Spatial Characteristics of the Diffusion of Residential Solar Photovoltaics in Urban Areas: A Case of Seoul, South Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
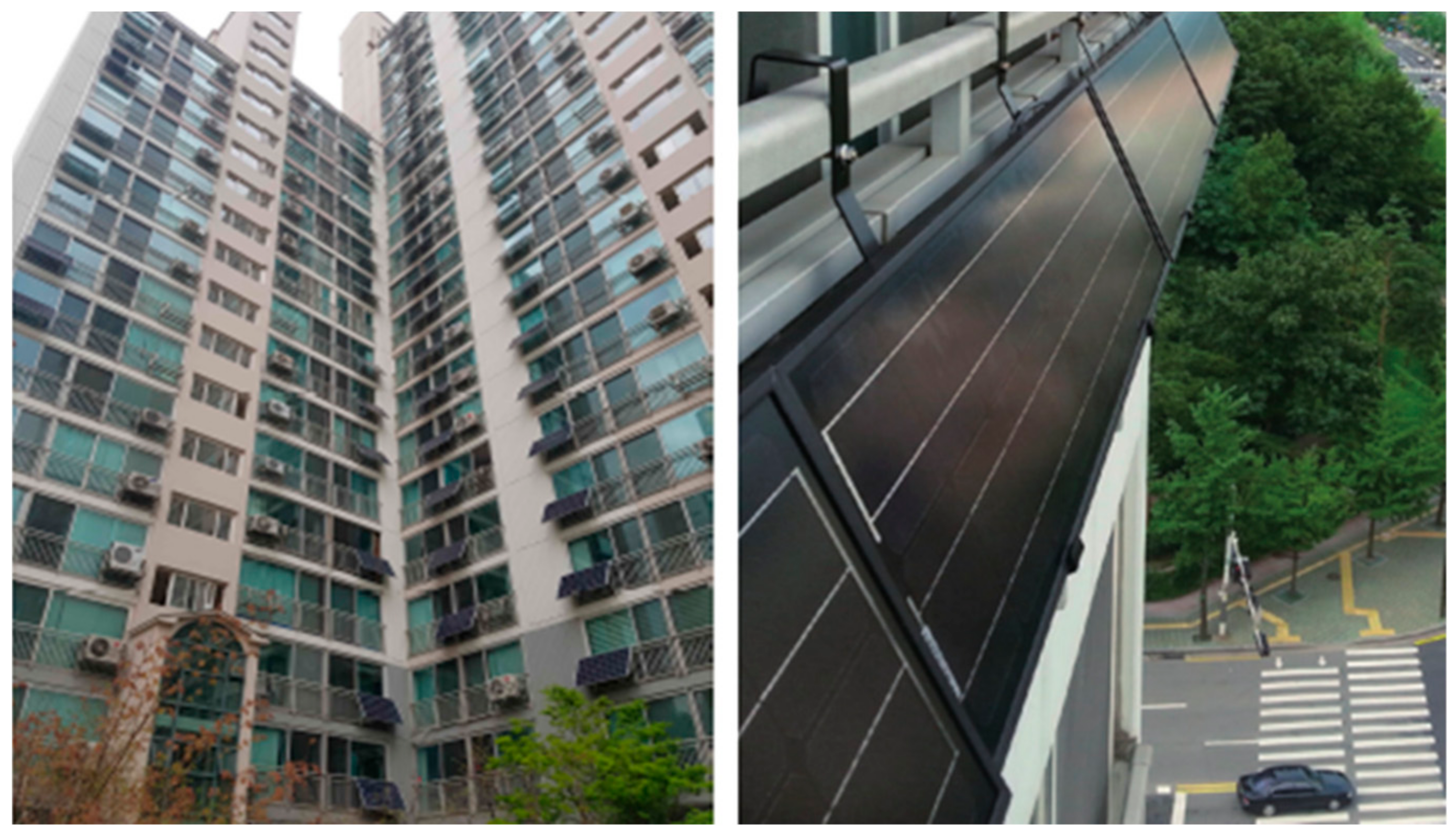
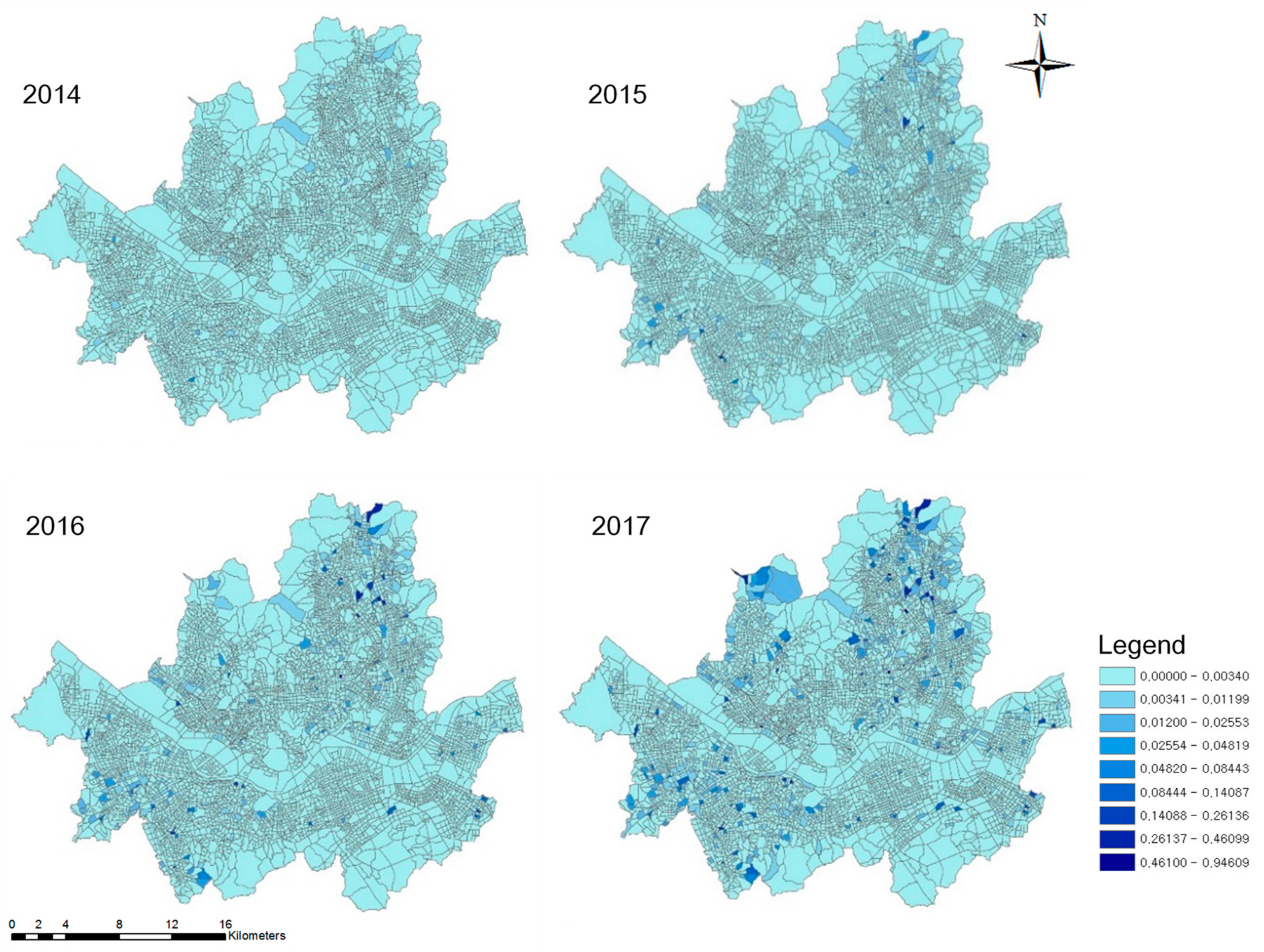
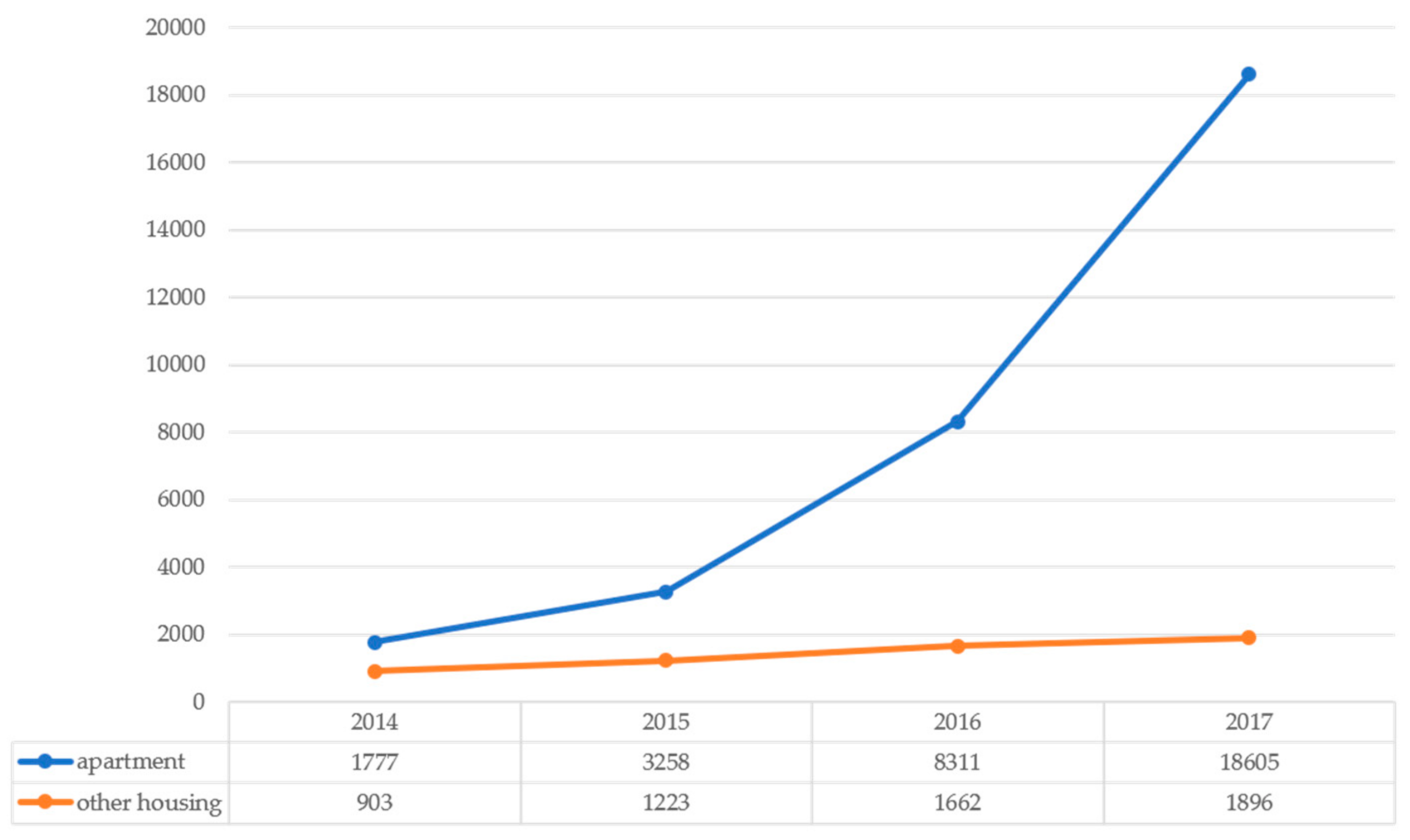
3.1. Study Area: Mini-Solar Photovoltaics in Seoul
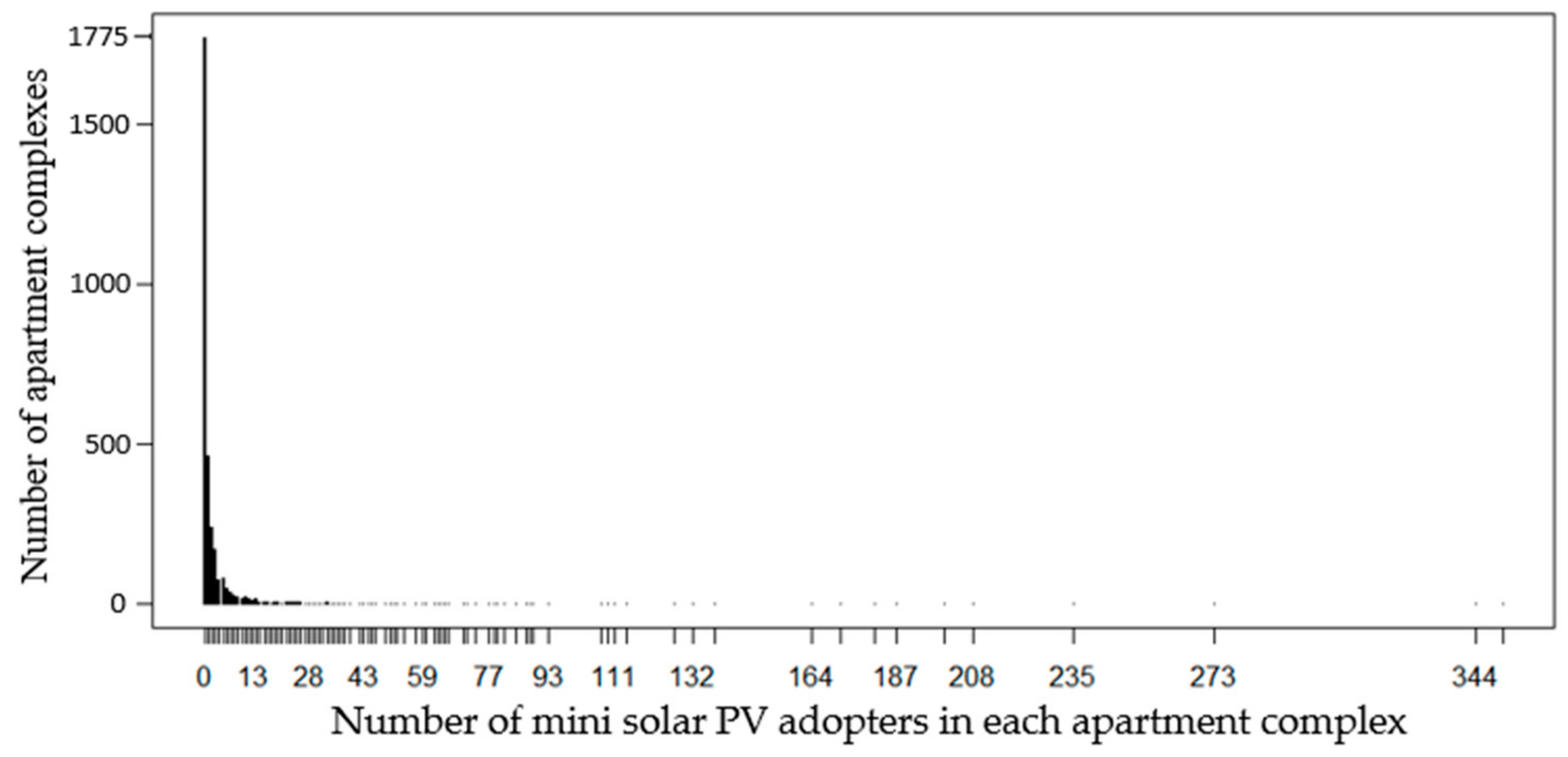
3.2. Dependent Variable
3.3. Independent Variables
3.3.1. Demographic Variables
3.3.2. Socio-Political Variables
3.3.3. Economic Variables
3.3.4. Built Environment Variables
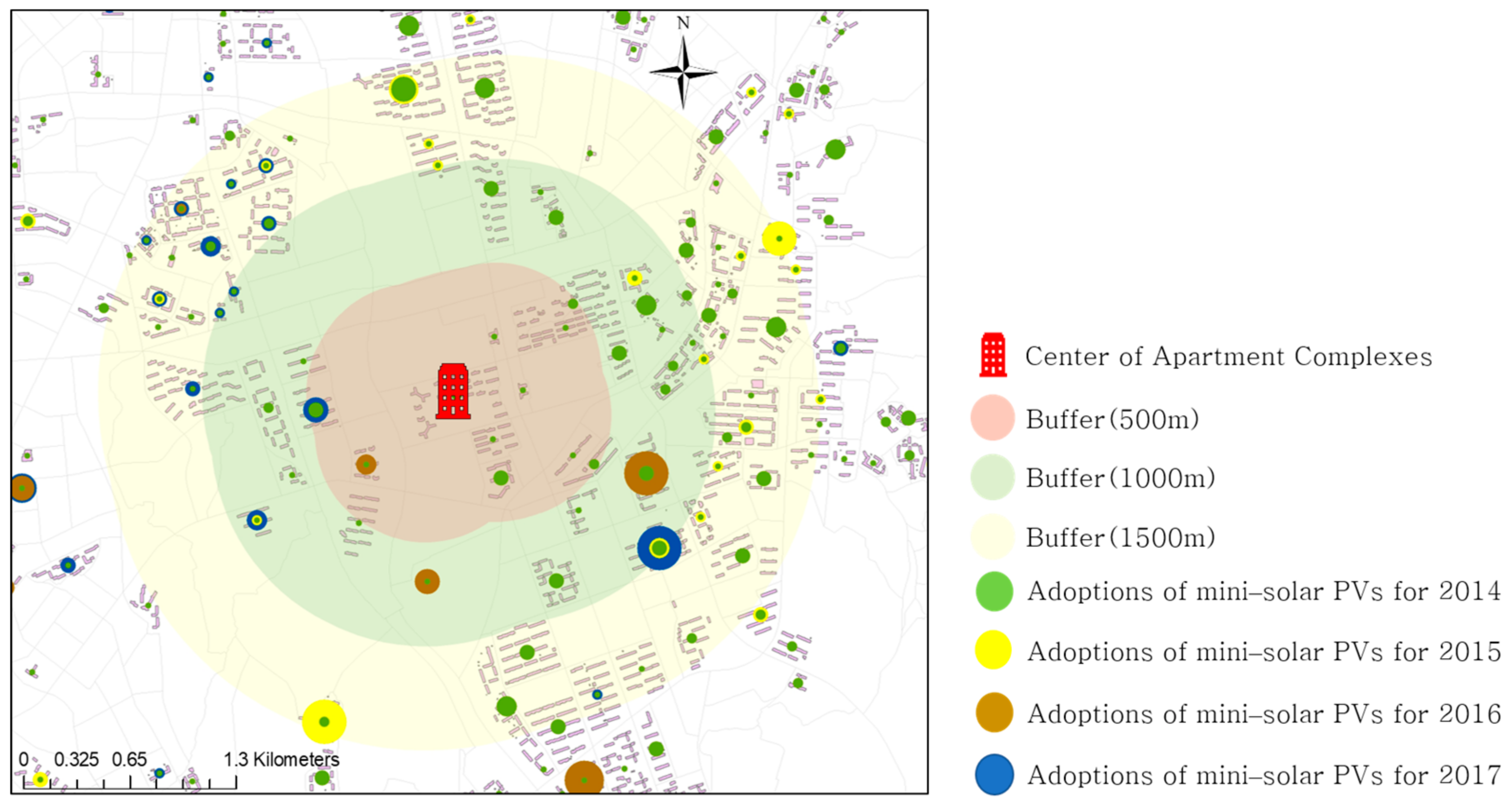
3.3.5. Peer Effect Variables
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Results Based on the Entire Sample
4.3. Energy Community
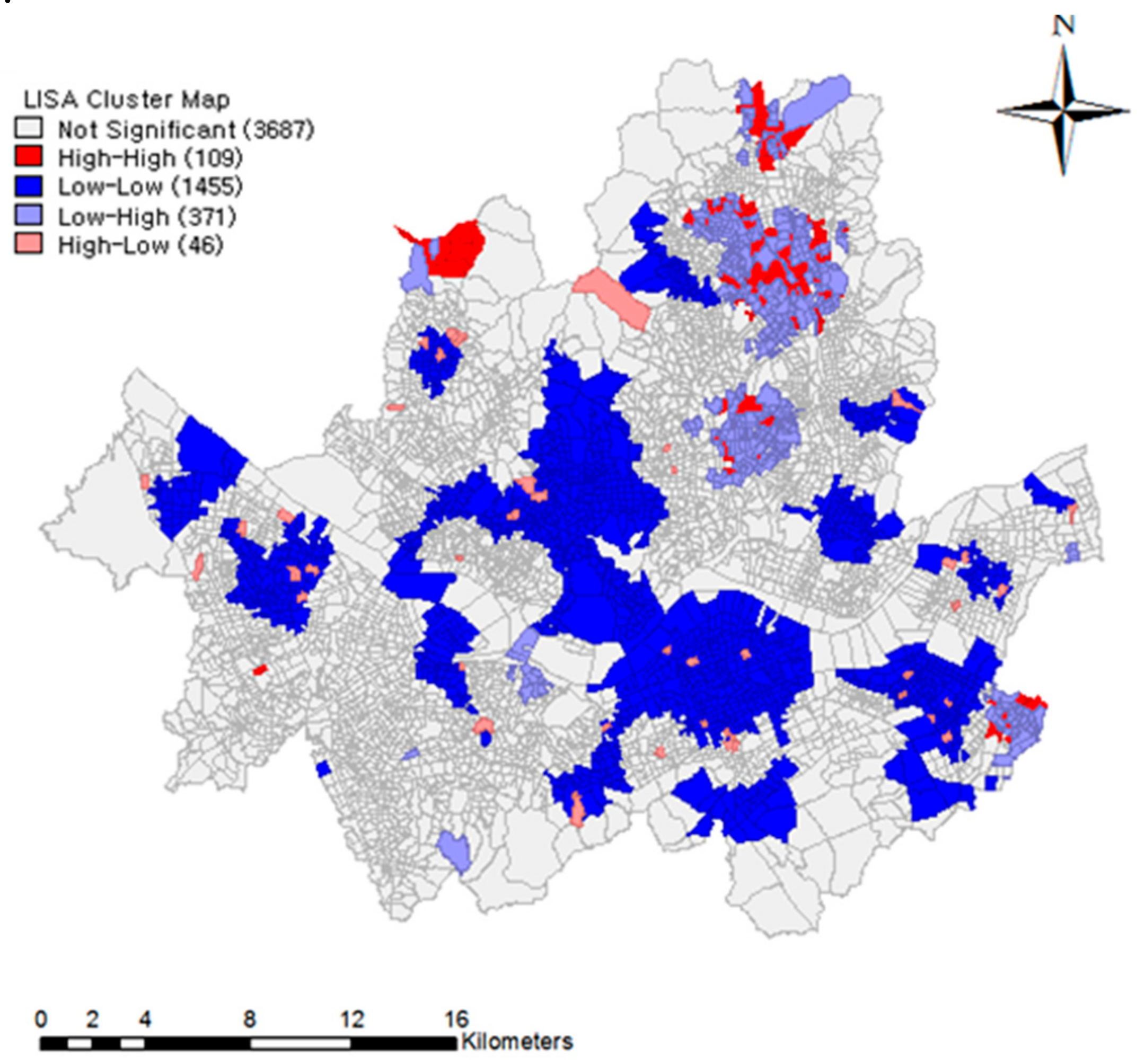
4.4. Hot/Cold Spots
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rockström, J.; Steffen, W.; Noone, K.; Persson, Å.; Chapin, I.I.I.F.S.; Lambin, E.; Lenton, T.M.; Scheffer, M.; Folke, C.; Schellnhuber, H.J.; et al. Planetary Boundaries: Exploring the Safe Operating Space for Humanity. 2009. Available online: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/iss_pub/64/ (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Steffen, W.; Richardson, K.; Rockström, J.; Cornell, S.E.; Fetzer, I.; Bennett, E.M.; Biggs, R.; Carpenter, S.R.; De Vries, W.; De Wit, C.A.; et al. Planetary boundaries: Guiding human development on a changing planet. Science 2015, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollinger, B.; Gillingham, K. Peer Effects in the Diffusion of Solar Photovoltaic Panels. Mark. Sci. 2012, 31, 900–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Robinson, S.A. Agent-based modeling of energy technology adoption: Empirical integration of social, behavioral, economic, and environmental factors. Environ. Model. Softw. 