Evaluation of the Benefits, Satisfaction, and Limitations of Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities: A General Population Survey in Spain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Instrument
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Analysis
3.2. Validation of the Instrument
3.2.1. Reliability Due to Internal Consistency
3.2.2. Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA)
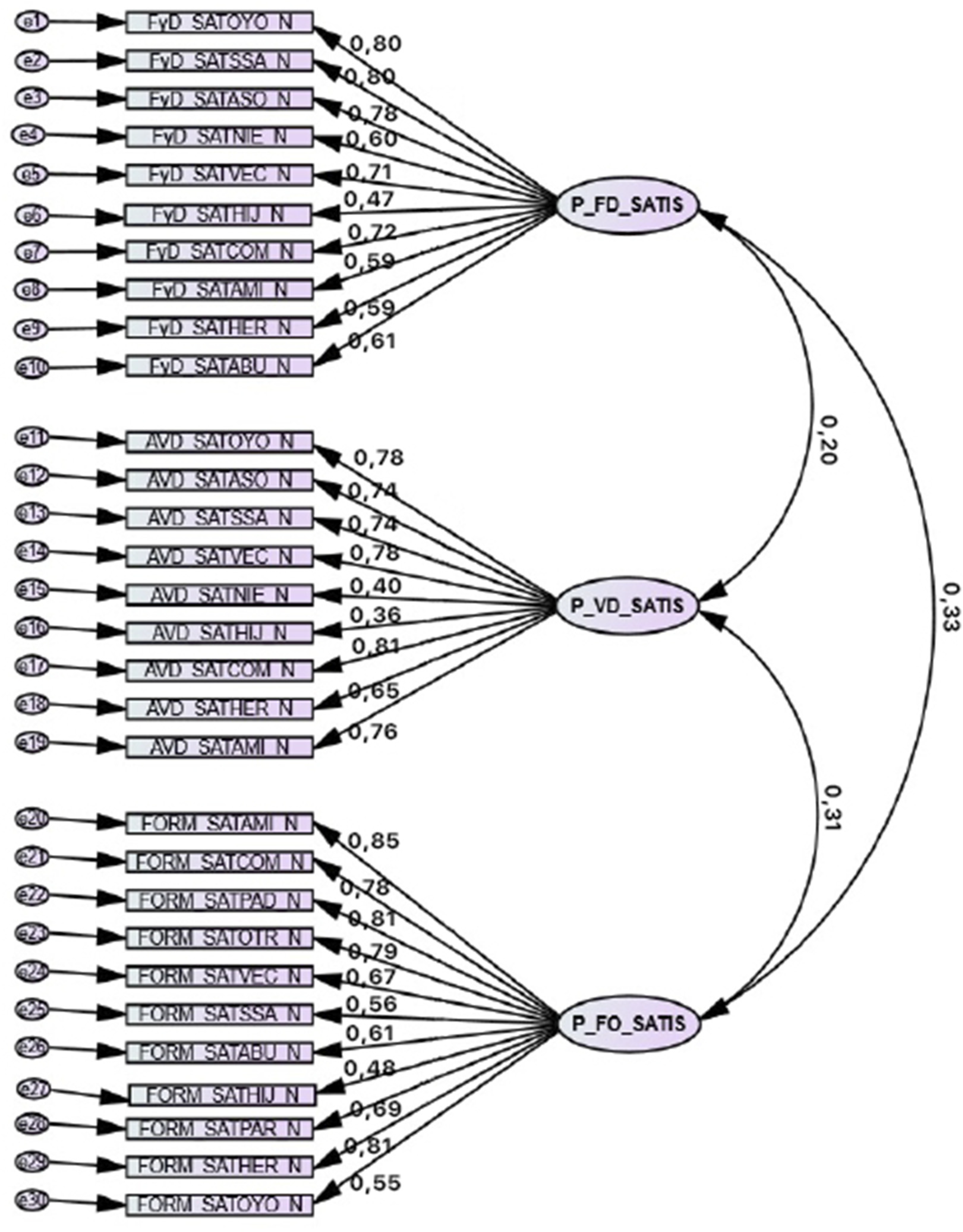
3.2.3. Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA)
3.3. Benefits of Performing Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities
3.4. Satisfaction of Performing Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities
3.5. Limitations of People Who Perform Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Demographics Collaborators. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950–2019: A comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1160–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Decade of Healthy Ageing: Baseline Report Geneva. 2020. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/mca-documents/decade-of-healthy-ageing-baseline-report_06012021.pdf?sfvrsn=eaad1517_1&download=true (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Malcolm, M.; Frost, H.; Cowie, J. Loneliness and social isolation causal association with health-related lifestyle risk in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Losada, A.; Márquez-González, M.; García-Ortiz, L.; Gómez-Marcos, M.A.; Fernández- Fernández, V.; Rodríguez-Sánchez, E. Loneliness and mental health in a representative sample of community-dwelling Spanish older adults. J. Psychol. 2012, 146, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnes, D.; Sheppard, C.; Henderson, C.R., Jr.; Wassel, M.; Cope, R.; Barber, C.; Pillemer, K. Interventions to reduce ageism against older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Public Health 2019, 109, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machielse, A.; Duyndam, J. Strategies of socially isolated older adults: Mechanisms of emergence and persistence. J. Aging. Stud. 2020, 53, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teater, B. Intergenerational programs to promote active aging: The experiences and perspectives of older adults. Act. Adapt. Aging 2016, 40, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.J.; Xue, Q.L.; Li, T.; Carlson, M.C.; Fried, L.P. Volunteering: A physical activity intervention for older adults—The Experience Corps program in Baltimore. J. Urban Health 2006, 83, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, M.C.; Erickson, K.I.; Kramer, A.F.; Voss, M.W.; Bolea, N.; Mielke, M.; McGill, S.; Rebok, G.W.; Seeman, T.; Fried, L.P. Evidence for neurocognitive plasticity in at-risk older adults: The experience corps program. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2009, 64, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, Y.; Ohba, H.; Yasunaga, M.; Nonaka, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Nishi, M.; Sakuma, N.; Uchida, H.; Shinkai, S.; Fujiwara, Y. The effect of intergenerational programs on the mental health of elderly adults. Aging Ment. Health 2015, 19, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, R.; Yasunaga, M.; Murayama, Y.; Ohba, H.; Nonaka, K.; Suzuki, H.; Sakuma, N.; Nishi, M.; Uchida, H.; Shinkai, S.; et al. Long-term effects of an intergenerational program on functional capacity in older adults: Results from a seven-year follow-up of the REPRINTS study. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2016, 64, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebok, G.W.; Carlson, M.C.; Glass, T.A.; McGill, S.; Hill, J.; Wasik, B.A.; Ialongo, N.; Frick, K.D.; Fried, L.P.; Rasmussen, M.D. Short-term impact of Experience Corps participation on children and schools: Results from a pilot randomized trial. J. Urban Health 2004, 81, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gualano, M.R.; Voglino, G.; Bert, F.; Thomas, R.; Camussi, E.; Siliquini, R. The impact of intergenerational programs on children and older adults: A review. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2018, 30, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa Hernández, G.B.; Murray, C.M.; Stanley, M. An intergenerational playgroup in an Australian residential aged-care setting: A qualitative case study. Health Soc. Care Community 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Lee, C.; Foster, M.J.; Bian, J. Intergenerational communities: A systematic literature review of intergenerational interactions and older adults’ health-related outcomes. Soc. Sci. Med. 2020, 264, 113374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canedo-García, A.; García-Sánchez, J.N.; Pacheco-Sanz, D.I. A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Intergenerational Programs. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canedo-García, A.; García-Sánchez, J.N.; Pacheco-Sanz, D.I. Acción conjunta intergeneracional (ACIG). Descripción de variables intervinientes. Int. J. Dev. Educ. Psychology. Rev. Infad Psicología 2019, 3, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, Y.; Murayama, H.; Hasebe, M.; Yamaguchi, J.; Fujiwara, Y. The impact of intergenerational programs on social capital in Japan: A randomized population-based cross- sectional study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Luo, Y.; Li, P. Intergenerational Solidarity and Life Satisfaction among Empty-Nest Older Adults in Rural China: Does Distance Matter? J. Fam. Issues 2020, 42, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dai, H. Determining the primary caregiver for disabled older adults in Mainland China: Spouse priority and living arrangements. J. Fam. Ther. 2019, 41, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, R.; Saito, T.; Houde, S.C.; Kai, I. Social interactions and depressive symptoms among community dwelling older adults in Nepal: A synergic effect model. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 53, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingerman, K.L.; Huo, M.; Birditt, K.S. Mothers, fathers, daughters, and sons: Gender differences in adults’ intergenerational ties. J. Fam. Issues 2020, 41, 1597–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaga, M.; Murayama, Y.; Takeuchi, R.; Ohba, H.; Nonaka, K.; Nishi, M.; Fujiwara, Y. Effect of Intergenerational Programs between Primary School Children and Senior Volunteers on the Social Support. Gerontologist 2012, 52, 555–556. [Google Scholar]
- Dorgo, S.; King, G.A.; Bader, J.O.; Limon, J.S. Comparing the effectiveness of peer mentoring and student mentoring in a 35-week fitness program for older adults. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 52, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorgo, S.; King, G.A.; Bader, J.O.; Limon, J.S. Outcomes of a peer mentor implemented fitness program in older adults: A quasi-randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2013, 50, 1156–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeman, T.; Merkin, S.S.; Goldwater, D.; Cole, S.W. Intergenerational mentoring, eudaimonic well-being and gene regulation in older adults: A pilot study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 111, 104468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.I.; Morrow-Howell, N. Health outcomes of Experience Corps: A high- commitment volunteer program. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 71, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Pardo, P.J.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Gil-Arias, A. Impact of a motivational resistance-training programme on adherence and body composition in the elderly. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herrmann, D.S.; Sipsas-Herrmann, A.; Stafford, M.; Herrmann, N.C. Benefits and risks of intergenerational program participation by senior citizens. Educ. Gerontol. 2005, 31, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruenewald, T.L.; Tanner, E.K.; Fried, L.P.; Carlson, M.C.; Xue, Q.L.; Parisi, J.M.; Rebok, G.W.; Yarnell, L.M.; Seeman, T.E. The Baltimore Experience Corps Trial: Enhancing generativity via intergenerational activity engagement in later life. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2016, 71, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.C.; Kuo, J.H.; Chuang, Y.F.; Varma, V.R.; Harris, G.; Albert, M.S.; Fried, L.P. Impact of the Baltimore experience Corps trial on cortical and hippocampal volumes. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2015, 11, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chippendale, T.; Boltz, M. Living Legends: Effectiveness of a program to enhance sense of purpose and meaning in life among community-dwelling older adults. Am. J. Occup. Ther. 2015, 69, p1–p11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, K.; Dabelko-Schoeny, H. A comprehensive evaluation of a lifelong learning program: Program 60. Int. J. Aging Hum. Dev. 2016, 84, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.J.; Rebok, G.W.; Yu, Q.; Frangakis, C.E.; Carlson, M.C.; Wang, T.; Fried, L.P. The long-term relationship between high-intensity volunteering and physical activity in older African American women. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2009, 64, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strand, K.A.; Francis, S.L.; Margrett, J.A.; Franke, W.D.; Peterson, M.J. Community- based exergaming program increases physical activity and perceived wellness in older adults. J. Aging Phys. Activ. 2014, 22, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arma, V.R.; Tan, E.J.; Gross, A.L.; Harris, G.; Romani, W.; Fried, L.P.; Rebok, G.W.; Carlson, M.C. Effect of community volunteering on physical activity: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2016, 50, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Granacher, U.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Kressig, R.W.; Zahner, L. An Intergenerational Approach in the Promotion of Balance and Strength for Fall Prevention-A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2011, 57, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granacher, U.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Kressig, R.W.; Zahner, L. Evidence- Based and Evidence-Inspired: An Intergenerational Approach in the Promotion of Balance and Strength for Fall Prevention. Gerontology 2011, 57, 424–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrow-Howell, N.; Hong, S.I.; McCrary, S.; Blinne, W. Changes in activity among older volunteers. Res. Aging 2012, 34, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.H., Jr.; Weaver, A.J. Making Connections: The Legacy of an Intergenerational Program. Gerontologist 2016, 56, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.L.; McFadden, S.H. Terror management Perspective on young adults´ ageism and attitudes toward dementia. Educ. Gerontol. 2012, 38, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shedletsky, L. Undergraduates Mentoring Older Adults: Breaking Stereotypes. J. Intergener. Relatsh. 2012, 10, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaga, M.; Murayama, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Ohba, H.; Suzuki, H.; Nonaka, K.; Kuraoka, M.; Sakurai, R.; Nishi, M.; Sakuma, N.; et al. Multiple impacts of an intergenerational program in Japan: Evidence from the Research on Productivity through Intergenerational Sympathy Project. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molpeceres, M.A.; Pinazo, S.; Aliena, R. Older Adult Mentors and Youth at Risk: Challenges for Intergenerational Mentoring Programs in Family-Centered Cultures. J. Intergener. Relatsh. 2012, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitten, T.; Vecchio, N.; Radford, K.; Fitzgerald, J.A. Intergenerational care as a viable intervention strategy for children at risk of delinquency. Aust. J. Soc. Issues 2017, 52, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

(A) Performing activities with people of another generation produces BENEFITS for your: -Physical health, -Mental health, -Mood, -Relationships, -Self-determination, -Social participation, -Economic well-being, -Professional well-being, -Academic education.
|
(B) With WHO & FREQUENCY do you perform activities? -Partner, -Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
(C) AGE of the people with whom you perform activities: -Partner, -Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
(D) GENDER of the people with whom you perform activities: -Partner, -Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
(E) AUTONOMY of the people with whom you perform activities: -Partner, -Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
(F) LIMITATION of the people with whom you perform activities: -Partner,- Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
(G) SATISFACTION you feel from perform activities with these people: -Partner, -Child, -Grandchild, -Parent, -Grandparent, -Sibling, -Other relative, -Friend, -Neighbor, -Colleague, -Person in the same situation, -Professional of an institution, -Professional of health, social or academic services.
