Profile of the Change in Depression during Proton-Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Influence of the Mucosal Break
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Study Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Change in Reflux Symptoms and Depression during Follow-Up
3.3. Factors Associated with the Change in Depression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dent, J.; El-Serag, H.B.; Wallander, M.A.; Johansson, S. Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review. Gut 2005, 54, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Sweet, S.; Winchester, C.C.; Dent, J. Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review. Gut 2014, 63, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiong, L.; Chen, H.; Xu, A.; He, L.; Hu, P. Prevalence, risk factors and impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms: A population-based study in South China. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, W.G. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and asthma. Diagnosis and management. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995, 155, 798–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahrilas, P.J.; Altman, K.W.; Chang, A.B.; Field, S.K.; Harding, S.M.; Lane, A.P.; Lim, K.; McGarvey, L.; Smith, J.; Irwin, R.S. Chronic Cough Due to Gastroesophageal Reflux in Adults: CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2016, 150, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jonge, P.J.F.; van Blankenstein, M.; Grady, W.M.; Kuipers, E.J. Barrett’s oesophagus: Epidemiology, cancer risk and implications for management. Gut 2014, 63, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Z.H.; Perng, C.L.; Hu, L.Y.; Lu, T.; Chen, P.M.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Huang, Y.S.; Chen, H.J. Risk of psychiatric disorders following gastroesophageal reflux disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkainen, J.; Aro, P.; Storskrubb, T.; Lind, T.; Bolling-Sternevald, E.; Junghard, O.; Talley, N.J.; Agreus, L. Gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms and health-related quality of life in the adult general population—The Kalixanda study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlqvist, P.; Karlsson, M.; Johnson, D.; Carlsson, J.; Bolge, S.C.; Wallander, M.A. Relationship between symptom load of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and health-related quality of life, work productivity, resource utilization and concomitant diseases: Survey of a US cohort. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peura, D.A.; Berardi, R.R.; Gonzalez, J.; Brunetti, L. The value of branded proton pump inhibitors: Formulary considerations. Pharm. Ther. 2011, 36, 434–445. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, Y.S.; Choi, M.G.; Jeong, J.J.; Chung, W.C.; Lee, I.S.; Kim, S.W.; Han, S.W.; Choi, K.Y.; Chung, I.S. Prevalence and clinical spectrum of gastroesophageal reflux: A population-based study in Asan-si, Korea. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershcovici, T.; Fass, R. Nonerosive Reflux Disease (NERD)—An Update. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 16, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuyama, M.; Takaishi, O.; Nakahara, K.; Iwakura, N.; Hasegawa, T.; Oyama, M.; Inoue, A.; Ishizu, H.; Satoh, H.; Fujiwara, Y. Associations among gastroesophageal reflux disease, psychological stress, and sleep disturbances in Japanese adults. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.A.H.S. Anxiety and depression in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disorder. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.M.; Yang, J.I.; Kang, S.J.; Han, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Chung, S.J.; Yoon, D.H.; Park, B.; Kim, Y.S. Association between Anxiety and Depression and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Results from a Large Cross-sectional Study. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilgi, M.M.; Vardar, R.; Yıldırım, E.; Veznedaroğlu, B.; Bor, S. Prevalence of Psychiatric Comorbidity in Symptomatic Gastroesophageal Reflux Subgroups. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Lim, H.; Kong, I.G.; Kim, M.; Choi, H.G. Bidirectional association between gastroesophageal reflux disease and depression: Two different nested case-control studies using a national sample cohort. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Jiang, H.M.; Hou, X.H.; Song, J. Anxiety and depression in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease and their effect on quality of life. World. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 4302–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, S.; Shafikhani, A.A. Anxiety and depression in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disorder. Electron. Physician 2017, 9, 5107–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, P.; Wang, F.; Ji, G.; Miao, L.; You, S. Psychological Results of 438 Patients with persisting Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms by Symptom Checklist 90-Revised Questionnaire. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2017, 7, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, C.; Nordenstedt, H.; Wallander, M.A.; Johansson, S.; Johnsen, R.; Hveem, K.; Lagergren, J. Severe gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms in relation to anxiety, depression and coping in a population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudisio, A.; Incalzi, R.; Gemma, A.; Giovannini, S.; Lo Monaco, R.; Vetrano, D.; Padua, L.; Bernabei, R.; Zuccal, G. Use of proton-pump inhibitors is associated with depression: A population-based study. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.S.; Bai, Y.M.; Hsu, J.W.; Huang, K.L.; Tsai, C.F.; Su, T.P.; Li, C.T.; Lin, W.C.; Tsai, S.J.; Pan, T.L.; et al. Use of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Risk of Major Depressive Disorder: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Psychother. Psychosom. 2018, 87, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.S.; Liu, T.T.; Wen, S.H.; Wang, C.C.; Yi, C.H.; Chen, J.H.; Lei, W.Y.; Orr, W.; Pace, F.; Chen, C.L. Clinical, metabolic, and psychological characteristics in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease overlap with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 27, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Yan, X.; Ma, X.Q.; Wang, R.; Johansson, S.; Wallander, M.A.; He, J. Validation of a survey methodology for gastroesophageal reflux disease in China. BMC Gastroenterol. 2008, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.J.; Talley, N.J.; Beebe, T.J.; Rockwood, T.; Carlsson, R.; Adlis, S.; Fendrick, A.M.; Jones, R.; Dent, J.; Bytzer, P. Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Dent, J.; Beebe, T.; Junghard, O.; Wiklund, I.; Lind, T.; Johnsson, F. The Reflux Disease Questionnaire: A measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Health Qual. Life. Outcomes. 2008, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Yang, M.J.; Lai, T.J.; Chiu, N.M.; Chau, T.T. Development of the Taiwanese Depression Questionnaire. Chang Gung Med. J. 2000, 23, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenhard, W.; Lenhard, A. Calculation of Effect Sizes. Psychometrica. Dettelbach (Germany). 2016. Available online: https://www.psychometrica.de/effect_size.html (accessed on 29 May 2021). [CrossRef]
- Altomare, A.; Guarino, M.P.L.; Cocca, S.; Emerenziani, S.; Cicala, M. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Update on inflammation and symptom perception. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6523–6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampa, J.; Westman, M.; Kadetoff, D.; Agréus, A.N.; Le Maître, E.; Gillis-Haegerstrand, C.; Andersson, M.; Khademi, M.; Corr, M.; Christianson, C.A.; et al. Peripheral inflammatory disease associated with centrally activated IL-1 system in humans and mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Williams, L.J.; Jacka, F.N.; O’Neil, A.; Pasco, J.A.; Moylan, S.; Allen, N.B.; Stuart, A.L.; Hayley, A.C.; Byrne, M.L.; et al. So depression is an inflammatory disease, but where does the inflammation come from? BMC Med. 2013, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivimäki, M.; Shipley, M.J.; Batty, G.D.; Hamer, M.