Density of Fast Food Outlets around Educational Facilities in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Geospatial Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
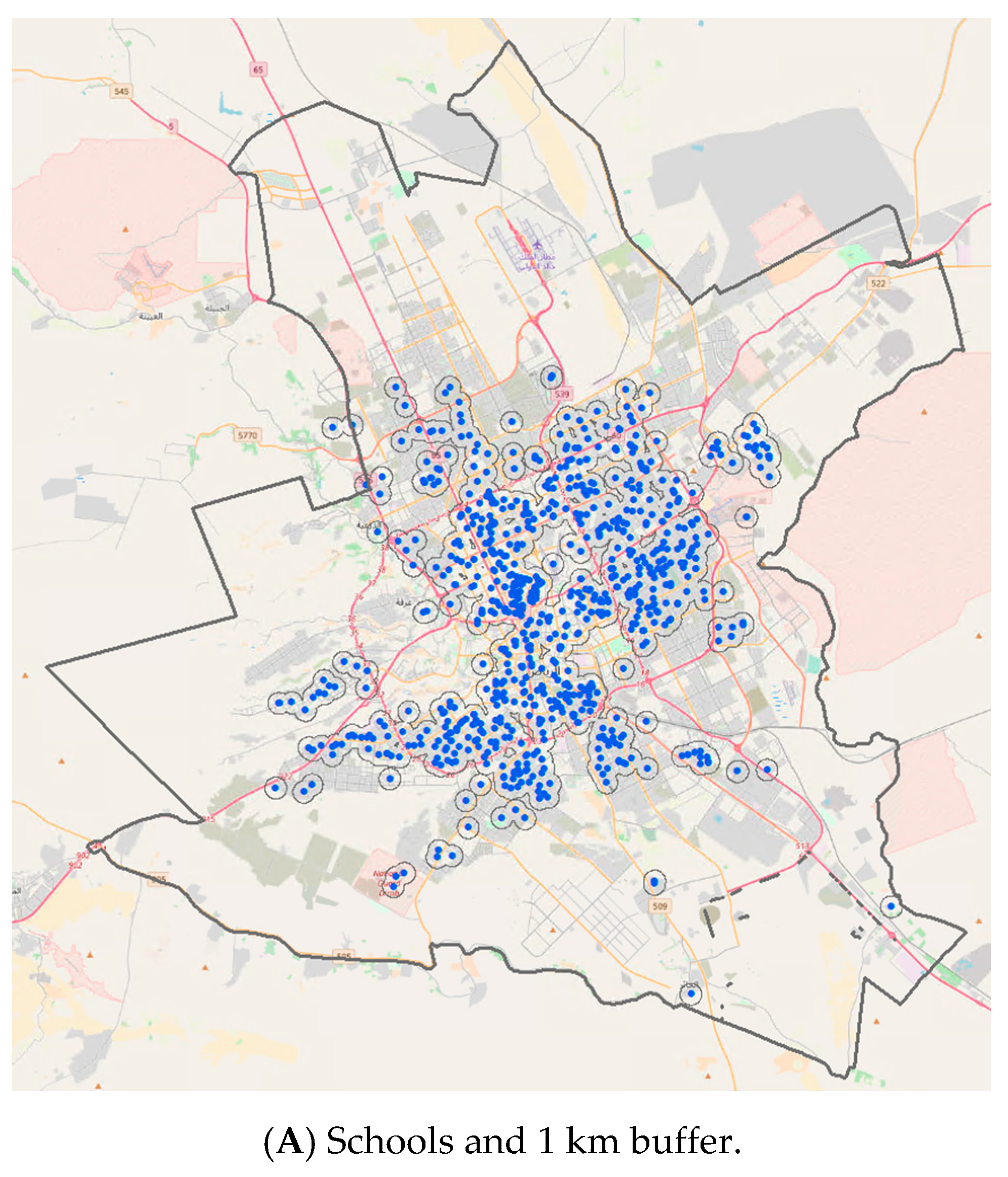
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organisation. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeNicola, E.; Aburizaiza, O.S.; Siddique, A.; Khwaja, H.; Carpenter, D.O. Obesity and public health in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Rev. Environ. Health 2015, 30, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Martinez, A.; Zhou, B.; Sophiea, M.K.; Bentham, J.; Paciorek, C.J.; Iurilli, M.L.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Bennett, E.J.; Di Cesare, M.; Taddei, C.; et al. Height and body-mass index trajectories of school-aged children and adolescents from 1985 to 2019 in 200 countries and territories: A pooled analysis of 2181 population-based studies with 65 million participants. Lancet 2020, 396, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asirvatham, J.; Thomsen, M.R.; Nayga, R.M.; Goudie, A. Do fast food restaurants surrounding schools affect childhood obesity? Econ. Hum. Biol. 2019, 33, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksey-Stowers, K.; Schwartz, M.B.; Brownell, K.D. Food Swamps Predict Obesity Rates Better Than Food Deserts in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.E.; Florax, R.J.; Snyder, S.D. Obesity and fast food in urban markets: A new approach using geo-referenced micro data. Health Econ. 2012, 22, 835–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.A.; Sharkey, J.R.; Horel, S. The effect of fast-food availability on fast-food consumption and obesity among rural residents: An analysis by race/ethnicity. Econ. Hum. Biol. 2011, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, A.P.; Warren, J.; Puett, R.; Porter, D.E.; Bottai, M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Liese, A.D. Spatial patterning of supermarkets and fast food outlets with respect to neighborhood characteristics. Health Place 2013, 23, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.; Cretikos, M.; Rogers, K.; King, L. The commercial food landscape: Outdoor food advertising around primary schools in Australia. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2008, 32, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memish, Z.A.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Tuffaha, M.; Robinson, M.; Daoud, F.; Jaber, S.; Mikhitarian, S.; Al Saeedi, M.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Mokdad, A.H.; et al. Obesity and Associated Factors—Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2013. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2014, 11, E174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwate, N.O.A.; Yau, C.-Y.; Loh, J.