|
| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 33.96 1 (16.01) 2 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 608 (30.2) |
| Female | 1405 (69.8) |
| Place of origin | |
| Rural area, small village | 440 (21.9) |
| Rural area, large village | 326 (16.2) |
| Urban area, small town | 906 (45.0) |
| Urban area, large town | 341 (16.9) |
| Education | |
| Primary school | 20 (1.0) |
| High school | 210 (10.4) |
| Vocational training | 138 (6.9) |
| College or university | 1645 (81.7) |
| Autonomy level | |
| Alone | 1705 (84.7) |
| Family support | 253 (12.6) |
| Professional support | 12 (0.6) |
| Other support | 43 (2.1) |
| Marital status | |
| Single | 1024 (50.9) |
| Married or in union | 761 (37.8) |
| Widowed | 23 (1.1) |
| Separated | 25 (1.2) |
| Divorced | 56 (2.8) |
| Living arrangements | |
| Living alone | 205 (10.2) |
| Living with a partner | 332 (16.5) |
| Living with a partner and children | 342 (17.0) |
| Living with a partner and grandchildren | 3 (0.1) |
| Living with a partner, children and grandchildren | 5 (0.2) |
| Living with children | 36 (1.8) |
| Living with children and grandchildren | 3 (0.1) |
| Living with parents | 562 (27.9) |
| Living with grandparents | 11 (0.5) |
| Living with parents and grandparents | 43 (2.1) |
| Living with other relatives | 43 (2.1) |
| Living with friends | 248 (12.3) |
| Other types | 180 (8.9) |
| Employment situation | |
| Unemployed | 938 (46.6) |
| Employed | 913 (45.4) |
| Retired | 151 (7.5) |
| Income level (EUR/month) | |
| >2500 | 862 (42.8) |
| 2001–2500 | 213 (10.6) |
| 1501–2000 | 264 (13.1) |
| 1001–1500 | 229 (11.4) |
| 501–1000 | 204 (10.1) |
| <500 | 116 (5.8) |
| Variables | Daily/Healthcare Activities | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities | Physical/Sport Activities | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | χ2 | p | N (%) | χ2 | P | N (%) | χ2 | p | |
| Age (years) | |||||||||
| <22 22–40 ≥40 | 105 (24.5) 158 (36.8) 166 (38.8) | 9.98 | 0.007 | 158 (23.0) 229 (33.4) 299 (43.6) | 38.25 | <0.001 | 164 (24.5) 257 (38.4) 249 (37.2) | 4.34 | 0.114 |
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male Female | 108 (25.1) 323 (74.9) | 10.44 | 0.001 | 204 (29.6) 485 (70.4) | 1.83 | 0.177 | 230 (34.3) 440 (65.7) | 3.55 | 0.600 |
| Place of origin | |||||||||
| Rural area Urban area | 157 (36.4) 274 (63.6) | 0.94 | 0.332 | 240 (34.8) 449 (65.2) | 3.56 | 0.059 | 263 (39.3) 407 (60.7) | 2.10 | 0.147 |
| Education | |||||||||
| Less than college or university College or university | 65 (15.1) 366 (84.9) | 3.84 | 0.050 | 112 (16.3) 577 (83.7) | 1.35 | 0.245 | 122 (18.2) 548 (81.8) | 1.07 | 0.300 |
| Autonomy level | |||||||||
| Alone Family/professional/other support | 362 (84.0) 69 (16.0) | 1.35 | 0.246 | 571 (82.9) 118 (17.1) | 8.44 | 0.004 | 577 (86.1) 93 (13.9) | 0.01 | 0.909 |
| Marital status | |||||||||
| Single Married or in union Widowed/separated/divorced | 193 (47.9) 196 (48.6) 14 (3.5) | 15.63 | <0.001 | 291 (45.0) 300 (46.4) 56 (8.7) | 31.47 | <0.001 | 320 (50.9) 265 (42.1) 44 (7.0) | 6.11 | 0.047 |
| Living arrangements | |||||||||
