Food Environments and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
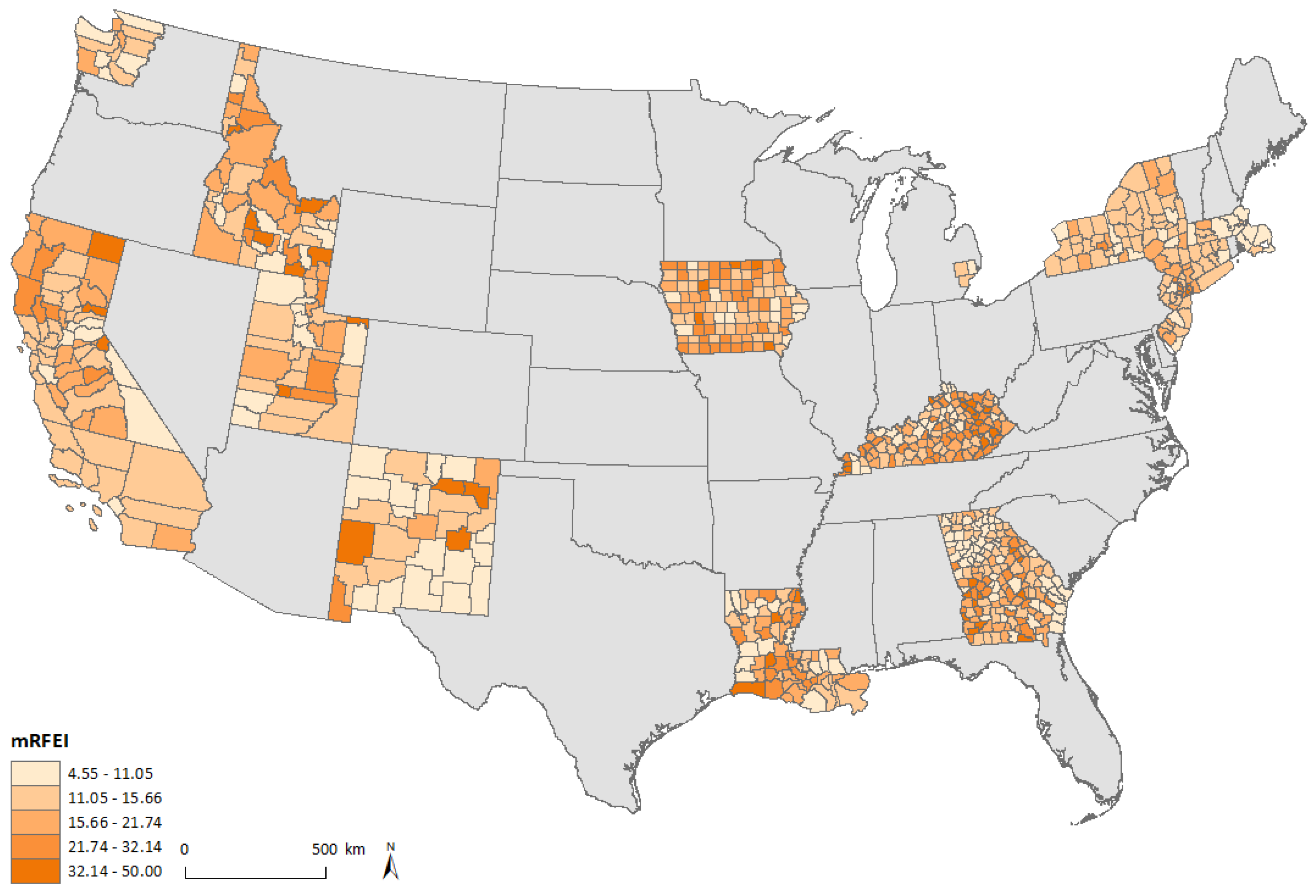
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El–Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epidemiology and Molecular Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VoPham, T. Environmental Risk Factors for Liver Cancer and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Epidemiol. Rep. 2019, 6, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; London, W.T. Global Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Emphasis on Demographic and Regional Variability. Clin. Liver Dis. 2015, 19, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.W.; Hsieh, H.H.; Pan, W.H.; Yang, C.S.; Chen, C.J. Vegetable Consumption, Serum Retinol Level, and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.-W.; Horng, I.-S.; Hsu, K.-H.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Liaw, Y.F.; Chen, C.-J. Plasma Selenium Levels and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma among Men with Chronic Hepatitis Virus Infection. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, N.D.; Cross, A.J.; McGlynn, K.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Everhart, J.E.; Sinha, R. Association of Meat and Fat Intake with Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the NIH-AARP Cohort. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2010, 102, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Simon, T.G.; Sui, J.; Wu, K.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; Zhang, X. Meat Intake and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Two Large US Prospective Cohorts of Women and Men. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 1863–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Sui, J.; Ma, Y.; Simon, T.G.; Petrick, J.L.; Lai, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Campbell, P.T.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; et al. High Dietary Intake of Vegetable or Polyunsaturated Fats Is Associated with Reduced Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2775–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; VoPham, T.; Ma, Y.; Simon, T.G.; Gao, X.; Chan, A.T.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Zhang, X. Plant-Based and Animal-Based Low-Carbohydrate Diets and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Among US Men and Women. Hepatology 2021, 73, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Simon, T.G.; Chong, D.Q.; Qi, Q.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; et al. Association of Intake of Whole Grains and Dietary Fiber with Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in US Adults. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.; Yang, W.; Ma, Y.; Li, T.Y.; Simon, T.G.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Liang, G.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; Zhang, X. A Prospective Study of Nut Consumption and Risk of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the U.S. Women and Men. Cancer Prev. Res. 2019, 12, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talamini, R.; Polesel, J.; Montella, M.; Maso, L.D.; Crispo, A.; Tommasi, L.G.; Izzo, F.; Crovatto, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Franceschi, S. Food Groups and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Case-control Study in Italy. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2916–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Sui, J.; Ma, Y.; Simon, T.G.; Chong, D.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Chan, A.T.; Zhang, X. A Prospective Study of Dairy Product Intake and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in U.S. Men and Women. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvaget, C.; Nagano, J.; Hayashi, M.; Spencer, E.; Shimizu, Y.; Allen, N. Vegetables and Fruit Intake and Cancer Mortality in the Hiroshima/Nagasaki Life Span Study. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yang, W.; Simon, T.G.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Fung, T.T.; Sui, J.; Chong, D.; Vo Pham, T.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Wen, D.; et al. Dietary Patterns and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma among U.S. Men and Women. Hepatology 2019, 70, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, A.S.; Story, M.; Jeffery, R.W. Environmental Influences on Eating and Physical Activity. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2001, 22, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagami, S.; Cohen, D.A.; Finch, B.K.; Asch, S.M. You Are Where You Shop: Grocery Store Locations, Weight, and Neighborhoods. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2006, 31, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morland, K.; Wing, S.; Roux, A.D. The Contextual Effect of the Local Food Environment on Residents’ Diets: The Ather-osclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Public Health 2002, 92, 1761–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.C.; Prochaska, J.D.; Yu, X.; Kaul, S. An Examination between Census Tract Unhealthy Food Availability and Colorectal Cancer Incidence. Cancer Epidemiol. 2020, 67, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canchola, A.J.; Shariff-Marco, S.; Yang, J.; Albright, C.; Hertz, A.; Park, S.Y.; Gomez, L.S.; Monroe, K.R.; Wilkens, L.R.; Cheng, I.; et al. Association between the Neighborhood Obesogenic Environment and Colorectal Cancer Risk in the Multi-ethnic Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017, 50, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitacek, E.J.; Brunnemann, K.D.; Suttajit, M.; Caplan, L.S.; Gagna, C.E.; Bhothisuwan, K.; Siriamornpun, S.; Hummel, C.F.; Ohshima, H.; Roy, R.; et al. Geographic Distribution of Liver and Stomach Cancers in Thailand in Relation to Estimated Dietary Intake of Nitrate, Nitrite, and Nitrosodimethylamine. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, A.; Polsky, J.Y.; Robitaille, E.; Lefebvre, M.; McBrien, T.; Minaker, M.L. Status Report-Geographic Retail Food Environment Measures for Use in Public Health. Health Promot. Chronic Dis. Prev. Can. 2017, 37, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, M.A.; Anderson, W.F.; Altekruse, S.; Penberthy, L.; Sherman, M.E. The Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program and Pathology: Toward Strengthening the Critical Relationship. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, e94–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Lloyd, S.; Decker, R.H.; Wilson, L.D.; Yu, J.B. Overview of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Database: Evolution, Data Variables, and Quality Assurance. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2012, 36, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enewold, L.; Parsons, H.; Zhao, L.; Bott, D.; Rivera, D.R.; Barrett, M.J.; Virnig, B.A.; Warren, J.L. Updated Overview of the SEER-Medicare Data: Enhanced Content and Applications. JNCI Monogr. 2020, 2020, 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- VoPham, T.; Bertrand, K.A.; Tamimi, R.M.; Laden, F.; Hart, J.E. Ambient PM2.5 Air Pollution Exposure and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in the United States. Cancer Causes Control 2018, 29, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VoPham, T.; Hart, J.E.; Bertrand, K.A.; Sun, Z.; Tamimi, R.M.; Laden, F. Spatiotemporal Exposure Modeling of Ambient Erythemal Ultraviolet Radiation. Environ. Health 2016, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritz, A.; Percy, C.; Shanmugaratnam, K.; Sobin, L.; Parkin, D.M.; Whelan, S. International Classification of Diseases for Oncology (ICD-O-3); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- VoPham, T.; Weaver, M.D.; Vetter, C.; Tamimi, R.M.; Laden, F.; Bertrand, K.A.; Hart, E.J. Circadian Misalignment and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Census Tract Level State Maps of the Modified Retail Food Environment Index (mRFEI); Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013.
- Food Environment Atlas; U.S. Department of Agriculture Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Carr, B. Heptaocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Treatment; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kauhl, B.; Heil, J.; Hoebe, C.J.P.A.; Schweikart, J.; Krafft, T.; Dukers-Muijrers, N.H.T.M. The Spatial Distribution of Hepatitis C Virus Infections and Associated Determinants—An Application of a Geographically Weighted Poisson Regression for Evidence-Based Screening Interventions in Hotspots. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results: County Attributes; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2019.
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Flaxman, A.D.; Ng, M.; Hansen, G.M.; Murray, C.J.L.; Mokdad, A.H. Drinking Patterns in US Counties From 2002 to 2012. Am. J. Public Health 2015, 105, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Srebotnjak, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Hansen, G.M.; Murray, C.J. Cigarette Smoking Prevalence in US Counties: 1996–2012. Popul. Health Metr. 2014, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Diabetes Prevalence by County in the U.S., 1999–2012; Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation: Seattle, WA, USA, 2016.
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; MacKenbach, J.P.; Van Lenthe, F.J.; Flaxman, A.D.; Mokdad, A.H. Diagnosed and Undiagnosed Diabetes Prevalence by County in the U.S., 1999–2012. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer-Lindgren, L.; Freedman, G.; Engell, E.R.; Fleming, T.D.; Lim, S.S.; Murray, C.J.; Mokdad, A.H. Prevalence of Physical Activity and Obesity in US Counties, 2001–2011: A Road Map for Action. Popul. Health Metr. 2013, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridged-Race Population Estimates 1990–2014; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2018.
