Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration with Depressive Symptoms and Its Interaction with Regular Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescent Girls
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design and Participants
3. Measurements
3.1. Assessment of Depressive Symptoms
3.2. Assessment of Nighttime Sleep Duration
3.3. Assessment of Regular Physical Activity
3.4. Assessment of Covariates
4. Statistical Analysis
5. Results
5.1. Characteristics of Study Participants
5.2. Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration and Regular Physical Activity with Depressive Symptoms
5.3. Effect of the Interaction between Nighttime Sleep Duration and Regular Physical Activity on Depressive Symptoms
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Casey, B.; Jones, R.M.; Levita, L.; Libby, V.; Pattwell, S.S.; Ruberry, E.J.; Soliman, F.; Somerville, L.H. The storm and stress of adolescence: Insights from human imaging and mouse genetics. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Adolescents: Health Risks and Solutions. 2018. Available online: https://wwwwhoint/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/adolescent-mental-health (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Rao, W.W.; Xu, D.D.; Cao, X.L.; Wen, S.Y.; Che, W.I.; Ng, C.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; He, F.; Xiang, Y.T. Prevalence of depressive symptoms in children and adolescents in China: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 272, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, L.; Campo, J.V. Depression in adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.; Dupuis, G.; Piche, J.; Clayborne, Z.; Colman, I. Adult mental health outcomes of adolescent depression: A systematic review. Depress. Anxiety 2018, 35, 700–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapar, A.; Collishaw, S.; Pine, D.S.; Thapar, A.K. Depression in adolescence. Lancet 2012, 379, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juul, E.M.L.; Hjemdal, O.; Aune, T. Prevalence of depressive symptoms among older children and young adolescents: A longitudinal population-based study. Scand. J. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Psychol. 2021, 9, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Avenevoli, S.; Costello, E.J.; Georgiades, K.; Green, J.G.; Gruber, M.J.; He, J.P.; Koretz, D.; McLaughlin, K.A.; Petukhova, M.; et al. Prevalence, persistence, and sociodemographic correlates of DSM-IV disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication Adolescent Supplement. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 372–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lovato, N.; Short, M.A.; Micic, G.; Hiller, R.M.; Gradisar, M. An investigation of the longitudinal relationship between sleep and depressed mood in developing teens. Nat. Sci. Sleep 2017, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.E.; Duong, H.T. The prospective association between sleep deprivation and depression among adolescents. Sleep 2014, 37, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirshkowitz, M.; Whiton, K.; Albert, S.M.; Alessi, C.; Bruni, O.; DonCarlos, L.; Hazen, N.; Herman, J.; Adams Hillard, P.J.; Katz, E.S.; et al. National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: Final report. Sleep Health 2015, 1, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paruthi, S.; Brooks, L.J.; D’Ambrosio, C.; Hall, W.A.; Kotagal, S.; Lloyd, R.M.; Malow, B.A.; Maski, K.; Nichols, C.; Quan, S.F.; et al. Recommended Amount of sleep for pediatric populations: A consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2016, 12, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galland, B.C.; Short, M.A.; Terrill, P.; Rigney, G.; Haszard, J.J.; Coussens, S.; Foster-Owens, M.; Biggs, S.N. Establishing normal values for pediatric nighttime sleep measured by actigraphy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 2018, 41, zsy017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivertsen, B.; Harvey, A.G.; Lundervold, A.J.; Hysing, M. Sleep problems and depression in adolescence: Results from a large population-based study of Norwegian adolescents aged 16-18 years. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2014, 23, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Sagar, R.; Mehta, M. Subjective sleep problems and sleep hygiene among adolescents having depression: A case-control study. Asian J. Psychiatry 2019, 44, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Paksarian, D.; Lamers, F.; Hickie, I.B.; He, J.; Merikangas, K.R. Sleep patterns and mental health correlates in US adolescents. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raniti, M.B.; Allen, N.B.; Schwartz, O.; Waloszek, J.M.; Byrne, M.L.; Woods, M.J.; Bei, B.; Nicholas, C.L.; Trinder, J. Sleep duration and sleep quality: Associations with depressive symptoms across adolescence. Behav. Sleep Med. 2017, 15, 198–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Choe, K.; Park, Y.; Kang, Y. Associations among daytime sleepiness, depression and suicidal ideation in Korean adolescents. Int. J. Adolesc. Med. Health 2017, 31, 20160161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, M.; Koyama, A.; Ushijima, H.; Mikami, A.; Katsumata, Y.; Kikuchi, Y.; Ichimi, N.; Jono, T.; Fujise, N.; Ikeda, M. Sleep duration and its association with sleepiness and depression in “ronin-sei” preparatory school students. Asian J. Psychiatry 2014, 9, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualdi-Russo, E.; Zaccagni, L. Physical activity for health and wellness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ashokan, K. Physical exercise: An overview of benefits from psychological level to genetics and beyond. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 731858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, A.K.; Barton, D.A. Depression and the link with cardiovascular disease. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belvederi Murri, M.; Folesani, F.; Zerbinati, L.; Nanni, M.G.; Ounalli, H.; Caruso, R.; Grassi, L. Physical activity promotes health and reduces cardiovascular mortality in depressed populations: A literature overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, S.; Shioda, K.; Morita, Y.; Kubota, C.; Ganeko, M.; Takeda, N. Exercise effects on sleep physiology. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Di, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G. Prevalence and risk factors for menopausal symptoms in middle-aged Chinese women: A community-based cross-sectional study. Menopause 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K. Enhancing the clinical utility of depression screening. CMAJ 2012, 184, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Bian, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Du, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, M. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) in the general population. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2014, 36, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volker, D.; Zijlstra-Vlasveld, M.C.; Brouwers, E.P.; Homans, W.A.; Emons, W.H.; van der Feltz-Cornelis, C.M. Validation of the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 for major depressive disorder in the occupational health setting. J. Occup. Rehabil. 2016, 6, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroenke, K.; Spitzer, R.L.; Williams, J.B. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2001, 16, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.; Gorely, T.; Pearson, N.; Bull, F.C. An assessment of self-reported physical activity instruments in young people for population surveillance: Project ALPHA. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denda, K.; Kako, Y.; Kitagawa, N.; Koyama, T. Assessment of depressive symptoms in Japanese school children and adolescents using the Birleson Depression Self-Rating Scale. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 2006, 36, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasen, F.; Otto, C.; Kriston, L.; Patalay, P.; Schlack, R.; Ravens-Sieberer, U.; BELLA study group. Risk and protective factors for the development of depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: Results of the longitudinal BELLA study. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jeong, W.; Jang, S.; Kim, Y.; Park, E. Association between sexual behavior and depression in South Korean adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beal, S.J.; Negriff, S.; Dorn, L.D.; Pabst, S.; Schulenberg, J. Longitudinal associations between smoking and depressive symptoms among adolescent girls. Prev. Sci. 2014, 15, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Fan, B.; Xie, B.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Y.; Lu, C. Association between habitual weekday sleep duration and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents: The role of mode of birth delivery. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 265, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Mendoza, J.; Calhoun, S.L.; Vgontzas, A.N.; Li, Y.; Gaines, J.; Liao, D.; Bixler, E.O. Insomnia phenotypes based on objective sleep duration in adolescents: Depression risk and differential behavioral profiles. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cheng, G.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Li, C.; Tian, G.; He, S.; Yan, Y. The associations between sleep duration, academic pressure, and depressive symptoms among Chinese adolescents: Results from China Family Panel studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.M.; Lee, S.W. Beneficial effects of appropriate sleep duration on depressive symptoms and perceived stress severity in a healthy population in Korea. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2018, 39, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehr, A.; Marusak, H.A.; Huntley, E.D.; Rabinak, C.A. Effects of duration and midpoint of sleep on corticolimbic circuitry in youth. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks) 2019, 3, 2470547019856332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerbrot, R.A.; Cheung, A.; Jensen, P.S.; Stein, R.E.K.; Laraque, D.; GLAD-PC Steering Group. Guidelines for adolescent depression in primary care (GLAD-PC): Part I. Practice preparation, identification, assessment, and initial management. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20174081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total | Non-Depressive Symptoms | Depressive Symptoms | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants, n (%) | 4952 | 3925 (79.3) | 1027 (20.7) | |
| Age, years, median (IQR) | 13 (11, 16) | 13 (11, 16) | 15 (13, 17) | <0.001 |
| Residence | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 2483 (50.1) | 1889 (48.1) | 594 (57.8) | |
| Rural | 2469 (49.9) | 2036 (51.9) | 433 (42.2) | |
| Education | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school or lower | 1772 (35.8) | 1564 (39.9) | 208 (20.3) | |
| Junior high school | 1541 (31.1) | 1208 (30.8) | 333 (32.4) | |
| Senior high school | 1179 (23.8) | 819 (20.9) | 360 (35.0) | |
| College or higher | 460 (9.3) | 334 (8.5) | 126 (12.3) | |
| Living arrangement | 0.348 | |||
| Living with parents | 3797 (76.7) | 2997 (76.4) | 800 (77.9) | |
| Living with grandparents/relatives | 442 (8.9) | 350 (8.9) | 92 (9.0) | |
| Living in a dormitory | 626 (12.6) | 512 (13.0) | 114 (11.1) | |
| Living with others | 87 (1.8) | 66 (1.7) | 21 (2.0) | |
| Discretionary expenses, RMB | <0.001 | |||
| <100 | 2487 (50.2) | 2033 (51.8) | 454 (44.2) | |
| 100–499 | 1316 (26.6) | 1047 (26.7) | 269 (26.2) | |
| ≥500 | 1149 (23.2) | 845 (21.5) | 304 (29.6) | |
| Regular physical activity | 0.413 | |||
| No | 3212 (64.9) | 2557 (65.1) | 655 (63.8) | |
| Yes | 1740 (35.1) | 1368 (34.9) | 372 (36.2) | |
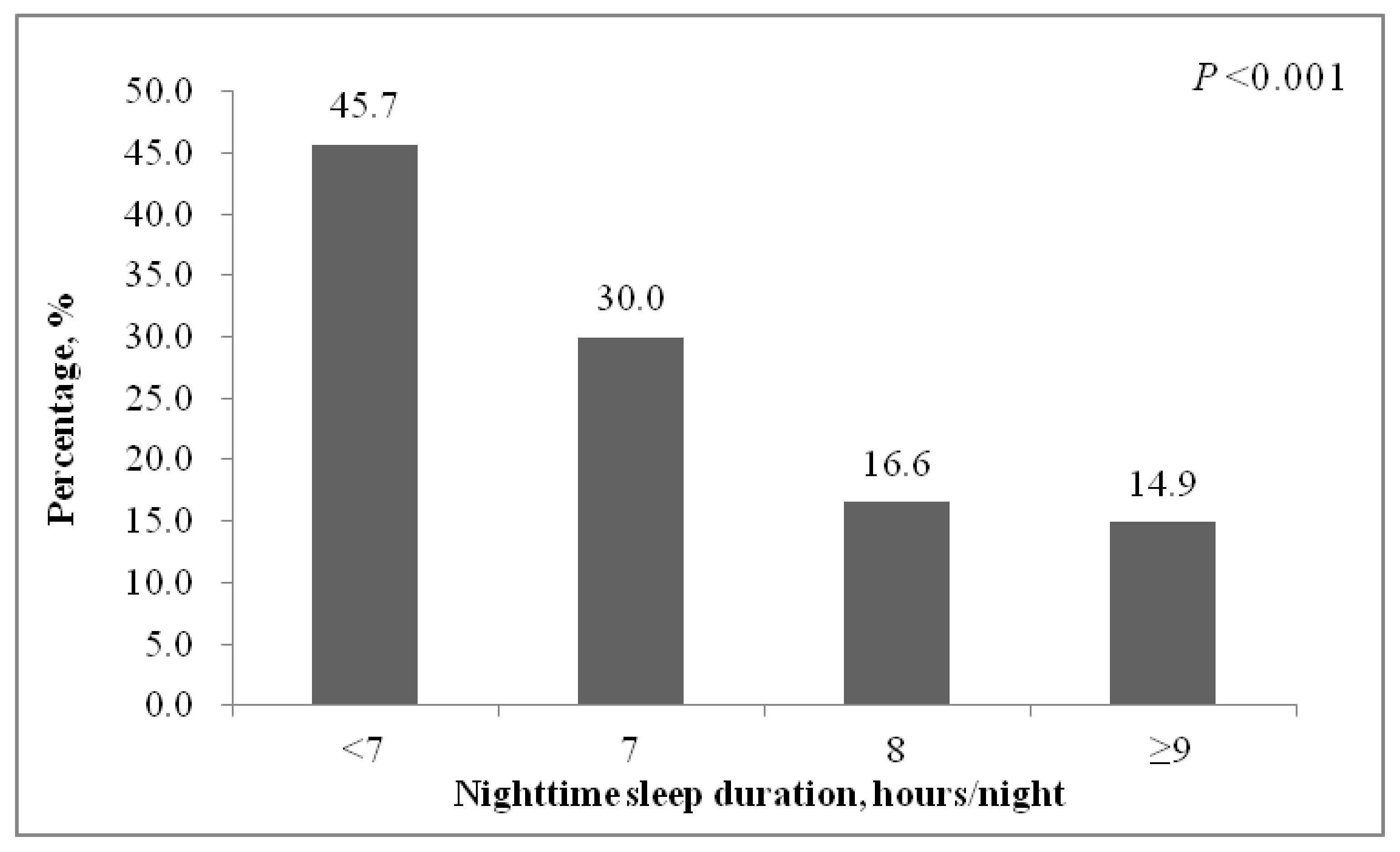
| Nighttime sleep duration, hours/night | <0.001 | |||
| <7 | 416 (8.4) | 226 (5.8) | 190 (18.5) | |
| 7 | 850 (17.2) | 595 (15.2) | 255 (24.8) | |
| 8 | 2006 (40.5) | 1674 (42.6) | 332 (32.3) | |
| ≥9 | 1680 (33.9) | 1430 (36.4) | 250 (24.4) | |
| Drinking | <0.001 | |||