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Kumari, M.; Jokela, M.; Virtanen, M.; Lowe, G.D.; Ebmeier, K.P.; et al. Long-term inflammation increases risk of common mental disorder: A cohort study. J. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, R.; Wisniewski, P.J.; Alderman, B.L.; Campbell, S.C. Microbes and mental health: A review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, N.; Alcalde, V.; Pujol, A.; Münter, L.-M.; Multhaup, G.; Lleó, A.; Coma, M.; Soler-López, M.; Aloy, P. The proton-pump inhibitor lansoprazole enhances amyloid beta production. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, G. The “Biopsychosocial Model”: 40 years of application in Psychiatry. Psychiatr. Psychiatr. 2017, 28, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, C.H.; Aziz, Q. Visceral hypersensitivity in non-erosive reflux disease. Gut 2008, 57, 674–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, W.Y.; Chang, W.C.; Wong, M.W.; Hung, J.S.; Wen, S.H.; Yi, C.H.; Liu, T.T.; Chen, J.H.; Hsu, C.S.; Hsieh, T.C.; et al. Sleep Disturbance and Its Association with Gastrointestinal Symptoms/Diseases and Psychological Comorbidity. Digestion 2019, 99, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Ma, S.; Hui, Y.Y.; Wang, B.; Yang, B.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Jiang, K.; et al. Efficacy of proton pump inhibitor on nighttime reflux symptoms and associated sleep disturbances in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A real-world study in northern China. Res. Sq. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.A.; Orr, W.C.; Crawley, J.A.; Traxler, B.; McCullough, J.; Brown, K.A.; Roth, T. Effect of esomeprazole on nighttime heartburn and sleep quality in patients with GERD: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J. Pathways from education to depression. J. Cross Cult. Gerontol. 2011, 26, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musliner, K.L.; Munk-Olsen, T.; Eaton, W.W.; Zandi, P.P. Heterogeneity in long-term trajectories of depressive symptoms: Patterns, predictors and outcomes. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 192, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaroslavsky, I.; Pettit, J.W.; Lewinsohn, P.M.; Seeley, J.R.; Roberts, R.E. Heterogeneous trajectories of depressive symptoms: Adolescent predictors and adult outcomes. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 148, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, D.; How, C.H.; Ang, T.L. Persistent gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms despite proton pump inhibitor therapy. Singap. Med. J. 2016, 57, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G. Observer bias in the assessment of anxiety and depression. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 1991, 26, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Baseline Characteristics | Total | MB | NoMB | pa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 172 | 52 | 120 | |
