Protocol for a Multi-Level Policy Analysis of Non-Communicable Disease Determinants of Diet and Physical Activity: Implications for Low- and Middle-Income Countries in Africa and the Caribbean
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Aim and Conceptual Frameworks
- To conduct a scoping review (between 2000–2019) of global, regional, national and local (city) policies (declarations, policy statements, written statement, policy intent) to identify the key policy opportunities for intersectoral action (earlier sentinel documents were included, as appropriate).
- To conduct a policy content analysis on policies that meet the inclusion criteria, across relevant sectors, identified from the scoping review to identify the key policy proposals for addressing diet and physical activity interventions.
- Examine the implications of global and regional policy prescripts for African LMICs.
- To examine whether and how policy is transferred from the global to the local level, and how global and regional policies find expression at a country level.
- To explore whether and how policy prescripts provide for intersectoral action in the mitigation of NCDs.
- Lastly, explore how policies address adolescents as an important subpopulation in the prevention of NCDs, and to highlight gender as an important construct in diet and physical activity-related NCD interventions.
3. Study Settings
4. Detail of Study Methods
4.1. The Scoping Reviews
- Identify policies across different sectors with implications for diet (reduction of sugar and salt intake specifically) and physical activity.
- Identify key characteristics of each policy, and the extent to which they incorporate an intersectoral approach to sugar and salt reduction and healthy placemaking.
- Examine the ways through which policies have the potential to impact on the reduction of sugar and salt intake and the promotion of healthy placemaking.
4.2. Identifying Key Sectors for Purposive Policy Document Identification
4.2.1. Data Storage, Coding and Analysis
- First, we will describe each document, outlining the identifying features of each document (as summarized in Table 1).
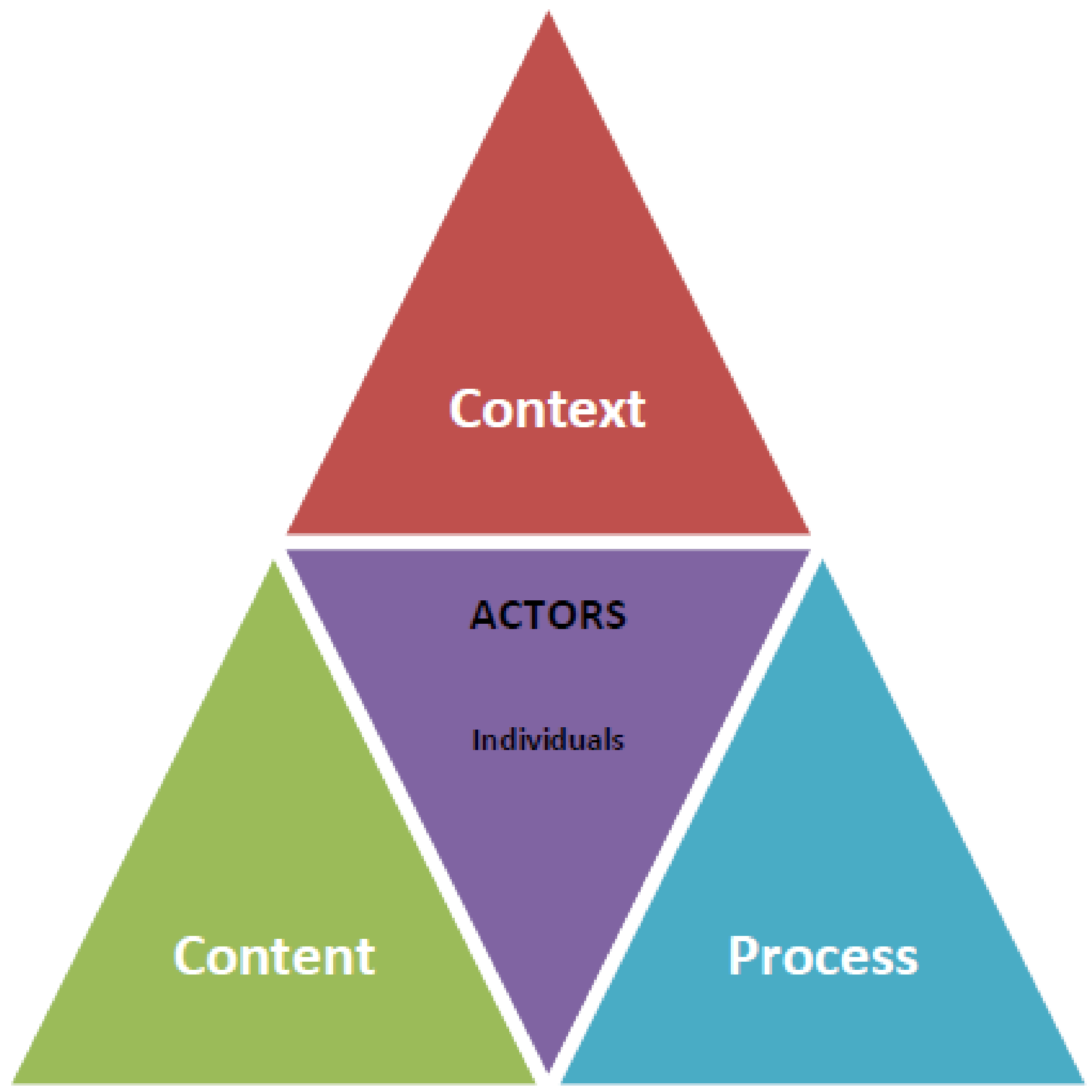
- Second, a high-level description, drawing on the dimensions of the Walt and Gilson policy triangle, will be produced, depending on the level of detail provided in the documents. We will describe:
- ○
- The context in which the document was created.
