Trends, Diagnoses, and Hospitalization Costs of Child Abuse and Neglect in the United States of America
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Child Maltreatment Hospitalizations Trends in the United States
1.2. Cost of Child Maltreatment Hospitalizations
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Measures
2.3. Analytic Strategy
3. Results
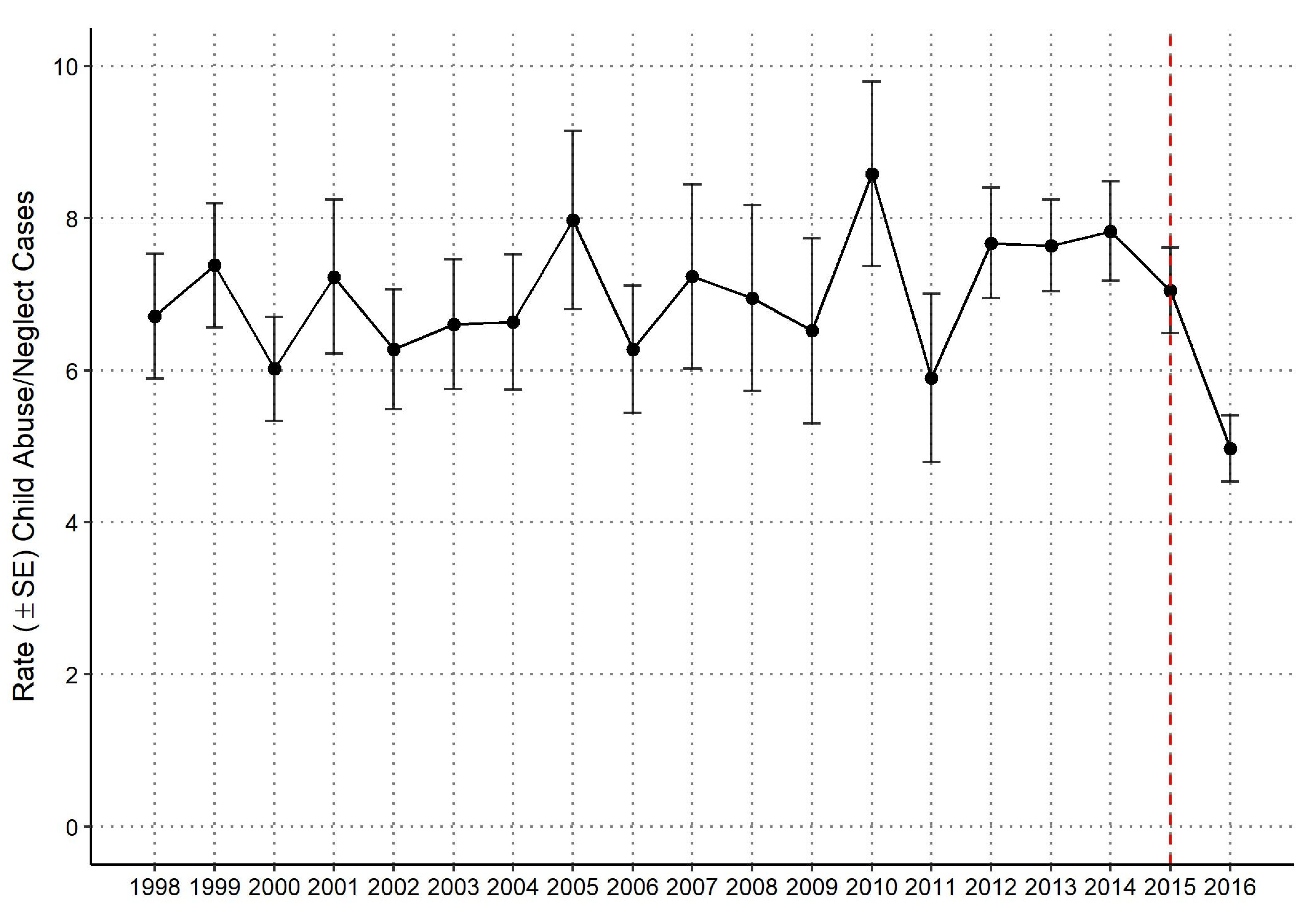
3.1. National Yearly Rate of Child Abuse and Neglect Hospitalizations
3.2. Demographic Characteristics of Children Hospitalized for Child Abuse or Neglect by Sex
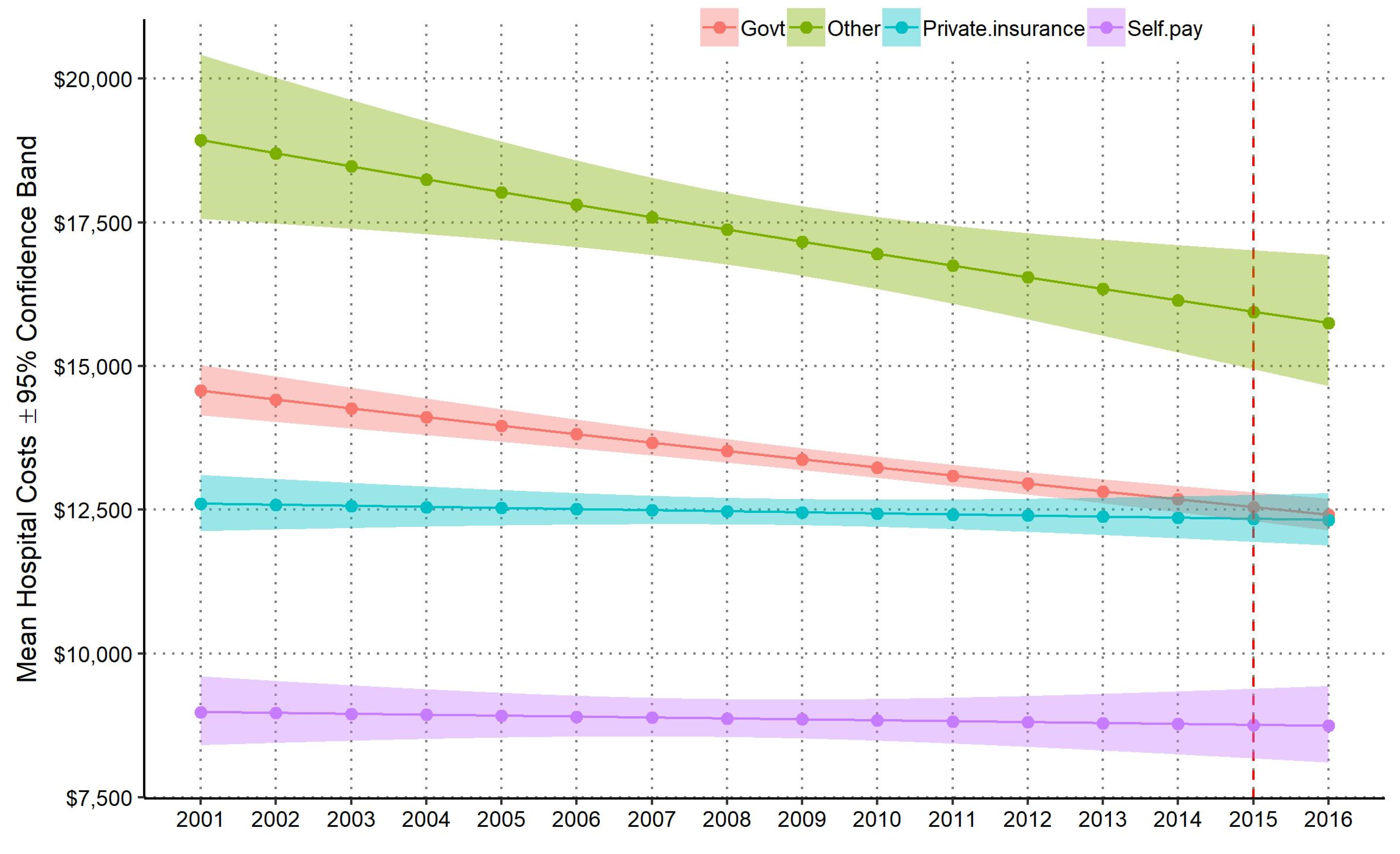
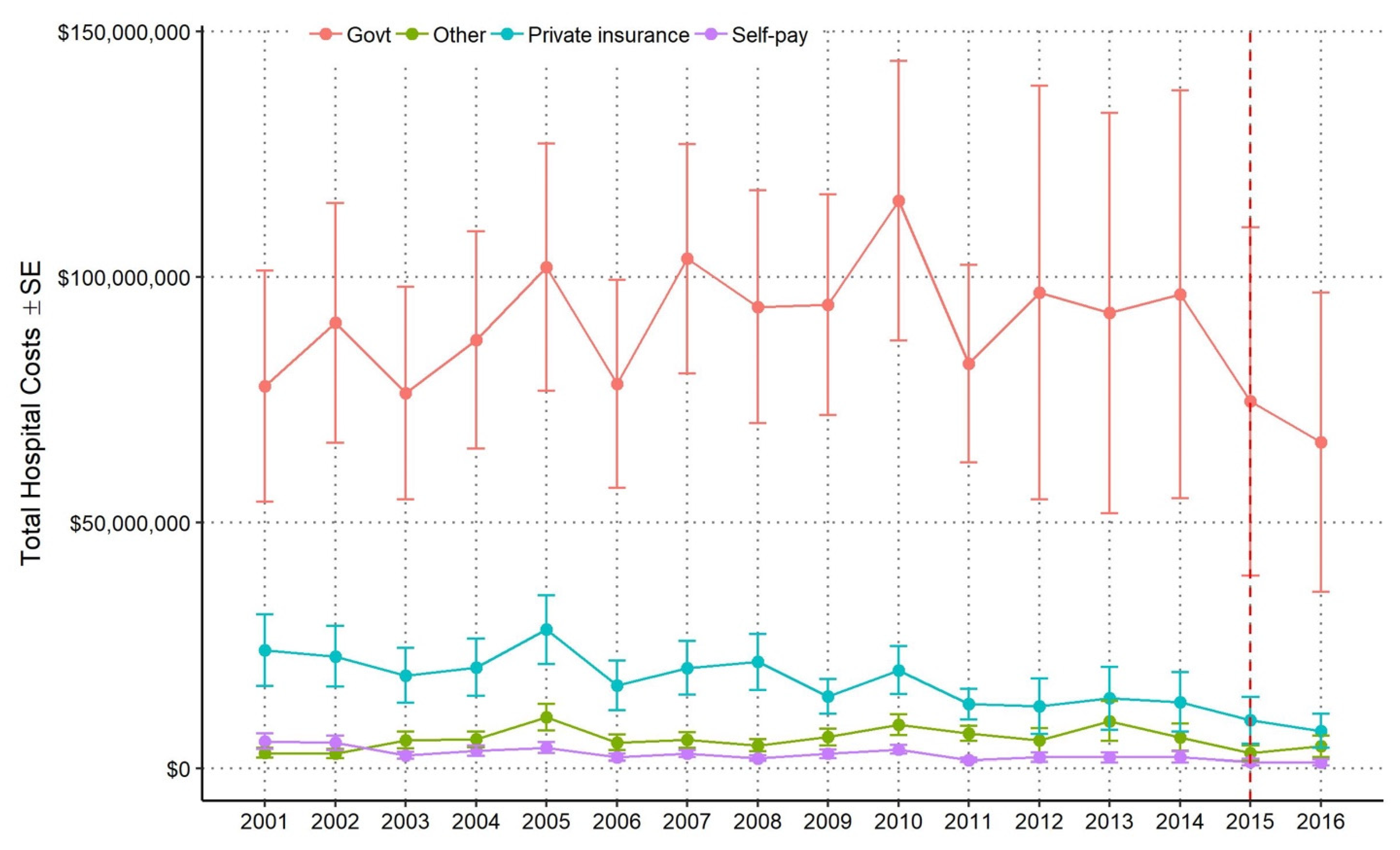
3.3. National Annual Mean and Total Hospital Costs by Payer Source
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Levey, E.J.; Apter, G.; Harrison, A.M. The global problem of child maltreatment: Perspectives on mecha-nisms of influence and illness presentation. Int. J. Cult. Ment Health. 