| Female | 106 (61.6) | 23 (44.2) | 83 (69.2) | <0.01 |
| Age (years) | 47.5 ± 21.0 | 44.0 ± 22.0 | 49.0 ± 22.0 | 0.20 |
| Level of education | ||||
| <University | 84 (48.8) | 26 (50.0) | 58 (48.3) | 0.87 |
| ≥University | 88 (51.2) | 26 (50.0) | 62 (51.7) | |
| Marriage | 129 (75.0) | 37 (71.2) | 92 (76.7) | 0.45 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.6 ± 5.4 | 24.3 ± 4.9 | 23.4 ± 5.0 | 0.21 |
| Alcohol | 69 (40.1) | 28 (53.8) | 41 (34.2) | 0.02 |
| Coffee | 78 (45.3) | 23 (44.2) | 55 (45.8) | 0.87 |
| Tea | 71 (41.3) | 23 (44.2) | 48 (40.0) | 0.62 |
| Exercise | 86 (50.0) | 27 (51.9) | 59 (49.2) | 0.87 |
| RDQt0 | 12.0 ± 14.0 | 12.0 ± 15.0 | 12.5 ± 13.0 | 0.66 |
| TDQt0 | 11.0 ± 12.0 | 10.0 ± 14.0 | 11.0 ± 12.0 | 0.07 |
| PSQI | 5.0 ± 5.0 | 6.0 ± 4.0 | 5.0 ± 5.0 | 0.95 |
| Measurement | Group | Number | Score (Mean ± Standard Deviation) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Improve (%) | p a | Baseline (t0) | After PPI (t1) | Change from Baseline | p b | Effect Size (Cohen’s d) | p c | ||
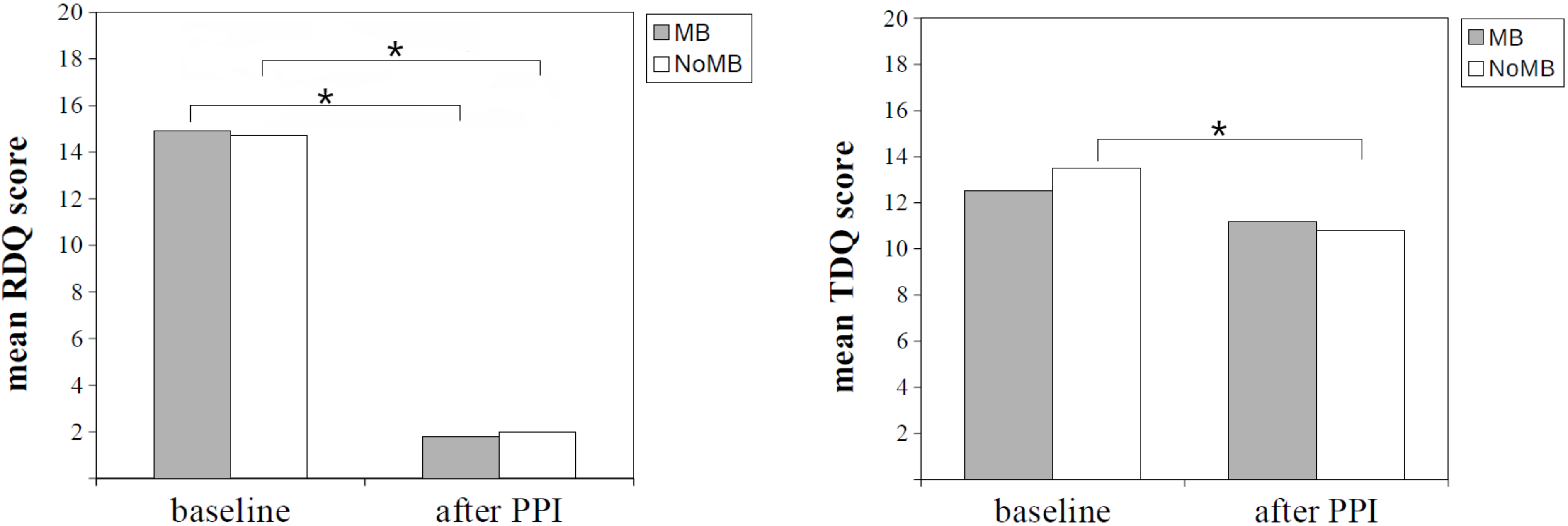
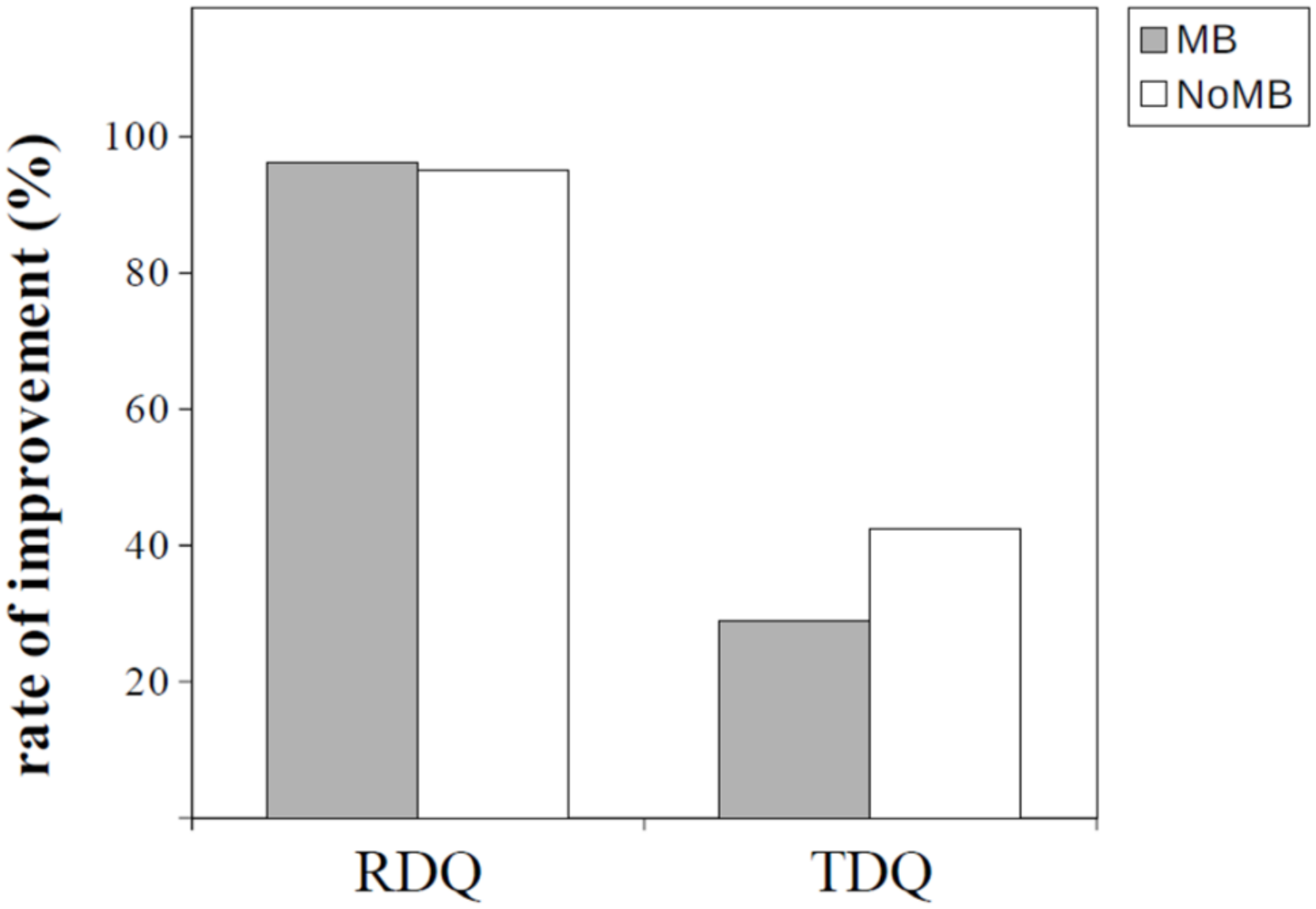
| RDQ | All | 172 | 164 (95.3) | 14.8 ± 8.6 | 1.9 ± 3.7 | −12.9 ± 8.9 | <0.01 | 1.12 | ||
| MB | 52 | 50 (96.2) | 0.99 | 14.9 ± 8.9 | 1.8 ± 3.5 | −13.2 ± 8.6 | <0.01 | 1.24 | 0.66 | |
| NoMB | 120 | 114 (95.0) | 14.7 ± 8.5 | 2.0 ± 3.7 | −12.7 ± 9.1 | <0.01 | 1.08 | |||
| TDQ | All | 172 | 66 (38.4) | 13.2 ± 10.1 | 10.9 ± 9.8 | −2.3 ± 7.5 | <0.01 | 0.30 | ||
| MB | 52 | 15 (28.8) | 0.12 | 12.5 ± 10.5 | 11.2 ± 9.2 | −1.2 ± 8.1 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.07 | |
| NoMB | 120 | 51 (42.5) | 13.5 ± 9.9 | 10.8 ± 10.0 | −2.7 ± 7.2 | <0.01 | 0.38 | |||
| Factors | Univariate Model | Multivariate Model a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B (n = 172) (95% CI) | p | B (n = 167) (95% CI) | p | |
| Mucosal break | 1.47 (−0.98, 3.92) | 0.24 | 3.31 (1.12, 5.51) | <0.01 |
| Female | 2.29 (−0.01, 4.59) | 0.05 | 3.74 (1.59, 5.89) | <0.01 |
| Age (years) | 0.06 (−0.02, 0.15) | 0.14 | 0.07 (−0.04, 0.17) | 0.21 |
| Education (ref: <university) | ||||
| ≥University | −3.01 (−5.23, −0.80) | 0.01 | −3.08 (−5.10, −1.06) | <0.01 |
| Marriage | 1.92 (−0.67, 4.52) | 0.15 | −0.61 (−3.41, 2.19) | 0.67 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | −0.20 (−0.50, 0.10) | 0.18 | −0.18 (−0.43, 0.08) | 0.18 |
| Alcohol | 0.67 (−1.64, 2.98) | 0.57 | 1.94 (−0.15, 4.02) | 0.07 |