2015, 70, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharshing, S. Household dynamics of technology adoption: A spatial econometric analysis of residential solar photovoltaic (PV) systems in Germany. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2017, 23, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.; Fiaschetti, M.; Atkinson-Palombo, C. Peer effects in the adoption of solar energy technologies in the United States: An urban case study. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 48, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, T.; Lee, Y. An experiment for urban energy autonomy in Seoul: The One ‘Less’ Nuclear Power Plant policy. Energy Policy 2014, 74, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations; Macmillian Publishing, Co.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, V.; Henry, A.D. Agent-based modelling of consumer energy choices. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manski, C.F. Identification of Endogenous Social Effects: The Reflection Problem. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1993, 60, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, L.L. Social Effects in the Diffusion of Solar Photovoltaic Technology in the UK. Cambidge Work. Papers Econ. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snape, J.R. Spatial and temporal characteristics of PV adoption in the UK and their implications for the smart grid. Energies 2016, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, M.; Gillingham, K. Spatial patterns of solar photovoltaic system adoption: The influence of neighbors and the built environmentz. J. Econ. Geogr. 2015, 15, 815–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Rode, J. The adoption of photovoltaic systems in Wiesbaden, Germany. Econ. Innov. New Technol. 2013, 22, 519–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rode, J.; Weber, A. Does localized imitation drive technology adoption? A case study on rooftop photovoltaic systems in Germany. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 2016, 78, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, V.; Robinson, S.A. Effective information channels for reducing costs of environmentally- friendly technologies: Evidence from residential PV markets. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul Solution. One Less Nuclear Power Plant Phase 2. 2015. Available online: https://www.seoulsolution.kr/ko/node/3299 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Lee, J. Analysis of Factors Affecting Mini-Solar PVs Demand in Seoul. Seoul Energy Corporation. 2018. Available online: http://www.i-se.co.kr/EI/ebrief/1086 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Lee, J. Estimation on the Appropriate Subsidies to Expand Small-Scale Solar PVs. Seoul Energy Corporation. 2018. Available online: http://www.i-se.co.kr/EI/resrep/914 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Wooldridge, J.M. Introductory Econometrics: A Modern Approach; Nelson Education: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, A.C.; Trivedi, P.K. Regression Analysis of Count Data, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkins, J.R.; Rollins, C.; Anders, S.; Comeau, L. Predicting intention to adopt solar technology in Canada: The role of knowledge, public engagement, and visibility. Energy Policy 2018, 114, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, C.L. Influence of local environmental, social, economic and political variables on the spatial distribution of residential solar PV arrays across the United States. Energy Policy 2012, 47, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahran, S.; Brody, S.D.; Vedlitz, A.; Lacy, M.G.; Schelly, C.L. Greening local energy: Explaining the geographic distribution of household solar energy use in the United States. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2008, 74, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, N.; Jayasinghe, C.L.; Weerasinghe, S.N. Local factors affecting the spatial diffusion of residential photovoltaic adoption in Sri Lanka. Energy Policy 2018, 119, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, S.W.; Hong, B.Y.; Eom, H.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, K.M. Representation of Population Distribution based on Residential Building Types by using the Dasymetric Mapping in Seoul. J. Korea Spat. Inf. Soc. 2014, 22, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mennis, J. Generating Surface Models of Population Using Dasymetric Mapping. Prof. Geogr. 2003, 55, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Leiserowitz, A. Climate change risk perception and policy preferences: The role of affect, imagery, and values. Clim. Chang. 2006, 77, 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liere, K.D.; Dunlap, R.E. The Social Bases of Environmental Concern: A Review of Hypotheses, Explanations and Empirical Evidence. Public Opin. Q. 1980, 46, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briguglio, M.; Formosa, G. When households go solar: Determinants of uptake of a Photovoltaic Scheme and policy insights. Energy Policy 2017, 108, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. An Analysis of the Influence of ICLEI Membership on the Energy Consumption of Local Governments in South Korea. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S. Reducing Consumption and Inducing Self-Production of Household Energy Consumption Through Non-Price Intervention. Ph.D. Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, J.H.; Yun, S. The Mini-PV Project as a Strategic Niche for One Less Nuclear Power Plant of Seoul and Changes in Energy Citizenship-Based on the Survey of ResidentsAwareness in Nowon-gu, Seoul. Seoul Stud. 2015, 16, 91–111. [Google Scholar]