| Living alone/with children/with grandchildren Living with a partner/a partner and children and/or grandchildren Living with parents and/or grandparents/ other relatives Living with friends/other types | 41 (9.7) 170 (39.4) 158 (36.7) 61 (14.2) | 25.21 | <0.001 | 98 (14.2) 280 (40.6) 197 (28.6) 114 (16.5) | 19.63 | <0.001 | 84 (12.5) 248 (37.0) 200 (29.9) 138 (20.6) | 0.84 | 0.839 |
| Employment situation | |||||||||
| Unemployed Employed Retired | 180 (41.8) 229 (53.1) 22 (5.1) | 23.02 | <.001 | 268 (38.9) 330 (47.9) 91 (13.2) | 44.72 | <0.001 | 310 (46.3) 297 (44.3) 63 (9.4) | 7.08 | 0.029 |
| Income level (€/month) | |||||||||
| >2001 1001–2000 <1000 | 230 (53.4) 126 (29.2) 75 (17.4) | 7.19 | 0.028 | 348 (50.5) 193 (28.0) 171 (25.5) | 22.31 | <0.001 | 374 (55.8) 148 (21.5) 125 (18.7) | 1.93 | 0.380 |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disagr ee | NA/ND | Agree | Disagr ee | NA/ND | Agree | Disagr ee | NA/ND | Agree | |
| Physic al health | 52 | 78 | 173 | 42 | 124 | 347 | 20 | 61 | 463 |
| (17.2) | (25.7) | (57.1) | (8.2) | (24.2) | (67.6) | (3.7) | (11.2) | (85.1) | |
| Mental health | 33 | 37 | 233 | 21 | 41 | 451 | 18 | 51 | 475 |
| (10.9) | (12.2) | (76.9) | (4.1) | (8.0) | (87.9) | (3.3) | (9.4) | (87.3) | |
| Mood | 33 | 29 | 241 | 19 | 34 | 460 | 17 | 41 | 486 |
| (10.9) | (9.6) | (79.5) | (3.7) | (6.6) | (89.7) | (3.1) | (7.5) | (89.3) | |
| Relationship s | 23 | 25 | 255 | 14 | 28 | 471 | 18 | 44 | 482 |
| (7.6) | (8.3) | (84.2) | (2.7) | (5.5) | (91.8) | (3.3) | (8.1) | (88.6) | |
| Self-determ ination | 29 | 71 | 203 | 35 | 110 | 368 | 35 | 163 | 346 |
| (9.6) | (23.4) | (67.0) | (6.8) | (21.4) | (71.7) | (6.4) | (30.0) | (63.6) | |
| Social partici pation | 19 | 49 | 235 | 21 | 38 | 454 | 23 | 100 | 421 |
| (6.3) | (16.2) | (77.6) | (4.1) | (7.4) | (88.5) | (4.2) | (18.4) | (77.4) | |
| Economic well-being | 77 | 103 | 123 | 136 | 186 | 191 | 145 | 236 | 163 |
| (25.4) | (34.0) | (40.6) | (26.5) | (36.3) | (37.2) | (26.7) | (43.4) | (30.0) | |
| Professional well-being | 68 | 110 | 125 | 80 | 160 | 273 | 118 | 217 | 209 |
| (22.4) | (36.3) | (41.3) | (15.6) | (31.2) | (53.2) | (21.7) | (39.9) | (38.4) | |
| Acade mic educat ion | 50 | 97 | 156 | 43 | 82 | 388 | 95 | 189 | 260 |
| (16.5) | (32.0) | (51.5) | (8.4) | (16.0) | (75.6) | (17.5) | (34.7) | (47.8) | |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–14 | 15–65 | >65 | 0–14 | 15–65 | >65 | 0–14 | 15–65 | >65 | |
| Partner | 2 | 172 | 7 | 5 | 292 | 23 | 5 | 295 | 11 |
| (1.1) | (95.0) | (3.9) | (1.6) | (91.3) | (7.2) | (1.6) | (94.9) | (3.5) | |
| Child | 66 | 30 | 1 | 89 | 86 | 1 | 92 | 74 | 0 |
| (68.0) | (30.9) | (1.0) | (50.6) | (48.9) | (0.6) | (44.6) | (0) | ||
| Grandchild | 13 | 1 | 1 | 43 | 6 | 2 | 48 | 6 | 2 |
| (86.7) | (6.7) | (6.7) | (84.3) | (11.8) | (3.9) | (85.7) | (10.7) | (3.6) | |
| Parent | 1 | 137 | 96 | 3 | 207 | 105 | 5 | 218 | 68 |
| (0.4) | (58.5) | (41.0) | (1.0) | (65.7) | (33.3) | (1.7) | (74.9) | (23.4) | |
| Grandparent | 0 | 4 | 112 | 3 | 10 | 130 | 4 | 6 | 110 |
| (0) | (3.4) | (96.6) | (2.1) | (7.0) | (90.9) | (3.3) | (5.0) | (91.7) | |
| Sibling | 15 | 144 | 3 | 15 | 240 | 5 | 19 | 218 | 3 |
| (9.3) | (88.9) | (1.9) | (5.8) | (92.3) | (1.9) | (7.9) | (90.8) | (1.3) | |
| Other relative | 9 | 87 | 27 | 15 | 168 | 20 | 27 | 160 | 14 |
