Ecological Predictors and Trajectory of Internet Addiction from Childhood through Adolescence: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Internet Addiction
1.2. Ecological Factors and Internet Addiction
1.3. Study Aims
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Resilience
2.3.2. Child Neglect
2.3.3. Positive School Experience
2.3.4. Perceived Community Violence
2.3.5. Internet Addiction
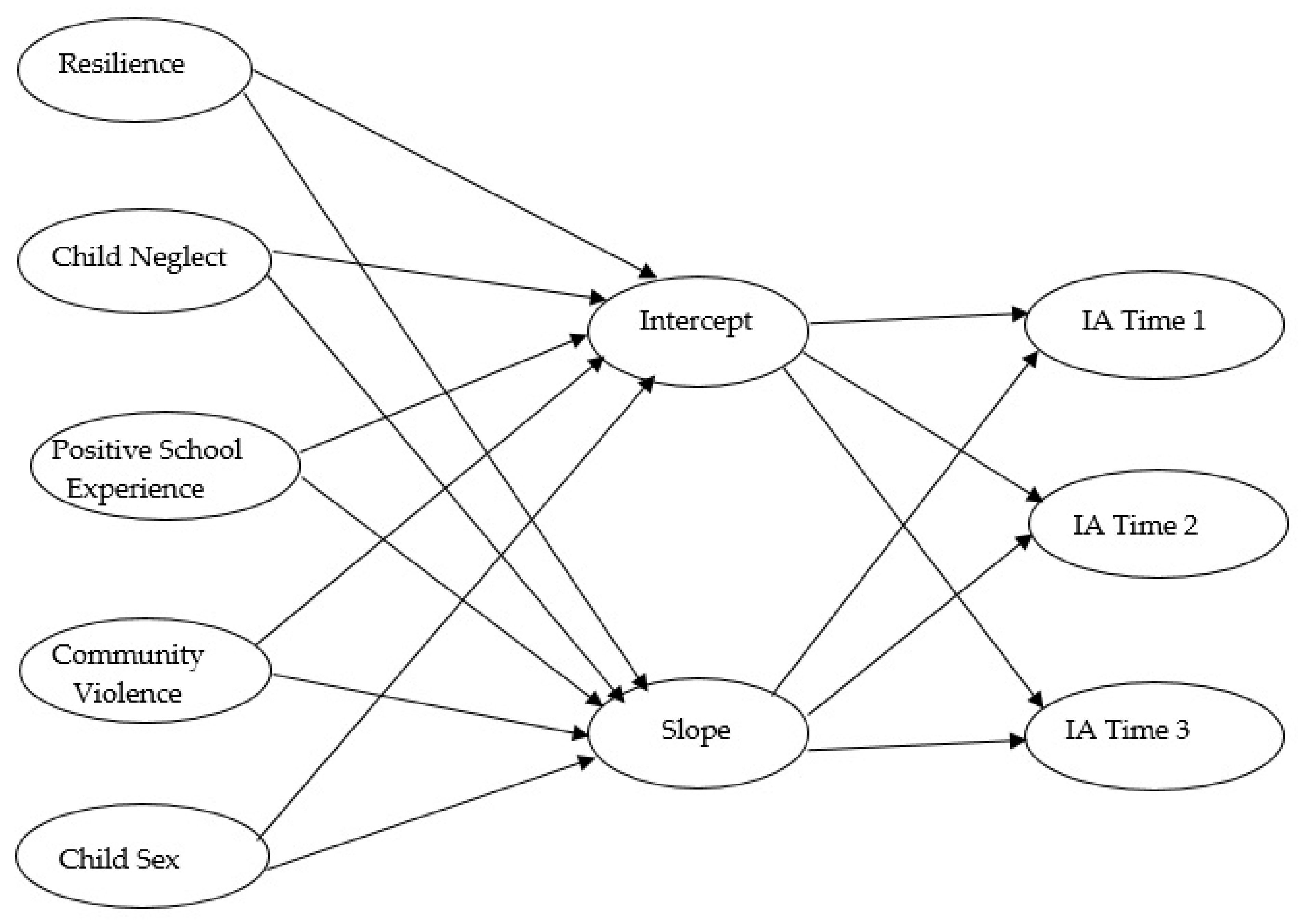
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Trajectory of Internet Addiction across Elementary and Middle School Years
3.2. Ecological Factors and Internet Addiction across Elementary and Middle School Years
4. Discussion
4.1. Primary Findings
4.2. Strengths
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, R.A. A Cognitive-Behavioral Model of Pathological Internet Use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2001, 17, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S.; Rogers, R.C. The Relationship Between Depression and Internet Addiction. Cyber Psychol. Behav. 1998, 1, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction and a Winning Strategy for Recovery; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Alimoradi, Z.; Lin, C.-Y.; Broström, A.; Bülow, P.H.; Bajalan, Z.; Griffiths, M.D.; Ohayon, M.M.; Pakpour, A.H. Internet Addiction and Sleep Problems: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 47, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, R.C.; Zhang, M.W.B.; Tsang, T.Y.; Toh, A.H.; Pan, F.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yip, P.S.; Lam, L.T.; Lai, C.-M.; et al. The Association between Internet Addiction and Psychiatric Co-Morbidity: A Meta-Analysis. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 284–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yen, J.-Y.; Yen, C.-F.; Chen, C.-S.; Chen, C.-C. The Association between Internet Addiction and Psychiatric Disorder: A Review of the Literature. Eur. Psychiatry 2012, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yen, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-C.; Huang, C.-F.; Yen, C.-F. The Associations Between Aggressive Behaviors and Internet Addiction and Online Activities in Adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2009, 44, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.; Yen, J.-Y.; Yen, C.; Chen, C.; Weng, C.; Chen, C. The Association between Internet Addiction and Problematic Alcohol Use in Adolescents: The Problem Behavior Model. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2008, 11, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.-H.; Ko, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-P.; Liu, T.-L.; Wang, P.-W.; Lin, H.-C.; Huang, M.-F.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Chou, W.-J.; Yen, C.-F. The Association between Suicidality and Internet Addiction and Activities in Taiwanese Adolescents. Compr. Psychiatry 2014, 55, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Li, A.Y. Internet Addiction Prevalence and Quality of (Real) Life: A Meta-Analysis of 31 Nations Across Seven World Regions. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2014, 17, 755–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S.; Yue, X.D.; Ying, L. Prevalence Estimates and Etiologic Models of Internet Addiction. Internet Addict. A Handb. Guide Eval. Treat. 2011, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-C.; Chiu, C.-H.; Lee, C.-M.; Chen, P.-H.; Miao, N.-F. Predictors of the Initiation and Persistence of Internet Addiction among Adolescents in Taiwan. Addict. Behav. 2014, 39, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-P.; Wu, J.Y.-W.; You, J.; Hu, W.-H.; Yen, C.-F. Prevalence of Internet Addiction and Its Risk and Protective Factors in a Representative Sample of Senior High School Students in Taiwan. J. Adolesc. 2018, 62, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, M.F.; van Geert, P.; Steenbeek, H.; Fischer, K.W. What Can Dynamic Systems Models of Development Offer to the Study of Developmental Psychopathology? In Developmental Psychopathology: Theory and Method; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 665–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. Internet Addiction: Stability and Change. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 2010, 25, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhen, R.; Wu, X. Trajectories of Problematic Internet Use among Adolescents over Time since Wenchuan Earthquake. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 84, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Tong, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, F.; Fang, X. Trajectory of Problematic Internet Use across the College Years: The Role of Peer Internet Overuse Behavior and Peer Attitude toward Internet Overuse. J. Adolesc. 2021, 86, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, J.J. Adolescent Storm and Stress, Reconsidered. Am. Psychol. 1999, 54, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, L.; Silverberg, S.B.; Steinberg, L.; Silverberg, S.B. The Vicissitudes of Autonomy in Early Adolescence. Child Dev. 1986, 57, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-P.; Shen, A.C.-T.; Wei, H.-S.; Feng, J.-Y.; Huang, S.C.-Y.; Hwa, H.-L. Multidimensional Victimization and Internet Addiction among Taiwanese Children. Chin. J. Psychol. 2016, 58, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Ecological Systems Theory; Jessica Kingsley Publishers: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Bronfenbrenner, U. Freedom and Discipline across the Decades. Sonderdr. Aus Ordn. Unordnung 1985, 326–339. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, T.W.; Yan, Z.; Rapoza, K.A. Is Resilience a Protective Factor of Internet Addiction? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 78, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, K.M.; Davidson, J.R.T. Development of a New Resilience Scale: The Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC). Depress. Anxiety (1091–4269) 2003, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masten, A.; Hubbard, J.; Gest, S.; Tellegen, A.; Garmezy, N.; Ramirez, M. Competence in the Context of Adversity: Pathways to Resilience and Maladaptation from Childhood to Late Adolescence. Dev. Psychopathol. 1999, 11, 143–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, G.E. The Metatheory of Resilience and Resiliency. J. Clin. Psychol. 2002, 58, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugade, M.M.; Fredrickson, B.L. Resilient Individuals Use Positive Emotions to Bounce Back from Negative Emotional Experiences. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 2004, 86, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjemdal, O.; Vogel, P.A.; Solem, S.; Hagen, K.; Stiles, T.C. The Relationship between Resilience and Levels of Anxiety, Depression, and Obsessive–Compulsive Symptoms in Adolescents. Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2011, 18, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.-P.; Shen, A.C.-T.; Wei, H.-S.; Feng, J.-Y.; Huang, S.C.-Y.; Hwa, H.-L. Associations between Child Maltreatment, PTSD, and Internet Addiction among Taiwanese Students. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 56, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoon, Y.W. Effect of Parental Neglect on Smartphone Addiction in Adolescents in South Korea. Child Abus. Negl. 2018, 77, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Child Maltreatment 2007—Google Search. Available online: https://www.google.com/search?client=firefox-b-1-d&q=Child+Maltreatment+2007 (accessed on 9 May 2021).