- Jacksohn, A.; Grösche, P.; Rehdanz, K.; Schröder, C. Drivers of renewable technology adoption in the household sector. Energy Econ. 2019, 81, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, A. Early adopters and their motives: Differences between earlier and later adopters of residential solar photovoltaics. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 133, 110142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.C. Climatic and economic influences on residential electricity consumption. Science 1998, 39, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Oreggia, E.; Yepez Garcia, R.A. Income and Energy Consumption in Mexican households. Policy Res. Work. Paper 2014, 1–34, WPS6864 6864. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262639788_Income_and_Energy_Consumption_in_Mexican_Households (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Soytas, U.; Sari, R.; Ewing, B.T. Energy consumption, income, and carbon emissions in the United States. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 62, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiks, E.R.; Stenner, K.; Hobman, E.V. Household energy use: Applying behavioural economics to understand consumer decision-making and behaviour. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, T.W. Social network thresholds in the diffusion of innovations. Soc. Netw. 1996, 18, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkesteijn, K.; Oerlemans, L. The early adoption of green power by Dutch households an empirical exploration of factors influencing the early adoption of green electricity for domestic purposes. Energy Policy 2005, 33, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braito, M.; Flint, C.; Muhar, A.; Penker, M.; Vogel, S. Individual and collective socio-psychological patterns of photovoltaic investment under diverging policy regimes of Austria and Italy. Energy Policy 2017, 109, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.E.; Kristensen, K.; van Benthem, K.J.; Magnusson, A.; Berg, C.W.; Nielsen, A.; Skaug, H.J.; Machler, M.; Bolker, B.M. glmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling. R J. 2017, 9, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seoul. Energy White Paper in 2017. 2018. Available online: https://news.seoul.go.kr/env/archives/79890 (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Kellstedt, P.M.; Zahran, S.; Vedlitz, A. Personal efficacy, the information environment, and attitudes toward global warming and climate change in the United States. Risk Analysis 2008, 28, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, B.; Schleich, J. Residential energy-efficient technology adoption, energy conservation, knowledge, and attitudes: An analysis of European countries. Energy Policy 2012, 49, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Lee, M.; Koo, C.; Jeong, K.; Kim, J. Development of a method for estimating the rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) potential by analyzing the available rooftop area using Hillshade analysis. Appl. Energy 2017, 194, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, A. Local factors driving the diffusion of solar photovoltaics in Sweden: A case study of five municipalities in an early market. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2016, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.A.; Jager, W. Stimulating diffusion of green products—Co-evolution between firms and consumers. J. Evol. Econ. 2002, 12, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, A. Peer effects in residential solar photovoltaics adoption—A mixed methods study of Swedish users. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2017, 26, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOTIE. Third Energy Master Plan. 2019. Available online: https://www.etrans.or.kr/ebook/05/files/assets/common/downloads/Third%20Energy%20Master%20Plan.pdf (accessed on 13 January 2021).

