Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
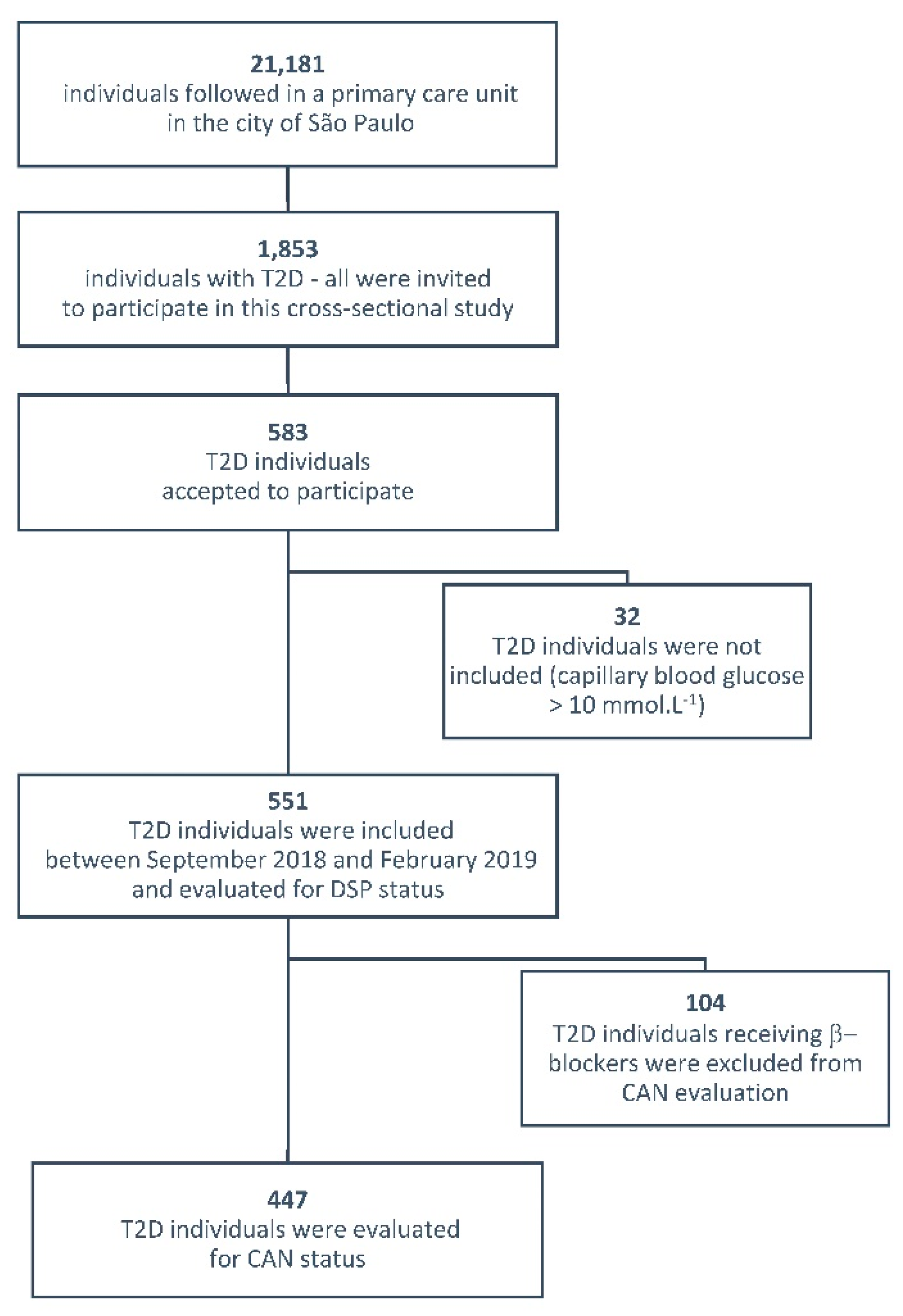
2. Methods
2.1. Participants and Evaluation of DSP and CAN
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boulton, A.J.; Malik, R.A.; Arezzo, J.C.; Sosenko, J.M. Diabetic somatic neuropathies. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1458–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.L.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.A.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.C.; Price, R.S.; Feldman, E.L. Distal Symmetric Polyneuropathy: A Review. JAMA 2015, 314, 2172–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinik, A.I.; Freeman, R.; Erbas, T. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Semin. Neurol. 2003, 23, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valensi, P.; Sachs, R.N.; Harfouche, B.; Lormeau, B.; Paries, J.; Cosson, E.; Paycha, F.; Leutenegger, M.; Attali, J.R. Predictive value of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetic patients with or without silent myocardial ischemia. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maser, R.E.; Mitchell, B.D.; Vinik, A.I.; Freeman, R. The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F.; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.O.; Castro, A.P.; Papelbaum, M.; Appolinário, J.C.; Ellinger, V.C.; Coutinho, W.F.; Zagury, L. Translation into Portuguese and assessment of the reliability of a scale for the diagnosis of diabetic distal polyneuropathy. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2005, 49, 944–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulton, A.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Albert, S.F.; Frykberg, R.G.; Hellman, R.; Kirkman, M.S.; Lavery, L.A.; Lemaster, J.W.; Mills, J.L.; Mueller, M.J.; et al. Comprehensive foot examination and risk assessment: A report of the task force of the foot care interest group of the American Diabetes Association, with endorsement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinik, A.I.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation 2007, 115, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agelink, M.W.; Malessa, R.; Baumann, B.; Majewski, T.; Akila, F.; Zeit, T.; Ziegler, D. Standardized tests of heart rate variability: Normal ranges obtained from 309 healthy humans, and effects of age, gender, and heart rate. Clin. Auton. Res. 2001, 11, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.O.; Soldera, A.L.; Cury, B.; Meireles, C.; Kupfer, R. Is cognitive impairment associated with the presence and severity of peripheral neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, T.R.M.; Melo, J.V.; Leite, N.C.; Salles, G.F.; Cardoso, C.R.L. Usefulness of the vibration perception thresholds measurement as a diagnostic method for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Results from the Rio de Janeiro type 2 diabetes cohort study. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2018, 32, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koekkoek, P.S.; Kappelle, L.J.; van den Berg, E.; Rutten, G.E.; Biessels, G.J. Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: Guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.G.; Apolinario, D.; Magaldi, R.M.; Busse, A.L.; Campora, F.; Jacob-Filho, W. Functional health literacy and glycaemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, S.H.; Brito, G.N.; Gomes, M.B. Health literacy skills in type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients from an university-affiliated hospital in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, L.; Molyneaux, L.; Yue, D.K. Insensate versus painful diabetic neuropathy: The effects of height, gender, ethnicity and glycaemic control. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2002, 57, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Griffin, S.J.; Rathmann, W.; Wareham, N.J. How should peripheral neuropathy be assessed in people with diabetes in primary care? A population-based comparison of four measures. Diabet. Med. 2003, 20, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlOlaiwi, L.A.; AlHarbi, T.J.; Tourkmani, A.M. Prevalence of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and gastroparesis symptoms among patients with type 2 diabetes who attend a primary health care center. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, S.T.; Witte, D.R.; Fleischer, J.; Andersen, H.; Lauritzen, T.; Jørgensen, M.E.; Jensen, T.S.; Pop-Busui, R.; Charles, M. Risk Factors for the Presence and Progression of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes: ADDITION-Denmark. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 2586–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottsäter, A.; Ahmed, M.; Fernlund, P.; Sundkvist, G. Autonomic neuropathy in Type 2 diabetic patients is associated with hyperinsulinaemia and hypertriglyceridaemia. Diabet. Med. 1999, 16, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, J.; Yderstraede, K.; Gulichsen, E.; Jakobsen, P.E.; Lervang, H.H.; Eldrup, E.; Nygaard, H.; Tarnow, L.; Ejskjaer, N. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy is associated with macrovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes: New technology used for routine large-scale screening adds new insight. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2014, 8, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Z. An association analysis of lipid profile and diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in a Chinese sample. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moţăţăianu, A.; Maier, S.; Bajko, Z.; Voidazan, S.; Bălaşa, R.; Stoian, A. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spallone, V. Update on the Impact, Diagnosis and Management of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Diabetes: What Is Defined, What Is New, and What Is Unmet. Diabetes Metab. J. 2019, 43, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giovanni, P.; Scampoli, P.; Meo, F.; Cedrone, F.; D’Addezio, M.; Di Martino, G.; Valente, A.; Romano, F.; Staniscia, T. The impact of gender on diabetes-related lower extremity amputations: An Italian regional analysis on trends and predictors. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Demographic, Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics | All Individuals (n = 551) | Without DSP by Monofilament (n = 472) | With DSP by Monofilament (n = 79) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65 (59–72) | 65 (59–72) | 65 (58–73) | 0.97 |
| Sex (% female) | 59.3 | 60 | 53 | 0.24 |
| Ethnicity (C/N/A) (%) | 68/31/1 | 67.7/31.6/0.7 | 67.0/30.4/2.6 | 0.18 |
| Height (cm) | 161 (154–169) | 161 (154–168) | 165 (156–173) | 0.008 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 29 (25.8–33.2) | 29.0 (25.8–32.9) | 29.9 (25.1–34.7) | 0.35 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 102 (94–112) | 102 (94–111) | 103 (92–118) | 0.42 |