- World Health Organization. Report of the Consultation on Child Abuse Prevention; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- English, D.J.; Thompson, R.; Graham, J.C.; Briggs, E.C. Toward a Definition of Neglect in Young Children. Child Maltreat. 2005, 10, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltenborgh, M.; Bakermans-Kranenburg, M.; IJzendoorn, M. The Neglect of Child Neglect: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Prevalence of Neglect. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2013, 48, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildyard, K.L.; Wolfe, D.A. Child Neglect: Developmental Issues and Outcomes. Child Abus. Negl. 2002, 26, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manly, J.T.; Kim, J.E.; Rogosch, F.A.; Cicchetti, D. Dimensions of Child Maltreatment and Children’s Adjustment: Contributions Ofdevelopmental Timing and Subtype. Dev. Psychopathol 2001, 13, 759–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschi, T. Causes of Delinquency; Routledge: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Eccles, J.S.; Midgley, C.; Wigfield, A.; Buchanan, C.M.; Reuman, D.; Flanagan, C.; Mac Iver, D. Development during Adolescence: The Impact of Stage-Environment Fit on Young Adolescents’ Experiences in Schools and in Families. Am. Psychol. 1993, 48, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Fredricks, J.A. The Reciprocal Links Between School Engagement, Youth Problem Behaviors, and School Dropout During Adolescence. Child Dev. 2014, 85, 722–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taş, İ. Relationship between Internet Addiction, Gaming Addiction and School Engagement among Adolescents. UJER 2017, 5, 2304–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Bao, Z.; Wen, F. School Connectedness and Problematic Internet Use in Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Model of Deviant Peer Affiliation and Self-Control. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2013, 41, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, W.; Liang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, H.; Dou, K.; Xie, X.; Gan, X. School Climate, Loneliness, and Problematic Online Game Use Among Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Effect of Intentional Self-Regulation. Front. Public Health 2019, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallen, J.; Rubin, R.H. The Role of the Family in Mediating the Effects of Community Violence on Children. Aggress. Violent Behav. 1997, 2, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterman, N.B.; Cameron, M.; Staller, K. Definitional and Measurement Issues in the Study of Community Violence among Children and Youths. J. Community Psychol. 2000, 28, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickett, P.K.; Durán, L.; Horn, J.L.; Durán, L. Community Violence as It Affects Child Development: Issues of Definition. Clin. Child Fam. Psychol. Rev. 2003, 6, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley-Quille, M.; Boyd, R.C.; Frantz, E.; Walsh, J. Emotional and Behavioral Impact of Exposure to Community Violence in Inner-City Adolescents. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2001, 30, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, C.; Bacchini, D.; Eisenberg, N.; Affuso, G. Effortful Control, Exposure to Community Violence, and Aggressive Behavior: Exploring Cross-Lagged Relations in Adolescence. Aggress. Behav. 2017, 43, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, K.M.; Piko, B.F.; Wright, D.R.; LaGory, M. Depressive Symptomatology, Exposure to Violence, and the Role of Social Capital Among African American Adolescents. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2005, 75, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.N.; Kung, E.M.; Farrell, A.D. Relation Between Witnessing Violence and Drug Use Initiation Among Rural Adolescents: Parental Monitoring and Family Support as Protective Factors. J. Clin. Child Adolesc. Psychol. 2004, 33, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, R. Building on the Foundation of General Strain Theory: Specifying the Types of Strain Most Likely to Lead to Crime and Delinquency. J. Res. Crime Delinq. 2001, 38, 319–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.M.; Fagan, A.A.; Pinchevsky, G.M. The Effects of Exposure to Violence and Victimization across Life Domains on Adolescent Substance Use. Child Abus. Negl. 2013, 37, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Li, X.; Zhang, W. Predicting Adolescent Problematic Online Game Use from Teacher Autonomy Support, Basic Psychological Needs Satisfaction, and School Engagement: A 2-Year Longitudinal Study. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2015, 18, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.K.; Finkelhor, D.; Kantor, G.K. Multiple Victimization Experiences of Urban Elementary School Students: Associations with Psychosocial Functioning and Academic Performance. Child Abus. Negl. 2007, 31, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, A.W. Evidence That School-Age Children Can Self-Report on Their Health. Ambul. Pediatr. Off. J. Ambul. Pediatr. Assoc. 2004, 4, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Limbers, C.A.; Burwinkle, T.M. How Young Can Children Reliably and Validly Self-Report Their Health-Related Quality of Life? An Analysis of 8591 Children across Age Subgroups with the PedsQLTM 4.0 Generic Core Scales. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2007, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell-Sills, L.; Stein, M.B. Psychometric Analysis and Refinement of the Connor–Davidson Resilience Scale (CD-RISC): Validation of a 10-Item Measure of Resilience. J. Trauma. Stress 2007, 20, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotor, A.J.; Runyan, D.K.; Dunne, M.P.; Jain, D.; Péturs, H.R.; Ramirez, C.; Volkova, E.; Deb, S.; Lidchi, V.; Muhammad, T.; et al. ISPCAN Child Abuse Screening Tool Children’s Version (ICAST-C): Instrument Development and Multi-National Pilot Testing. Child Abus. Negl. 2009, 33, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Mallery, P. SPSS for Windows Step by Step: A Simple Guide and Reference. 11.0 Update; Allyn & Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- van Griethuijsen, R.A.L.F.; van Eijck, M.W.; Haste, H.; den Brok, P.J.; Skinner, N.C.; Mansour, N.; Savran Gencer, A.; BouJaoude, S. Global Patterns in Students’ Views of Science and Interest in Science. Res. Sci. Educ. 2015, 45, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taber, K.S. The Use of Cronbach’s Alpha When Developing and Reporting Research Instruments in Science Education. Res. Sci. Educ. 2018, 48, 1273–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pynoos, R.; Rodriguez, N.; Steinberg, A.; Stuber, M.; Frederick, C. UCLA PTSD Index for DSM-IV (Revision 1); UCLA Trauma Psychiatry Program: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-H.; Weng, L.-J.; Su, Y.-J.; Wu, H.-M.; Yang, P.-F. Development of a Chinese Internet Addiction Scale and Its Psychometric Study. Chin. J. Psychol. 2003, 45, 279–294. [Google Scholar]
- Raudenbush, S.W. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods, 2nd ed.; Advanced Quantitative Techniques in the Social Sciences; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, J.D. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.S.; Blum, T.C. Assessing the Non-Random Sampling Effects of Subject Attrition in Longitudinal Research. J. Manag. 1996, 22, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravetter, F.J.; Wallnau, L.B.; Forzano, L.-A.B.; Witnauer, J.E. Essentials of Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.B. Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, 4th ed.; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yen, C.-F.; Yen, C.-N.; Yen, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, S.-H. Screening for Internet Addiction: An Empirical Study on Cut-off Points for the Chen Internet Addiction Scale. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2005, 21, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.W. Missing Data Analysis: Making It Work in the Real World. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2008, 60, 549–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAfee. The Secret Online Lives of Teens; McAfee: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson, A.I. Parents Versus Peers: Exploring the Significance of Peer Mediation of Antisocial Television. Commun. Res. 2001, 28, 251–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Lwin, M.O. How Does “Talking about the Internet with Others” Affect Teenagers’ Experience of Online Risks? The Role of Active Mediation by Parents, Peers, and School Teachers. New Media Soc. 2017, 19, 1109–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Hsieh, Y.