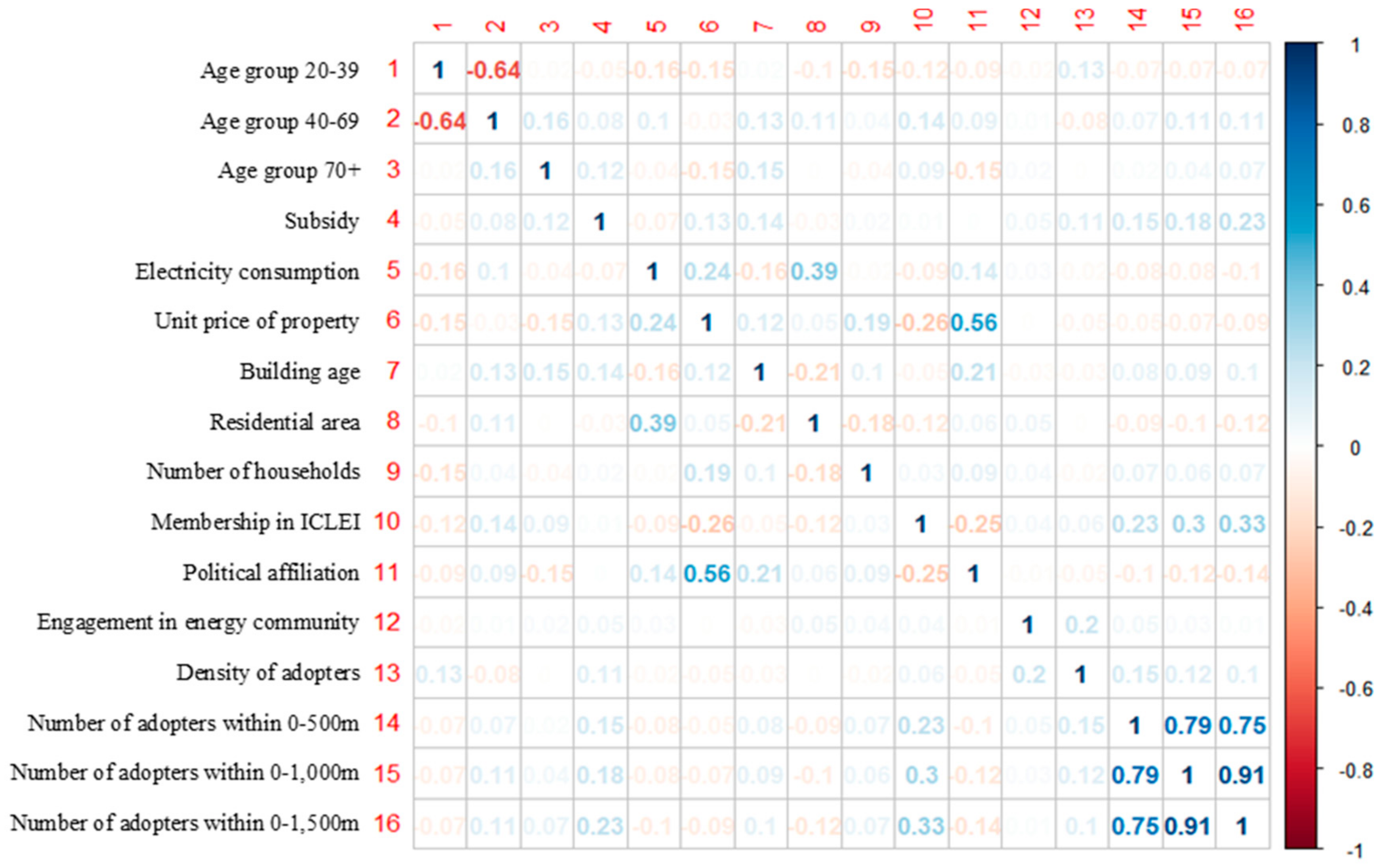
| Variables | Unit | N | Mean | S.D. | Min | Max | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | ||||||||
| Number of yearly new adopters | Households | 3180 | 2.374 | 12.641 | 0 | 348 | Ministry of the Interior and Safety (MOIS) | |
| Independent variables | ||||||||
| Demographic variables | Age group 20–39 | % | 3180 | 28.45 | 4.553 | 10.377 | 69.301 | National Geographic Information Institute, administrated by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport (MOLIT) |
| Age group 40–69 | % | 3180 | 44.382 | 2.755 | 22.641 | 62.585 | ||
| Age group 70+ | % | 3180 | 8.118 | 2.752 | 0 | 26.128 | ||
| Economic variables | Subsidy | 10,000 won | 3180 | 4.23 | 4.48 | 0 | 10 | Lee [18] |
| Electricity consumption | kWh (log) | 3180 | 2.572 | 0.128 | 2.095 | 3.373 | Electronic Architectural Administration Information System (E-AIS), administered by MOLIT | |
| Unit price of property | Million won (log) | 3180 | 1.292 | 0.159 | 0.971 | 1.938 | Seoul Real Estate Information Plaza, administered by the Seoul Metropolitan Government | |
| Built environment variables | Building age | Year | 3180 | 19.564 | 7.725 | 2 | 46 | Korean Management System for Multi-family Housing (K-apt), administered by MOLIT |
| Residential area | m2 (log) | 3180 | 2.029 | 0.197 | 0.413 | 4.435 | ||
| Number of households | 100 households | 3180 | 8.8258 | 7.502 | 1.56 | 56.78 | ||
| Socio-political variables | Membership in ICLEI | 0 or 1 | 3180 | 0.295 | 0.456 | 0 | 1 | ICLEI Korea |
| Political affiliation | 0 or 1 | 3180 | 0.209 | 0.407 | 0 | 1 | Each of the 25 district governments of Seoul | |
| Engagement in energy community | 0 or 1 | 3180 | 0.01 | 0.1 | 0 | 1 | Seoul Information Communication Plaza, administered by the Seoul Metropolitan Government | |
| Peer effects | Density of adopters | Adopters/ 100 households | 3180 | 0.196 | 1.225 | 0 | 32.08 | MOIS |
| Number of adopters within 0–500 m | Adopters | 3180 | 20.862 | 72.866 | 0 | 975 | ||
| Number of adopters within 0–1000 m | Adopters | 3180 | 49.549 | 143.02 | 0 | 2005 | ||
| Number of adopters within 0–1500 m | Adopters | 3180 | 85.615 | 207.96 | 0 | 2158 | ||
| Descriptions | Type | Frequency (Average Value) for All Apartment Complexes in Seoul | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | ||
| Adoption of mini-solar PVs | New | 591 (0.74) | 790 (0.99) | 1565 (1.97) | 4603 (5.79) |
| Accumulated | 591 (0.74) | 1381 (1.74) | 2946 (3.71) | 7549 (9.50) | |
| Engaging in energy community | 4 | 6 | 8 | 18 | |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic variables | Age group of 20–39 | −0.00958 | −0.0246 | 0.02264 | 0.01169 | −0.07498 * |
| (0.01282) | (0.01726) | (0.02785) | (0.02291) | (0.04422) | ||
| Age group of 40–69 | 0.00559 | −0.02244 | 0.05165 | 0.0715 ** | −0.09577 | |
| (0.02265) | (0.03111) | (0.05062) | (0.03518) | (0.09395) | ||
| Age group of 70+ | −0.03566 ** | −0.0795 *** | −0.0736 * | 0.02897 | −0.0799 | |
| (0.0173) | (0.02427) | (0.03773) | (0.02771) | (0.06408) | ||
| Economic variables | Incentive | 0.1832 *** | 0.1869 *** | 0.1764 *** | 0.2103 *** | 0.1649 *** |
