Abstract
Blood transfusion is a fundamental and life-saving procedure where the consequence of errors can be fatal. Nurses’ knowledge plays an essential role in ensuring quality and safety in blood transfusion. The objective of this study was to assess blood transfusion-associated knowledge of tertiary hospital nurses on the east coast of Malaysia. This was a cross-sectional study with 200 registered nurses involved in blood transfusion procedures at Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia. The knowledge of the nurses was evaluated by using the routine blood transfusion knowledge questionnaire based on five parts, and <50%, 50–74%, or ≥75% of the knowledge was considered as poor, moderate, or high, respectively. Based on the scoring system, the overall knowledge of blood transfusion among Malaysian nurses (33.2 ± 8.4 years) was estimated to be 54.9 ± 7.6%. In individual items, the scoring was 81.0%, 45.4%, 49.2%, 63.0%, and 90.0% in knowledge prior to blood transfusion, on pre-transfusion, on post-transfusion, on complications, and on transfusion policy, respectively. The findings of this study indicated that most of the nurses’ overall knowledge of blood transfusion was at a moderate level; therefore, training courses and continuous medical education are warranted to improve knowledge and skills of the nurses to ensure good practices of blood transfusion.
1. Introduction
Blood transfusion is a vital, life-saving process in patients with both acute and chronic conditions, aiming to replace lost components of the blood. Millions of people all over the world undergo this process every year, and, generally, it is considered as safe, however, not beyond adverse effects including immunological complications, immunomodulation, or transfusion-transmitted infection [1]. Many human error-associated risks have been reported in blood transfusion processes, which comprise approximately 85% of the total preventable hazards [2]. Acute hemolytic reaction is one of these consequences, resulting in fatality that is mainly caused due to ABO incompatibilities [1].
Considering the risks associated with blood transfusion, there is a growing body of research on creating the optimal safety and care to the patients, where, apprising and improving nurses’ knowledge play a vital role. Blood transfusion is a nursing procedure and adequate knowledge plays a critical role in safe and sound practice. Poor knowledge associated with the compatibility test, blood administration delay, and identification of abnormal reactions followed by blood transfusion are considered as some of the key elements in blood transfusion-related errors [3,4]. In Malaysia, there are a few degrees associated with nursing, such as Diploma (3 years), Bachelor’s degree (4 years), and Master’s degree (2–4 years) in nursing with blood transfusion being part of the curricula. Exploring, evaluating, training, and updating the knowledge of nurses have been the new trends in nursing research towards developing an evidence-based clinical practice as nurses need knowledge in order to make appropriate decisions, and sound knowledge is essential to ensure blood transfusion safety along with high-quality patient care [5,6].
To date, there is no study published assessing the knowledge of nurses in blood transfusion in Malaysia. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the knowledge of Malaysian nurses on blood transfusion.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection
This was a cross-sectional study where the registered nurses involved in blood transfusion procedures and having a minimum of 6 months of experience were included from Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia. A total of 200 nurses were involved this study, based on Hijji et al. [4], where SD = 7.20, Precision (∆) = 1.000, and α = 0.050.
2.2. The Routine Blood Transfusion Knowledge Questionnaire (RBTKQ)
For this study, we used the modified version of the Routine Blood Transfusion Knowledge Questionnaire (RBTKQ) [4], which has a good reliability score of 68.3 based on the Flesch Reading Ease Index [7]. This questionnaire has seven sections including a total of 43 items. Eight items comprising section A are about the demographic and training information of the nurses. Sections B to F have 33 items about the knowledge assessment of blood bag collection from the blood bank and patient preparation prior to blood transfusion, pre- and post-transfusion nursing responsibilities, and complications related to blood transfusion. The last section (section G) consists of two items addressing the knowledge appraisal on the policies and procedures of blood transfusion in the hospital. Each correct response was awarded with 1 point. The item on the identification of the patient was awarded with 5 points due to its multi-step procedure and was of core competency. No point was awarded if two conflicting responses were selected. The maximum possible score for the RBTKQ is 56 points. Finally, the total score was converted into a percentage and, if the scoring was <50%, 50–74%, or ≥75%, the knowledge was considered as poor, moderate, or high, respectively [8].
