Application of Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer to Obtain Chemical Signatures of Various Combustion Aerosols
Abstract
1. Introduction
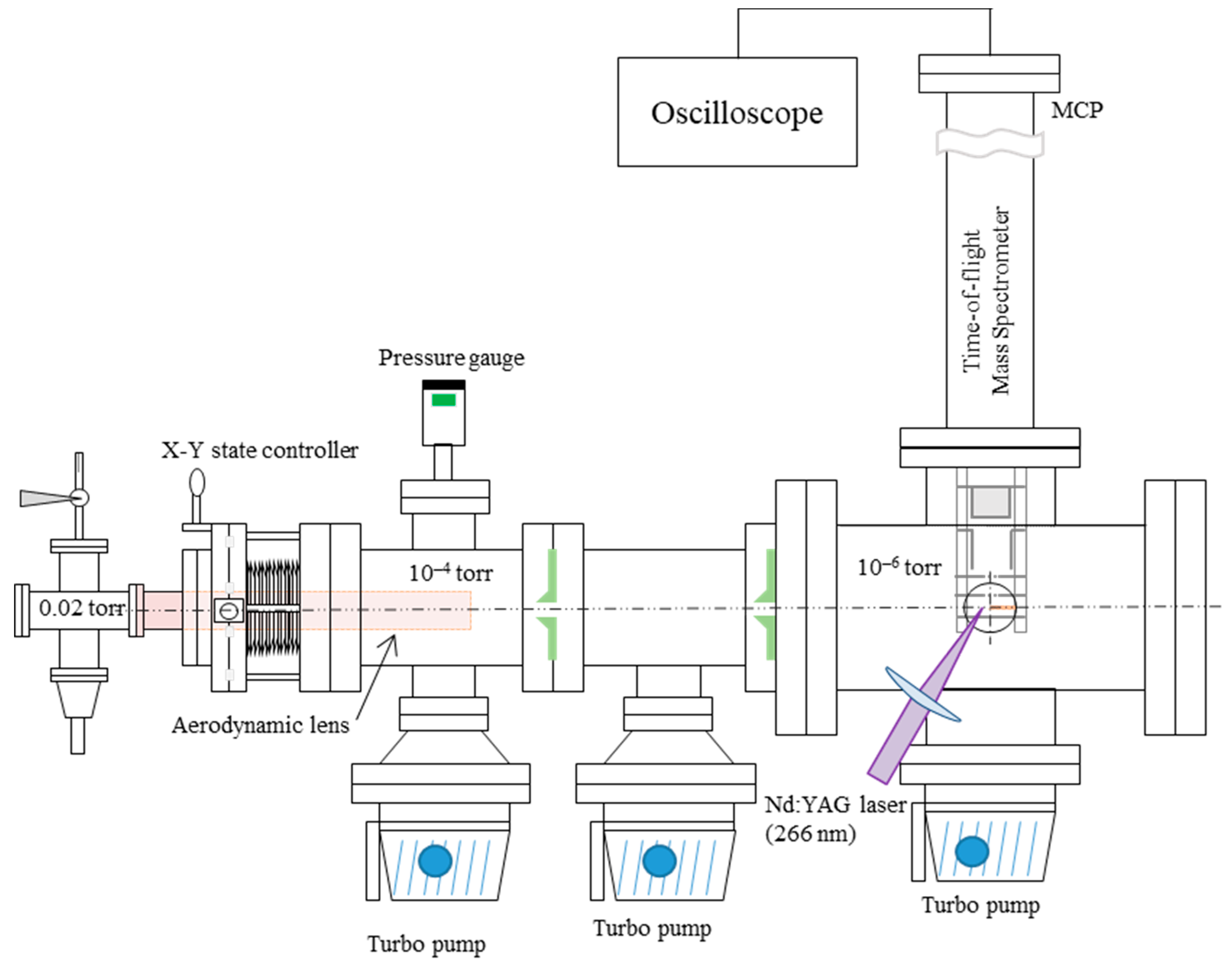
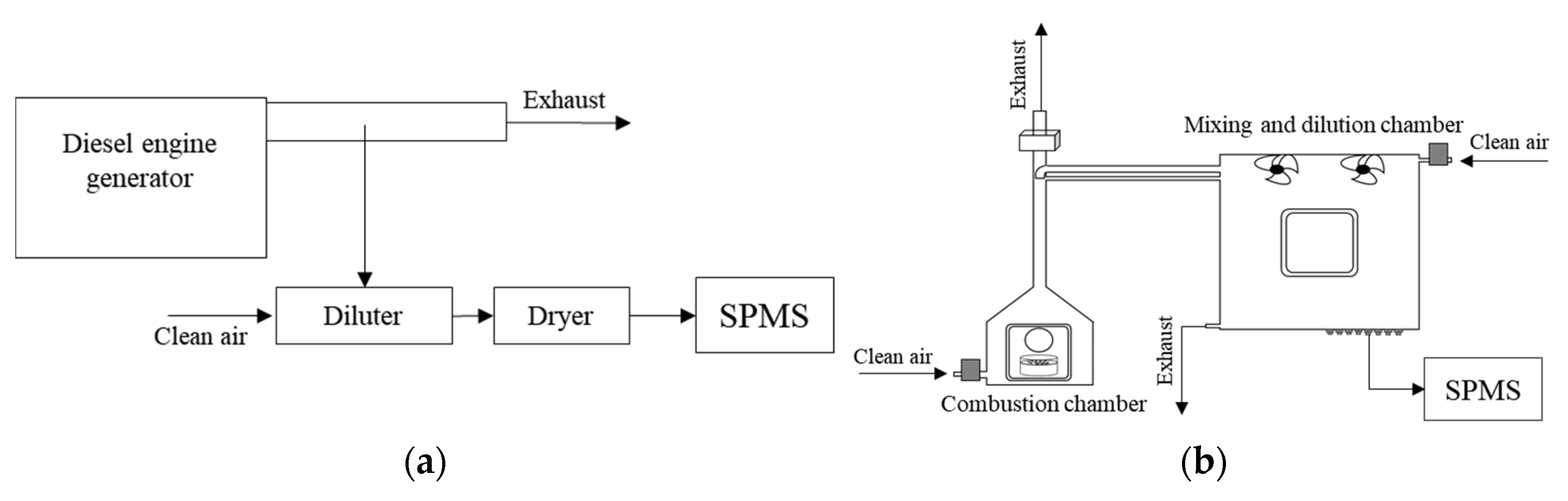
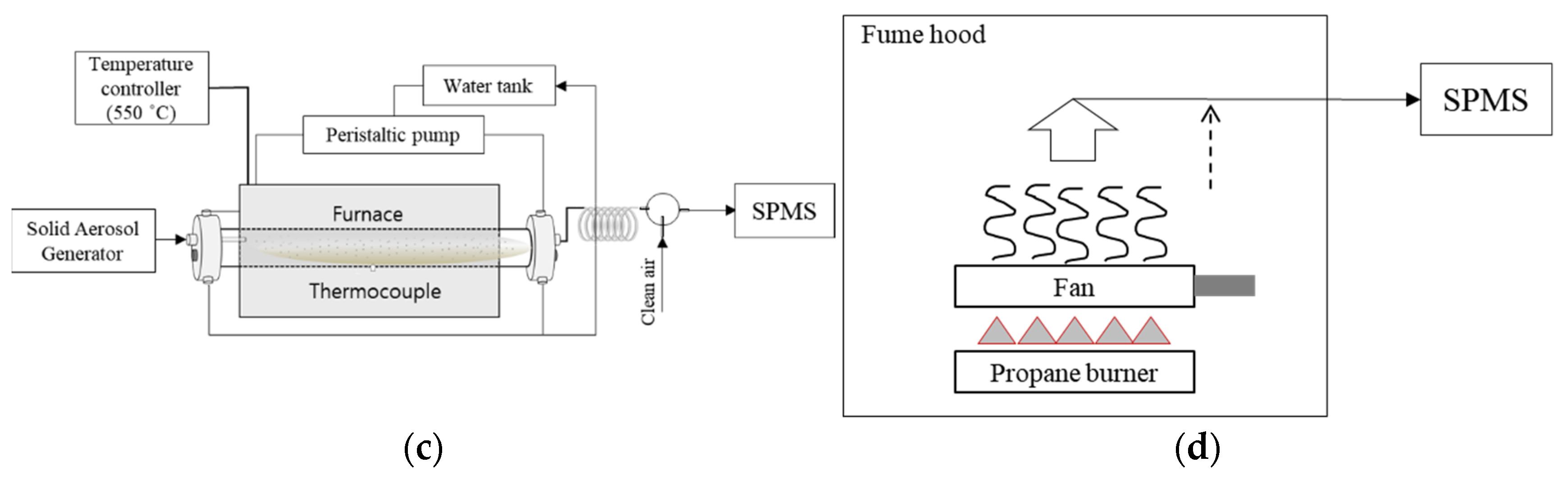
2. Materials and Methods
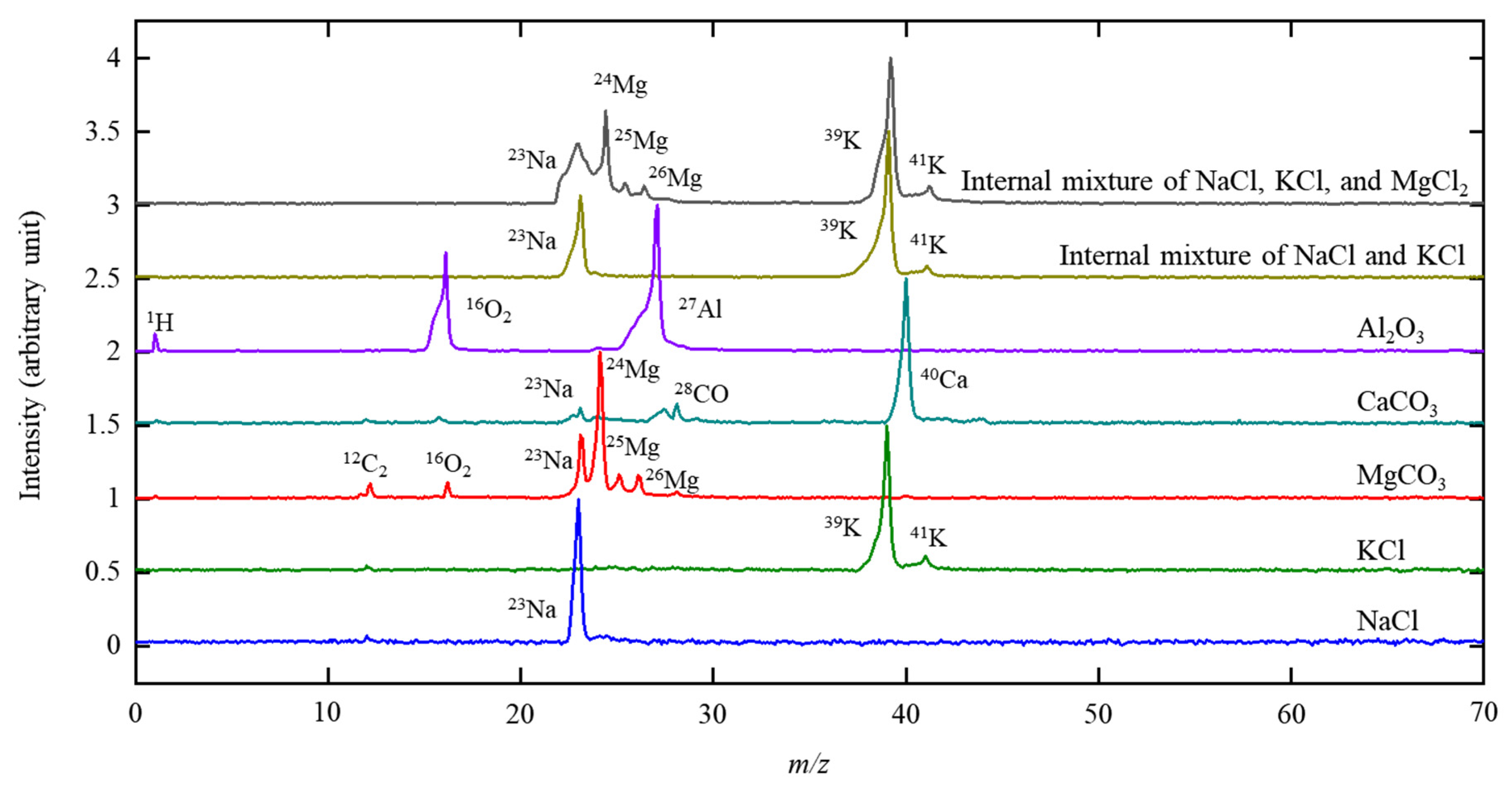
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pöschl, U. Atmospheric aerosols: Composition, transformation, climate and health effects. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 7520–7540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., III; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassee, F.R.; Héroux, M.E.; Gerlofs-Nijland, M.E.; Kelly, F.J. Particulate matter beyond mass: Recent health evidence on the role of fractions, chemical constituents and sources of emission. Inhal. Toxicol. 2013, 25, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shao, L.; Zhang, D.; Ro, C.-U.; Hu, M.; Bi, X.; Geng, H.; Matsuki, A.; Niu, H.; Chen, J. A review of single aerosol particle studies in the atmosphere of East Asia: Morphology, mixing state, source, and heterogeneous reactions. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1330–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gard, E.; Mayer, J.E.; Morrical, B.D.; Dienes, T.; Fergenson, D.P.; Prather, K.A. Real-Time Analysis of Individual Atmospheric Aerosol Particles: Design and Performance of a Portable ATOFMS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4083–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, J.T.; Leard, D.C.; Zhang, X.; Davidovits, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kolb, C.E.; Worsnop, D.R. Development of an Aerosol Mass Spectrometer for Size and Composition Analysis of Submicron Particles. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2000, 33, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, R.; Lee, D.; Sakurai, H.; Zachariah, M. Measurement of condensed-phase reaction kinetics in the aerosol phase using single particle mass spectrometry. J. Phys. Chem. A 2002, 106, 11083–11092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, C.A.; Prather, K.A. Real-time single particle mass spectrometry: A historical review of a quarter century of the chemical analysis of aerosols. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2000, 19, 248–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.M. The design of single particle laser mass spectrometers. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartonen, K.; Laitinen, T.; Riekkola, M.