Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Muscular Strength Moderates the Relationship between FNDC5 Polymorphism and Adiposity in Children and Adolescents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delgado, A.M.; Vaz Almeida, M.D.; Parisi, S. Food and Nutrient Features of the Mediterranean Diet. In Chemistry of the Mediterranean Diet; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund, U.; Anderssen, S.A.; Froberg, K.; Sardinha, L.B.; Andersen, L.B.; Brage, S. Independent associations of physical activity and cardiorespiratory fitness with metabolic risk factors in children: The European youth heart study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1832–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise Metabolism and the Molecular Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Adaptation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, P.; Wu, J.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Korde, A.; Ye, L.; Lo, J.C.; Rasbach, K.A.; Boström, E.A.; Choi, J.H.; Long, J.Z.; et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fat-like development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature 2012, 481, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.Y.; Panagiotou, G.; Mougios, V.; Brinkoetter, M.; Vamvini, M.T.; Schneider, B.E.; Mantzoros, C.S. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1725–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kraemer, R.R.; Shockett, P.; Webb, N.D.; Shah, U.; Castracane, V.D. A transient elevated irisin blood concentration in response to prolonged, moderate aerobic exercise in young men and women. Horm. Metab. Res. 2014, 46, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Sjostrom, M. Physical fitness in childhood and adolescence: A powerful marker of health. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mäestu, E.; Harro, J.; Veidebaum, T.; Kurrikoff, T.; Jürimäe, J.; Mäestu, J. Changes in cardiorespiratory fitness through adolescence predict metabolic syndrome in young adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha Filho, N.; Reuter, C.P.; Renner, J.D.P.; Barbian, C.D.; De Castro Silveira, J.F.; De Borba Schneiders, L.; Pohl, H.H. Low levels of cardiorespiratory fitness and abdominal resistance are associated with metabolic risk in schoolchildren. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 32, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, C.P.; Brand, C.; da Silva, P.T.; Reuter, É.M.; Renner, J.D.P.; Franke, S.I.R.; de Mello, E.D.; Burgos, L.T.; de Borba Schneiders, L.; Burgos, M.S.; et al. Relationship between Dyslipidemia, Cultural Factors, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Schoolchildren. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2019, 112, 6729–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Lippi, G.; Mayero, S.; Perez-Quilis, C.; García-Giménez, J.L. Irisin: A new potential hormonal target for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes 2012, 4, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Todendi, P.F.; Klinger, E.I.; Geraldo, A.C.R.; Brixner, L.; Reuter, C.P.; Lindenau, J.D.R.; Valim, A.R.M.; Fiegenbaum, M. Genetic risk score based on fat mass and obesity-associated, transmembrane protein 18 and fibronectin type III domain containing 5 polymorphisms is associated with anthropometric characteristics in South Brazilian children and adolescents. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 121, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos, S.A. Historical Roots of the “Whitening” of Brazil. Lat. Am. Perspect. 2002, 29, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, F.C.; Amado, R.C.; Lambertucci, J.R.; Rocha, J.; Antunes, C.M.; Pena, S.D.J. Color and genomic ancestry in Brazilians. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PROESP-BR. Manual de Testes e Avaliação. 2016. Available online: https://www.ufrgs.br/proesp/ (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maalouf, G.; El Khoury, D. Exercise-Induced Irisin, the Fat Browning Myokine, as a Potential Anticancer Agent. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 6561726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, F.; Yang, M.; Sun, J.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, D. The effect of irisin as a metabolic regulator and its therapeutic potential for obesity. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 2021, 6572342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurdiova, T.; Balaz, M.; Vician, M.; Maderova, D.; Vlcek, M.; Valkovic, L.; Srbecky, M.; Imrich, R.; Kyselovicova, O.; Belan, V.; et al. Effects of obesity, diabetes and exercise on Fndc5 gene expression and irisin release in human skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: In vivo and in vitro studies. J. Physiol. 2014, 592, 1091–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.O.; Wyatt, H.R.; Peters, J.C. Energy balance and obesity. Circulation 2012, 126, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craigie, A.M.; Lake, A.A.; Kelly, S.A.; Adamson, A.J.; Mathers, J.C. Tracking of obesity-related behaviours from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review. Maturitas 2011, 70, 266–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umer, A.; Kelley, G.A.; Cottrell, L.E.; Giacobbi, P.; Innes, K.E.; Lilly, C.L. Childhood obesity and adult cardiovascular disease risk factors: A systematic review with meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Labayen, I.; Lavie, C.J.; Blair, S.N. The Fat but Fit paradox: What we know and don’t know about it. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mintjens, S.; Menting, M.D.; Daams, J.G.; van Poppel, M.N.M.; Roseboom, T.J.; Gemke, R.J.B.J. Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Childhood and Adolescence Affects Future Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review of Longitudinal Studies. Sport Med. 2018, 48, 2577–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Izquierdo, M. Is Muscular Fitness Associated with Future Health Benefits in Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Sport Med. 2019, 49, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, T. Oxygen uptake and endurance fitness in children, revisited. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2013, 25, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, P.R.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; McCambridge, T.M. Resistance Training for Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20201011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner-Urdiales, D.; Ruiz, J.R.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Ortega, F.B.; Rey-Lopez, J.P.; España-Romero, V.; Casajús, J.A.; Molnar, D.; Widhalm, K.; Dallongeville, J.; et al. Associations of muscular and cardiorespiratory fitness with total and central body fat in adolescents: The HELENA study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Raskiliene, A.; Smalinskiene, A.; Kriaucioniene, V.; Lesauskaite, V.; Petkeviciene, J. Associations of MC4R, LEP, and LEPR Polymorphisms with Obesity-Related Parameters in Childhood and Adulthood. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topham, G.L.; Washburn, I.J.; Hubbs-Trait, L.; Keneddy, T.S.; Rutledge, J.M.; Page, M.C.; Swindle, T.; Shriver, L.H.; Harrist, A.W. The Families and Schools for Health Project: A Longitudinal Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial Targeting Children with Overweight and Obesity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Mean (SD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Total (n = 1701) | Boys (n = 758) | Girls (n = 943) | Effect Size |