| (7.3) | (70.7) | (22.0) | (7.4) | (82.8) | (9.9) | (13.4) | (79.6) | (7.0) | |
| Friend | 1 | 151 | 5 | 4 | 359 | 24 | 6 | 359 | 17 |
| (0.6) | (96.2) | (3.2) | (1.0) | (92.8) | (6.2) | (1.6) | (94.0) | (4.5) | |
| Neighbor | 2 | 61 | 14 | 10 | 135 | 22 | 9 | 157 | 12 |
| (2.6) | (79.2) | (18.2) | (6.0) | (80.8) | (13.2) | (5.1) | (88.2) | (6.7) | |
| Colleague | 3 | 104 | 0 | 4 | 244 | 9 | 6 | 180 | 6 |
| (2.8) | (97.2) | (0) | (1.6) | (94.9) | (3.5) | (3.1) | (93.8) | (3.1) | |
| Person in the same situation | 3 | 50 | 0 | 4 | 93 | 6 | 10 | 74 | 4 |
| (5.7) | (94.3) | (0) | (3.9) | (90.3) | (5.8) | (11.4) | (84.1) | (4.5) | |
| Professional of an institution | 4 | 43 | 2 | 6 | 96 | 10 | 12 | 77 | 6 |
| (8.2) | (87.8) | (4.1) | (5.4) | (85.7) | (8.9) | (12.6) | (81.1) | (6.3) | |
| Professional of social services | 4 | 42 | 0 | 4 | 88 | 4 | 11 | 59 | 6 |
| (8.7) | (91.3) | (0) | (4.2) | (91.7) | (4.2) | (14.5) | (77.6) | (7.9) | |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | |
| Partner | 130 (73.9) | 46 (26.1) | 217 (69.3) | 96 (30.7) | 205 (66.6) | 103 (33.4) |
| Child | 47 (50.0) | 47 (50.0) | 91 (53.2) | 80 (46.8) | 96 (59.3) | 66 (40.7) |
| Grandchild | 10 (66.7) | 5 (33.3) | 23 (52.3) | 21 (47.7) | 34 (58.6) | 24 (41.4) |
| Parent | 52 (23.0) | 174 (77.0) | 86 (29.2) | 209 (70.8) | 102 (36.7) | 176 (63.3) |
| Grandparent | 21 (18.3) | 94 (81.7) | 31 (23.7) | 100 (76.3) | 41 (35.0) | 76 (65.0) |
| Sibling | 77 (48.1) | 83 (51.9) | 121 (47.8) | 132 (52.2) | 123 (51.5) | 116 (48.5) |
| Other relative | 55 (45.1) | 67 (54.9) | 77 (37.7) | 127 (62.3) | 86 (43.9) | 110 (56.1) |
| Friend | 50 (33.1) | 101 (66.9) | 134 (36.2) | 236 (63.8) | 178 (47.6) | 196 (52.4) |
| Neighbor | 36 (48.6) | 38 (51.4) | 69 (42.9) | 92 (57.1) | 91 (51.7) | 85 (48.3) |
| Colleague | 42 (40.8) | 61 (59.2) | 99 (41.1) | 142 (58.9) | 99 (51.8) | 92 (48.2) |
| Person in the same situation | 18 (35.3) | 33 (64.7) | 35 (36.5) | 61 (63.5) | 32 (37.6) | 53 (62.4) |
| Professional of an institution | 22 (44.0) | 28 (56.0) | 48 (44.4) | 60 (55.6) | 48 (53.9) | 41 (46.1) |
| Professional of social services | 23 (46.9) | 26 (53.1) | 50 (53.8) | 43 (46.2) | 45 (58.4) | 32 (41.6) |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not NS | NS | Not NS | NS | Not NS | NS | |
| Partner | 171 (92.4) | 14 (7.6) | 302 (95.3) | 15 (4.7) | 302 (97.1) | 9 (2.9) |
| Child | 63 (64.3) | 35 (35.7) | 148 (81.8) | 33 (18.2) | 152 (91.0) | 15 (9.0) |
| Grandchild | 16 (84.2) | 3 (15.8) | 44 (84.6) | 8 (15.4) | 53 (88.3) | 7 (11.7) |
| Parent | 160 (66.9) | 79 (33.1) | 271 (85.5) | 46 (14.5) | 266 (90.8) | 27 (9.2) |
| Grandparent | 32 (26.2) | 90 (73.8) | 74 (49.7) | 75 (50.3) | 75 (58.6) | 53 (41.4) |
| Sibling | 128 (78.5) | 35 (21.5) | 232 (89.9) | 26 (10.1) | 235 (95.5) | 11 (4.5) |
| Other relative | 94 (75.2) | 31 (24.8) | 188 (87.0) | 28 (13.0) | 192 (90.6) | 20 (9.4) |
| Friend | 124 (84.4) | 23 (15.6) | 348 (93.5) | 24 (6.5) | 370 (96.1) | 15 (3.9) |
| Neighbor | 61 (81.3) | 14 (18.7) | 151 (86.8) | 23 (13.2) | 174 (95.1) | 9 (4.9) |
| Colleague | 89 (89.0) | 11 (11.0) | 235 (93.3) | 17 (6.7) | 190 (95.5) | 9 (4.5) |
| Person in the same situation | 41 (73.2) | 15 (26.8) | 89 (86.4) | 14 (13.6) | 92 (93.9) | 6 (6.1) |