2.3. Data Analyses
All descriptive data were reported as mean and percentages with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Continuous data were described as mean ± standard deviation (SD). A p-value of <0.05 was defined as the level of statistical significance. Data analyses were performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 27 software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). A simple linear regression was performed to explore the associated factors between gender, qualification, training program, type of ward, working duration, frequency of performing blood transfusion, and mean knowledge score.
2.4. Ethics
Ethics were approved from the Human Research Ethics Committee, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM/JEPeM/140120487). All the nurses received the participant information sheet and signed the informed consent form.
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics
Detailed characteristics of the nurses are presented in Table 1. In brief, among the participant nurses (33.2 ± 8.4 years), a majority of them were of Malay race (98.0%) and female (94.5%). Most of the nurses possessed a diploma (92.0%) with more than 5 years of working experience (68.5%); however, there was a lack of training experience related to blood transfusions in 92.5% of the participants.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the participants (n = 200).
3.2. Overall Knowledge
Based on the scoring system, the overall knowledge of blood transfusion among Malaysian nurses was estimated to be 54.9% ± 7.6%, which was considered as a moderate level of knowledge.
3.3. Knowledge Prior to Blood Transfusion
Nurses possessed a high knowledge (>75%) on 80% of the patient preparation and blood pack collection items, except for moderate knowledge on blood bag collection after administration of prescribed pre-medications (68.0%) and ABO basic terminology (67.5%) (Table 2). Overall, in this category, the nurses possessed high level of knowledge (81.2%) (Figure 1).

Table 2.
Nurses’ knowledge on blood transfusion based on the Routine Blood Transfusion Knowledge Questionnaire (n = 200).
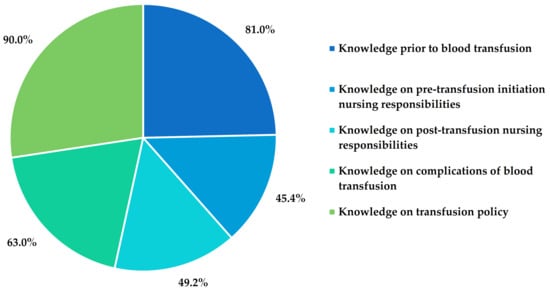
Figure 1.
Nurses’ knowledge in different sections of blood transfusion process.
3.4. Knowledge on Pre-Transfusion Initiation Nursing Responsibilities
Interestingly, in the case of knowledge-assessing items under pre-transfusion nursing responsivities, only 18.2% possessed high knowledge, 27.3% had moderate, and 54.5% had poor knowledge (Table 2). A majority of nurses were not aware of clinical indications of blood warming. Overall, about one-third answered correctly for each indication of blood warming (exchange transfusion of infants, rapid transfusion, and patients with cold agglutinin). Most of the nurses (60.5%) knew the best practice of starting the transfusion immediately after bringing a unit of blood to the ward. However, most of the nurses were not sure of blood handling after delivery to the ward from the blood bank. Most of the nurses reported that they would wrap the blood bag with a blanket, allow it to wait at room temperature, immerse it in hot water, and place it in a microwave. A majority of the nurses (64.0%) selected the incorrect filter size. Surprisingly, 26.0% would omit the final bedside identity check in the cases of an unconscious patient, barrier-nursed patient, or when a nurse clearly knows the patient. Overall, in this category, the nurses possessed a poor level of knowledge (45.4%) (Figure 1).
3.5. Knowledge on Post-Transfusion Initiation Nursing Responsibilities
Among the questionnaire items related to post-transfusion activities, 44.5% of the nurses had poor knowledge, whereas 33.3% and 22.2% of them possessed moderate and high knowledge, respectively. Among the nurses who worked with adult patients, only half of them were aware of the correct rate to initiate a blood transfusion in adult patients. About three-quarters of the nurses working with pediatric patients were aware of the correct rate to initiate a blood transfusion. A majority of the nurses (91.5%) knew that normal saline is compatible with a blood transfusion (Table 2). Overall, in this category, the nurses possessed a poor level of knowledge (49.2%) (Figure 1).
