Association between Survival and Time of On-Scene Resuscitation in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Study Setting
2.3. Study Population
2.4. Main Outcomes
2.5. Definition of Variables
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes
3.2. Association between STI and Clinical Outcomes
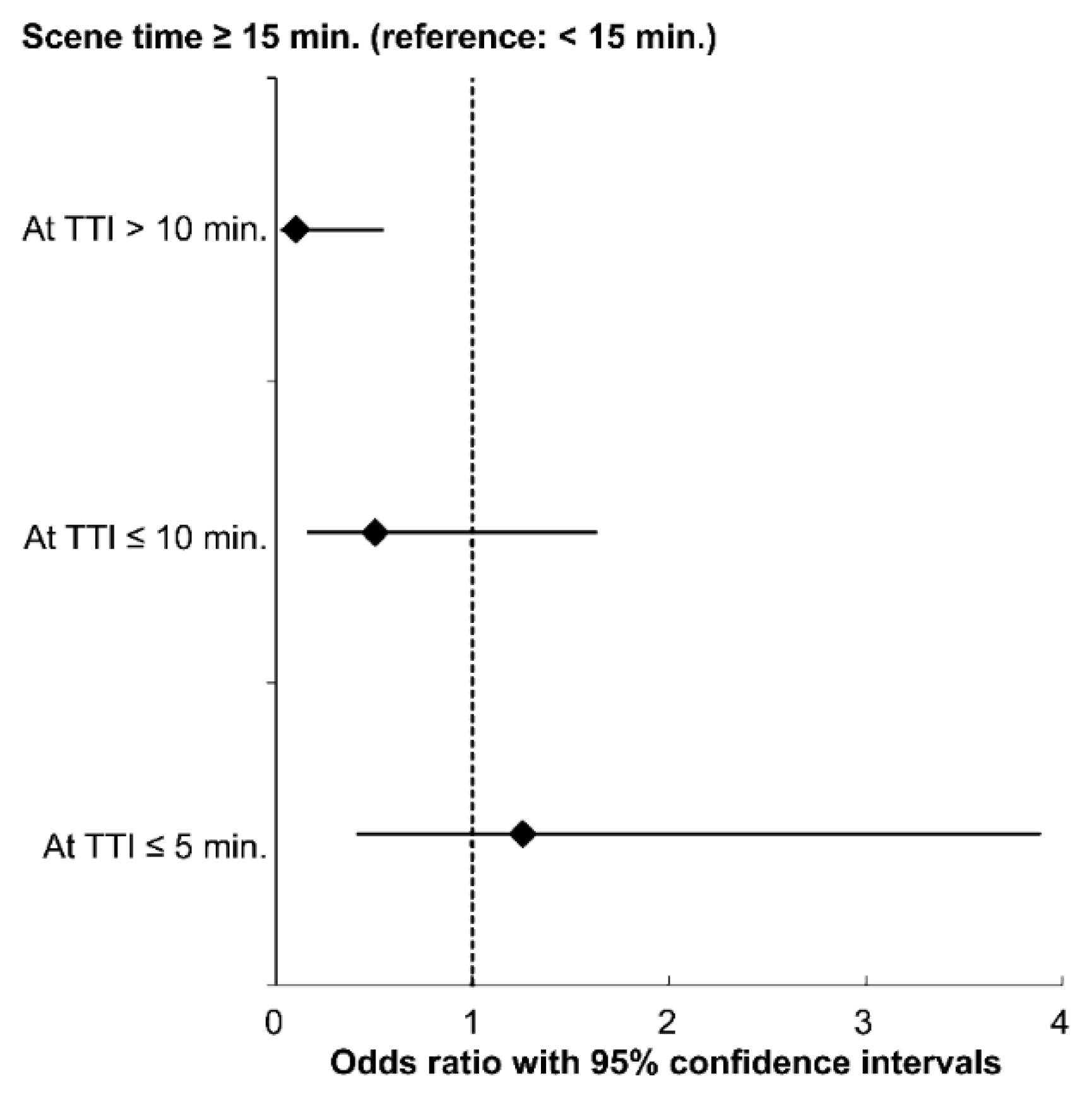
3.3. Association between STI and Good Neurological Outcome Stratified by TTI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yoon, H.; Kwon, Y.; An, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, Y.T. Main outcomes of the sudden cardiac arrest survey 2006 to 2016. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2019, 6, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunau, B.; Reynolds, J.C.; Scheuermeyer, F.X.; Stenstrom, R.; Pennington, S.; Cheung, C.; Li, J.; Habibi, M.; Ramanathan, K.; Barbic, D.; et al. Comparing the prognosis of those with initial shockable and non-shockable rhythms with increasing durations of CPR: Informing minimum durations of resuscitation. Resuscitation 2016, 101, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiell, I.G.; Wells, G.A.; DeMaio, V.J.; Spaite, D.W.; Field, B.J.; Munkley, D.P.; Lyver, M.B.; Luinstra, L.G.; Ward, R. Modifiable factors associated with improved cardiac arrest survival in a multicenter basic life support/defibrillation system: OPALS study phase I results. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1999, 33, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiell, I.G.; Nichol, G.; Leroux, B.G.; Rea, T.D.; Ornato, J.P.; Powell, J.; Christenson, J.; Callaway, C.W.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Aufderheide, T.P.; et al. ROC Investigators Early versus later rhythm analysis in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 787–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugasundaram, M.; Lotun, K. Refractory out of hospital cardiac arrest. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2018, 14, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, D.; Bartos, J.A.; Raveendran, G.; Conterato, M.; Frascone, R.J.; Trembley, A.; John, R.; Connett, J.; Benditt, D.G.; Lurie, K.G.; et al. Coronary Artery Disease in Patients With Out-of-Hospital Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation Cardiac Arrest. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, M.; Weiser, C.; Holzer, M.; Sulzgruber, P.; Datler, P.; Keferböck, M.; Zeiner, S.; Lobmeyr, E.; van Tulder, R.; Ziegler, A.; et al. The incidence of “load & go” out-of-hospital cardiac arrest candidates for emergency department utilization of emergency extracorporeal life support: A one-year review. Resuscitation 2015, 91, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaty, G.; Babaz, V.; Durand, M.; Gaide-Chevronnay, L.; Fournel, E.; Blancher, M.; Bouvaist, H.; Chavanon, O.; Maignan, M.; Bouzat, P.; et al. Prognostic factors for extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation recipients following out-of-hospital refractory cardiac arrest. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Resuscitation 2017, 112, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannopoulos, D.; Bartos, J.A.; Martin, C.; Raveendran, G.; Missov, E.; Conterato, M.; Frascone, R.J.; Trembley, A.; Sipprell, K.; John, R.; et al. Minnesota Resuscitation Consortium’s Advanced Perfusion and Reperfusion Cardiac Life Support Strategy for Out-of-Hospital Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bol, M.E.; Suverein, M.M.; Lorusso, R.; Delnoij, T.S.R.; Bruinsma, G.J.B.B.; Otterspoor, L.; Kuijpers, M.; Lam, K.Y.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; Kraemer, C.V.E.; et al. Early initiation of extracorporeal life support in refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Design and rationale of the INCEPTION trial. Am. Heart J. 2019, 210, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, C.; Paul, C.; Michels, G.; Pfister, R.; Sabashnikov, A.; Hinkelbein, J.; Braumann, S.; Djordjevic, L.; Blomeyer, R.; Krings, A.; et al. One year experience with fast track algorithm in patients with refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resuscitation 2019, 144, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, L.J.; Kierzek, G.; Diekema, D.S.; Sayre, M.R.; Silvers, S.M.; Idris, A.H.; Mancini, M.E. Part 3: Ethics: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2010, 122, S665–S675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.C.; Frisch, A.; Rittenberger, J.C.; Callaway, C.W. Duration of resuscitation efforts and functional outcome after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: When should we change to novel therapies? Circulation 2013, 128, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.E.; Diekema, D.S.; Hoadley, T.A.; Kadlec, K.D.; Leveille, M.H.; McGowan, J.E.; Munkwitz, M.M.; Panchal, A.R.; Sayre, M.R.; Sinz, E.H. Part 3: Ethical issues: 2015 american heart association guidelines update for cardiopulmonary resuscitation and emergency cardiovascular care. Circulation 2015, 132, S383–S396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, C.; Beesems, S.G.; Koster, R.W. Time of on-scene resuscitation in out of-hospital cardiac arrest patients transported without return of spontaneous circulation. Resuscitation 2019, 138, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunau, B.; Reynolds, J.; Scheuermeyer, F.; Stenstom, R.; Stub, D.; Pennington, S.; Cheskes, S.; Ramanathan, K.; Christenson, J. Relationship between Time-to-ROSC and Survival in Out-of-hospital Cardiac Arrest ECPR Candidates: When is the Best Time to Consider Transport to Hospital? Prehospital Emerg. Care 2016, 20, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, S.O.; Shin, S.D.; Yang, H.J.; Chung, S.P.; Lee, S.W.; Song, K.J.; Hwang, S.S.; Cho, G.C.; Moon, S.W.; et al. KoCARC Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC): Rationale, development, and implementation. Clin. Exp. Emerg. Med. 2018, 5, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, H.; Kim, G.; Lee, C.