Investigating the Dynamics of China’s Green Building Policy Development from 1986 to 2019
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
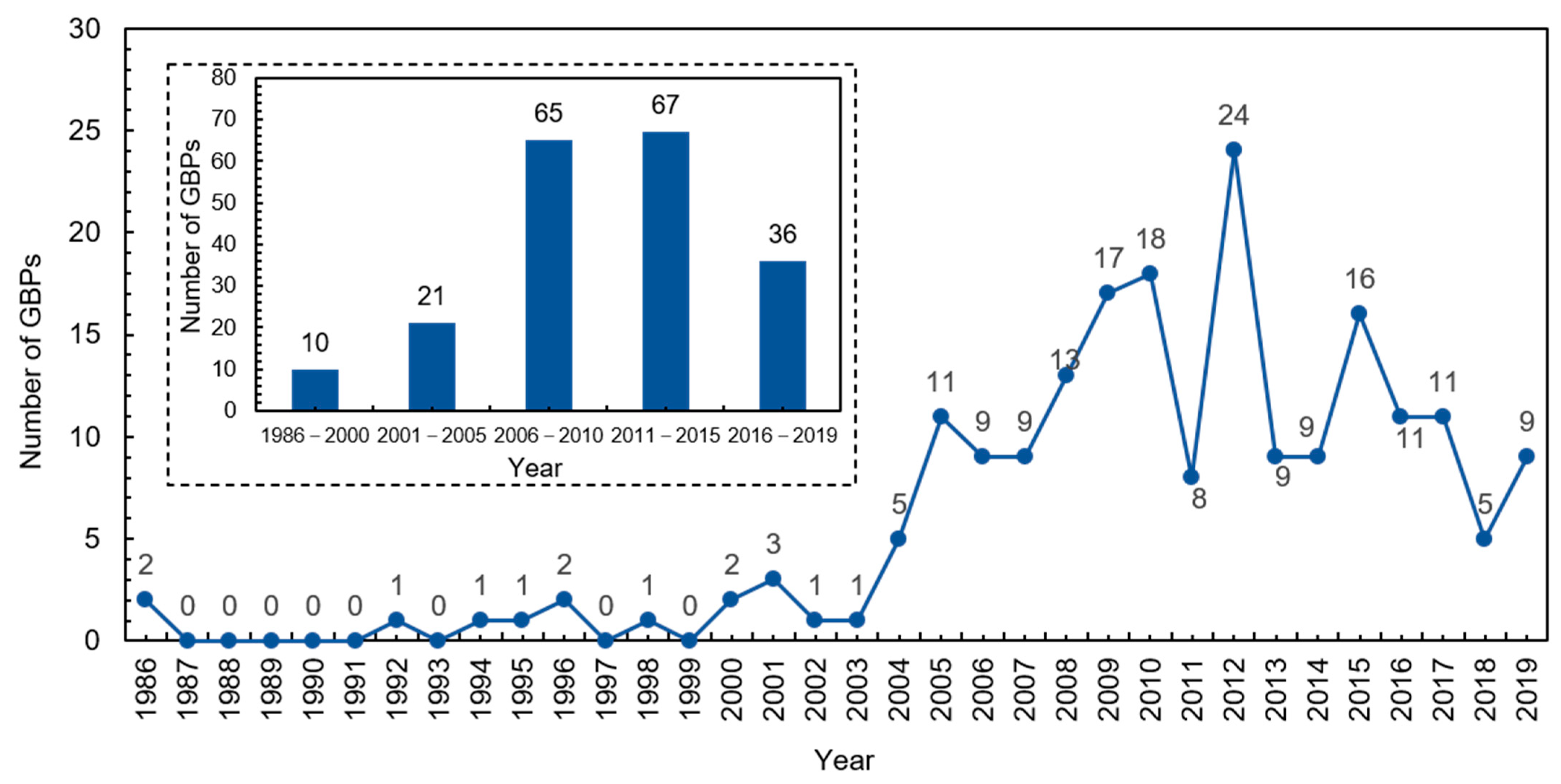
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.2.2. Text Mining
3. Results
3.1. GBP Topics in Different Stages
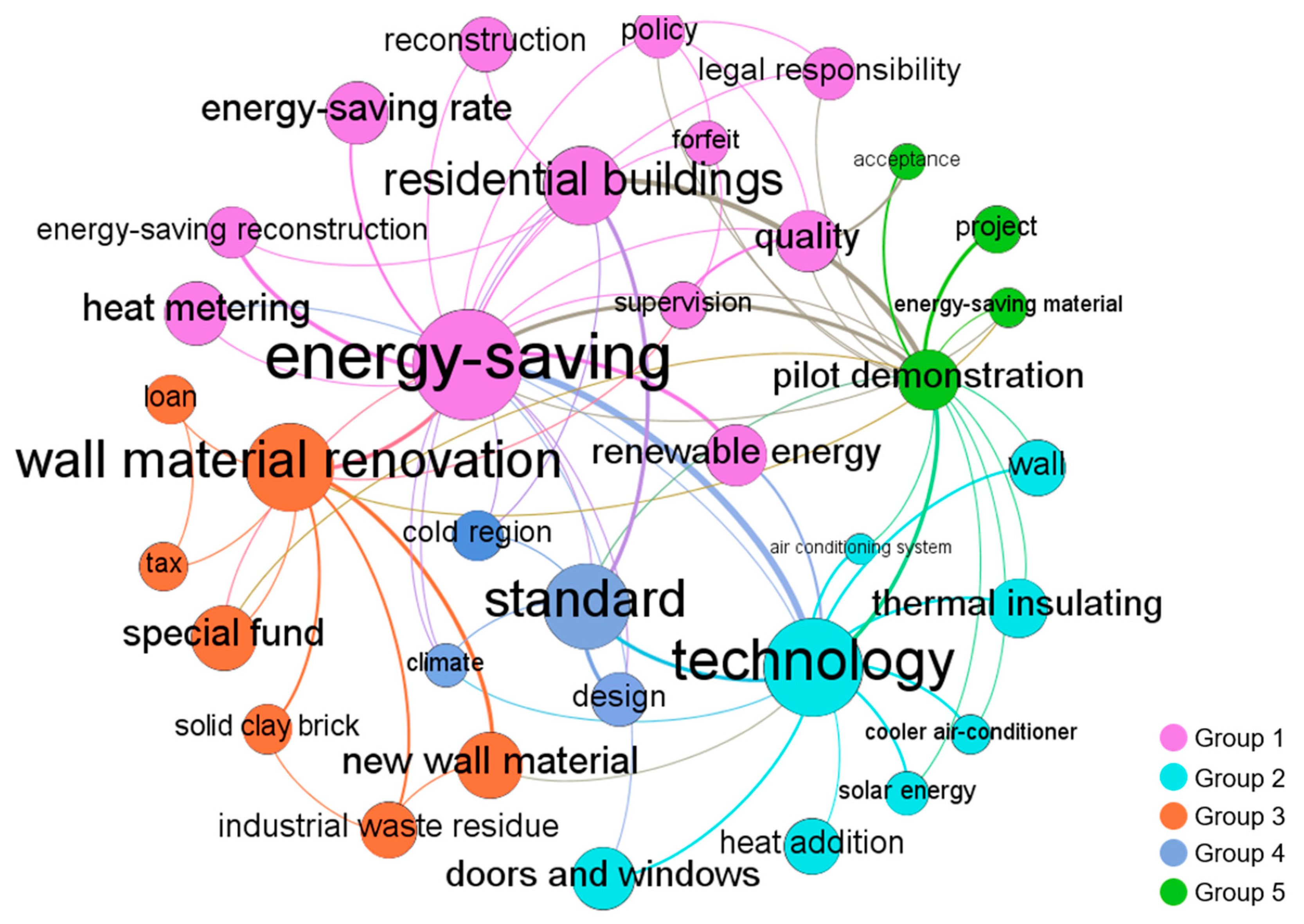
3.1.1. Topics Discovered in Stage 1 (1986–2000)
3.1.2. Topics Discovered in Stage 2 (2001–2005)
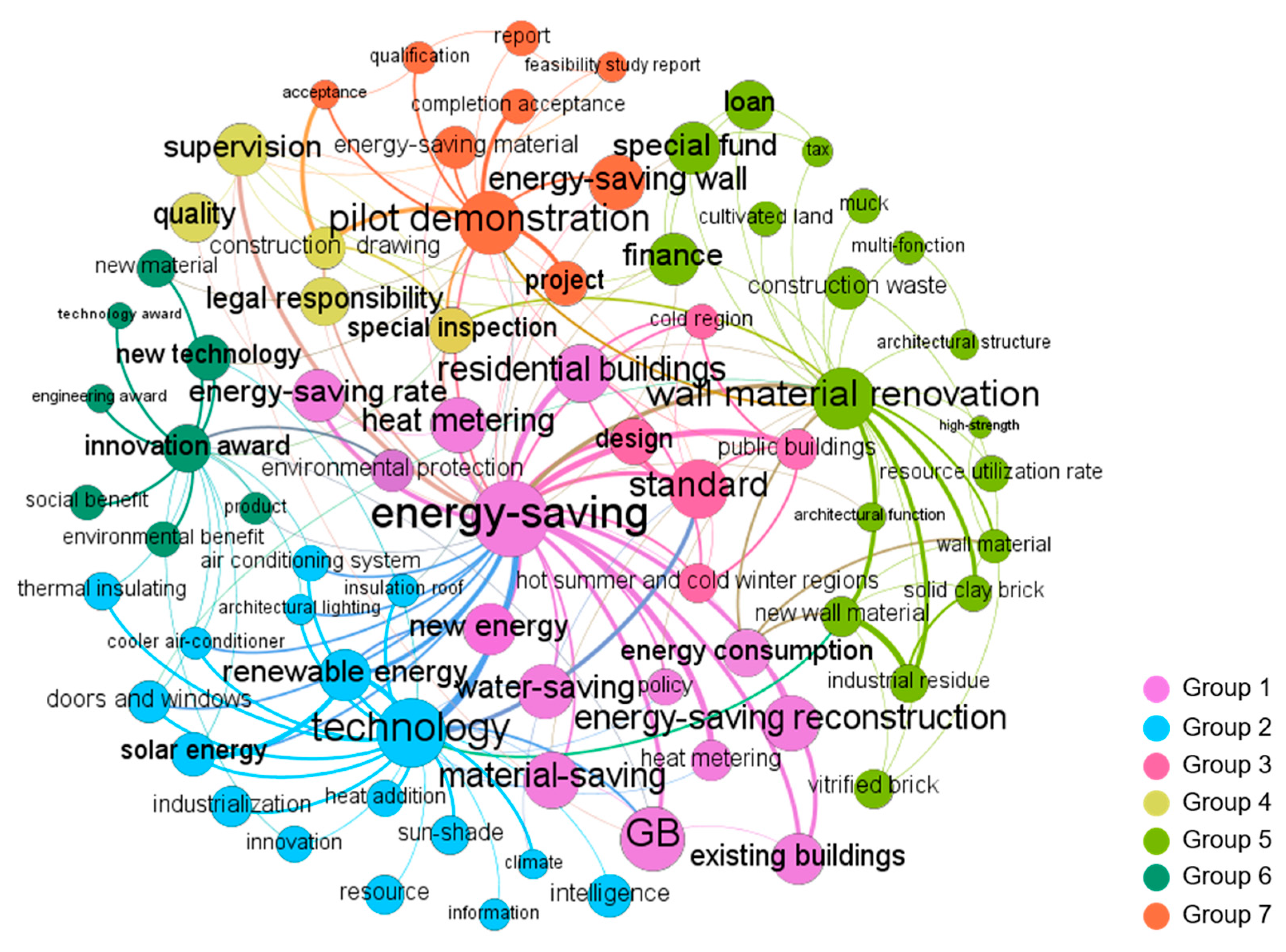
3.1.3. Topics Discovered in Stage 3 (2006–2010)
3.1.4. Topics Discovered in Stage 4 (2011–2015)
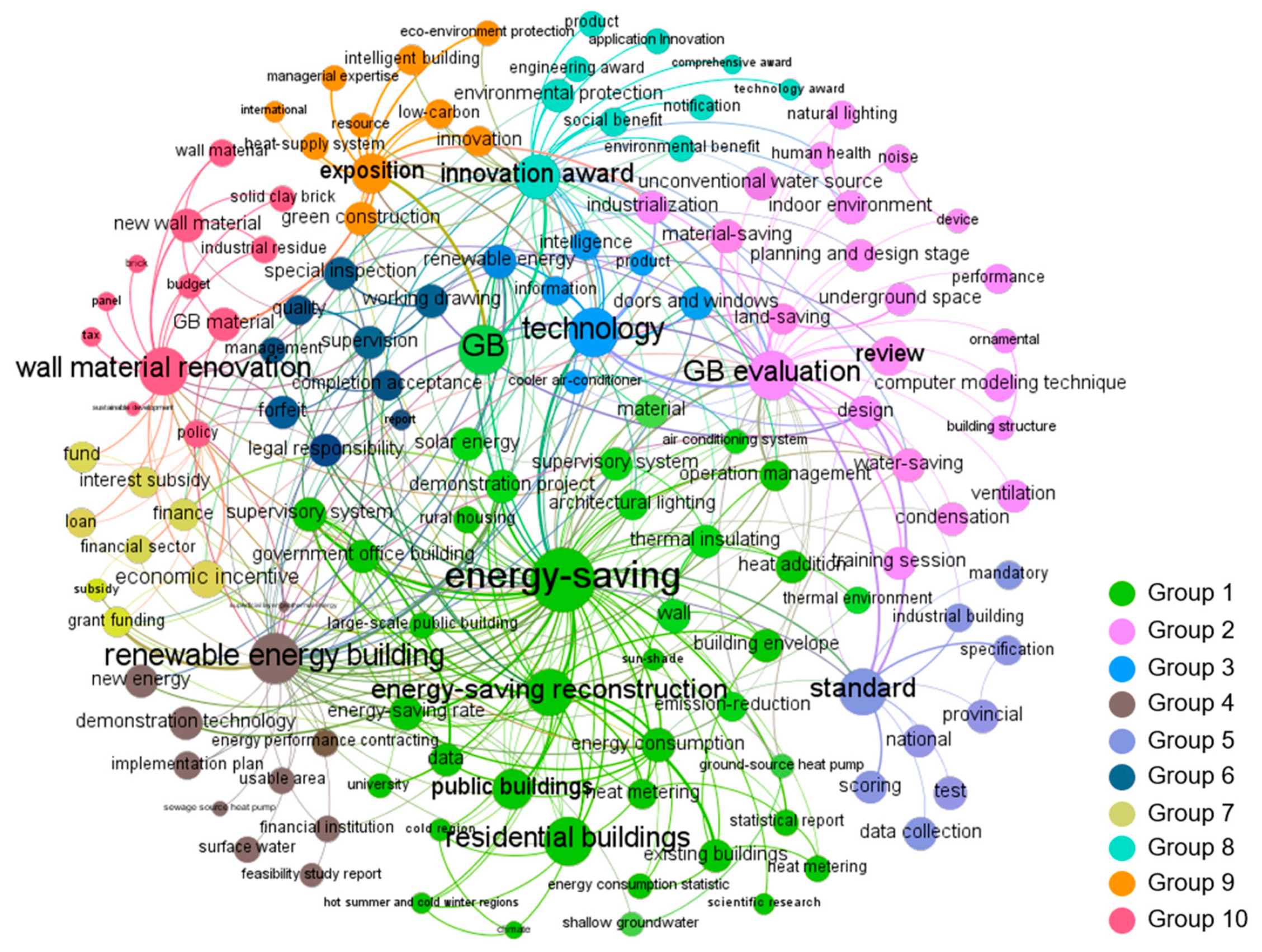
3.1.5. Topics Discovered in Stage 5 (2016–2019)
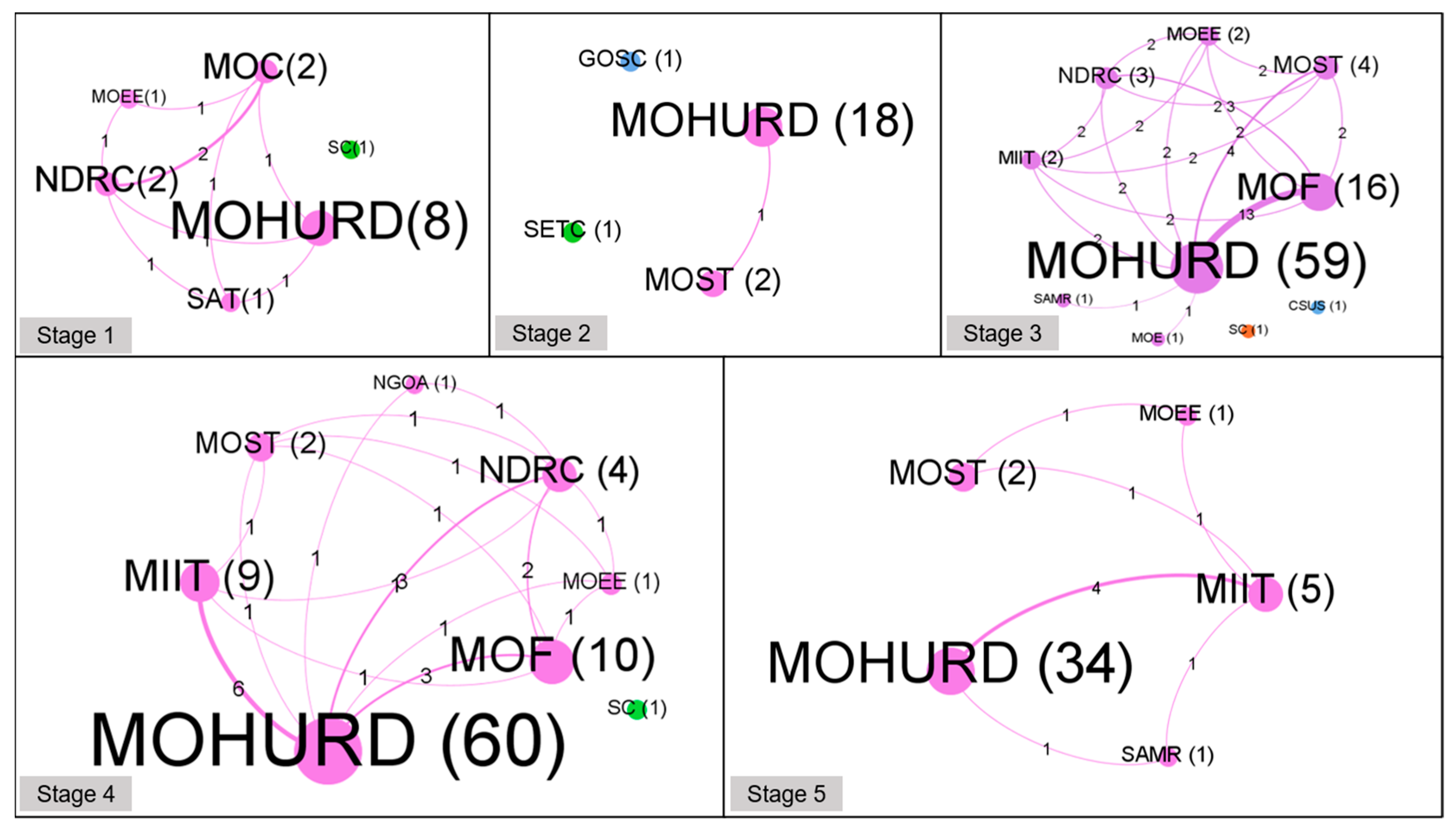
3.2. GB Policymaking Agencies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.A.; Yang, L.; He, B.J.; Zhao, D.D. Green building in China: Needs great promotion. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2014, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Zhao, Z. Green building research-current status and future agenda: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.W.; Poon, C.S. An off-site snapshot methodology for estimating building construction waste composition—A case study of Hong Kong. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 77, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.Z.; Peng, C.; Xu, Y.L. Changes of energy consumption with economic development when an economy becomes more productive. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Edziah, B.K.; Sun, C.; Kporsu, A.K. Institutional quality, green innovation and energy efficiency. Energy Policy 2019, 135, 111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, A.G.; Palazzo, G.; Seidl, D. Managing legitimacy in complex and heterogeneous environments: Sustainable development in a globalized world. J. Manag. Stud. 2013, 50, 259–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, C.R.S.; Palaniappan, S. Comparision of green building rating schemes used in North America, Europe and Asia. Habitat Int. 2019, 89, 101989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opoku, A. Biodiversity and the built environment: Implications for the sustainable development goals (SDGs). Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 141, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, R.; Samanta, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Pariari, A.; Majumdar, D.; Satpati, B.; Wang, L.; Singha, A.; Mandal, P. Probing lattice dynamics and electron-phonon coupling in the topological nodal-line semimetal ZrSiS. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 97, 94112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.W.; Wang, H.; Wei, Y.; Huo, X. Driving factors for construction waste minimization: Empirical studies in Hong Kong and Shenzhen. J. Green Build. 2019, 14, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamouris, M. Innovating to zero the building sector in Europe: Minimising the energy consumption, eradication of the energy poverty and mitigating the local climate change. Sol. Energy 2016, 128, 61–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Musa, S.N.; Onn, C.C.; Ramesh, S.; Liang, L.; Wang, W.; Ma, K. The role and contribution of green buildings on sustainable development goals. Build. Environ. 2020, 107091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyas, G.S.; Jha, K.N. What does it cost to convert a non-rated building into a green building? Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 36, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Jiang, M.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, S. What Hinders the Development of Green Building? An Investigation of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, T.; Tao, Y. Influential factors of national and regional CO2 emission in China based on combined model of DPSIR and PLS-SEM. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 698–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Lee, W.M.; Lu, W. Implementing on-site construction waste recycling in Hong Kong: Barriers and facilitators. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Zhang, C.; Chan, A.P.C. Drivers for green building: A review of empirical studies. Habitat Int. 2017, 60, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Olanipekun, A.O.; Bai, L. A successful delivery process of green buildings: The project owners’ view, motivation and commitment. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, O.; Puppim de Oliveira, J.A. Sustainable buildings for healthier cities: Assessing the co-benefits of green buildings in Japan. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 163, S68–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubunmi, O.A.; Xia, P.B.; Skitmore, M. Green building incentives: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; Hwang, B.-g. Green building rating systems: Global reviews of practices and research efforts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M. Development of a ‘green building sustainability model’ for green buildings in India. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 190, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yu, T.; Guo, L. Understanding Stakeholders’ Influence on Project Success with a New SNA Method: A Case Study of the Green Retrofit in China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kang, J.; Jin, H. A review of green building development in China from the perspective of energy saving. Energies 2018, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOHURD. 12th Five-Year Plan for Green Building Development Plan. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2013-04/18/content_2380994.htm (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Investigating the Crucial Aspects of Developing a Healthy Dormitory based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs—A Case Study of Shenzhen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, R.d.; Soebarto, V.; Zhao, Z.y.; Zillante, G. Facilitating the transition to sustainable construction: China’s policies. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 131, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Lai, X.; Xie, X.; Zuo, J. Assessment of green building policies-A fuzzy impact matrix approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 36, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Tan, Y.; Li, X. China’s policies of building green retrofit: A state-of-the-art overview. Build. Environ. 2020, 169, 106554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lin, H.; Lin, C.; Liu, B. Developments of green building standards in China. Renew. Energy 2015, 73, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Xue, X.L.; Yu, T.; Wang, Y.W. Mapping the dynamics of China’s prefabricated building policies from 1956 to 2019: A bibliometric analysis. Build. Res. Inf. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Xue, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, X.; Shang, S. New media data-driven measurement for the development level of prefabricated construction in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C. Critical analysis of green building research trend in construction journals. Habitat Int. 2016, 57, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Huo, X.; Owusu-Manu, D.-G. A scientometric analysis and visualization of global green building research. Build. Environ. 2019, 149, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dat Tien, D.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Naismith, N.; Zhang, T.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A.; Tookey, J. A critical comparison of green building rating systems. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Fu, H. Visualized analysis of knowledge development in green building based on bibliographic data mining. J. Supercomput. 2020, 76, 3266–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y. Comparison of evaluation standards for green building in China, Britain, United States. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zuo, J. Transition to low carbon energy policies in China-from the Five-Year Plan perspective. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 3855–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.-G. The Five-Year Plan: A new tool for energy saving and emissions reduction in China. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2016, 7, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupic, I.; Cater, T. Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ. Res. Methods 2015, 18, 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, C.; Su, J. A bibliometrics-based research framework for exploring policy evolution: A case study of China’s information technology policies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 157, 120116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, Q.; Zhong, D.; Ye, X. The pattern of policy change on disaster management in China: A bibliometric analysis of policy documents, 1949–2016. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2018, 9, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Su, J.; Xie, X.; Ye, X.; Li, Z.; Porter, A.; Li, J. A bibliometric study of China’s science and technology policies: 1949–2010. Scientometrics 2015, 102, 1521–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanra, S.; Dhir, A.; Mantymaki, M. Big data analytics and enterprises: A bibliometric synthesis of the literature. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2020, 14, 737–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, H. Improving the co-word analysis method based on semantic distance. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.-H. Corporate social responsibility for supply chain management: A literature review and bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 158, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, N.; Brown, M.A.; Peng, Y.; Shuai, Y. A bibliographic analysis of recent solar energy literatures: The expansion and evolution of a research field. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Li, B.; Brown, M.A.; Mao, G.; Rameezdeen, R.; Chen, H. Expanding and shifting trends in carbon market research: A quantitative bibliometric study. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 103, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, M.; Ho, Y. Trends in research on global climate change: A science citation index expanded-based analysis. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2011, 77, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Feng, T.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X. Understanding aging policies in China: A bibliometric analysis of policy documents, 1978–2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhang, C. A bibliometric study of China’s resource recycling industry policies: 1978–2016. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 134, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, J.; Kittas, A.; Bennett, L.; Tsoka, S. DyCoNet: A Gephi plugin for community detection in dynamic complex networks. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Liu, Y.; Ju, Y.B. Sustainable public procurement policies on promoting scientific and technological innovation in China: Comparisons with the US, the UK, Japan, Germany, France, and South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Fan, C. A thematic network-based methodology for the research trend identification in building energy management. Energies 2020, 13, 4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.K.; Li, Z.J.; Fan, C. Building energy savings: Analysis of research trends based on text mining. Autom. Constr. 2018, 96, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOHURD. Ninth Five-Year Plan and the 2010 Plan for Building Energy-Saving. Available online: http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SGJS608.000.htm (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- MOHURD. Outline of the 10th Five-Year Plan for Building Energy Saving. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/200611/t20061101_158478.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Ma, M.; Cai, W.; Wu, Y. China act on the energy efficiency of civil buildings (2008): A decade review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOHURD. 11th Five-Year Plan for Building Energy Conservation Task. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2010-05/18/content_1608438.htm (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Kong, X.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y. A Review of Building Energy Efficiency in China during “Eleventh Five-Year Plan” Period. Energy Policy 2012, 41, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhu, N. Measures to enforce mandatory civil building energy efficiency codes in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 119, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MOHURD; MOF. Implementation Opinions on Promoting the Application of Renewable Energy in the Building Sector. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/200611/t20061101_158510.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- MOHURD; MOF. Implementation Opinions on Accelerating the Development of Green Buildings in China. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/fgjs/xgbwgz/201205/t20120510_209831.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- MOHURD. Green Building and Green Ecological Urban Development Planning. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201304/t20130412_213405.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- MOHURD. 13th Five-Year Plan for Building Energy Saving and Green Buildings Development. Available online: http://www.mohurd.gov.cn/wjfb/201703/t20170314_230978.html (accessed on 18 September 2020).
- Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, W. Impact of zero energy buildings on medium-to-long term building energy consumption in China. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yu, A.T.W.; Shen, L. Investigating the determinants of contractor’s construction and demolition waste management behavior in Mainland China. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Ji, W.; Wang, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhu, Y. A review of operating performance in green buildings: Energy use, indoor environmental quality and occupant satisfaction. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 500–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Shui, B. A comprehensive analysis of building energy efficiency policies in China: Status quo and development perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 326–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Government Department | Abbreviations | Description | No. of GBPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development | MOHURD | Government department | 180 |
| Ministry of Finance | MOF | Government department | 25 |
| Ministry of Industry and Information Technology | MIIT | Government department | 16 |
| Ministry of Science and Technology | MOST | Government department | 9 |
| National Development and Reform Commission | NDRC | Government department | 8 |
| Ministry of Ecology and Environment | MOEE | Government department | 4 |
| State Council | SC | The highest organ of state administration | 4 |
| State Administration of Market Regulation | SAMR | Government department | 3 |
| Ministry of Commerce | MOC | Government department | 2 |
| State Economic and Trade Commission | SETC | Government department | 1 |
| Chinese Society of Urban Science | CSUS | Social organization | 1 |
| State Administration of Taxation | SAT | Government department | 1 |
| National Government Offices Administration | NGOA | Government department | 1 |
| Ministry of Education | MOE | Government department | 1 |
| Stage 1 (1986–2000) | Stage 2 (2001–2005) | Stage 3 (2006–2010) | Stage 4 (2011–2015) | Stage 5 (2016–2019) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Policy targets |
|
|
|
|
|
| Policy objects |
|
|
|
|
|
| Policy instruments | DP/RP | DP/RP/FP/SP/KI | DP/RP/EP/FP/SP/OP/KI | DP/RP/EP/FP/SP/OP/KI | DP/RP/EP/FP/SP/OP/KI |
| GB performance indicators |
|
|
|
|
|
| Collaboration structure | Some agencies with close collaboration | Few agencies with simple collaboration | More agencies with complex and close collaboration | More agencies with decreased and decentralized collaboration | Few agencies with centralized collaboration |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; He, Q.; Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, K. Investigating the Dynamics of China’s Green Building Policy Development from 1986 to 2019. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010196
Wu Z, He Q, Yang K, Zhang J, Xu K. Investigating the Dynamics of China’s Green Building Policy Development from 1986 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(1):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010196
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zezhou, Qiufeng He, Kaijie Yang, Jinming Zhang, and Kexi Xu. 2021. "Investigating the Dynamics of China’s Green Building Policy Development from 1986 to 2019" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18, no. 1: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010196
APA StyleWu, Z., He, Q., Yang, K., Zhang, J., & Xu, K. (2021). Investigating the Dynamics of China’s Green Building Policy Development from 1986 to 2019. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(1), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18010196