- Liu, B.; Widener, M.; Burgoine, T.; Hammond, D. Association between Time-weighted Activity Space-based Exposures to Fast Food Outlets and Fast Food Consumption among Young Adults in Urban Canada. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, S.L.; Shariff-Marco, S.; De Rouen, M.; Keegan, T.H.M.; Yen, I.H.; Mujahid, M.; Satariano, W.A.; Glaser, S.L. The Impact of Neighborhood Social and Built Environment Factors Across the Cancer Continuum: Current Research, Methodological Considerations, and Future Directions. Cancer 2015, 121, 2314–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodor, J.N.; Rose, D.; Farley, A.T.; Swalm, C.; Scott, S.K. Neighbourhood Fruit and Vegetable Availability and Consumption: The Role of Small Food Stores in an Urban Environment. Public Health Nutr. 2008, 11, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheadle, A.; Psaty, B.M.; Curry, S.; Wagner, E.; Diehr, P.; Koepsell, T.; Kristal, A. Community-level Comparisons between the Grocery Store Environment and Individual Dietary Practices. Prev. Med. 1991, 20, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.V.; Roux, A.V.D.; Brines, S. Comparing Perception-Based and Geographic Information System (GIS)-Based Characterizations of the Local Food Environment. J. Hered. 2008, 85, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, D.; Richards, R. Food Store Access and Household Fruit and Vegetable Use among Participants in the US Food Stamp Program. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuirt, J.T.; Pitts, S.B.J.; Gustafson, A. Association between Spatial Access to Food Outlets, Frequency of Grocery Shopping, and Objectively-Assessed and Self-Reported Fruit and Vegetable Consumption. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erinosho, T.O.; Oh, A.; Moser, R.; Davis, K.; Nebeling, L.; Yaroch, A. Association Between Perceived Food Environment and Self-Efficacy for Fruit and Vegetable Consumption Among US Adults, 2007. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2011, 9, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, G.-Y.; He, G.; Ali, S.R.; Holzer, R.G.; Österreicher, C.H.; Takahashi, H.; Karin, M. Dietary and Genetic Obesity Promote Liver Inflammation and Tumorigenesis by Enhancing IL-6 and TNF Expression. Cell 2010, 140, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, F.D.; Myers, G.C.; Angel, J.L.; Galle, O.R. Geographic Concentration, Migration, and Population Redistribution Among the Elderly. In Demography of Aging; Martin, L.G., Preston, S.H., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Howden, L.M.; Meyer, J.A. Age and Sex Composition: 2010. In 2010 Census Briefs. 2011; United States Census Bureau: Suitland, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Humes, K.R.; Jones, N.A.; Ramirez, R.R. Overview of Race and Hispanic Origin: 2010; US Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Le, A.; Judd, S.E.; Allison, D.B.; Oza-Frank, R.; Affuso, O.; Safford, M.M.; Howard, V.J.; Howard, G. The Geographic Distribution of Obesity in the US and the Potential Regional Differences in Misreporting of Obesity. Obesity 2013, 22, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, L.E.; Kirtland, K.A.; Gregg, E.W.; Geiss, L.S.; Thompson, T.J. Geographic Distribution of Diagnosed Diabetes in the U.S.: A Diabetes Belt. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2011, 40, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, W.C. Categorizing US State Drinking Practices and Consumption Trends. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, E.S.; Rosenthal, E.; Hall, E.W.; Barker, L.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Sullivan, P.S.; Dietz, P.; Mermin, J.; Ryerson, A.B. Prevalence of Hepatitis C Virus Infection in US States and the District of Columbia, 2013 to 2016. JAMA Netw. Open 2018, 1, e186371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.L.; Thrift, A.P.; Kanwal, F.; Davila, J.; El-Serag, H.B. Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in All 50 United States, From 2000 Through 2012. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davila, A.J.; Petersena, N.J.; Nelson, A.H.; El-Serag, H.B. Geographic Variation within the United States in the Incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2003, 56, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulton, C.J.; Korbin, J.; Chan, T.; Su, M. Mapping Residents’ Perceptions of Neighborhood Boundaries: A Methodological Note. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2001, 29, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulton, C.J.; Jennings, M.Z.; Chan, T. How Big is My Neighborhood? Individual and Contextual Effects on Perceptions of Neighborhood Scale. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2012, 51, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagami, S.; Cohen, D.A.; Brown, A.F.; Asch, S.M. Body Mass Index, Neighborhood Fast Food and Restaurant Concentration, and Car Ownership. J. Hered. 