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, K.; Choi, H.; Jeong, W. Prehospital advanced cardiac life support by EMT with a smartphone-based direct medical control for nursing home cardiac arrest. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 37, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, S.; Choi, H.J.; Moon, H.; Kim, G. Effect of Prehospital Epinephrine on Outcomes of Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Bayesian Network Approach. Emerg. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 8057106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lin, J.W.; Yu, H.Y.; Ko, W.J.; Jerng, J.S.; Chang, W.T.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, S.C.; Chi, N.H.; Wang, C.H.; et al. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation with assisted extracorporeal life-support versus conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation in adults with in-hospital cardiac arrest: An observational study and propensity analysis. Lancet 2008, 372, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.D.; Jacobs, I.G.; Nadkarni, V.M.; Berg, R.A.; Bhanji, F.; Biarent, D.; Bossaert, L.L.; Brett, S.J.; Chamberlain, D.; de Caen, A.R.; et al. Cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation outcome reports: Update of the Utstein Resuscitation Registry Templates for Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A statement for healthcare professionals from a task force of the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (American Heart Association, European Resuscitation Council, Australian and New Zealand Council on Resuscitation, Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, InterAmerican Heart Foundation, Resuscitation Council of Southern Africa, Resuscitation Council of Asia); and the American Heart Association Emergency Cardiovascular Care Committee and the Council on Cardiopulmonary, Critical Care, Perioperative and Resuscitation. Circulation 2015, 132, 1286–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, C.; Donders, D.N.V.; Beesems, S.G.; Henriques, J.P.S.; Koster, R.W. Time to Return of Spontaneous Circulation and Survival: When to Transport in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest? Available online: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/showCitFormats?doi=10.1080%2F10903127.2020.1752868&area=0000000000000001 (accessed on 9 January 2021).