2017, 10, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoltenbrogh, M.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.J.; van IJzendoorn, M.H.; Alink, L.R.A. Cultral-geographical differences in the occurrence of child physical abuse? A meta-analysis of global prevalence. Int. J. Psychol. 2013, 48, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillis, S.; Mercy, J.; Amobi, A.; Kress, H. Global prevalence of past-year violence against children: A systematic review and minimum estimates. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20154079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindert, J.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Grashow, R.; Gal, G.; Braehler, E.; Weisskopf, M.G. Sexual and physical abuse in childhood is associated with depression and anxiety over the life course: Systematic review and me-ta-analysis. Int. J. Public Health 2014, 59, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.B.; Esposito-Smythers, C.; Weismoore, J.T.; Renshaw, K.D. The Relation between Child Maltreatment and Adolescent Suicidal Behavior: A Systematic Review and Critical Examination of the Literature. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 16, 146–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanni, V.; Uher, R.; Danese, A. Childhood Maltreatment Predicts Unfavorable Course of Illness and Treatment Outcome in Depression: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2012, 169, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Norman, R.E.; Byambaa, M.; De, R.; Butchart, A.; Scott, J.; Vos, T. The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Felitti, V.J.; Anda, R.F.; Nordenberg, D.; Williamson, D.F.; Spitz, A.M.; Edwards, V.; Koss, M.P.; Marks, J.S. Relationship of Childhood Abuse and Household Dysfunction to Many of the Leading Causes of Death in Adults: The Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study. Am. J. Prev. Med. 1998, 14, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Wildeman, C.; Jonson-Reid, M.; Drake, B. Lifetime prevalence of investigating child maltreatment among US children. Am. J. Public Health 2017, 107, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildeman, C.; Emanuel, N.; Leventhal, J.M.; Putnam-Hornstein, E.; Waldfogel, J.; Lee, H. The Prevalence of Confirmed Maltreatment among US Children, 2004 to 2011. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; Administration for Children and Families; Administration on Children; Youth and Families, Children’s Bureau. Child Maltreatment 2019. 2021. Available online: https://www.acf.hhs.gov/cb/research-data-technology/statistics-research/child-maltreatment (accessed on 3 April 2021).