| Professional of an institution | 42 (77.8) | 12 (22.2) | 101 (92.7) | 8 (7.3) | 92 (97.9) | 2 (2.1) |
| Professional of social services | 42 (87.5) | 6 (12.5) | 94 (94.9) | 5 (5.1) | 79 (97.5) | 2 (2.5) |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sometime a Year/Month | Sometime a Week/(Almost) Everyday | Sometime a Year/Month | Sometime a Week/(Almost) Everyday | Sometime a Year/Month | Sometime a Week/(Almost) Everyday | |
| Partner | 36 (20.6) | 139 (79.4) | 98 (31.3) | 215 (68.7) | 137 (43.6) | 177 (56.4) |
| Child | 28 (27.5) | 74 (72.5) | 76 (41.5) | 107 (58.5) | 101 (59.4) | 69 (40.6) |
| Grandchild | 17 (77.3) | 5 (22.7) | 34 (59.6) | 23 (40.4) | 47 (77.0) | 14 (23.0) |
| Parent | 55 (24.3) | 171 (75.7) | 171 (54.5) | 143 (45.5) | 170 (58.0) | 123 (42.0) |
| Grandparent | 48 (41.4) | 68 (58.6) | 91 (62.8) | 54 (37.2) | 94 (77.0) | 28 (23.0) |
| Sibling | 82 (51.3) | 78 (48.8) | 161 (61.5) | 101 (38.5) | 164 (67.5) | 79 (32.5) |
| Other relative | 77 (59.7) | 52 (40.3) | 159 (72.3) | 61 (27.7) | 151 (75.5) | 49 (24.5) |
| Friend | 74 (44.6) | 92 (55.4) | 147 (37.4) | 246 (62.6) | 153 (38.7) | 242 (61.3) |
| Neighbor | 76 (85.4) | 13 (14.6) | 117 (63.2) | 68 (36.8) | 112 (62.2) | 68 (37.8) |
| Colleague | 57 (51.8) | 53 (48.2) | 161 (59.0) | 112 (41.0) | 121 (59.0) | 84 (41.0) |
| Person in the same situation | 43 (64.2) | 24 (35.8) | 81 (68.6) | 37 (31.4) | 79 (80.6) | 19 (19.4) |
| Professional of an institution | 48 (76.2) | 15 (23.8) | 84 (62.7) | 50 (37.3) | 79 (75.2) | 26 (24.8) |
| Professional of social services | 49 (72.1) | 19 (27.9) | 86 (73.5) | 31 (26.5) | 69 (77.5) | 20 (22.5) |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Not/Little Satisfied | NS/ ND | Quite/Very Satisfied | Not/Little Satisfied | NS/ ND | Quite/Very Satisfied | Not/Little Satisfied | NS/ ND | Quite/Very Satisfied | |
| Partner | 13 (6.6) | 12 (6.1) | 172 (87.3) | 10 (3.2) | 8 (2.5) | 296 (94.3) | 8 (2.6) | 16 (5.1) | 287 (92.3) |
| Child | 12 (10.3) | 6 (5.2) | 98 (84.5) | 14 (7.7) | 3 (1.6) | 165 (90.7) | 15 (9.0) | 10 (6.0) | 141 (84.9) |
| Grandchild | 8 (32.0) | 2 (8.0) | 15 (60.0) | 12 (21.8) | 3 (2.5) | 40 (72.7) | 15 (23.8) | 5 (7.9) | 43 (68.3) |
| Parent | 13 (5.1) | 22 (8.6) | 221 (86.3) | 9 (2.9) | 15 (4.8) | 288 (92.3) | 5 (1.7) | 18 (6.2) | 268 (92.1) |
| Grandparent | 6 (4,6) | 17 (13.0) | 108 (82.4) | 6 (4.1) | 8 (5.5) | 131 (90.3) | 6 (5.0) | 13 (10.7) | 102 (84.3) |
| Sibling | 12 (7.1) | 24 (14.2) | 133 (78.7) | 8 (3.1) | 15 (5.8) | 235 (91.1) | 9 (3.7) | 12 (4.9) | 222 (91.4) |
| Other relative | 5 (3.6) | 22 (15.7) | 113 (80.7) | 8 (3.5) | 15 (6.6) | 204 (89.9) | 7 (3.4) | 17 (8.3) | 182 (88.3) |
| Partner | 5 (3.0) | 14 (8.5) | 145 (88.4) | 8 (2.1) | 8 (2.1) | 360 (95.7) | 7 (1.8) | 18 (4.7) | 356 (93.4) |
| Neighbor | 9 (11.1) | 21 (25.9) | 51 (63.0) | 10 (5.8) | 34 (19.8) | 128 (74.4) | 9 (4.9) | 22 (12.0) | 152 (83.1) |
| Colleague | 6 (5.3) | 22 (19.3) | 86 (75.4) | 9 (3.7) | 24 (9.8) | 212 (86.5) | 9 (4.7) | 18 (9.4) | 165 (85.9) |
| Person in the same situation | 9 (16.4) | 6 (10.9) | 40 (72.7) | 10 (10.1) | 9 (9,1) | 80 (80.8) | 13 (14.9) | 14 (16.1) | 60 (69.0) |
