42 (21.65) | 5 (5.21) | 25 (26.04) | 10 (10.20) | 17 (17.35) | |||
| Toymbe | 7 | 15 | 2 | 10 | 5 | 5 | |||
| Valsalva | 8 | 27 | 3 | 15 | 5 | 12 | 0.1 | ||
| Grossly Impaired | 38 (19.59) | 12 (6.18) | 28 (29.17) | 8 (8.33) | 10 (10.20) | 4 (4.08) | |||
| Tympanometry measurements | T-Test | T-Test | T-Test | ||||||
| (p-value) | (p-value) | (p-value) | |||||||
| ECV (cc) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 1.73 ± 0.69 | 1.50 ± 0.46 | (0.0001) | 1.85 ± 0.62 | 1.60 ± 0.49 | (0.002) | 1.60 ± 0.72 | 1.39 ± 0.38 | (0.01) |
| SC (cc) | |||||||||
| Mean ± SD | 1.18 ± 0.37 | 1.17 ± 0.28 | (0.72) | 1.30 ± 0.28 | 1.23 ± 0.29 | (0.10) | 1.06 ± 0.41 | 1.11 ± 0.25 | (0.31) |
| William’s Test | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ETDQ-7 | Pre-Surgery | Post-Surgery | ||||
| Normally | Partially Impaired | Grossly Impaired | Normally | Partially Impaired | Grossly Impaired | |
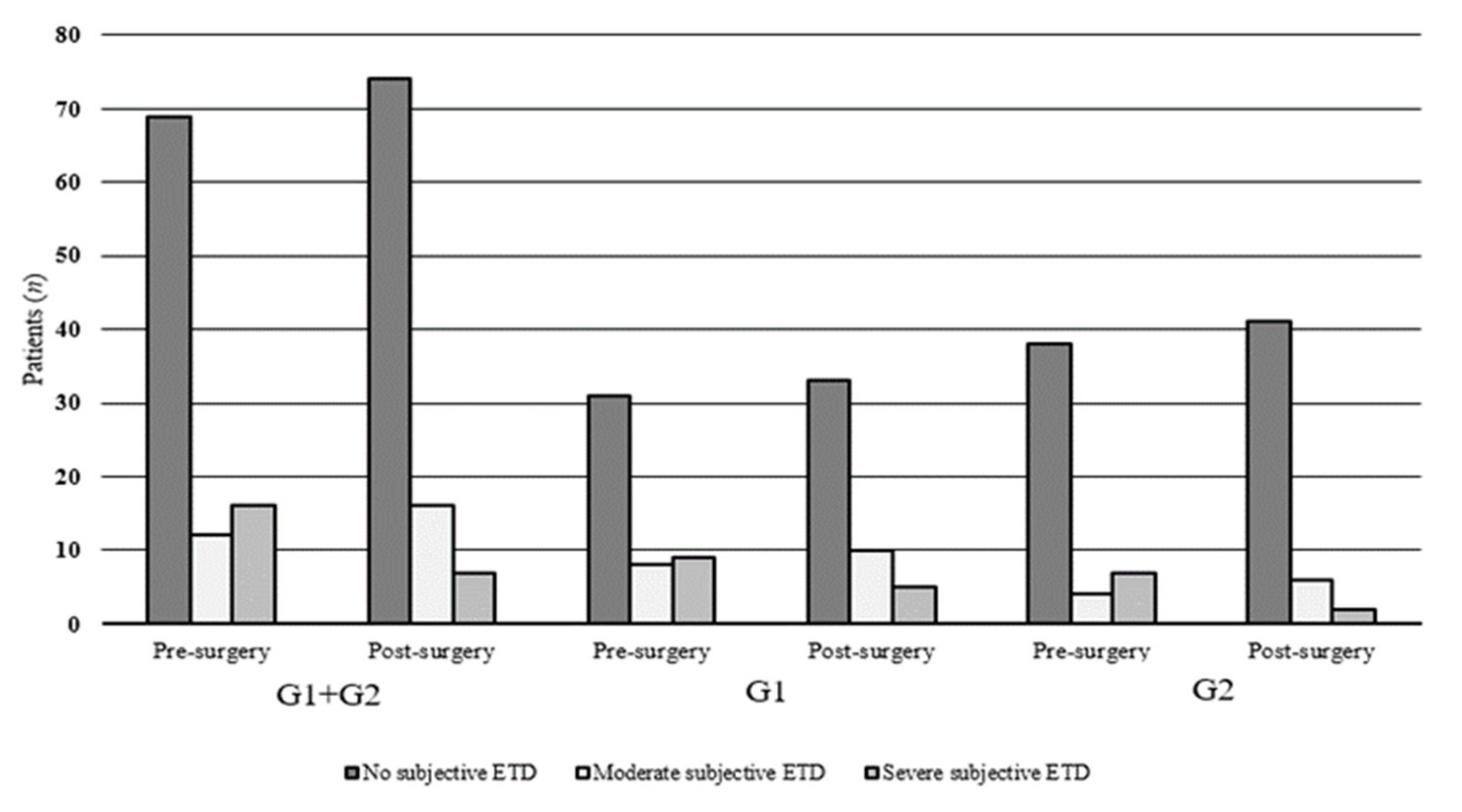
| 1.0–1.9 No subjective ETD | 132 | 6 | 0 | 125 | 23 | 0 |
| 2.0–2.9 Moderately subjective ETD | 7 | 5 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 5 |
| >3.0 Severe subjective ETD | 2 | 4 | 26 | 2 | 5 | 7 |
| TOTAL | 141 | 15 | 38 | 140 | 42 | 12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martines, F.; Dispenza, F.; Sireci, F.; Gallina, S.; Salvago, P. Eustachian Tube Function Assessment after Radiofrequency Turbinate Reduction in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030881
Martines F, Dispenza F, Sireci F, Gallina S, Salvago P. Eustachian Tube Function Assessment after Radiofrequency Turbinate Reduction in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030881
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartines, Francesco, Francesco Dispenza, Federico Sireci, Salvatore Gallina, and Pietro Salvago. 2021. "Eustachian Tube Function Assessment after Radiofrequency Turbinate Reduction in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030881
APA StyleMartines, F., Dispenza, F., Sireci, F., Gallina, S., & Salvago, P. (2021). Eustachian Tube Function Assessment after Radiofrequency Turbinate Reduction in Atopic and Non-Atopic Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18030881