- ○
- The process by which the document was produced, where this was evident in the documents.
- ○
- The actors involved in the policy, captured either as individuals, or by organization and grouped by sector. This part of the analysis will allow us to ‘map’ all the actors that appear were identified in the documents as participating in the policy process (individuals, networks, agencies, etc.).
- First, we will provide a descriptive account of what the policy statements contain, for example, the exact phrases and terms used and the number of times important concepts appear (such as, for example how many times children or adolescent issues are addressed).
- Then, we will conduct a deeper discourse analysis, where we will assign interpretative meanings, overtly and possibly hidden, in the policy statements. We will interpret these statements within the contexts in which the policy documents were produced.
- A cross-code analysis will follow the detailed analysis of individual codes, where the research team for each sub-study will extract key analytical messages across codes. These will form the basis for reporting the results of each study and presenting them for peer review in a number of different formats (for example, peer review journal publications, policy briefs, policy roundtable discussions). The issues we will explore are outlined in Table 2.
- Finally, we plan to reflect on our findings from across the different sub-studies, particularly across the three studies at the country level, to identify similarities and differences between countries and identify leverages of support for diet and physical activity interventions where possible at the global, regional and country level.
4.2.2. Privacy and Confidentiality
4.2.3. Dissemination of Findings
5. Study Strengths and Limitations
5.1. Strengths
5.2. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Noncommunicable Diseases. Fact Sheet; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 31 March 2021).
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Naghavi, M.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Carter, A.; Casey, D.C.; Charlson, F.J.; Chen, A.Z.; Coates, M.M.; et al. Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2016, 388, 1459–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- United Nations General Assembly. Resolution. Political Declaration of the Third High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases (A/73/L.2); United Nations: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/710899/?ln=en (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- World Health Organization. Updated WHO Projections of Mortality and Causes of Death 2016–2060. Available online: https://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/projections_method.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Hawkes, C.; Harris, J.; Gillespie, S. Changing diets: Urbanization and the Nutrition Transition. In Global Food Policy Report; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI): Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Chapter 4; pp. 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oni, T.; Assah, F.; Erzse, A.; Foley, L.; Govia, I.; Hofman, K.J.; Lambert, E.V.; Micklesfield, L.K.; Shung-King, M.; Smith, J.; et al. The global diet and activity research (GDAR) network: A global public health partnership to address upstream NCD risk factors in urban low and middle-income contexts. Glob. Health 2020, 16, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Mason, C. The physical activity transition. J. Phys. Act. Health 2009, 6, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Sixty-Ninth World Health Assembly Resolutions and Decisions Annexes. WHA69/2016/REC/1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/sustainable-development-goals#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- World Health Organization. Interventions on Diet and Physical Activity: What Works. Summary Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lachat, C.; Otchere, S.; Roberfroid, D.; Abdulai, A.; Seret, F.M.A.; Milesevic, J.; Xuereb, G.; Candeias, V.; Kolsteren, P. Diet and Physical Activity for the Prevention of Noncommunicable Diseases in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: A Systematic Policy Review. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allen, L.N.; Pullar, J.; Wickramasinghe, K.K.; Williams, J.; Roberts, N.; Mikkelsen, B.; Varghese, C.; Townsend, N. Evaluation of research on interventions aligned to WHO ‘Best Buys’ for NCDs in low-income and lowermiddle-income countries: A systematic review from 1990 to 2015. BMJ Glob. Health 2018, 3, e000535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juma, P.A.; Mohamed, S.F.; Matanje Mwagomba, B.L.; Ndinda, C.; Mapa-tassou, C.; Oluwasanu, M.; Oladepo, O.; Abiona, O.; Nkhata, M.J.; Wisdom, J.P.; et al. Non-communicable disease prevention policy process in five African countries. BMC Public Health 2018, 18 (Suppl. S1), 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afshin, A.; Micha, R.; Khatibzadeh, S.; Schmidt, L.; Mozaffarian, D. Dietary policies to reduce noncommunicable diseases. In The Handbook of Global Health Policy; Brown, G., Yamey, G., Wamala, S., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwel: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Moscow Declaration Adopted at the First Global Ministerial Conference on Healthy Lifestyles and Noncommunicable Disease Control; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; Available online: http://www.who.int/nmh/events/moscow_ncds_2011/conference_documents/en/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Afshin, A.; Penalvo, J.; Del Gobbo, L.; Kashaf, M.; Micha, R.; Morrish, K.; Pearson-Stuttard, J.; Rehm, C.; Shangguan, S.; Smith, J.D.; et al. CVD Prevention Through Policy: A Review of Mass Media, Food/Menu Labeling, Taxation/Subsidies, Built Environment, School Procurement, Worksite Wellness, and Marketing Standards to Improve Diet. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2015, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Angell, S.Y.; Lang, T.; Rivera, J.A. Role of government policy in nutrition—Barriers to and opportunities for healthier eating. BMJ 2018, 361, k2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowen, G.A. Document analysis as a qualitative research method. Qual. Res. J. 2009, 9, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buse, K. Addressing the theoretical, practical and ethical challenges inherent in prospectice health policy analysis. Health Policy Plan. 2008, 23, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilson, L.; Raphaely, N. The terrain of health policy analysis in low-and-middle-income countries: A review of published literature 1994–2007. Health Policy Plan. 2008, 23, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walt, G.; Gilson, L. Reforming the health sector in developing countries-the central role of policy analysis. Health Policy Plan. 1994, 9, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- IDS. Understanding Policy Processes. A Review of IDS Research on the Environment. Available online: https://www.ids.ac.uk/files/Policy_Processes06.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Soekarjo, D.D.; Roshita, A.; Thow, A.-M.; Li, M.; Rah, J.H. Strengthening Nutrition-Specific Policies for Adolescents in Indonesia: A Qualitative Policy Analysis. Food Nutr. Bull. 2018, 39, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thow, A.M.; Greenberg, S.; Hara, M.; Friel, S.; duToit, A.; Sanders, D. Improving policy coherence for food security and nutrition in South Africa: A qualitative policy analysis. Food Secur. 2018, 10, 1105–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thow, A.M.; Kadiyala, S.; Khandelwal, S.; Menon, P.; Downs, S.; Reddy, K.S. toward Food Policy for the Dual Burden of Malnutrition: An Exploratory Policy Space Analysis in India. Food Nutr. Bull. 2016, 37, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barlow, P.; Labonte, R.; McKee, M.; Stuckler, D. WHO response to WTO member state challenges on tobacco, food and beverage policies. Bull. World Health Organ. 2019, 97, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Title |
| Year of publication |
| Country |
| Level at which document was produced (National, subnational, local) |
| Producing agency (Government department, non-Governmental agency, etc.) |
| Primary ‘ownership’ of the document, for example, the Department of Health, or Labour or WHO |
| Stated purpose of the document |
| Intended target audience(s) of the document |
| Intended timespan, if stated |
| How is the problem of focus conceptualized in the policy documents? |
| How does this vary between issues and between sectors? |
| How are the target populations defined and described? |
| How are policy positions framed with respect to children and adolescents? |
| What values are embedded in the ideas of the policies about children and adolescents? |
| How are policy positions framed with respect to gender? |
| What values are embedded in the ideas of policies about gender? |
| How might these policy positions influence implementation? |
| Were deviations from global level policies evident in regional and country-level policies and how, by whom and why are these differences expressed? |
| How might these different meanings influence implementation, or explain/shape contestation among actors? |
| How do policies promote implementation (of which aspects and how)? |
| What are the ‘missing aspects’: missing actors, missing policy positions, missing sectors? |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shung-King, M.; Weimann, A.; McCreedy, N.; Tatah, L.; Mapa-Tassou, C.; Muzenda, T.; Govia, I.; Were, V.; Oni, T. Protocol for a Multi-Level Policy Analysis of Non-Communicable Disease Determinants of Diet and Physical Activity: Implications for Low- and Middle-Income Countries in Africa and the Caribbean. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413061
Shung-King M, Weimann A, McCreedy N, Tatah L, Mapa-Tassou C, Muzenda T, Govia I, Were V, Oni T. Protocol for a Multi-Level Policy Analysis of Non-Communicable Disease Determinants of Diet and Physical Activity: Implications for Low- and Middle-Income Countries in Africa and the Caribbean. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(24):13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413061
Chicago/Turabian StyleShung-King, Maylene, Amy Weimann, Nicole McCreedy, Lambed Tatah, Clarisse Mapa-Tassou, Trish Muzenda, Ishtar Govia, Vincent Were, and Tolu Oni. 2021. "Protocol for a Multi-Level Policy Analysis of Non-Communicable Disease Determinants of Diet and Physical Activity: Implications for Low- and Middle-Income Countries in Africa and the Caribbean" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 24: 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413061
APA StyleShung-King, M., Weimann, A., McCreedy, N., Tatah, L., Mapa-Tassou, C., Muzenda, T., Govia, I., Were, V., & Oni, T. (2021). Protocol for a Multi-Level Policy Analysis of Non-Communicable Disease Determinants of Diet and Physical Activity: Implications for Low- and Middle-Income Countries in Africa and the Caribbean. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(24), 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182413061