3.6. Knowledge on Complications of Blood Transfusion
Although nurses had a moderate level of knowledge (55.0%) on interventions to minimize the risk of transfusion reactions and signs and symptoms of acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (AHTR) (64.4%), they possessed a high knowledge level (80.1%) on how to manage AHTR (Table 2). Overall, in this category, the nurses possessed a moderate level of knowledge (63.0%) (Figure 1).
3.7. Knowledge on Blood Transfusion Policy
3.8. Association between Knowledge Score and Characteristics of the Nurses
There was no significant difference of knowledge level in different genders (p = 0.466), educational level (p = 0.185), types of wards (p = 0.897), working experience (p = 0.350), and previous training exposure (p = 0.177). Interestingly, higher blood transfusion experience in the last 6 months was significantly associated with better knowledge (0 times vs. 1–4 times, p = 0.020 and 1–4 times vs. >5 times, p = 0.035). From both simple and multiple linear regression models, we observed that nurses who performed blood transfusions between 1 to 4 times (within the past 6 months) had a 4.13% significantly higher (p = 0.005) blood transfusion knowledge score (Table 3).

Table 3.
Associated factors of knowledge score by Simple Linear Regression model (n = 200).
4. Discussion
Blood transfusion is one of the high-risk invasive procedures for life-saving practice in various medical conditions. Nurses have a multifunctional role in the blood transfusion process, which requires evidence-based knowledge, various skills, and qualities [9]. Even though having adequate knowledge does not always represent good practice, it is necessary to have a proper education in blood transfusion to ensure patients’ safety and minimize blood transfusion-related hazards [10]. In this study, we assessed the knowledge of a tertiary hospital’s nurses on the east coast of Malaysia on blood transfusion using the Routine Blood Transfusion Knowledge Questionnaire (RBTKQ). In our study, most of the respondents were female (94.5%) with Malay ethnicity (98%). Malaysia has a higher rate of female nurses (98.2%) in the hospital, while Malay ethnicity is predominant in our study area of Kota Bharu [11].
This study showed that nurses had a moderate level of overall blood transfusion knowledge (54.9% ± 7.6%). Similarly, previous findings showed that the overall knowledge of nurses about blood transfusion has found to be low to moderate in general [12,13,14,15]. Nearly half of the nurses do not have adequate knowledge of blood transfusion. Knowledge deficits among nurses have been identified in several key aspects of blood transfusion [15].
This study found that nurses have a high knowledge (>75%) on 80% of the patient preparation and blood pack collection items, which is almost similar to a study in Iran (98.4%) [16] and compared to a study in the UAE that reported only 6% of the nurses did establish patency of the venous route before blood collection [17]. More than two-thirds of our nurses (68.0%) understood that the collection of blood bags could be done after any prescribed medication was given with knowledge of ABO basic terminology (67.5%), which compared better than the study conducted by Hijji et al. [15], where only one-third of the nurses were aware of this requirement. Most of our nurses had high knowledge that they should provide patients with the indications and risks of blood transfusion and reaction symptoms. A survey on blood transfusion informed consent among healthcare givers and patients found that transfusion hazards were more likely to be understated [18]. Most nurses at Oxford University Hospital reported that they clarified the need for blood transfusion to the patients [19].
Our study demonstrated that the overall knowledge score on pre-transfusion initiation nursing responsibilities is of a poor level (45.4%). Proper bedside identification of patients who are scheduled for transfusion is important to avoid new errors and identify those errors that may have happened earlier [20]. However, considering that, only two-thirds of our nurses (65.5%) acknowledged that the most important nursing action before transfusion begins was patient identification. Nurses showed better responses about this important step compared to Jordanian nurses, where only 30% had this knowledge [15]. The primary cause of incorrect transfusions that could result in substantial morbidity and mortality of patients is insufficient patient identification. Nurses are also crucially responsible for early patient identification as a key competency [20].