| Age (years) | 11.73 (2.75) | 11.58 (2.84) | 11.85 (2.84) | 0.09 |
| Height (m) | 1.50 (0.14) | 1.51 (0.16) | 1.50 (0.13) * | 0.06 |
| Weight (kg) | 47.54 (15.95) | 47.84 (17.34) | 47.30 (14.74) | 0.03 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 20.43 (4.33) | 20.19 (4.22) | 20.62 (4.41) * | 0.09 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 67.03 (10.73) | 67.78 (11.08) | 66.42 (10.40) * | 0.12 |
| WHtR | 0.44 (0.06) | 0.44 (0.06) | 0.44 (0.06) | 0.00 |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness (m) | 885.07 (188.81) | 971.09 (209.05) | 814.94 (134.77) * | 0.88 |
| Lower limb strength (m) | 1.30 (0.28) | 1.41 (0.30) | 1.21 (0.22) * | 0.76 |
| n (%) | ||||
| rs16835198 FNDC5 | ||||
| TT | 220 (12.9) | 86 (11.3) | 134 (14.2) | - |
| GT + GG | 1481 (87.1) | 672 (88.7) | 809 (85.8) | - |
| Living area | ||||
| Urban | 1311 (77.1) | 565 (74.5) | 746 (79.2) ** | - |
| Rural | 389 (22.8) | 193 (25.5) | 196 (20.8) | - |
| School network | ||||
| Municipal | 426 (25.0) | 189 (24.9) | 237 (25.1) | - |
| State | 1239 (72.8) | 551 (72.7) | 688 (73.0) | - |
| Private | 35 (20.1) | 18 (2.4) | 17 (1.8) | - |
| KERRYPNX | Waist Circumference (cm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β | CI (95%) | p | R2 | |
| Cardiorespiratory fitness | 0.224 | |||
| CRF | −0.016 | −0.019; −0.013 | <0.001 | |
| rs16835198 FNDC5 | ||||
| TT | 7.918 | 1.409; 14.427 | 0.017 | |
| GT + GG | 1 | |||
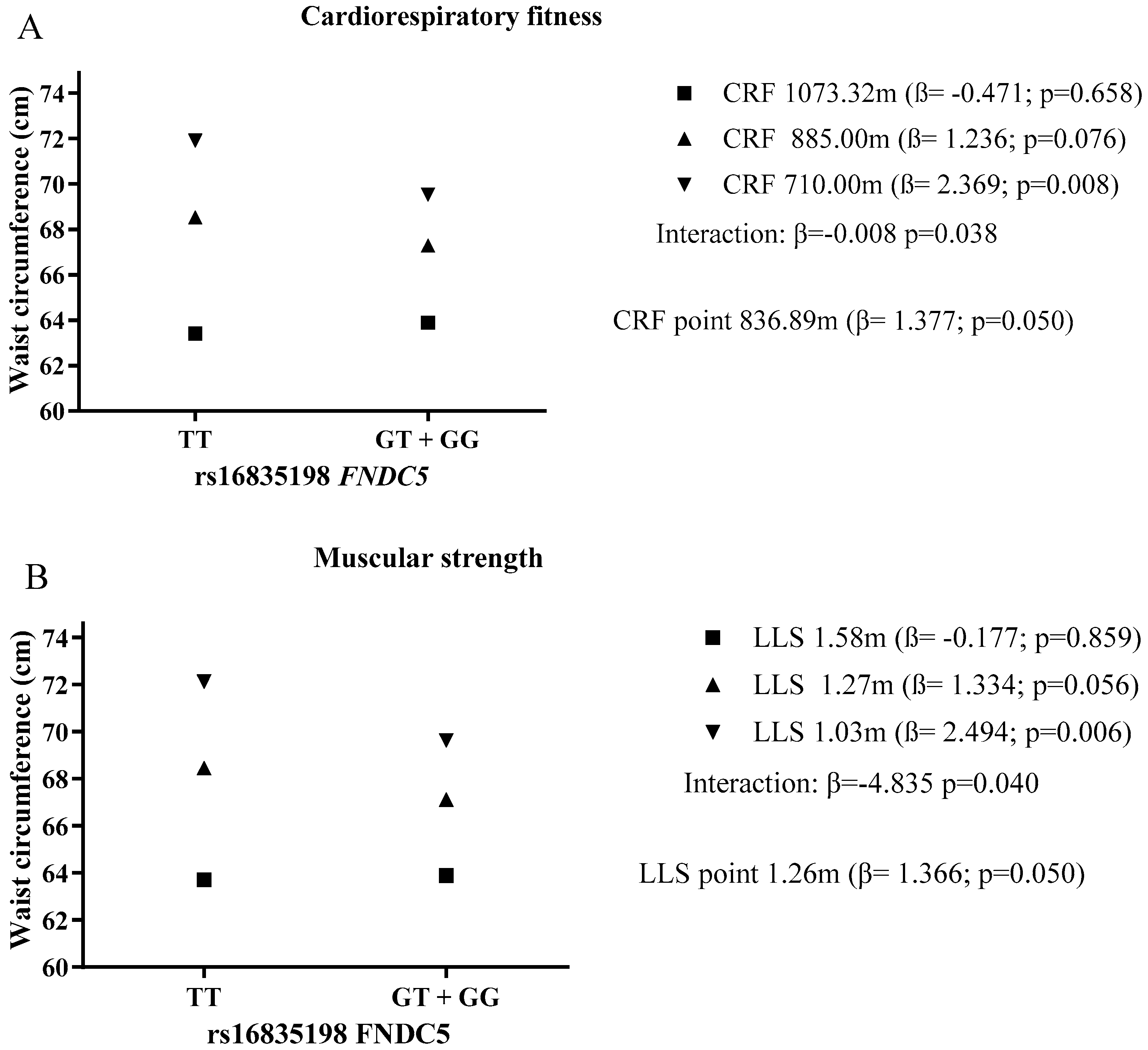
| CRF × rs16835198 FNDC5 | −0.008 | −0.015; −0.001 | 0.038 | |
| Muscular strength | 0.218 | |||
| LLS | −10.447 | −12.538; −8.356 | <0.001 | |
| rs16835198 FNDC5 | ||||
| TT | 7.474 | 1.442; 13.507 | 0.015 | |
| GT + GG | 1 | |||
| LLS x rs16835198 FNDC5 | −4.835 | −9.445; −0.225 | 0.040 | |
| BMI (z-score) | ||||
| Cardiorespiratory fitness | 0.201 | |||
| CRF | −0.002 | −0.002; −0.001 | <0.001 | |
| rs16835198 FNDC5 | ||||
| TT | 0.951 | 0.332; 1.570 | 0.003 | |
| GT + GG | 1 | |||
| CRF × rs16835198 FNDC5 | −0.001 | −0.002; 0.001 | 0.007 | |
| Muscular strength | 0.197 | |||
| LLS | −1.147 | −1.345; −0.949 | <0.001 | |
| rs16835198 FNDC5 | ||||
| TT | 0.707 | 0.136 1.277 | 0.015 | |
| GT + GG | 1 | |||
| LLS × rs16835198 FNDC5 | −0.449 | −0.885; −0.012 | 0.044 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todendi, P.F.; Brand, C.; de Castro Silveira, J.F.; Burns, R.D.; Martínez, J.A.; Fiegenbaum, M.; Reis Gaya, A.; Pollo Renner, J.D.; Reuter, C.P.; de Moura Valim, A.R. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Muscular Strength Moderates the Relationship between FNDC5 Polymorphism and Adiposity in Children and Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189797
Todendi PF, Brand C, de Castro Silveira JF, Burns RD, Martínez JA, Fiegenbaum M, Reis Gaya A, Pollo Renner JD, Reuter CP, de Moura Valim AR. Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Muscular Strength Moderates the Relationship between FNDC5 Polymorphism and Adiposity in Children and Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189797
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodendi, Pâmela Ferreira, Caroline Brand, João Francisco de Castro Silveira, Ryan Donald Burns, J. Alfredo Martínez, Marilu Fiegenbaum, Anelise Reis Gaya, Jane Dagmar Pollo Renner, Cézane Priscila Reuter, and Andréia Rosane de Moura Valim. 2021. "Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Muscular Strength Moderates the Relationship between FNDC5 Polymorphism and Adiposity in Children and Adolescents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189797