-M.; Williams, D. Inequality in obesigenic environments: Fast food density in New York City. Health Place 2009, 15, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, C.; Rainham, D.; Blanchard, C.; Dummer, T.; Lyons, R.; Kirk, S. Measuring food availability and accessibility among adolescents: Moving beyond the neighbourhood boundary. Soc. Sci. Med. 2015, 133, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hussaini, A.; Bashir, M.S.; Khormi, M.; Alturaiki, M.; Alkhamis, W.; Alrajhi, M.; Halal, T. Overweight and obesity among Saudi children and adolescents: Where do we stand today? Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, S.B.; Melly, S.J.; Sanchez, B.N.; Patel, A.; Buka, S.; Gortmaker, S.L. Clustering of Fast-Food Restaurants Around Schools: A Novel Application of Spatial Statistics to the Study of Food Environments. Am. J. Public Heal. 2005, 95, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurjanah, N.; Manglapy, Y.M.; Handayani, S.; Ahsan, A.; Sutomo, R.; Dewi, F.S.T.; Chang, P.; Kusuma, D. Density of tobacco advertising around schools. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisasmito, W.; Amir, V.; Atin, A.; Megraini, A.; Kusuma, D. Density of cigarette retailers around educational facilities in Indonesia. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2020, 24, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puspikawati, S.I.; Dewi, D.M.S.K.; Astutik, E.; Kusuma, D.; Melaniani, S.; Sebayang, S.K. Density of outdoor food and beverage advertising around gathering place for children and adolescent in East Java, Indonesia. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, D.T.; Kawachi, I.; Subramanian, S.V.; Aldstadt, J.; Melly, S.J.; Williams, D.R. Examination of How Neighborhood Definition Influences Measurements of Youths’ Access to Tobacco Retailers: A Methodological Note on Spatial Misclassification. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, L.; Feighery, E.C.; Schleicher, N.C.; Cowling, D.W.; Kline, R.S.; Fortmann, S.P. Is adolescent smoking related to the density and proximity of tobacco outlets and retail cigarette advertising near schools? Prev. Med. 2008, 47, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poti, J.M.; Braga, B.; Qin, B. Ultra-processed Food Intake and Obesity: What Really Matters for Health—Processing or Nutrient Content? Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, P.R.E.S.; Noll, M.; de Abreu, L.C.; Baracat, E.C.; Silveira, E.A.; Sorpreso, I.C.E. Ultra-processed food consumption by Brazilian adolescents in cafeterias and school meals. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rongen, S.; Poelman, M.P.; Thornton, L.; Abbott, G.; Lu, M.; Kamphuis, C.B.M.; Verkooijen, K.; De Vet, E. Neighbourhood fast food exposure and consumption: The mediating role of neighbourhood social norms. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syed, N.K.; Syed, M.H.; Meraya, A.M.; Albarraq, A.A.; Al-Kasim, M.A.; Alqahtani, S.; Makeen, H.A.; Yasmeen, A.; Banji, O.J.F.; Elnaem, M.H. The association of dietary behaviors and practices with overweight and obesity parameters among Saudi university students. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhakbany, M.A.; AlZamil, H.A.; Alabdullatif, W.A.; Aldekhyyel, S.N.; Alsuhaibani, M.N.; Al-Hazzaa, H.M. Lifestyle Habits in Relation to Overweight and Obesity among Saudi Women Attending Health Science Colleges. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2018, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikraman, S.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Caloric Intake from Fast Food Among Children and Adolescents in the United States, 2011–2012 Key findings Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. 2011. Available online: https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/cdc/42486 (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.; Xue, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. Fast food consumption and its associations with obesity and hypertension among children: Results from the baseline data of the Childhood Obesity Study in China Mega-cities. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BBC News. Reality Check: Why Ban Fast Food within 400 m of Schools? 2017. Available online: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-42172579 (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Burgoine, T.; Forouhi, N.G.; Griffin, S.J.; Wareham, N.J.; Monsivais, P. Associations between exposure to takeaway food outlets, takeaway food consumption, and body weight in Cambridgeshire, UK: Population based, cross sectional study. BMJ 2014, 348, g1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudi Ministry of Health. Healthy Schools. 2020. Available online: https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/Projects/Healthy-Schools/Pages/default.aspx (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Saudi Food Drug Agency. Healthy Food Program. 2019. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiI4JTGkZzxAhXESH0KHV5fC3AQFjAAegQIAxAD&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.abce.me%2Fpdf%2FP1-Healthy-Food-Program.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3qETmaz_8Ql-kFjpuamHWE (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Fakeeh, M.I.; Shanawaz, M.; Azeez, F.K.; Arar, I.A. Overweight and obesity among the boys of primary public schools of Baish City in Jazan Province, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional study. Indian J. Public Health 2019, 63, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| (a) Fast food outlets | 708 | |
| Western chain | 442 | 62.4% |
| Saudi chain | 266 | 37.6% |
| Herfy | 151 | 21.3% |
| Domino’s Pizza | 98 | 13.8% |
| McDonald’s | 92 | 13.0% |
| KFC | 73 | 10.3% |
| Pizza Hut | 68 | 9.6% |
| Shawarmer | 60 | 8.5% |
| Burger King | 52 | 7.3% |
| Hardee’s | 39 | 5.5% |
| TomTom | 24 | 3.4% |
| Kudu | 19 | 2.7% |
| Maestro Pizza | 12 | 1.7% |
| Texas Chicken | 9 | 1.3% |
| Popeyes | 6 | 0.8% |
| Shake Shack | 5 | 0.7% |
| (b) Schools | 858 | |
| Government | 416 | 48.5% |
| Private | 442 | 51.5% |
| Girls only | 286 | 33.3% |
| Boys only | 258 | 30.1% |
| Both | 314 | 36.6% |
| All grades (kindergarten to high school) | 357 | 41.6% |
| Kindergarten only | 41 | 4.8% |
| Elementary school only | 240 | 28.0% |
| Middle school only | 127 | 14.8% |
| High school only | 89 | 10.4% |
| Diploma/university | 4 | 0.5% |