The last chance to detect any anomalies and to prevent any transfusion mistakes is the final bedside checking procedure. Failure to properly perform the final bedside check may lead to the administration of incorrect blood [21]. Our study found that, in cases of an unconscious patient, a barrier-nursed patient, or when nurses know the patient, 26% of nurses will omit the final bedside identity search. This finding is similar to other reported studies where nurses failed to comply with this simple task [4,15,22,23]. These results indicated that, in the most significant steps in the transfusion chain process, there was a lack of understanding and proper knowledge. Some of the factors that promote the incidence of transfusion error were (1) blood monitoring away from the bedside, (2) nursing staff confusion, and (3) transfusion performance in clinical emergencies. The blood-warming procedure is one of the most important steps in transfusion because the increased temperature is associated with hemolysis, which leads to fever, coagulopathy, and renal insufficiency, sometimes causing death [24]. Only one-third of our nurses answered correctly for each indication of blood warming (exchange transfusion of infants, rapid transfusion, and patients with cold agglutinin). To date, many devices such as counter-current heat exchange, dry heat, and thermostatically controlled water baths are equipped with a warning system to avoid excessive heat and are available on the market [25].
Nurses had a poor level of overall knowledge score (49.2%) on post-transfusion-related nursing responsibilities. One-third of our nurses (32%) correctly responded that the flow rate should be set immediately after the start of the blood transfusion. This result is comparable to the research carried out in the UAE and Jordan [4,15]. Most of our nurses (89%) recognized that heart disease patients are indicated for slow blood transfusion, to avoid transfusion-associated circulatory overload [26,27]. Another finding is that only half of the respondents were aware of the correct rate to initiate blood transfusion. Each nurse should understand that, during the first 15 min of setting up a transfusion, the most serious reactions occur [4]. However, nurses may initiate a transfusion at a rate other than a recommended one without proper knowledge. This could result in either prolonging the length of the transfusion with an increased risk of a bacterial infection or in the incidence of a serious transfusion reaction [28].
Blood transfusions are one of hospitals’ most common procedures that have major risks. Thus, the complications associated with blood transfusion must be known by all concerned nurses. Most of our nurses had a moderate level of knowledge about interventions to minimize the risk of transfusion reactions and AHTR. They had a high level of knowledge (80.1%) about how to manage AHTR, similar to the study reported in India and Iran [29,30].
Most of our responding nurses (91%) were aware of the availability of their wards’ written blood transfusion policy, and most of them had read the policy. While half of the nurses had an overall deficit of blood transfusion knowledge, the policy and guidelines already provided the information about the transfusion procedure chain, blood component transfusion indications, transfusion complications, and the role of each staff involved in the transfusion [31]. Another study also showed that nurses have high knowledge regarding blood transfusion policy while there was a major deficit of overall knowledge [15]. In this study, only the frequency of blood transfusion activity among nurses was found to have a major impact on the knowledge score for blood transfusion. For those who also assisted in blood transfusion, as a result of repetitive functional skills, the performance was higher, requiring the nurses to remember their experience and knowledge.