| (0.01338) | (0.02227) | (0.03729) | (0.02203) | (0.05891) | ||
| Electricity consumption | −1.521 *** | −1.573 ** | −1.7858 * | −0.5624 | −1.419 | |
| (0.4817) | (0.7212) | (0.93297) | (0.7108) | (1.738) | ||
| Unit price of the property | −3.188 *** | −2.625 *** | −3.203 *** | −2.291 ** | −8.367 *** | |
| (0.4351) | (0.7) | (1.08599) | (1.12) | (1.808) | ||
| Build environment variables | Year | −0.0526*** | −0.0397*** | −0.0527*** | −0.0397*** | −0.0167 |
| (0.00698) | (0.01034) | (0.01529) | (0.01256) | (0.02142) | ||
| Residential area | 0.5014 | 0.7869 | −0.3311 | 0.9506** | 0.02804 | |
| (0.3172) | (0.5798) | (0.68414) | (0.4063) | (1.075) | ||
| Number of households | 0.0823 *** | 0.05918 *** | 0.119 *** | 0.0865 *** | 0.0634 ** | |
| (0.00517) | (0.0081) | (0.01082) | (0.00769) | (0.02756) | ||
| Socio-political variables | Membership in ICLEI | 0.08625 | 0.03974 | –0.12208 | 0.3608 ** | 0.5036 |
| (0.1019) | (0.1533) | (0.22449) | (0.1497) | (0.8353) | ||
| Political affiliation | −0.6378 *** | −0.8554 *** | −1.0574 *** | ― | −0.01315 | |
| (0.1407) | (0.2117) | (0.31912) | ― | (0.6386) | ||
| Engagement in energy community | 2.526 *** | 2.811 *** | ― | 2.465 *** | 2.303 * | |
| (0.3797) | (0.4423) | ― | (0.4976) | (1.289) | ||
| Peer effect variables | Density of adopters | 0.231 *** | 0.1991 ** | 0.49 ** | 0.1878 *** | −0.1352 |
| (0.07478) | (0.08974) | (0.1964) | (0.06882) | (0.413) | ||
| Number of adopters within 0–500 m | 0.001694 * | 0.00159 * | 0.00413 | 0.00131 * | −0.00562 | |
| (0.00088) | (0.00088) | (0.00673) | (0.0007) | (0.00809) | ||
| Number of adopters within 0–1000 m | −0.0007 * | −0.0006 | −0.00747** | −0.000136 | 0.003303 | |
| (0.00038) | (0.00039) | (0.00312) | (0.00036) | (0.00631) | ||
| Intercept | 6.631 *** | 7.478 *** | 6.3241 * | −2.233 | 20.19 *** | |
| (1.744) | (2.339) | (3.629) | (3.080) | (7.043) | ||
| Observations | 3180 | 1592 | 804 | 952 | 476 | |
| AIC | 8319.6 | 4318.7 | 2110.1 | 3301.1 | 590.7 | |
| BIC | 8446.9 | 4431.5 | 2203.4 | 3398.3 | 678.1 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-H.; Gim, T.-H.T. Spatial Characteristics of the Diffusion of Residential Solar Photovoltaics in Urban Areas: A Case of Seoul, South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020644
Kim M-H, Gim T-HT. Spatial Characteristics of the Diffusion of Residential Solar Photovoltaics in Urban Areas: A Case of Seoul, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(2):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020644
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Moon-Hyun, and Tae-Hyoung Tommy Gim. 2021. "Spatial Characteristics of the Diffusion of Residential Solar Photovoltaics in Urban Areas: A Case of Seoul, South Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 2: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020644
APA StyleKim, M.-H., & Gim, T.-H. T. (2021). Spatial Characteristics of the Diffusion of Residential Solar Photovoltaics in Urban Areas: A Case of Seoul, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020644