- Spaite, D.W.; Bobrow, B.J.; Vadeboncoeur, T.F.; Chikani, V.; Clark, L.; Mullins, T.; Sanders, A.B. The impact of prehospital transport interval on survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Implications for regionalization of post-resuscitation care. Resuscitation 2008, 79, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.C.; Lee, S.C.; Shin, S.D.; Song, K.J.; Sung, A.J.; Hwang, S.S. Regionalisation of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest care for patients without prehospital return of spontaneous circulation. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geri, G.; Gilgan, J.; Wu, W.; Vijendira, S.; Ziegler, C.; Drennan, I.R.; Morrison, L.; Lin, S. Does transport time of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients matter? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Resuscitation 2017, 115, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Ro, Y.S.; Kim, S.; Cha, W.C.; Shin, S.D. The Effect of Transport Time Interval on Neurological Recovery after Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest in Patients without a Prehospital Return of Spontaneous Circulation. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregers, E.; Kjærgaard, J.; Lippert, F.; Thomsen, J.H.; Køber, L.; Wanscher, M.; Hassager, C.; Søholm, H. Refractory out-of-hospital cardiac arrest with ongoing cardiopulmonary resuscitation at hospital arrival—Survival and neurological outcome without extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wengenmayer, T.; Rombach, S.; Ramshorn, F.; Biever, P.; Bode, C.; Duerschmied, D.; Staudacher, D.L. Influence of low-flow time on survival after extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation (eCPR). Crit. Care 2017, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnes, J.L.; Brouwer, M.A.; Navarese, E.P.; Verhaert, D.V.M.; Verheugt, F.W.A.; Smeets, J.L.R.M.; de Boer, M.J. Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Versus CPR Including a Mechanical Chest Compression Device in Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Comprehensive Meta-analysis From Randomized and Observational Studies. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2016, 67, 349–360.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubertsson, S.; Lindgren, E.; Smekal, D.; Östlund, O.; Silfverstolpe, J.; Lichtveld, R.A.; Boomars, R.; Ahlstedt, B.; Skoog, G.; Kastberg, R.; et al. Mechanical chest compressions and simultaneous defibrillation vs conventional cardiopulmonary resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: The LINC randomized trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Ahn, K.O.; Shin, S.D. The role of prehospital advanced airway management on outcomes for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2016, 34, 2101–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total | Non-Survival Discharge | Survival Discharge | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | ||
