Impact of Air Pollution (PM2.5) on Child Mortality: Evidence from Sixteen Asian Countries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Variable Description | Observations | Mean | Standard Deviation | Min | Max | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Premature Deaths (WHO) | 288 | 39,924.17 | 89,881.62 | 213 | 442,544 | World Health OrganizationGlobal Health Repository |
| Premature Child Mortality per 1000 live births (WB data) | 288 | 36.13 | 25.81 | 7.4 | 112.6 | Work Bank Tables |
| PM2.5 (Particulate Matter) | 160 | 44.1774 | 24.51686 | 11.09962 | 100.7844 | Work Bank Tables |
| GDP Per Capita | 288 | 3805.489 | 3454.672 | 346.7747 | 14,936.4 | Work Bank Tables |
| Population Density | 288 | 223.1709 | 265.3905 | 1.543189 | 1265.036 | Work Bank Tables |
| Mortality (Less than 5 years) | 288 | 36.13681 | 25.81633 | 7.4 | 112.6 | Work Bank Tables |
| Average Education | 287 | 72.92878 | 20.52273 | 20.01234 | 120.6316 | Work Bank Tables |
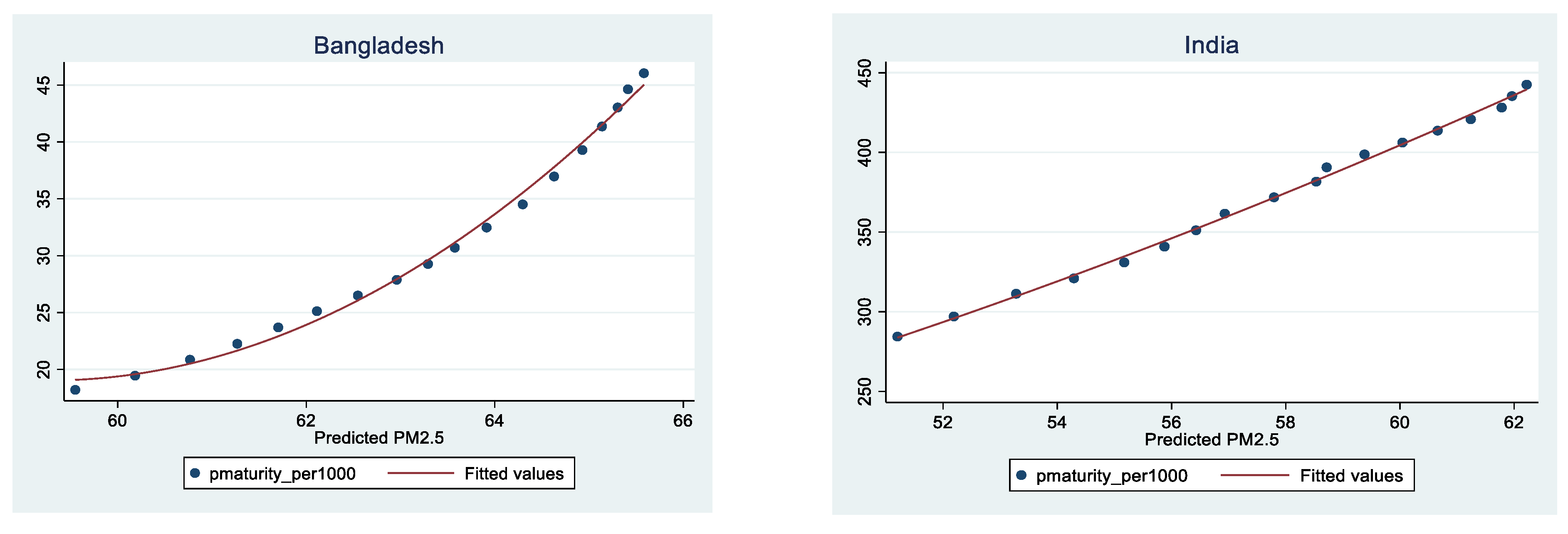
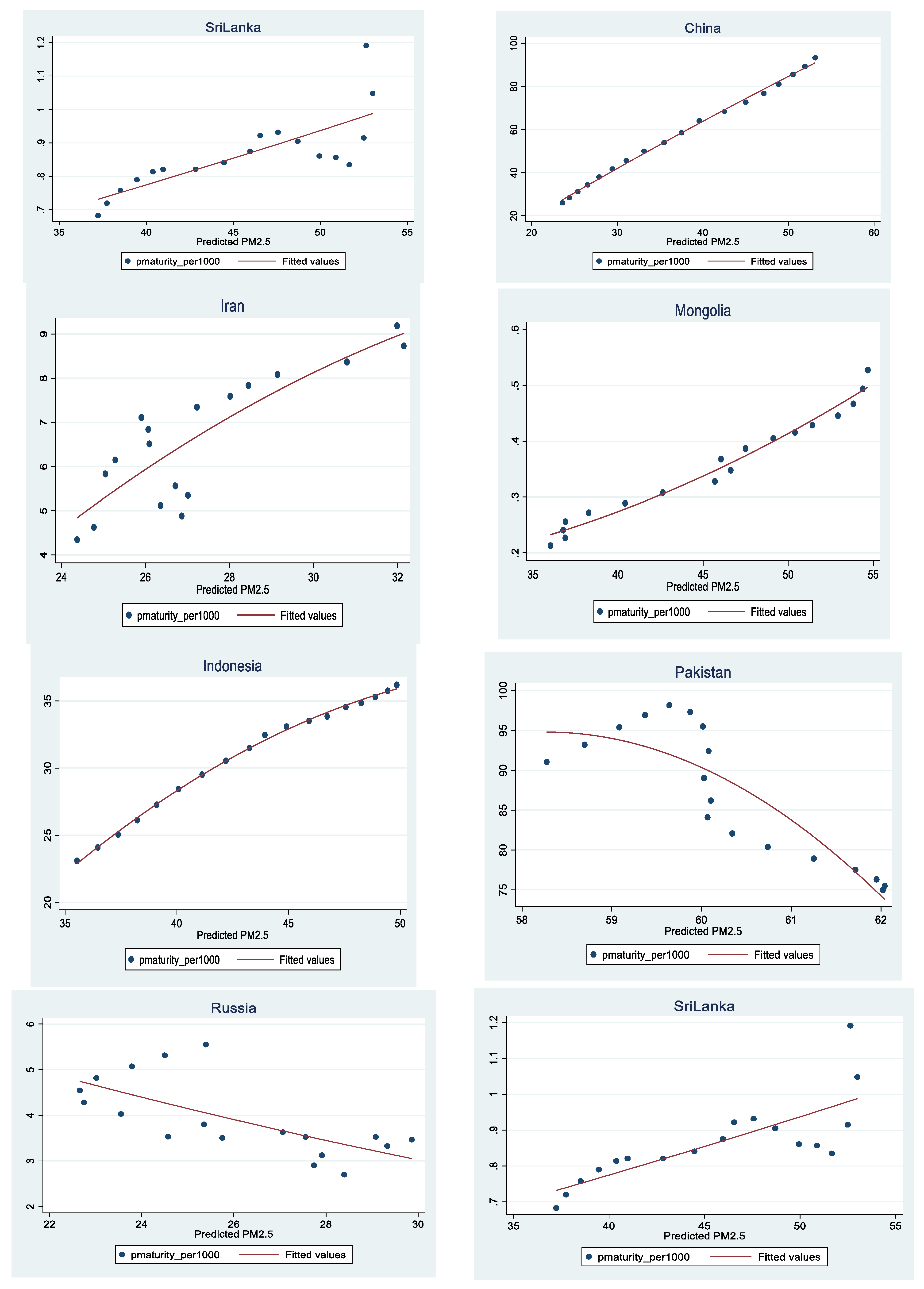
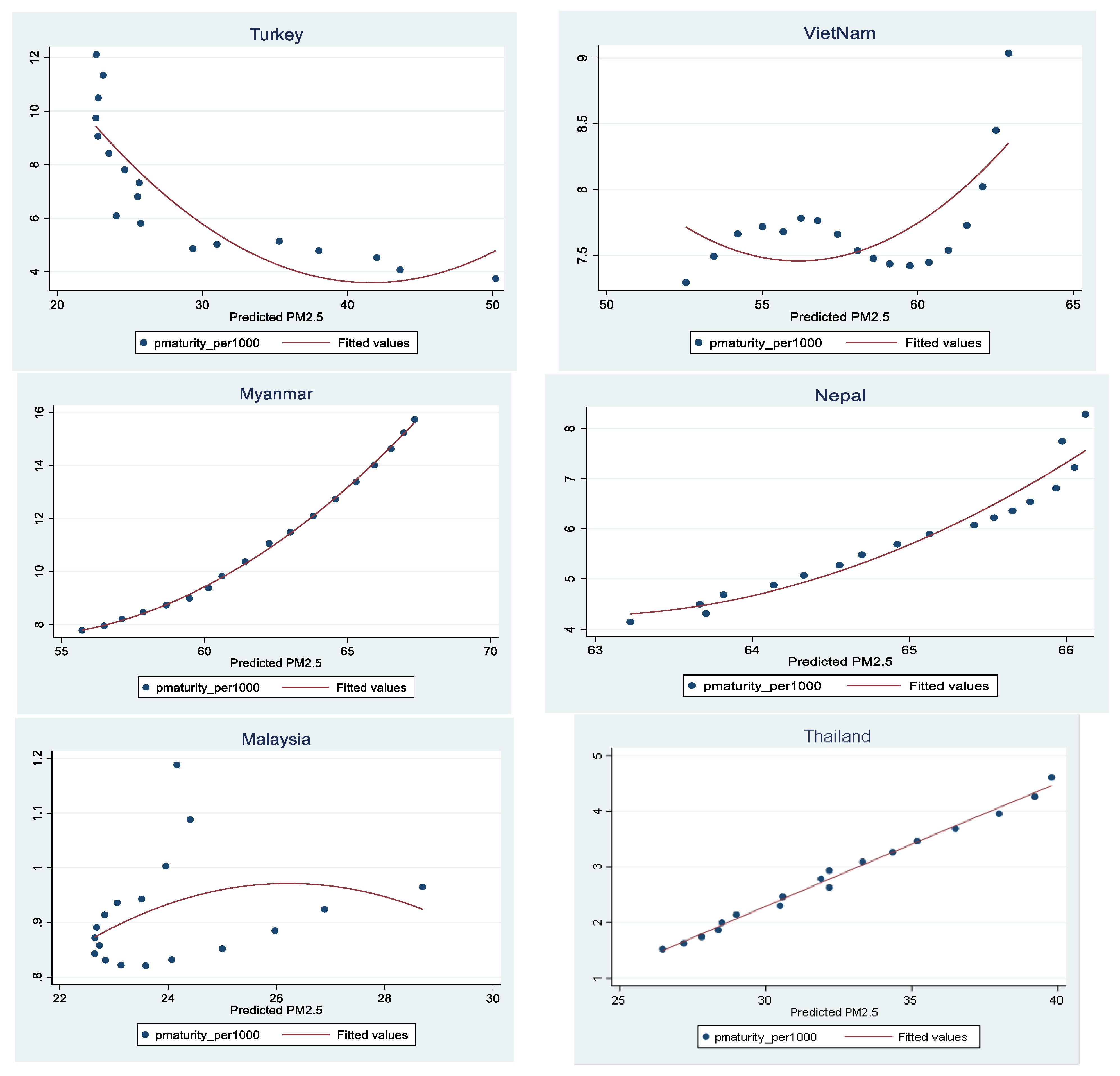
References
- Lelieveld, J.; Haines, A.; Pozzer, A. Age-Dependent Health Risk from Ambient Air Pollution: A Modelling and Data Analysis of Childhood Mortality in Middle-Income and Low-Income Countries. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e292–e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, R.T.; Pope, C.A., III; Ezzati, M.; Olives, C.; Lim, S.S.; Mehta, S.; Shin, H.H.; Singh, G.; Hubbell, B.; Brauer, M.; et al. An Integrated Risk Function for Estimating the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Fine Particulate Matter Exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Ayub, M.; Khan, N.; Flahault, A. Nexus between Air Pollution and Neonatal Deaths: A Case of Asian Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S. Environmental Regulations on Air Pollution in China and Their Impact on Infant Mortality. J. Health Econ. 2015, 42, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zanobetti, A.; Kloog, I.; Coull, B.A.; Koutrakis, P.; Melly, S.J.; Schwartz, J.D. Low-Concentration PM2.5 and Mortality: Estimating Acute and