-P.; Clary, K.L.; Rose, T.; Russ, R.; Voisin, D.R. Peer Victimization, Internalizing Problems, and Substance Use in Urban African American Adolescents in Chicago: The Relevance of the Self-Medication Hypothesis. Violence Vict. 2019, 34, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruska, B.; Delahanty, D.L. Application of the Stressor Vulnerability Model to Understanding Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and Alcohol-Related Problems in an Undergraduate Population. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2012, 26, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, D.G.; Cummings, L.L.; Dunham, R.B.; Pierce, J.L. Single-Item versus Multiple-Item Measurement Scales: An Empirical Comparison. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1998, 58, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.A.; Barrett, G.V.; Alliger, G.M.; Carson, K.P. Towards a General Model of Non-Random Sampling and the Impact on Population Correlation: Generalizations of Berkson’s Fallacy and Restriction of Range. Br. J. Math. Stat. Psychol. 1986, 39, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Variables | 1. | 2. | 3. | 4. | 5. | 6. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Resilience | -- | |||||
| 2. Child neglect | −0.14 ** 1 | -- | ||||
| 3. Positive school experience | 0.24 ** | −0.20 ** | -- | |||
| 4. Internet addiction T1 | −0.17 ** | 0.23 ** | −0.22 ** | -- | ||
| 5. Internet addiction T2 | −0.21 ** | 0.17 ** | −0.19 ** | 0.32 ** | -- | |
| 6. Internet addiction T3 | −0.30 ** | 0.12 ** | −0.17 ** | 0.20 ** | 0.43 ** | -- |
| Mean | 3.56 | 1.22 | 3.88 | 1.82 | 1.86 | 1.20 |
| SD 2 | 0.61 | 1.68 | 0.98 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.75 |
| Scale range | 1–5 | 0–10 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 | 1–5 |
| Internet Addiction | ||
|---|---|---|
| Study Variables | Coefficient | SE |
| Fixed Effects | ||
| Initial status, π0i | ||
| Intercept | 1.84 *** | 0.02 |
| Gender | 0.10 *** | 0.01 |
| Resilience | −0.12 *** | 0.02 |
| Child neglect | 0.07 *** | 0.01 |
| Positive school experience | −0.14 *** | 0.02 |
| Community violence | 0.12 *** | 0.02 |
| Rate of change, π1i | ||
| Intercept | 0.08 *** | 0.01 |
| Gender | −0.04 *** | 0.01 |
| Resilience | −0.11 *** | 0.02 |
| Child neglect | −0.03 *** | 0.01 |
| Positive school experience | 0.04 *** | 0.01 |
| Community violence | −0.05 *** | 0.01 |
| Variance components | ||
| Level 1 | ||
| Level 2 | ||
| Within-person, σε2 | 0.32 *** | |
| In initial status, σ02 | 0.17 *** | |
| In rate of change, σ12 | 0.06 *** | |
| Correlation between ζ0i and ζ1i, τ | −0.48 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, Y.-P.; Hwa, H.-L.; Shen, A.C.-T.; Wei, H.-S.; Feng, J.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y. Ecological Predictors and Trajectory of Internet Addiction from Childhood through Adolescence: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126253
Hsieh Y-P, Hwa H-L, Shen AC-T, Wei H-S, Feng J-Y, Huang C-Y. Ecological Predictors and Trajectory of Internet Addiction from Childhood through Adolescence: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(12):6253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126253
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Yi-Ping, Hsiao-Lin Hwa, April Chiung-Tao Shen, Hsi-Sheng Wei, Jui-Ying Feng, and Ching-Yu Huang. 2021. "Ecological Predictors and Trajectory of Internet Addiction from Childhood through Adolescence: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 12: 6253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126253
APA StyleHsieh, Y.-P., Hwa, H.-L., Shen, A. C.-T., Wei, H.-S., Feng, J.-Y., & Huang, C.-Y. (2021). Ecological Predictors and Trajectory of Internet Addiction from Childhood through Adolescence: A Nationally Representative Longitudinal Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(12), 6253. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126253