| No | 4781 (96.6) | 3842 (97.9) | 939 (91.4) | |
| Yes | 171 (3.4) | 83 (2.1) | 88 (8.6) | |
| Smoking | <0.001 | |||
| No | 4897 (98.9) | 3896 (99.3) | 1001 (97.5) | |
| Yes | 55 (1.1) | 29 (0.7) | 26 (2.5) | |
| Interpersonal relationship | <0.001 | |||
| Average or good | 4601 (92.9) | 3715 (94.6) | 886 (86.3) | |
| Poor | 351 (7.1) | 210 (5.4) | 141 (13.7) | |
| Academic pressure | <0.001 | |||
| Average or above | 3964 (80.1) | 3297 (84.0) | 667 (65.0) | |
| Low | 988 (19.9) | 628 (16.0) | 360 (35.0) |
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Nighttime sleep duration, hours/night | ||||||
| <7 | 4.24 (3.38, 5.31) | <0.001 | 2.28 (1.76, 2.95) | <0.001 | 2.28 (1.76, 2.95) | <0.001 |
| 7 | 2.16 (1.79, 2.61) | <0.001 | 1.82 (1.48, 2.24) | <0.001 | 1.82 (1.48, 2.24) | <0.001 |
| 8 | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| ≥9 | 0.88 (0.74, 1.05) | 0.166 | 1.18 (0.97, 1.44) | 0.098 | 1.18 (0.97, 1.44) | 0.098 |
| Regular physical activity | ||||||
| No | Reference | Reference | Reference | |||
| Yes | 1.06 (0.92, 1.23) | 0.414 | 1.03 (0.88, 1.20) | 0.755 | 1.03 (0.88, 1.20) | 0.742 |
| p for interaction * | 0.004 | 0.036 | N/A | |||
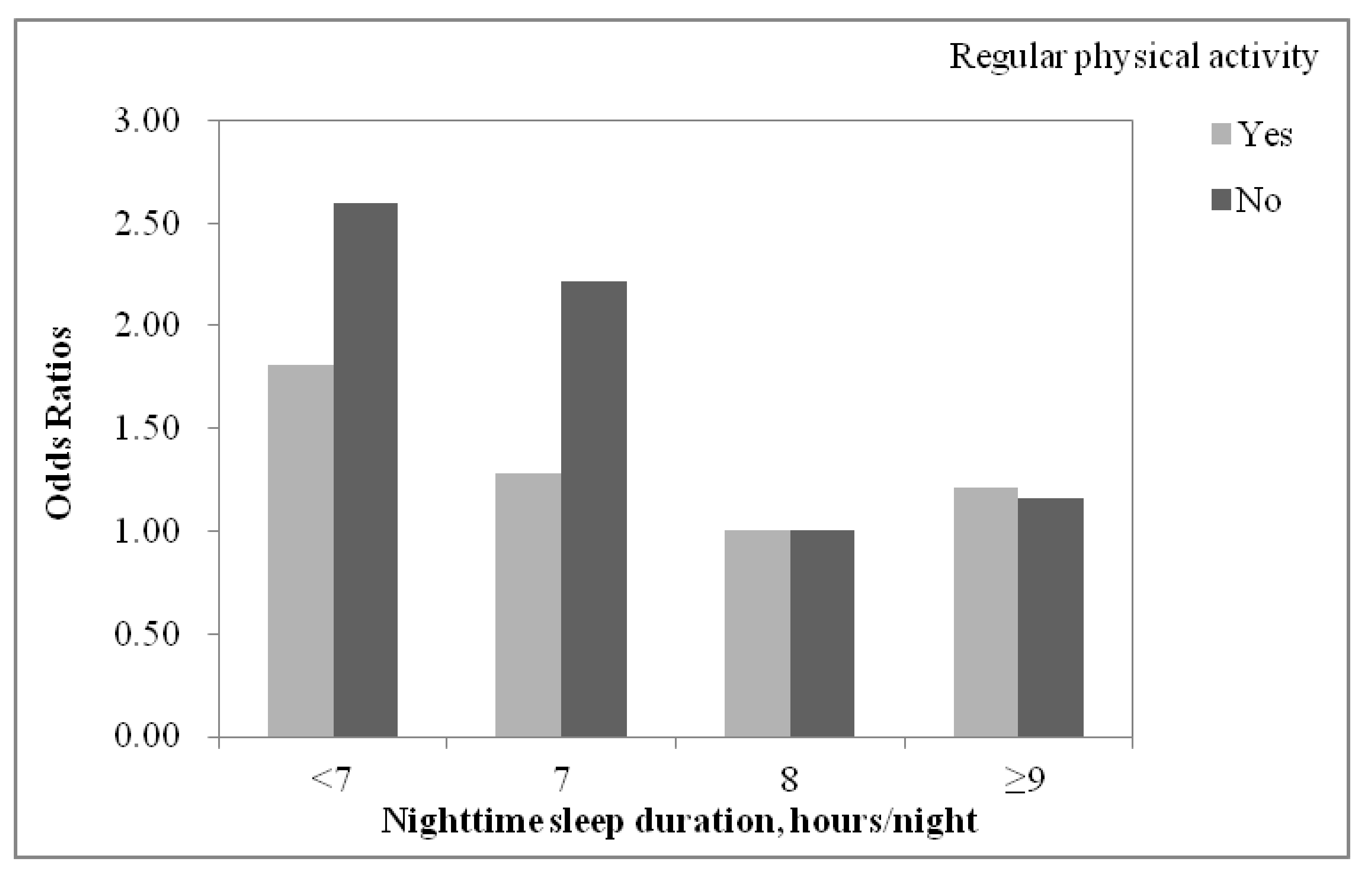
| Nighttime Sleep Duration, Hours/Night | Regular Physical Activity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | |||
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| <7 | 2.60 (1.88, 3.58) | <0.001 | 1.81 (1.16, 2.81) | 0.008 |
| 7 | 2.22 (1.72, 2.88) | <0.001 | 1.28 (0.91, 1.81) | 0.158 |
| 8 | Reference | Reference | ||
| ≥9 | 1.16 (0.90, 1.49) | 0.257 | 1.21 (0.88, 1.67) | 0.241 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Di, J.; Zhao, G.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration with Depressive Symptoms and Its Interaction with Regular Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescent Girls. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111199
Wang X, Di J, Zhao G, Wang L, Zhang X. Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration with Depressive Symptoms and Its Interaction with Regular Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescent Girls. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(21):11199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111199
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xueyin, Jiangli Di, Gengli Zhao, Linhong Wang, and Xiaosong Zhang. 2021. "Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration with Depressive Symptoms and Its Interaction with Regular Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescent Girls" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 21: 11199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111199
APA StyleWang, X., Di, J., Zhao, G., Wang, L., & Zhang, X. (2021). Association of Nighttime Sleep Duration with Depressive Symptoms and Its Interaction with Regular Physical Activity among Chinese Adolescent Girls. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(21), 11199. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph182111199