Chronic Effects in a Population-Based Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korek, M.J.; Bellander, T.D.; Lind, T.; Bottai, M.; Eneroth, K.M.; Caracciolo, B.; De Faire, U.H.; Fratiglioni, L.; Hilding, A.; Leander, K.; et al. Traffic-Related Air Pollution Exposure and Incidence of Stroke in Four Cohorts from Stockholm. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Dey, S.; Smith, K.R. Ambient PM 2.5 Exposure and Expected Premature Mortality to 2100 in India under Climate Change Scenarios. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Bae, J. Does Trade Openness Affect CO2 Emissions: Evidence from Ten Newly Industrialized Countries? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 17616–17625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, N.; Junger, W.L.; Romieu, I.; Cifuentes, L.A.; de Leon, A.P.; Vera, J.; Strappa, V.; Hurtado-Díaz, M.; Miranda-Soberanis, V.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; et al. Effects of Air Pollution on Infant and Children Respiratory Mortality in Four Large Latin-American Cities. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, R.; Henry, N.J.; Collison, M.L.; Marczak, L.B.; Sligar, A.; Watson, S.; Marquez, N.; Abbasalizad-Farhangi, M.; Abbasi, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; et al. Mapping 123 Million Neonatal, Infant and Child Deaths between 2000 and 2017. Nature 2019, 574, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplitz, S.N.; Jacob, D.J.; Sulprizio, M.P.; Myllyvirta, L.; Reid, C. Burden of Disease from Rising Coal-Fired Power Plant Emissions in Southeast Asia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.; Zhong, L.; Chen, D.; Wang, X. Trends of Outdoor Air Pollution and the Impact on Premature Mortality in the Pearl River Delta Region of Southern China during 2006–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Matsunaga, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Zhao, A.; Li, Z.; Gu, X. Long-Term Trends and Spatial Patterns of PM2.5-Induced Premature Mortality in South and Southeast Asia from 1999 to 2014. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, W.-H.; Opiyo Owili, P.; Muga, M.A.; Lin, T.