| 344 | 246 | 98 | |||||
| Age, years (mean, SD) | 59.0 | 13.7 | 61.0 | 14.2 | 54.2 | 11.1 | <0.001 |
| Sex, male | 283 | 82.3 | 202 | 82.1 | 81 | 82.7 | 0.91 |
| Smoking status | <0.001 | ||||||
| Current smoker | 61 | 17.7 | 33 | 13.4 | 28 | 28.6 | |
| Ex-smoker | 23 | 6.7 | 12 | 4.9 | 11 | 11.2 | |
| Never smoker | 23 | 6.7 | 42 | 17.1 | 33 | 33.7 | |
| Missing | 185 | 53.8 | 159 | 64.6 | 26 | 26.5 | |
| Hypertension | 125 | 36.3 | 88 | 35.8 | 37 | 37.8 | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 60 | 17.4 | 46 | 18.7 | 14 | 14.3 | <0.001 |
| Time of event | 0.87 | ||||||
| 07:00–19:00 (day) | 192 | 55.8 | 138 | 56.1 | 54 | 55.1 | |
| 19:00–07:00 (night) | 152 | 44.2 | 108 | 43.9 | 44 | 44.9 | |
| Day of week | 0.93 | ||||||
| Weekday | 227 | 66.0 | 162 | 65.9 | 65 | 66.3 | |
| Weekend, holidays | 117 | 34.0 | 84 | 34.1 | 33 | 33.7 | |
| Witnessed (yes) | 258 | 75.0 | 183 | 74.4 | 75 | 76.5 | 0.53 |
| Bystander CPR (yes) | 213 | 61.9 | 155 | 63.0 | 58 | 59.2 | 0.51 |
| Arrest location | 0.36 | ||||||
| Non-public | 175 | 50.9 | 129 | 52.4 | 46 | 46.9 | |
| Public | 169 | 49.1 | 117 | 47.6 | 52 | 53.1 | |
| RTI, minutes | 8 | (6–10) | 8 | (6–10) | 7 | (6–8) | 0.003 |
| STI, minutes | 15 | (13–19) | 16 | (13–21) | 14 | (12–16) | <0.001 |
| STI groups | <0.001 | ||||||
| <15 min | 151 | 43.9 | 91 | 37.0 | 60 | 61.2 | |
| ≥15 min | 193 | 56.1 | 155 | 63.0 | 38 | 38.8 | |
| TTI, minutes | 7 | (4–10) | 7 | (4–10) | 7 | (4–10) | 0.90 |
| TPT, minutes | 31 | (26–37) | 32 | (27–38) | 29 | (25–33) | <0.001 |
| Number of shocks delivered | 4 | (3–6) | 5 | (4–6) | 4 | (3–5) | 0.002 |
| Airway types | 0.003 | ||||||
| Bag valve mask | 80 | 23.3 | 53 | 21.5 | 27 | 27.6 | |
| Supraglottic airway | 230 | 66.9 | 176 | 71.5 | 54 | 55.1 | |
| Endotracheal intubation | 34 | 9.9 | 17 | 6.9 | 17 | 17.3 | |
| Prehospital epinephrine given | 84 | 24.4 | 73 | 29.7 | 11 | 11.2 | <0.001 |
| Prehospital amiodarone given | 42 | 12.2 | 39 | 15.9 | 3 | 3.1 | 0.001 |
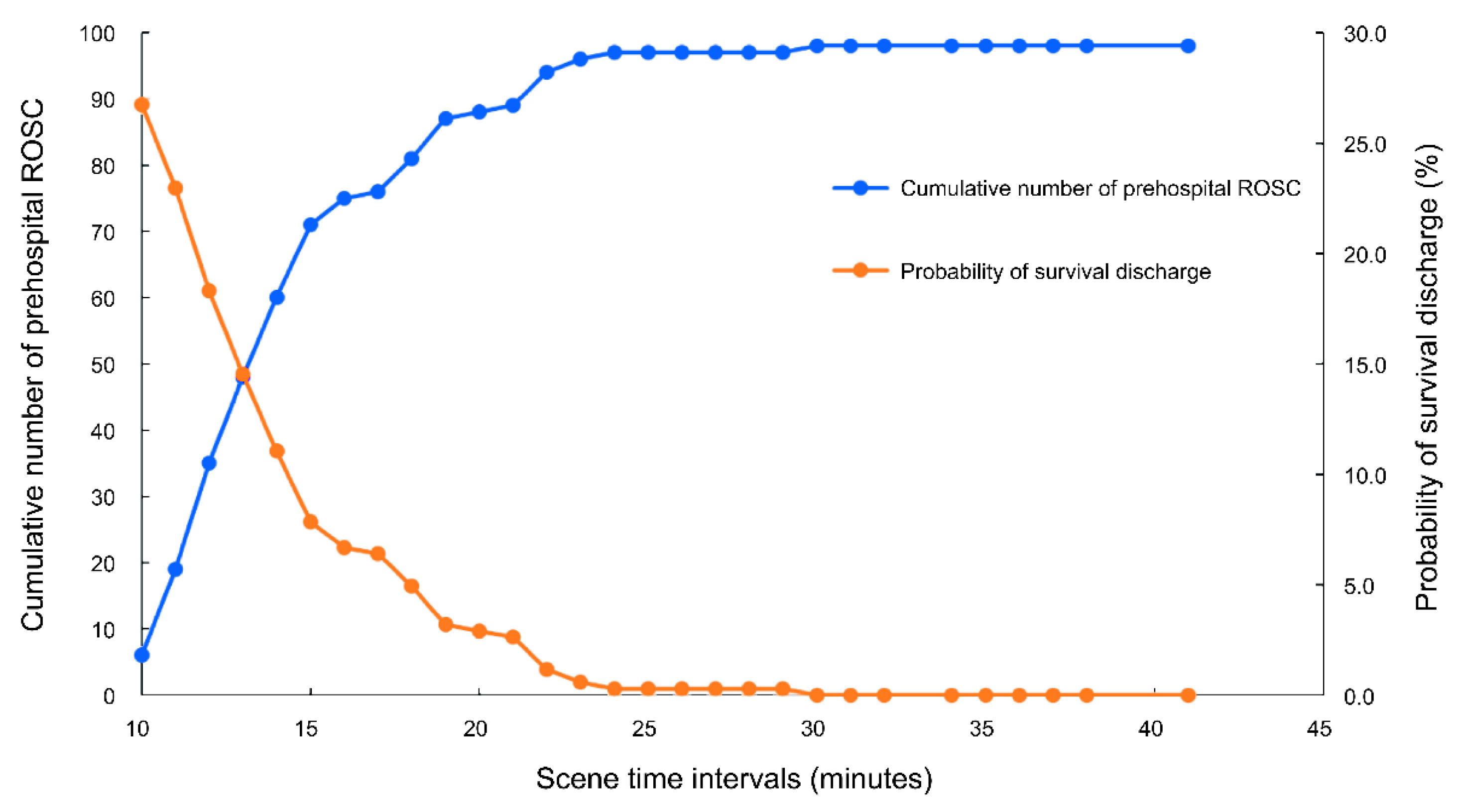
| Prehospital ROSC | 99 | 28.8 | 27 | 11.0 | 72 | 73.5 | <0.001 |
| ECLS applied | 26 | 7.6 | 17 | 6.9 | 9 | 9.2 | 0.47 |
| TTM applied | 62 | 18.0 | 16 | 6.5 | 46 | 46.9 | <0.001 |
| Good neurological outcome | 83 | 24.1 | 0 | 0.0 | 83 | 84.7 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Total | Prehospital ROSC | Without Prehospital ROSC | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 344 | 99 | 245 | |||||
| RTI, minutes | 8 | (6–10) | 7 | (6–9) | 8 | (6–10) | 0.02 |
| STI, minutes | 15 | (13–19) | 14 | (12–18) | 16 | (13–21) | 0.001 |
| STI groups | 0.01 | ||||||
| <15 min | 151 | 43.9 | 55 | 55.6 | 96 | 39.2 | |
| ≥15 min | 193 | 56.1 | 44 | 44.4 | 149 | 60.8 | |
| TTI, minutes | 7 | (4–10) | 8 | (4–11) | 6 | (4–9) | 0.07 |
| TPT, minutes | 31 | (26–37) | 29 | (25–35) | 32 | (27–37) | 0.07 |