-L. Current instrumentation for aerosol mass spectrometry. Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canagaratna, M.R.; Jayne, J.T.; Jimenez, J.L.; Allan, J.D.; Alfarra, M.R.; Zhang, Q.; Onasch, T.B.; Drewnick, F.; Coe, H.; Middlebrook, A.; et al. Chemical and microphysical characterization of ambient aerosols with the aerodyne aerosol mass spectrometer. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2007, 26, 185–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.K.Y.; Willis, M.D.; Healy, R.M.; Onasch, T.B.; Abbatt, J.P.D. Mixing state of carbonaceous aerosol in an urban environment: Single particle characterization using the soot particle aerosol mass spectrometer (SP-AMS). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 1823–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, A.M.; Williams, L.R.; Fortner, E.C.; Robinson, W.A.; Onasch, T.B. Particle detection using the dual-vaporizer configuration of the soot particle Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (SP-AMS). Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, D.; Rai, A.; Mukherjee, D.; Zachariah, M.R. Size-Resolved Kinetic Measurements of Aluminum Nanoparticle Oxidation with Single Particle Mass Spectrometry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 7290–7299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brands, M.; Kamphus, M.; Böttger, T.; Schneider, J.; Drewnick, F.; Roth, A.; Curtius, J.; Voigt, C.; Borbon, A.; Beekmann, M.; et al. Characterization of a Newly Developed Aircraft-Based Laser Ablation Aerosol Mass Spectrometer (ALABAMA) and First Field Deployment in Urban Pollution Plumes over Paris During MEGAPOLI 2009. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemayel, R.; Hellebust, S.; Temime-Roussel, B.; Hayeck, N.; Van Elteren, J.T.; Wortham, H.; Gligorovski, S. The performance and the characterization of laser ablation aerosol particle time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LAAP-ToF-MS). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 1947–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Ramisetty, R.; Mohr, C.; Huang, W.; Leisner, T.; Saathoff, H. Laser ablation aerosol particle time-of-flight mass spectrometer (LAAPTOF): Performance, reference spectra and classification of atmospheric samples. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 2325–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, M.; Guo, T.; Xu, L.; Dong, J.; Feng, J.; Cheng, P.; Zhou, Z. Laser ablation single particle aerosol mass spectrometry for the direct analysis of raw coal samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2018, 33, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froyd, K.D.; Murphy, D.M.; Brock, C.A.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Dibb, J.E.; Jimenez, J.-L.; Kupc, A.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Schill, G.P.; Thornhill, K.L.; et al. A new method to quantify mineral dust and other aerosol species from aircraft platforms using single-particle mass spectrometry. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 6209–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Kozlovskiy, V.; Du, X.; Lv, J.; Nikiforov, S.; Yu, J.; Kolosov, A.; Gao, W.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Z.; et al. Increase of the particle hit rate in a laser single-particle mass spectrometer by pulse delayed extraction technology. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Sipin, M.F.; Furutani, H.; Prather, K.A. Development and Characterization of an Aerosol Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer with Increased Detection Efficiency. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenyuk, A.; Imre, D. Single Particle Laser Ablation Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer: An Introduction to SPLAT. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 554–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaie-Levrel, F.; Perrier, S.; Perraudin, E.; Stoll, C.; Grand, N.; Schwell, M. Development and characterization of a single particle laser ablation mass spectrometer (SPLAM) for organic aerosol studies. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, K.A.; Prather, K.A. Mass spectrometry of atmospheric aerosols--recent developments and applications. Part II: On-line mass spectrometry techniques. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, N.; Flynn, M.J.; Taylor, J.W.; Allan, J.D.; Coe, H. Evaluating the influence of laser wavelength and detection stage geometry on optical detection efficiency in a single-particle mass spectrometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 6051–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, K.; Zachariah, M.R. Determination of the Size Distribution of Polydisperse Nanoparticles with Single-Particle Mass Spectrometry: The Role of Ion Kinetic Energy. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, K.-S.; Hwang, T.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, D. Numerical simulations on aerodynamic focusing of particles in a wide size range of 30 nm–10 μm. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, D. Reducing particle loss in a critical orifice and an aerodynamic lens for focusing aerosol particles in a wide size range of 30 nm–10 μm. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ziemann, P.J.; Kittelson, D.B.; McMurry, P.H. Generating Particle Beams of Controlled Dimensions and Divergence: I. Theory of Particle Motion in Aerodynamic Lenses and Nozzle Expansions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1995, 22, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ziemann, P.J.; Kittelson, D.B.; McMurry, P.H. Generating Particle Beams of Controlled Dimensions and Divergence: II. Experimental Evaluation of Particle Motion in Aerodynamic Lenses and Nozzle Expansions. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 1995, 22, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; McMurry, P.H. A Design Tool for Aerodynamic Lens Systems. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Joo, H.S.; Lee, K.; Jang, M.; Kim, S.D.; Kim, I.; Borlaza, L.J.S.; Lim, H.; Shin, H.; Chung, K.H.; et al. Differential toxicities of fine particulate matters from various sources. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, H.S.; Batmunkh, T.; Borlaza, L.J.S.; Park, M.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Chang, Y.W.; Park, K. Physicochemical properties and oxidative potential of fine particles produced from coal combustion. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, I.; Lee, K.; Bae, M.S.; Park, M.; Maskey, S.; Seo, A.; Borlaza, L.J.S.; Cosep, E.M.R.; Park, K. Comparison of physical and chemical characteristics and oxidative potential of fine particles emitted from rice straw and pine stem burning. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115599–115611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Zhuanshi, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, G.U. Chemical Composition of Post-Harvest Biomass Burning Aerosols in Gwangju, Korea. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2004, 54, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Kwon, B.G.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.H.; Chun, K.J. Characteristics of biomass burning aerosol and its impact on regional air quality in the summer of 2003 at Gwangju, Korea. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Kim, Y.J. Tracking sources of severe haze episodes and their physicochemical and hygroscopic properties under Asian continental outflow: Long-range transport pollution, postharvest biomass burning, and Asian dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D02206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, D.B.; Wang, J.; Frost, K.; Johnston, M.V. Detection of Negative Ions from Individual Ultrafine Particles. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streets, D.; Yarber, K.; Woo, J.H.; Carmichael, G. Biomass burning in Asia: Annual and seasonal estimates and atmospheric emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1099–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, J.; Koppmann, R.; Eck, T.; Eleuterio, D. A review of biomass burning emissions part II: Intensive physical properties of biomass burning particles. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 799–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Alves, N.; Vessoni, A.T.; Quinet, A.; Fortunato, R.S.; Kajitani, G.S.; Peixoto, M.S.; de Souza Hacon, S.; Artaxo, P.; Saldiva, P.; Menck, C.F.M. Biomass burning in the Amazon region causes DNA damage and cell death in human lung cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.P.S.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Tsiodra, I.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Violaki, K.; Kanakidou, M.; Sciare, J.; Nenes, A.; Weber, R.J. Effects of Atmospheric Processing on the Oxidative Potential of Biomass Burning Organic Aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 6747–6756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros-González, K.; Sullivan, A.P.; Morales-Betancourt, R. Estimating the air quality and health impacts of biomass burning in northern South America using a chemical transport model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanasiou, A.; Alastuey, A.; Amato, F.; Renzi, M.; Stafoggia, M.; Tobias, A.; Reche, C.; Forastiere, F.; Gumy, S.; Mudu, P.; et al. Short-term health effects from outdoor exposure to biomass burning emissions: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, P.; Wu, C.Y. Control of Toxic Metal Emissions from Combustors Using Sorbents: A Review. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1998, 48, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Biswas, P. Submicrometer particle formation and control in a bench-scale pulverized coal combustor. Energy Fuels 2001, 15, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Mondal, S.S. A complete review based on various aspects of pulverized coal combustion. Int. J. Energy Res. 2019, 43, 3134–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerimray, A.; Rojas-Solórzano, L.; Amouei Torkmahalleh, M.; Hopke, P.K.; Gallachóir, B.P.