| Density per Square km | Comparison | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | <500 m | 500 m–1 km | Difference | Ratio | p-Value | |||
| Density | SD | Density | SD | |||||
| [1] | [2] | [3] | [4] = [3 − 2] | [5] = [2/3] | [6] | |||
| All schools | 858 | 0.74 | 1.59 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 1.13 | <0.001 |
| Government | 416 | 0.61 | 1.53 | 0.69 | 0.91 | 0.07 | 1.12 | <0.001 |
| Private | 442 | 0.86 | 1.65 | 0.98 | 1.07 | 0.12 | 1.14 | 0.202 |
| Girls only | 286 | 0.74 | 1.65 | 0.80 | 0.99 | 0.07 | 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Boys only | 258 | 0.59 | 1.50 | 0.59 | 0.82 | 0.01 | 1.01 | 0.001 |
| Both | 314 | 0.87 | 1.61 | 1.07 | 1.10 | 0.20 | 1.23 | 0.112 |
| All grades | 357 | 0.86 | 1.65 | 0.98 | 1.06 | 0.12 | 1.15 | 0.372 |
| Kindergarten only | 41 | 0.99 | 1.56 | 1.14 | 1.17 | 0.15 | 1.16 | 0.188 |
| Elementary school only | 240 | 0.65 | 1.72 | 0.81 | 1.02 | 0.15 | 1.23 | <0.001 |
| Middle school only | 127 | 0.51 | 1.12 | 0.54 | 0.70 | 0.03 | 1.06 | 0.001 |
| High school only | 89 | 0.75 | 1.64 | 0.65 | 0.89 | −0.10 | 0.86 | <0.001 |
| Diploma/university | 4 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.64 | N/A | N/A |
| (a) Fast food outlets within dissolved school buffer | |||||
| Total Outlets | <500 m | <1 km | |||
| n | n | % of Total | n | % of Total | |
| All schools | 708 | 297 | 42% | 558 | 79% |
| Government | 708 | 153 | 22% | 405 | 57% |
| Private | 708 | 211 | 30% | 449 | 63% |
| (b) Number of schools and % of total with at least one outlet within school buffer | |||||
| Total Schools | <500 m | <1 km | |||
| n | n | % of Total | n | % of Total | |
| All schools | 858 | 245 | 29% | 591 | 69% |
| Government | 416 | 94 | 23% | 252 | 61% |
| Private | 442 | 151 | 34% | 339 | 77% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlQurashi, A.A.; Kusuma, D.; AlJishi, H.; AlFaiz, A.; AlSaad, A. Density of Fast Food Outlets around Educational Facilities in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Geospatial Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126502
AlQurashi AA, Kusuma D, AlJishi H, AlFaiz A, AlSaad A. Density of Fast Food Outlets around Educational Facilities in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Geospatial Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(12):6502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126502
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlQurashi, Alaa Ashraf, Dian Kusuma, Hala AlJishi, Ali AlFaiz, and Abdulaziz AlSaad. 2021. "Density of Fast Food Outlets around Educational Facilities in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Geospatial Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 12: 6502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126502
APA StyleAlQurashi, A. A., Kusuma, D., AlJishi, H., AlFaiz, A., & AlSaad, A. (2021). Density of Fast Food Outlets around Educational Facilities in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: Geospatial Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(12), 6502. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126502