-H. Ambient Particulate Matter Exposure and Under-Five and Maternal Deaths in Asia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owili, P.O.; Lien, W.-H.; Muga, M.A.; Lin, T.-H.; Dirks, K.N. The Associations between Types of Ambient PM 2.5 and Under-Five and Maternal Mortality in Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkodie, S.A.; Strezov, V.; Jiang, Y.; Evans, T. Proximate Determinants of Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Emission, Mortality and Life Expectancy in Europe, Central Asia, Australia, Canada and the US. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepeule, J.; Laden, F.; Dockery, D.; Schwartz, J. Chronic Exposure to Fine Particles and Mortality: An Extended Follow-up of the Harvard Six Cities Study from 1974 to 2009. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloog, I.; Ridgway, B.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J.D. Long- and Short-Term Exposure to PM2.5 and Mortality: Using Novel Exposure Models. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Woodward, A.; Vardoulakis, S.; Kovats, S.; Wilkinson, P.; Li, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; et al. Haze, Public Health and Mitigation Measures in China: A Review of the Current Evidence for Further Policy Response. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 578, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kiesewetter, G.; Klimont, Z.; Cofala, J.; Heyes, C.; Schöpp, W.; Zhu, T.; Cao, G.; Gomez Sanabria, A.; Sander, R.; et al. Mitigation Pathways of Air Pollution from Residential Emissions in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.M., III. The Measurement of Environmental and Resource Values; RFF Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotourehchi, Z. Health Effects of Air Pollution: An Empirical Analysis for Developing Countries. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Tian, X. The Impact of Fine Particulate Matter (PM 2.5 ) on China’s Agricultural Production from 2001 to 2010. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onafowora, O.A.; Owoye, O. Bounds Testing Approach to Analysis of the Environment Kuznets Curve Hypothesis. Energy Econ. 2014, 44, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraby, T.; Bauch, C.; Anand, M. The Environmental Kuznets Curve Fails in a Globalized Socio-Ecological Metapopulation: A Sustainability Game Theory Approach. In Handbook of Statistics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 39, pp. 215–341. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jin, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jantunen, M.; Bi, J.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Trends in the Mortality Burden of Air Pollution in China: 2004–2012. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egondi, T.; Ettarh, R.; Kyobutungi, C.; Ng, N.; Rocklöv, J. Exposure to Outdoor Particles (PM 2.5) and Associated Child Morbidity and Mortality in Socially Deprived Neighborhoods of Nairobi, Kenya. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghude, S.D.; Chate, D.M.; Jena, C.; Beig, G.; Kumar, R.; Barth, M.C.; Pfister, G.G.; Fadnavis, S.; Pithani, P. Premature Mortality in India Due to PM2.5 and Ozone Exposure. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 4650–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taksande, A.M.; Yeole, M. Risk Factors of Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) in under-Fives in a Rural Hospital of Central India. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2016, 5, 50105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.; Hug, L.; Ejdemyr, S.; Idele, P.; Hogan, D.; Mathers, C.; Gerland, P.; New, J.R.; Alkema, L. Global, Regional, and National Levels and Trends in under-5 Mortality between 1990 and 2015, with Scenario-Based Projections to 2030: A Systematic Analysis by the Un Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. Lancet 2015, 386, 2275–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Tenconi, R.; Lelii, M.; Preti, V.; Nazzari, E.; Consolo, S.; Patria, M.F. Possible Molecular Mechanisms Linking Air Pollution and Asthma in Children. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ding, H.; Wang, X. Acute Effects of Total Suspended Particles and Sulfur Dioxides on Preterm Delivery: A Community-Based Cohort Study. Arch. Environ. Health 1995, 50, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiv, S.K.; Mendola, P.; Loomis, D.; Herring, A.H.; Neas, L.M.; Savitz, D.A.; Poole, C.A. Time-Series Analysis of Air Pollution and Preterm Birth in Pennsylvania, 1997-2001. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bové, H.; Bongaerts, E.; Slenders, E.; Bijnens, E.M.; Saenen, N.D.; Gyselaers, W.; Van Eyken, P.; Plusquin, M.; Roeffaers, M.B.J.; Ameloot, M.; et al. Ambient Black Carbon Particles Reach the Fetal Side of Human Placenta. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, A.; Khan, N.; Ayub, M.; Nawaz, F.; Shah, A.; Flahault, A. Modeling and Predicting Dengue Incidence in Highly Vulnerable Countries Using Panel Data Approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Log of Child Mortality (WHO Dataset) | Log of Child Mortality (WB Dataset) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| Log of PM2.5 | −0.0984 | −0.0885 | −0.176 | −0.168 |
| (−1.047) | (−0.821) | (−1.392) | (−1.093) | |
| Log of GDP Per Capita | 1.079 | 0.961 | 1.152 | 1.058 |
| (1.414) | (1.351) | (1.289) | (1.305) | |
| Log of (GDP Per Capita)2 | −0.121 ** | −0.104 ** | −0.126 ** | −0.110 * |
| (−2.441) | (−2.209) | (−2.306) | (−2.088) | |
| Log of Population Density | −0.356 | −0.403 | −1.458 | −1.486 |
| (−0.388) | (−0.449) | (−1.533) | (−1.542) | |
| Log of (Population Density)2 | 0.0330 | 0.0551 | 0.0577 | 0.0709 |
| (0.389) | (0.582) | (0.661) | (0.758) | |
| Average Education | −0.00556 ** | −0.00538 ** | ||
| (−2.239) | (−2.148) | |||
| Constant | 9.399 ** | 9.267 *** | 8.236 ** | 8.130 ** |
| (2.886) | (3.290) | (2.292) | (2.460) | |
| Country FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 160 | 159 | 160 | 159 |
| R-squared | 0.745 | 0.769 | 0.853 | 0.874 |
| Number of Countries | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
| Dep. Var: PM2.5 | OLS | OLS-FE | OLS RE |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Per Capita | −0.0105 * | −0.00279 *** | −0.00314 *** |
| (−1.990) | (−3.109) | (−3.491) | |
| (GDP Per Capita)2 | 6.23 × 10−7 * | 1.24 × 10−7 ** | 1.39 × 10−7 *** |
| (1.840) | (2.648) | (2.886) | |
| Population Density | 0.0164 | 0.00626 | 0.0239 |