- Chen, M.; Chan, K.L. Effects of parenting programs on child maltreatment prevention: A metaanalysis. Trauma Violence Abus. 2016, 17, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altafim, E.L.P.; Linhares, M.B.M. Universal violence and child maltreatment prevention pro-grams for parents: A systematic review. Psychosoc. Interv. 2016, 25, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farst, K.; Ambadwar, P.B.; King, A.J.; Bird, T.M.; Robbins, J.M. Trends in hospitalization rates and severity of inju-ries from abuse in young children, 1997–2009. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1796–e1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zins, Z.P.; Wheeler, K.K.; Brink, F.; Armstrong, M.; Shi, J.; Groner, J.I.; Xiang, H. Trends in US physician diagnosis of child physical abuse and neglect injuries, 2006–2014. Child. Abus. Negl. 2019, 98, 104179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebbe, R.; Martinson, M.L.; Mienko, J.A. The Incidence of Child Maltreatment Resulting in Hospitalizations for Children under Age 3 Years. J. Pediatrics 2020, 228, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.S.; Fang, X.; Florence, C.S. Medical Costs Attributable to Child Maltreatment: A Systematic Review of Short- and Long-Term Effects. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 41, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovi, S.; Chen, P.H.; Johnson, M.S. The economic burden of hospitalizations associated with child abuse and neglect. AJPH 2004, 94, 586–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leventhal, J.M.; Martin, K.D.; Gaither, J.R. Using US data to estimate the incidence of serious physical abuse in children. Pediatrics 2012, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, C.A.; Hambrick, M.M.; Owens, P.L. Hospital Stays Related to Child Maltreatment; HCUP Statistical Brief #49. April 2008; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2005. Available online: http://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/reports/statbriefs/sb49.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Peterson, C.; Xu, L.; Florence, C.; Parks, S.E. Annual Cost of U.S. Hospital Visits for Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma. Child. Maltreatment 2015, 20, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project—National Inpatient Sample; HCUP Databases: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM). 2015. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/icd/icd9cm.htm (accessed on 8 October 2020).
- Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. NIS-Provided User-Guide. Available online: https://www.hcup-us.ahrq.gov/db/state/costtocharge.jsp#how (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Little, T.D.; Jorgensen, T.D.; Lang, K.M.; Moore, W.G. On the joys of missing data. J. Ped. Psychol. 2014, 39, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Child Welfare Information Gateway. Child Maltreatment Prevention: Past, Present, and Future; US. Department of Health and Human Services, Children’s Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Gelles, R.J.; Perlman, S. Estimated Annual Cost of Child Abuse and Neglect; Prevent Child Abuse America: Chicago, IL, USA. Available online: http://www.preventchildabuse.org/downloads/PCAA_Cost_Report_2012_Gelles_Perlman_final.pdf (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Garner, A.S.; Shonkoff, J.P.; Siegel, B.S.; Dobbins, M.I.; Earls, M.F.; McGuinn, L.; Pascoe, J.; Wood, D.L. Early Childhood Adversity, Toxic Stress, and the Role of the Pediatrician: Translating Developmental Science into Lifelong Health. Pediatrics 2011, 129, e224–e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrick, M.T.; Ford, D.C.; Ports, K.A.; Guinn, A.S. Prevalence of Adverse Childhood Experiences From the 2011–2014 Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System in 23 States. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowak, C.; Heinrichs, N. A comprehensive meta-analysis of Triple P-Positive Parenting Program using hier-archical linear modeling: Effectiveness and moderating variables. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2008, 11, 114–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, R.J.; Sanders, M.R.; Shapiro, C.J.; Whitaker, D.J.; Lutzker, J.R. Population-based prevention of child maltreatment: U.S. Triple P System Population Trial. Prev. Sci. 2009, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, R.G.; Rivara, F.P.; Barr, M.; Cummings, P.A.; Taylor, J.; Lengua, L.J.; Meredith-Benitz, E. Effectiveness of Educational Materials Designed to Change Knowledge and Behaviors Regarding Crying and Shaken-Baby Syndrome in Mothers of Newborns: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.S.; Smith, K.; Deguehery, K.; Mazur, P.; Li, V.; Shaffer, M.L. Preventing Abusive Head Trauma Among Infants and Young Children: A Hospital-Based, Parent Education Program. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e470–e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oral, R.; Ramirez, M.; Coohey, C.; Nakada, S.; Walz, A.; Kuntz, A.; Benoit, J.; Peek-Asa, C. Adverse childhood expe-riences and trauma informed care: The future of health care. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oral, R.; Bayman, L.; McKissic, D.; Dahlberg, G.; Theurer, J. Two-generational trauma-informed assessment improves diagnostic accuracy in a child protection program. Child. Abuse Negl. 2018, under review. [Google Scholar]
- Corbin, T.J.; Purtle, J.; Rich, L.J.; Rich, J.A.; Adams, E.J.; Yee, G.; Bloom, S.L. The prevalence of trauma nad childhoodadversity in an urban, hospital-based violence intervention program. J. Health Care Poor Underserved. 2013, 24, 1021–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buthcart, A.; Phinney Harvey, A. Preventing Child Maltreatment: A Guide to Taking Action and Generating Evidence; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijken, M.W.; Stams, G.J.J.; DeWinter, M. Can community-based interventions prevent child maltreatment? Child Youth Ser. Rev. 2016, 61, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Female | Male | Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | No. (%) | No. (%) | |
| Sex | 47,811 (47.0) | 53,993 (53.0) | 101,804 (100) |
| Age | |||
| <1 | 19,973 (41.8) | 28,141 (52.1) | 48,114 (47.3) |
| 1–3 | 10,575 (22.1) | 14,019 (26.0) | 24,594 (24.2) |
| 4–6 | 2687 (5.6) | 3177 (5.9) | 5864 (5.8) |
| 7–9 | 2104 (4.4) | 2598 (4.8) | 4702 (4.6) |
| 10–12 | 2752 (5.8) | 2513 (4.7) | 5265 (5.2) |
| 13–15 | 5457 (11.4) | 2172 (4.0) | 7629 (7.5) |
| 16–18 | 4262 (8.9) | 1373 (2.5) | 5635 (5.5) |
| Race/Ethnicity | |||
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 621 (1.3) | 672 (1.2) | 1293 (1.3) |
| Black | 11,676 (24.4) | 13,109 (24.3) | 24,784 (24.3) |
| Hispanic | 8102 (16.9) | 8582 (15.9) | 16,684 (16.4) |
| Other | 2594 (5.4) | 2722 (5.0) | 5316 (5.2) |
| Native American | 587 (1.2) | 467 (0.9) | 1054 (1.0) |
| White | 24,231 (50.7) | 28,442 (52.7) | 52,673 (51.7) |
| Income Quartile based on ZIP Code | |||
| Quartile 1 | 16,417 (34.3) | 18,279 (33.9) | 34,696 (34.1) |
| Quartile 2 | 13,826 (28.9) | 15,587 (28.9) | 29,413 (28.9) |
| Quartile 3 | 10,567 (22.1) | 12,308 (22.8) | 22,875 (22.5) |
| Quartile 4 | 7000 (14.6) | 7819 (14.5) | 14,819 (14.6) |
| Type of Maltreatment (Diagnosis) | |||
| Multiple | 2675 (5.6) | 2258 (4.2) | 4933 (4.8) |
| Neglect | 6150 (12.9) | 7996 (14.8) | 14,147 (13.9) |
| Not otherwise specified, other, none | 11,314 (23.7) | 13,123 (24.3) | 24,437 (24.0) |