2009, 86, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VoPham, T.; Brooks, M.M.; Yuan, J.-M.; Talbott, E.O.; Ruddell, D.; Hart, J.E.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Weissfeld, J.L. Pesticide Exposure and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk: A Case-control Study Using a Geographic Information System (GIS) to Link SEER-Medicare and California Pesticide Data. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VoPham, T.; Bertrand, K.A.; Hart, J.E.; Laden, F.; Brooks, M.M.; Yuan, J.-M.; Talbott, E.O.; Ruddell, D.; Chang, C.-C.H.; Weissfeld, J.L. Pesticide Exposure and Liver Cancer: A Review. Cancer Causes Control. 2017, 28, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicotera, N. Measuring Neighborhood: A Conundrum for Human Services Researchers and Practitioners. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2007, 40, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainham, D.; McDowell, I.; Krewski, D.; Sawada, M. Conceptualizing the Healthscape: Contributions of Time Geography, Location Technologies and Spatial Ecology to Place and Health Research. Soc. Sci. Med. 2010, 70, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, J.J.; Abdelbary, B.; Klaas, K.; Tapia, B.; Sexton, K. Socioeconomic Context and the Food Landscape in Texas: Results from Hotspot Analysis and Border/Non-Border Comparison of Unhealthy Food Environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 5640–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Howard, V.; Harrington, K.F.; Creger, T.; Judd, S.E.; Fontaine, K.R. Does Adherence to Mediterranean Diet Mediate the Association Between Food Environment and Obesity Among Non-Hispanic Black and White Older US Adults? A Path Analysis. Am. J. Health Promot. 2020, 34, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alter, M.J. Epidemiology of Hepatitis C Virus Infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Story, M.; Kaphingst, K.M.; Robinson-O’Brien, R.; Glanz, K. Creating Healthy Food and Eating Environments: Policy and Environmental Approaches. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2008, 29, 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Individual-level | 90,578 |
| Age at diagnosis (years) (mean ± SD) | 62.7 ± 11.5 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 70,167 (77.5) |
| Female | 20,411 (22.5) |
| Race/ethnicity | |
| Non-Hispanic white | 45,404 (50.0) |
| Non-Hispanic black | 12,841 (14.2) |
| Hispanic | 17,804 (19.7) |
| Non-Hispanic Asian or Pacific Islander | 13,713 (15.1) |
| Non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native | 816 (0.9) |
| Year of diagnosis | |
| 2000–2007 | 32,362 (35.7) |
| 2008–2016 | 58,216 (64.3) |
| County-level | 727 |
| mRFEI † (mean ± SD) | 16.9 ± 8.3 |
| Percent alcohol consumption (mean ± SD) | 8.4 ± 2.4 |
| Percent smoking (mean ± SD) | 29.0 ± 4.9 |
| Percent obese (mean ± SD) | 28.4 ± 3.6 |
| Percent diabetes (mean ± SD) | 12.2 ± 1.6 |
| Median household income ($10,000) (mean ± SD) | 36.3 ± 10.3 |
| Percent bachelor’s degree or higher (mean ± SD) | 16.9 ± 8.7 |
| Percent unemployed (mean ± SD) | 6.3 ± 2.6 |
| Percent poverty (mean ± SD) | 15.1 ± 7.2 |
| Percent foreign-born (mean ± SD) | 4.6 ± 6.4 |
| Urbanicity | |
| Urban | 614 (84.5) |
| Rural | 113 (15.5) |
| Region | |
| Northeast | 31,628 (34.9) |
| South | 12,387 (13.7) |
| Midwest | 4835 (5.3) |
| West | 41,728 (46.1) |
| mRFEI † Exposure | N Cases | Basic ‡ | Fully Adjusted § | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRR (95% CI) | p | IRR (95% CI) | p | ||
| mRFEI (per IQR increase) ¶ | 90,578 | 1.00 (0.97, 1.03) | 0.97 | 0.99 (0.96, 1.01) | 0.36 |
| mRFEI quintiles | 0.99 | 0.69 | |||
| Quintile 1 (<10.67) | 18,857 | Referent | Referent | ||
| Quintile 2 (10.67–12.99) | 38,519 | 1.04 (0.97, 1.12) | 1.00 (0.95, 1.05) | ||
| Quintile 3 (>12.99–16.67) | 18,088 | 1.04 (0.96, 1.13) | 1.01 (0.96, 1.07) | ||
| Quintile 4 (>16.67–22.22) | 5125 | 0.94 (0.87, 1.02) | 0.97 (0.90, 1.04) | ||
| Quintile 5 (>22.22) | 9989 | 1.03 (0.93, 1.14) | 0.98 (0.87, 1.10) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ton, M.; Widener, M.J.; James, P.; VoPham, T. Food Environments and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115740
Ton M, Widener MJ, James P, VoPham T. Food Environments and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(11):5740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115740
Chicago/Turabian StyleTon, Mimi, Michael J. Widener, Peter James, and Trang VoPham. 2021. "Food Environments and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 11: 5740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115740
APA StyleTon, M., Widener, M. J., James, P., & VoPham, T. (2021). Food Environments and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11), 5740. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18115740