Limitations and Recommendations
This was the first survey of nurses’ knowledge of blood transfusion in Malaysia with an excellent response rate. Although the sample is small but randomly selected, the results could be used to educate nurses in other Malaysian and overseas hospitals. One of the weaknesses was that nurses may have recorded details that they did not necessarily use in the practice. Knowledge status does not reflect the actual practice of the procedure of blood transfusion. Furthermore, the results established various levels of knowledge deficiencies in all aspects of blood transfusion. For all Malaysian nurses involved in the blood transfusion process, a compulsory ongoing educational program is required for a better outcome. There are various limitations to measuring knowledge. Certain aspects of blood transfusion that future research might include may likely have been overlooked by this questionnaire, such as the signs and symptoms of AHTR (i.e., back or kidney pain). Further studies are warranted to determine the educational effect on the knowledge and practice of blood transfusion by nurses and what they should follow. These are the critical and corrective measures to be taken to protect patients, eliminate preventable risks of blood transfusion, and increase the efficacy of the transfusion process.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study showed that most of the nurses’ overall knowledge on blood transfusion was at a moderate level, comprising a lack of understanding about ABO blood grouping, blood warming, transfusion rate, and possible complications. Immediate actions from the governing authority including the provision of training courses to deliver the appropriate knowledge is warranted. Continuous medical education for the improvement of nurses’ knowledge and skills as well as routine assessments should be carried out to ensure good practice in blood transfusion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.H.M.N.; methodology, N.H.S.; software, N.H.S.; validation, M.N.H., M.R., R.B., S.M.Y., S.I., W.S.W.A.R. and Z.Z.; formal analysis, N.H.S.; investigation, N.H.S.; resources, N.H.M.N.; data curation, N.H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.I., M.K. and N.H.S.; writing—review and editing, M.A.I. and N.H.M.N.; visualization, M.A.I. and M.K.; supervision, N.H.M.N.; project administration, N.H.M.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethics were approved from the Human Research Ethics Committee, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM/JEPeM/140120487).
Informed Consent Statement
All the nurses received the participant information sheet and signed the informed consent form.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Belal Mahmoud Hijji, Benghazi University, Libya, for permitting us to use the modified version of the Routine Blood Transfusion Knowledge Questionnaire (RBTKQ) for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sadani, D.; Urbaniak, S.; Bruce, M.; Tighe, J. Repeat ABO—incompatible platelet transfusions leading to haemolytic transfusion reaction. Transfus. Med. 2006, 16, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton-Maggs, P. Serious hazards of transfusion—conference report: Celebration of 20 years of UK haemovigilance. Transfus. Med. 2017, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saillour-Glénisson, F.; Tricaud, S.; Mathoulin-Pélissier, S.; Bouchon, B.; Galpérine, I.; Fialon, P.; Salmi, L. Factors associated with nurses’ poor knowledge and practice of transfusion safety procedures in Aquitaine, France. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2002, 14, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijji, B.; Parahoo, K.; Hussein, M.M.; Barr, O. Knowledge of blood transfusion among nurses. J. Clin. Nurs. 2012, 22, 2536–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, P.-L.; Chen, S.-H.; Chang, L.-C. School Nurses’ Perceptions, Knowledge, and Related Factors Associated with Evidence-Based Practice in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavenski, K.; Stanworth, S.; Fung, M.; Wood, E.M.; Pink, J.; Murphy, M.F.; Hume, H.; Nahirniak, S.; Webert, K.E.; Tanael, S. Quality of evidence-based guidelines for transfusion of red blood cells and plasma: A systematic review. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2018, 32, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pande, K.C.; de Takats, D.; Kanis, J.A.; Edwards, V.; Slade, P.; McCloskey, E.V. Development of a questionnaire (OPQ) to assess patient’s knowledge about osteoporosis. Maturitas 2000, 37, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Elhy, A.H.; Aziz Kasemy, Z. Nurses’ Knowledge Assessment Regarding Blood Transfusion to Ensure Patient Safety. J. Nurs. Health Sci. 2017, 6, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Freixo, A.; Matos, I.; Leite, A.; Silva, A.; Bischoff, F.; Carvalho, M.; Monteiro, C.; Ferreira, A.; Fernandes, S.; Lemos, N. Nurses knowledge in Transfusion Medicine in a Portuguese university hospital: The impact of an education. Blood Transfus. 