| EMS arrival to Prehospital ROSC | 12 | (9–16) | |||||
| Survival discharge | 98 | 28.5 | 72 | 72.7 | 26 | 10.6 | <0.001 |
| Good neurological outcome | 83 | 24.1 | 65 | 65.7 | 18 | 7.3 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Survival Discharge | Good Neurological Outcome | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | aOR | 95% CI | |
| STI ≥ 15 min (<15 min) | 0.37 | (0.23–0.60) | 0.33 | (0.17–0.65) | 0.42 | (0.25–0.69) | 0.43 | (0.22–0.86) |
| Age, years | 0.96 | (0.95–0.98) | 0.95 | (0.93–0.97) | 0.96 | (0.94–0.98) | 0.95 | (0.93–0.98) |
| Male | 1.04 | (0.56–1.92) | 0.78 | (0.34–1.78) | 0.97 | (0.51–1.85) | 0.69 | (0.29–1.64) |
| Bystander CPR done | 0.85 | (0.53–1.37) | 0.90 | (0.47–1.72) | 0.97 | (0.59–1.62) | 1.08 | (0.55–2.13) |
| Public location (non-public) | 1.25 | (0.78–1.99) | 0.77 | (0.4–1.51) | 1.49 | (0.9–2.45) | 1.14 | (0.57–2.26) |
| RTI, minute | 0.89 | (0.81–0.97) | 0.89 | (0.78–1.00) | 0.91 | (0.83–0.99) | 0.92 | (0.81–1.04) |
| TTI, minute | 1.03 | (1.00–1.06) | 1.02 | (0.98–1.06) | 1.03 | (1.00–1.06) | 1.02 | (0.98–1.06) |
| Supraglottic airway (bag valve mask) | 0.60 | (0.35–1.05) | 0.78 | (0.37–1.65) | 0.74 | (0.41–1.34) | 1.09 | (0.49–2.41) |
| Endotracheal intubation (bag valve mask) | 1.96 | (0.87–4.44) | 2.29 | (0.74–7.11) | 1.97 | (0.85–4.58) | 2.43 | (0.76–7.80) |
| Prehospital ROSC | 22.46 | (12.32–40.96) | 21.65 | (11.19–41.90) | 24.11 | (12.79–45.47) | 22.05 | (11.19–43.48) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, H.A.; Ahn, K.O.; Lee, E.J.; Park, J.O.; on behalf of the Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC) Investigators. Association between Survival and Time of On-Scene Resuscitation in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020496
Park HA, Ahn KO, Lee EJ, Park JO, on behalf of the Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC) Investigators. Association between Survival and Time of On-Scene Resuscitation in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(2):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020496
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Hang A, Ki Ok Ahn, Eui Jung Lee, Ju Ok Park, and on behalf of the Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC) Investigators. 2021. "Association between Survival and Time of On-Scene Resuscitation in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 2: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020496
APA StylePark, H. A., Ahn, K. O., Lee, E. J., Park, J. O., & on behalf of the Korean Cardiac Arrest Research Consortium (KoCARC) Investigators. (2021). Association between Survival and Time of On-Scene Resuscitation in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Cross-Sectional Retrospective Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(2), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18020496