| Physical abuse | 16,149 (33.8) | 22,164 (41.0) | 38,313 (37.6) |
| Psychological abuse | 547 (1.1) | 376 (0.7) | 923 (0.9) |
| Shaken baby syndrome | 4409 (9.2) | 6738 (12.5) | 11,147 (10.9) |
| Sexual abuse | 6566 (13.7) | 1338 (2.5) | 7904 (7.8) |
| Died | |||
| No | 46,163 (96.6) | 51,702 (95.8) | 97,865 (96.1) |
| Yes | 1648 (3.4) | 2291 (4.2) | 3939 (3.9) |
| Perpetrator (E-Code) | |||
| Father, step-father, boyfriend | 7256 (15.2) | 8636 (16.0) | 15,891 (15.6) |
| Mother, step-mother, girlfriend | 4605 (9.6) | 5490 (10.2) | 10,095 (9.9) |
| Multiple | 986 (2.1) | 917 (1.7) | 1903 (1.9) |
| Non-relative | 968 (2.0) | 1219 (2.3) | 2186 (2.1) |
| Not otherwise specified, other, none | 31,579 (66.0) | 36,053 (66.8) | 67,631 (66.4) |
| Other relative | 2418 (5.1) | 1679 (3.1) | 4097 (4.0) |
| Hospital Location: Teaching Status | |||
| Rural | 3479 (7.3) | 3651 (6.8) | 7131 (7.0) |
| Urban: Non-teaching | 6844 (14.3) | 6739 (12.5) | 13,583 (13.3) |
| Urban: Teaching | 37,487 (78.4) | 43,603 (80.8) | 81,090 (79.7) |
| Hospital Region | |||
| Midwest | 12,573 (26.3) | 14,314 (26.5) | 26,887 (26.4) |
| Northeast | 7781 (16.3) | 8021 (14.9) | 15,802 (15.5) |
| South | 19,015 (39.8) | 21,807 (40.4) | 40,823 (40.1) |
| West | 8441 (17.7) | 9852 (18.2) | 18,293 (18.0) |
| Year | Government | All Other Payer Sources | Total Costs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costs | % of Total Costs | Costs | % of Total Costs | ||
| 2001 | 77,700,000 | 70.4 | 32,700,000 | 29.6 | 110,000,000 |
| 2002 | 90,600,000 | 74.6 | 30,900,000 | 25.4 | 122,000,000 |
| 2003 | 76,300,000 | 73.7 | 27,300,000 | 26.3 | 104,000,000 |
| 2004 | 87,200,000 | 74.4 | 30,000,000 | 25.6 | 117,000,000 |
| 2005 | 102,000,000 | 70.4 | 42,800,000 | 29.6 | 145,000,000 |
| 2006 | 78,200,000 | 76.3 | 24,300,000 | 23.7 | 103,000,000 |
| 2007 | 104,000,000 | 78.1 | 29,200,000 | 21.9 | 133,000,000 |
| 2008 | 93,900,000 | 76.8 | 28,400,000 | 23.2 | 122,000,000 |
| 2009 | 94,400,000 | 79.8 | 23,900,000 | 20.2 | 118,000,000 |
| 2010 | 115,000,000 | 78.0 | 32,600,000 | 22.0 | 148,000,000 |
| 2011 | 82,300,000 | 79.0 | 21,800,000 | 21.0 | 104,000,000 |
| 2012 | 96,800,000 | 82.5 | 20,600,000 | 17.5 | 117,000,000 |
| 2013 | 92,600,000 | 78.0 | 26,100,000 | 22.0 | 119,000,000 |
| 2014 | 96,500,000 | 81.3 | 22,100,000 | 18.7 | 119,000,000 |
| 2015 | 74,700,000 | 84.0 | 14,200,000 | 16.0 | 88,800,000 |
| 2016 | 66,400,000 | 83.3 | 13,300,000 | 16.7 | 79,700,000 |
| Total | 1,430,000,000 | 77.3 | 420,000,000 | 22.7 | 1,850,000,000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojciak, A.S.; Butcher, B.; Conrad, A.; Coohey, C.; Oral, R.; Peek-Asa, C. Trends, Diagnoses, and Hospitalization Costs of Child Abuse and Neglect in the United States of America. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147585
Wojciak AS, Butcher B, Conrad A, Coohey C, Oral R, Peek-Asa C. Trends, Diagnoses, and Hospitalization Costs of Child Abuse and Neglect in the United States of America. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(14):7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147585
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojciak, Armeda Stevenson, Brandon Butcher, Aislinn Conrad, Carol Coohey, Resmiye Oral, and Corinne Peek-Asa. 2021. "Trends, Diagnoses, and Hospitalization Costs of Child Abuse and Neglect in the United States of America" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 14: 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147585
APA StyleWojciak, A. S., Butcher, B., Conrad, A., Coohey, C., Oral, R., & Peek-Asa, C. (2021). Trends, Diagnoses, and Hospitalization Costs of Child Abuse and Neglect in the United States of America. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(14), 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18147585