2017, 15, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Universal Access to Safe Blood Transfusion. 2008. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/69747/WHO_EHT_08.03_eng.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- World Health Organization. Human Resources for Health Country Profiles: Malaysia. 2014. Available online: https://iris.wpro.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665.1/10530/9789290616375_eng.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- Nunes da Silva, K.F.; Dagma Duarte, R.; Floriano, D.R.; Foroni Andrade, L.; Lumênia Tavares, J.; dos Santos Felix, M.M.; Bonato Zuffi, F.; da Silva Pires, P.; Barbosa, M.H. Blood transfusion in Intensive Care Units: Knowledge of the nursing team. Adv. Nurs. Sci. 2017, 35, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, R.D.; da SILVA, K.F.N.; dos Santos Félix, M.M.; Tavares, J.L.; Zuffi, F.B.; Barbosa, M.H. Knowledge about blood transfusion in a critical unit of a teaching hospital. Biosci. J. 2017, 33, 788–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Panchawagh, S.J.; Melinkeri, S.; Panchawagh, M.J. Assessment of Knowledge and Practice of Blood Transfusion Among Nurses in a Tertiary Care Hospital in India. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2020, 36, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijji, B.M.; Oweis, A.E.; Dabbour, R.S. Measuring knowledge of blood transfusion: A survey of Jordanian nurses. Am. Int. J. Contemp. Res. 2012, 2, 77–94. [Google Scholar]
- Nemati, F.; Maali, A.; Ahmadi, M.H.; Poorkarim, H.; Rahmani, H.; Tabatabaei, Z.S.; Azad, M. The Study of Nurses Knowledge and Performance Quality of Qazvin Hospitals about the Process of Blood Transfusion. Adv. Nurs. Midwifery 2019, 28, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hijji, B.; Parahoo, K.; Hossain, M.M.; Barr, O.; Murray, S. Nurses’ practice of blood transfusion in the United Arab Emirates: An observational study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 19, 3347–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; Arja, W.; Batra, R.; Daniel, S.; Hoehn, D.; Paniz, A.M.; Selegean, S.; Slova, D.; Srivastava, S.; Vergara, N. Informed consent for blood transfusion: What do medicine residents tell? What do patients understand? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.; Vincent, C.; Sud, A.; Noel, S.; Moss, R.; Asgheddi, M.; Abdur-Rahman, I.; Murphy, M. Consent to transfusion: Patients’ and healthcare professionals’ attitudes towards the provision of blood transfusion information. Transfus. Med. 2012, 22, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Harris, A.; Atkinson, S.; Atterbury, C.; Bolton-Maggs, P.; Elliott, C.; Hawkins, T.; Hazra, E.; Howell, C.; New, H. The administration of blood components: A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Transfus. Med. 2018, 28, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.; Akers, C.; Davis, A.K.; Wood, E.; Hennessy, C.; Bielby, L. The evolving role of the transfusion practitioner. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Shibata, Y.; Miyata, S.; Inaba, S.; Asai, T.; Hoshi, Y.; Takamatsu, J.; Takahashi, K.; Ohto, H.; Juji, T. Consecutive national surveys of ABO-incompatible blood transfusion in Japan. Vox Sang. 2009, 97, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, E.; Grant-Casey, J. Promoting safer blood transfusion practice in hospital. Nurs. Stand. 2007, 21, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poder, T.G.; Nonkani, W.G.; Leponkouo, É.T. Blood warming and hemolysis: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2015, 29, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasiliki, K.; Hematologist, M. Enhancing transfusion safety: Nurse’s role. Int. J. Caring Sci. 2011, 4, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Delaney, M.; Wendel, S.; Bercovitz, R.S.; Cid, J.; Cohn, C.; Dunbar, N.M.; Apelseth, T.O.; Popovsky, M.; Stanworth, S.J.; Tinmouth, A. Transfusion reactions: Prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. The Lancet 2016, 388, 2825–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panch, S.R.; Montemayor-Garcia, C.; Klein, H.G. Hemolytic transfusion reactions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, W.J. Transfusion reactions. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Sonker, A.; Chaudhary, R. Evaluation of health care workers’ knowledge and functioning of blood centres in north India: A questionnaire based survey. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2013, 49, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, P.A.; Aziz, S.V.; Ali, M.A.; Marjan, M.H.; Reza, T.M. Evaluation of knowledge of healthcare workers in hospitals of Zabol city on proper methods of blood and components transfusion. Asian J. Transfus. Sci. 2009, 3, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayob, Y.; Abdul Karim, F.; Abu Bakar, E. Guideline for the Rational Use of Blood and Blood Products; National Blood Centre, Ministry of Health Malaysia: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2008.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).