| Coffee | 1.55 (−0.71, 3.81) | 0.18 | 0.52 (−1.50, 2.53) | 0.56 |
| Tea | −0.88 (−3.18, 1.41) | 0.45 | −0.18 (−2.18, 1.83) | 0.86 |
| Exercise | 0.51 (−1.75, 2.77) | 0.66 | 0.24 (−1.72, 2.20) | 0.81 |
| PPI duration (days) | −0.02 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.17 | −0.04 (−0.07, −0.01) | 0.02 |
| RDQt0 | −0.14 (−0.27, −0.01) | 0.03 | −0.07 (−0.19, 0.04) | 0.20 |
| PSQI | −0.41 (−0.73, −0.09) | 0.01 | −0.61 (−0.90, −0.31) | <0.01 |
| Factors | Univariate Model | Multivariate Model a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | Adjusted Odds Ratio (95% CI) | p | |
| Mucosal break | 0.55 (0.27, 1.10) | 0.09 | 0.38 (0.17, 0.86) | 0.02 |
| Female | 0.76 (0.40, 1.42) | 0.39 | 0.58 (0.27, 1.23) | 0.15 |
| Age (years) | 1.00 (0.97, 1.02) | 0.53 | 0.98 (0.95, 1.01) | 0.22 |
| Education (ref: <university) | ||||
| ≥University | 1.86 (1.00, 3.47) | 0.05 | 2.20 (1.07, 4.51) | 0.03 |
| Marriage | 1.07 (0.52, 2.18) | 0.10 | 2.03 (0.73, 5.66) | 0.18 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 1.03 (0.95, 1.12) | 0.42 | 1.05 (0.96, 1.15) | 0.28 |
| Alcohol | 0.70 (0.37, 1.32) | 0.27 | 0.52 (0.25, 1.10) | 0.09 |
| Coffee | 0.75 (0.40, 1.39) | 0.36 | 0.91 (0.44, 1.85) | 0.79 |
| Tea | 1.32 (0.71, 2.46) | 0.07 | 1.46 (0.72, 2.98) | 0.29 |
| Exercise | 1.10 (0.60, 2.04) | 0.75 | 1.40 (0.69, 2.81) | 0.35 |
| PPI duration (days) | 1.01 (1.00, 1.02) | 0.04 | 1.01 (1.00, 1.03) | 0.01 |
| RDQt0 | 1.03 (0.99, 1.06) | 0.18 | 1.01 (0.97, 1.05) | 0.65 |
| PSQI | 1.07 (0.98, 1.17) | 0.12 | 1.11 (1.00, 1.24) | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, C.-L.; Chen, C.-L.; Wen, S.-H. Profile of the Change in Depression during Proton-Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Influence of the Mucosal Break. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115964
Wu C-L, Chen C-L, Wen S-H. Profile of the Change in Depression during Proton-Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Influence of the Mucosal Break. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(11):5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115964
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Chia-Liang, Chien-Lin Chen, and Shu-Hui Wen. 2021. "Profile of the Change in Depression during Proton-Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Influence of the Mucosal Break" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 11: 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115964
APA StyleWu, C.-L., Chen, C.-L., & Wen, S.-H. (2021). Profile of the Change in Depression during Proton-Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: Influence of the Mucosal Break. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11), 5964. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115964