| Professional of an institution | 7 (12.7) | 13 (23.6) | 35 (63.3) | 14 (12.1) | 13 (11.2) | 89 (76.7) | 14 (15.1) | 10 (10.8) | 69 (74.2) |
| Professional of Social services | 9 (15.5) | 10 (17.2) | 39 (67.2) | 11 (11.0) | 14 (14.0) | 75 (75.0) | 14 (17.5) | 11 (13.8) | 55 (68.8) |
| Daily/Healthcare Activities N (%) | Educational/Cultural/Leisure Activities N (%) | Physical/Sport Activities N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Limitation | Any Limitation | No Limitation | Any Limitation | No Limitation | Any Limitation | |
| Partner | 146 (89.6) | 17 (10.4) | 272 (88.6) | 35 (11.4) | 276 (90.5) | 29 (9.5) |
| Child | 64 (68.8) | 29 (31.2) | 146 (83.0) | 30 (17.0) | 143 (86.7) | 22 (13.3) |
| Grandchild | 16 (76.2) | 5 (23.8) | 42 (79.2) | 11 (20.8) | 56 (86.2) | 9 (13.8) |
| Parent | 142 (63.1) | 83 (36.9) | 245 (79.8) | 62 (20.2) | 246 (84.2) | 46 (15.8) |
| Grandparent | 56 (46.3) | 65 (53.7) | 81 (56.3) | 63 (43.8) | 77 (57.9) | 56 (42.1) |
| Sibling | 126 (83.4) | 25 (16.6) | 226 (91.5) | 21 (8.5) | 217 (90.8) | 22 (9.2) |
| Other relative | 82 (72.6) | 31 (27.4) | 170 (82.1) | 37 (17.9) | 178 (87.7) | 25 (12.3) |
| Friend | 120 (85.1) | 21 (14.9) | 318 (90.1) | 35 (9.9) | 342 (90.7) | 35 (9.3) |
| Neighbor | 62 (81.6) | 14 (18.4) | 141 (83.4) | 28 (16.6) | 164 (89.1) | 20 (10.9) |
| Colleague | 81 (89.0) | 10 (11.0) | 208 (88.1) | 28 (11.9) | 173 (91.1) | 17 (8.9) |
| Person in the same situation | 44 (77.2) | 13 (22.8) | 83 (79.8) | 21 (20.2) | 76 (83.5) | 15 (16.5) |
| Professional of an Institution | 40 (78.4) | 11 (21.6) | 92 (80.2) | 23 (20.0) | 83 (83.8) | 16 (16.2) |
| Professional of Social services | 38 (82.6) | 8 (17.4) | 84 (84.0) | 16 (16.0) | 67 (84.8) | 12 (15.2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canedo-García, A.; García-Sánchez, J.-N.; Díaz-Prieto, C.; Pacheco-Sanz, D.-I. Evaluation of the Benefits, Satisfaction, and Limitations of Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities: A General Population Survey in Spain. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189683
Canedo-García A, García-Sánchez J-N, Díaz-Prieto C, Pacheco-Sanz D-I. Evaluation of the Benefits, Satisfaction, and Limitations of Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities: A General Population Survey in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(18):9683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189683
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanedo-García, Alejandro, Jesús-Nicasio García-Sánchez, Cristina Díaz-Prieto, and Deilis-Ivonne Pacheco-Sanz. 2021. "Evaluation of the Benefits, Satisfaction, and Limitations of Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities: A General Population Survey in Spain" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 18: 9683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189683
APA StyleCanedo-García, A., García-Sánchez, J.-N., Díaz-Prieto, C., & Pacheco-Sanz, D.-I. (2021). Evaluation of the Benefits, Satisfaction, and Limitations of Intergenerational Face-to-Face Activities: A General Population Survey in Spain. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(18), 9683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18189683








