A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Incidence of Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscess—A 10-Year Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database
2.2. Study Sample
2.3. Population Data
2.4. Statistical Analysis
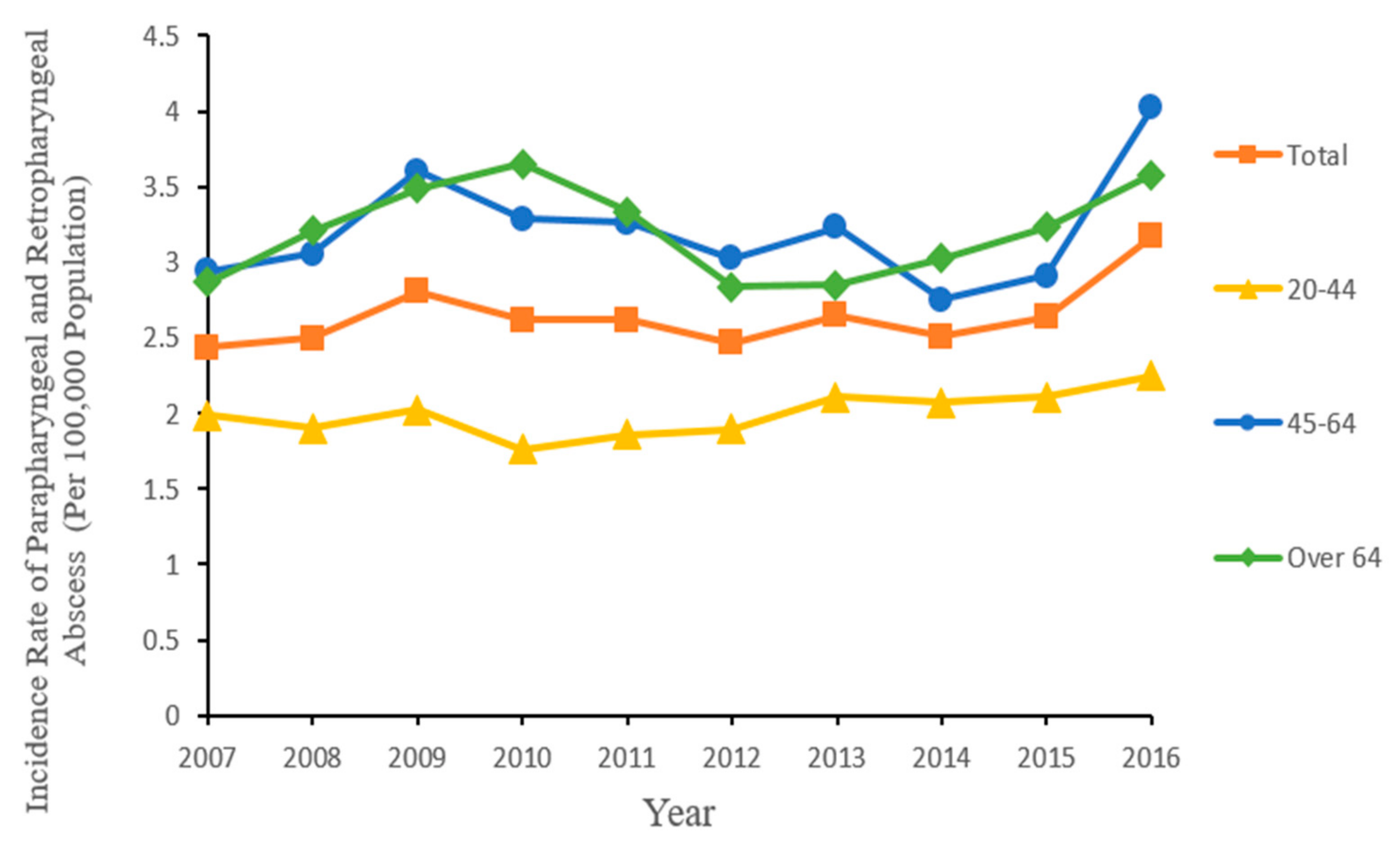
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woods, C.R.; Cash, E.D.; Smith, A.M.; Smith, M.J.; Myers, J.A.; Espinosa, C.M.; Chandran, S.K. Retropharyngeal and Parapharyngeal Abscesses Among Children and Adolescents in the United States: Epidemiology and Management Trends, 2003–2012. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, J.; Harris, A.S.; Addams-Williams, J. Ten years of deep neck space abscesses. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Kimura, Y.; Obara, T. Gas in the retropharyngeal space: Descending necrotising mediastinitis. Lancet 2014, 384, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynehchi, B.B.; Har-El, G. Deep Neck Infection. In Bailey’s Head and Neck Surgery-Otolaryngology, 5th ed.; Johnson, J., Ed.; Lippincott Williams & WJ. Lkins, A Wolters Kluwer Business: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 794–816. [Google Scholar]
- Hurley, R.H.; Douglas, C.M.; Montgomery, J.; Clark, L.J. The hidden cost of deep neck space infections. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2018, 100, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.T.; Liu, T.C.; Chen, P.R.; Tseng, F.Y.; Yeh, T.H.; Chen, Y.S. Deep neck infection: Analysis of 185 cases. Head Neck 2004, 26, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klug, T.E.; Fischer, A.S.; Antonsen, C.; Rusan, M.; Eskildsen, H.; Ovesen, T. Parapharyngeal abscess is frequently associated with concomitant peritonsillar abscess. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monobe, H.; Suzuki, S.; Nakashima, M.; Tojima, H.; Kaga, K. Peritonsillar abscess with parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal involvement: Incidence and intraoral approach. Acta Otolaryngol. Suppl. 2007, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, T.P.; Hazboun, I.M.; Fernandes, F.L.; Bento, L.R.; Zappelini, C.E.M.; Chone, C.T.; Crespo, A.N. Deep neck abscesses: Study of 101 cases. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 83, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gotzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; Initiative, S. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. Int. J. Surg. 2014, 12, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, H.A.; Ference, E.H.; Tan, B.K.; Chandra, R.K.; Kern, R.C.; Smith, S.S. National trends in retropharyngeal abscess among adult inpatients with peritonsillar abscess. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejzlik, J.; Celakovsky, P.; Tucek, L.; Kotulek, M.; Vrbacky, A.; Matousek, P.; Stanikova, L.; Hoskova, T.; Pazs, A.; Mittu, P.; et al. Univariate and multivariate models for the prediction of life-threatening complications in 586 cases of deep neck space infections: Retrospective multi-institutional study. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.F.; Kuo, W.R.; Tsai, S.M.; Huang, K.J. Characterizations of life-threatening deep cervical space infections: A review of one hundred ninety-six cases. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2003, 24, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridder, G.J.; Technau-Ihling, K.; Sander, A.; Boedeker, C.C. Spectrum and management of deep neck space infections: An 8-year experience of 234 cases. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2005, 133, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velhonoja, J.; Laaveri, M.; Soukka, T.; Irjala, H.; Kinnunen, I. Deep neck space infections: An upward trend and changing characteristics. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 277, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Nie, G.; Li, X.; Lin, D.; Luo, J.; Qin, H.; Wu, J.; Wen, W.; et al. Deep Neck Infection: A Review of 130 Cases in Southern China. Medicine 2015, 94, e994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez Pascual, P.; Pinacho Martinez, P.; Friedlander, E.; Martin Oviedo, C.; Scola Yurrita, B. Peritonsillar and deep neck infections: A review of 330 cases. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 84, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panduranga Kamath, M.; Shetty, A.B.; Hegde, M.C.; Sreedharan, S.; Bhojwani, K.; Padmanabhan, K.; Agarwal, S.; Mathew, M.; Rajeev Kumar, M. Presentation and management of deep neck space abscess. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2003, 55, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windfuhr, J.P.; Chen, Y.S. Hospital admissions for acute throat and deep neck infections versus tonsillectomy rates in Germany. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, A.S.; Upile, N.S.; Wilkie, M.D.; Leong, S.C.; Swift, A.C. The rising rate of admissions for tonsillitis and neck space abscesses in England, 1991–2011. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2014, 96, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Wang, M.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, K.S.; Chou, P. Tonsillectomy and the risk for deep neck infection-a nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Min, C.; Lee, W.H.; Choi, H.G. Tonsillectomy increases the risk of retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscesses in adults, but not in children: A national cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celakovsky, P.; Kalfert, D.; Tucek, L.; Mejzlik, J.; Kotulek, M.; Vrbacky, A.; Matousek, P.; Stanikova, L.; Hoskova, T.; Pasz, A. Deep neck infections: Risk factors for mediastinal extension. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 271, 1679–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total No/Mean | %/SD |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 52.16 | 16.61 |
| Age Group (Years) | ||
| 20–44 | 1950 | 33.7 |
| 45–64 | 2438 | 42.2 |
| >64 | 1391 | 24.1 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 3711 | 64.2 |
| Female | 2068 | 35.8 |
| Geographical Location | ||
| Northern | 2818 | 48.8 |
| Central | 1332 | 23 |
| Southern | 1508 | 26.1 |
| Eastern | 121 | 2.1 |
| In-hospital mortality | 115 | 2.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, T.-H.; Xirasagar, S.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Wu, C.-S.; Kao, Y.-W.; Lin, H.-C. A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Incidence of Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscess—A 10-Year Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031049
Yang T-H, Xirasagar S, Cheng Y-F, Wu C-S, Kao Y-W, Lin H-C. A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Incidence of Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscess—A 10-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(3):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031049
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Tzong-Hann, Sudha Xirasagar, Yen-Fu Cheng, Chuan-Song Wu, Yi-Wei Kao, and Herng-Ching Lin. 2021. "A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Incidence of Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscess—A 10-Year Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 3: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031049
APA StyleYang, T.-H., Xirasagar, S., Cheng, Y.-F., Wu, C.-S., Kao, Y.-W., & Lin, H.-C. (2021). A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Incidence of Parapharyngeal and Retropharyngeal Abscess—A 10-Year Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(3), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18031049