Ó. Coal use for residential heating: Patterns, health implications and lessons learned. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2017, 40, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Wang, S.; Rumchev, K.; Mead-Hunter, R.; Morawska, L.; Hao, J. Impacts of household coal and biomass combustion on indoor and ambient air quality in China: Current status and implication. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Men, Y.; Luo, Z.; Xiong, R.; Li, J.; Cheng, H.; Tao, S.; Shen, G. Indoor Coal Combustion for Heating Exacerbates CO2 Exposure Approaching Harmful Levels. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, K.L.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. Emissions and indoor concentrations of particulate matter and its specific chemical components from cooking: A review. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 260–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonanno, G.; Morawska, L.; Stabile, L. Particle emission factors during cooking activities. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.-j.; Kim, J.; Kwak, N.; Kwak, H.; Son, T.; Lee, D.; Park, K. Application of Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer to Obtain Chemical Signatures of Various Combustion Aerosols. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111580
Cho H-j, Kim J, Kwak N, Kwak H, Son T, Lee D, Park K. Application of Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer to Obtain Chemical Signatures of Various Combustion Aerosols. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(21):11580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111580
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hee-joo, Joonwoo Kim, Nohhyeon Kwak, Heesung Kwak, Taewan Son, Donggeun Lee, and Kihong Park. 2021. "Application of Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer to Obtain Chemical Signatures of Various Combustion Aerosols" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 21: 11580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111580
APA StyleCho, H.-j., Kim, J., Kwak, N., Kwak, H., Son, T., Lee, D., & Park, K. (2021). Application of Single-Particle Mass Spectrometer to Obtain Chemical Signatures of Various Combustion Aerosols. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(21), 11580. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111580