| (0.228) | (0.134) | (0.624) | |
| (Population Density)2 | −6.90 × 10−6 | −4.57 × 10−6 | −1.14 × 10−5 |
| (−0.132) | (−0.227) | (−0.641) | |
| Constant | 65.91 *** | 51.21 *** | 49.03 *** |
| (3.497) | (6.588) | (9.313) | |
| F-Test | 15.85 | 12.79 | - |
| R-squared | 0.349 | 0.117 | - |
| Observations | 160 | 160 | 160 |
| Child Mortality (WHO Dataset) | Child Mortality (WB Dataset) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | |
| PM2.5 | 0.145 *** | 0.0935 | 0.152 ** | 0.1000 |
| (2.760) | (1.568) | (2.460) | (1.463) | |
| Population Density | −0.000218 | 0.00415 | −0.00514 | −0.00154 |
| (−0.0255) | (0.553) | (−0.567) | (−0.191) | |
| (Population Density)2 | −8.28 × 10−7 | −2.57 × 10−6 | 1.25 × 10−6 | −1.65 × 10−7 |
| (−0.225) | (−0.806) | (0.323) | (−0.0490) | |
| Average Education | −0.0109 | −0.0109 | ||
| (−1.392) | (−1.140) | |||
| Constant | 2.742 | 5.054 | −2.492 | −0.0135 |
| (3.253) | (3.343) | (3.695) | (3.718) | |
| Country FE | YES | YES | YES | YES |
| Observations | 160 | 159 | 160 | 159 |
| Number of country1 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, A.; Ullah, I.; Younis, M.; Flahault, A. Impact of Air Pollution (PM2.5) on Child Mortality: Evidence from Sixteen Asian Countries. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126375
Anwar A, Ullah I, Younis M, Flahault A. Impact of Air Pollution (PM2.5) on Child Mortality: Evidence from Sixteen Asian Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(12):6375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126375
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Asim, Inayat Ullah, Mustafa Younis, and Antoine Flahault. 2021. "Impact of Air Pollution (PM2.5) on Child Mortality: Evidence from Sixteen Asian Countries" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 12: 6375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126375
APA StyleAnwar, A., Ullah, I., Younis, M., & Flahault, A. (2021). Impact of Air Pollution (PM2.5) on Child Mortality: Evidence from Sixteen Asian Countries. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(12), 6375. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126375