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 72 | 71 | 77 | 0.30 |
| Smoking (%) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 0.96 |
| eGFR (mL.min−1.1.73 m2) | 77 (59.6–92.6) | 77.0 (60.0–92.0) | 77.0 (59.0–93.0) | 0.74 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol·L−1) | 5.04 (4.24–5.76) | 5.06 (4.26–5.76) | 4.68 (4.08–5.5) | 0.14 |
| HDL (mmol·L−1) | 1.2 (0.96–1.4) | 1.2 (0.98–1.4) | 1.1 (0.85–1.5) | 0.31 |
| LDL (mmol·L−1) | 2.9 (2.3–3.6) | 3.0 (2.3–3.6) | 2.9 (2.4–3.5) | 0.59 |
| Triglycerides (mmol·L−1) | 1.8 (1.3–2.5) | 1.8 (1.3–2.5) | 1.8 (1.2–2.6) | 0.47 |
| Hypercholesterolemia (%) | 72 | 73 | 67 | 0.30 |
| Diabetes status | ||||
| Diabetes duration (years) | 10 (5–15) | 8.0 (4.0–15.0) | 13.0 (6.0–21.0) | 0.0008 |
| HbA1C (mmol·L−1) | 55 (45–76) | 54 (44–75) | 65 (48–85) | 0.02 |
| eGFR < 60 mL.min−1.1.73 m2 (%) | 23.5 | 23 | 23 | 0.84 |
| DSP by NSS and NDS (%) | 6.3 | 2 | 33 | <0.0001 |
| DSP by monofilament (%) | 14.3 | - | - | - |
| Amputation (%) | 1.6 | 0 | 11.4 | <0.0001 |
| Incipient CAN (%) | 12.5 | 10.0 | 11.4 | 0.91 |
| Definitive CAN (%) | 10 | 12.7 | 11.4 | 0.91 |
| Metformin (%) | 75 | 76 | 68 | 0.13 |
| Sulphonylureas (%) | 35.3 | 36 | 38 | 0.32 |
| NPH insulin (%) | 25 | 23 | 41 | 0.0006 |
| Regular Insulin (%) | 8.3 | 6 | 19 | 0.0001 |
| Statins (%) | 31 | 32 | 32 | 0.91 |
| ACEI (%) | 29 | 29 | 33 | 0.48 |
| ARB (%) | 29.2 | 29 | 25 | 0.49 |
| Beta-blockers (%) | 18.5 | 19 | 18 | 0.74 |
| Fibrates (%) | 4.5 | 4 | 5 | 0.80 |
| Demographic, Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics | All Individuals (n = 447) | Individuals without Definitive CAN (n = 408) | Individuals with Definitive CAN (n = 39) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 65 (59–72) | 65 (59–72) | 62 (56–70) | 0.33 |
| Sex (% female) | 59.1 | 59 | 56 | 0.72 |
| Ethnicity (C/N/A) (%) | 68/31/1 | 68.0/31.0/1.0 | 62.0/33.0/5.0 | 0.36 |
| Height (cm) | 162 (154–169) | 162 (155–169) | 162 (152–166) | 0.56 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 29 (25.7–32.9) | 28.9 (25.6–32.9) | 31.5 (26.4–34.2) | 0.10 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 102 (94–112) | 102 (94–112) | 103 (94–112) | 0.86 |
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 66 | 65 | 80 | 0.06 |
| Smoking (%) | 10 | 10.5 | 7.7 | 0.57 |
| eGFR (mL.min−1.1.73 m2) | 78 (60.5–93.6) | 79 (60.5–93.6) | 75 (60.5–90.8) | 0.32 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol·L−1) | 5.0 (4.3–5.8) | 5.0 (4.3–5.8) | 5.3 (4.9–6.0) | 0.03 |
| HDL mmol·L-1) | 1.2 (1.1–1.4) | 1.2 (1.1–1.4) | 1.2 (0.9–1.4) | 0.70 |
| LDL (mmol·L-1) | 3.0 (2.4–3.7) | 3.0 (2.4–3.7) | 3.3 (2.6–4.0) | 0.13 |
| Triglycerides (mmol·L−1) | 1.8 (1.3–2.5) | 1.8 (1.2–2.4) | 2.1 (1.5–2.7) | 0.07 |
| Hypercholesterolemia (%) | 70 | 68 | 84 | 0.03 |
| Diabetes status | ||||
| Diabetes duration (years) | 8 (4–15) | 8 (4–15) | 11 (6–18) | 0.08 |
| HbA1C (mmol·L−1) | 55 (45–76) | 54 (45–76) | 58 (50–84) | 0.14 |
| eGFR < 60 mL.min−1.1.73 m2 (%) | 21.8 | 22 | 21 | 0.92 |
| DSP by NSS and NDS (%) | 6.9 | 6.6 | 10.3 | 0.39 |
| DSP by monofilament (%) | 14.6 | 14.3 | 18.0 | 0.53 |
| Amputation (%) | 2 | 2 | 2.3 | 0.56 |
| Metformin (%) | 75.8 | 74 | 92 | 0.01 |
| Sulphonylureas (%) | 36 | 35 | 46 | 0.16 |
| NPH insulin (%) | 23 | 23 | 26 | 0.66 |
| Regular Insulin (%) | 7.6 | 8 | 2.6 | 0.21 |
| Statins (%) | 28 | 26 | 41 | 0.05 |
| ACEI (%) | 28.6 | 27 | 38 | 0.15 |
| ARB (%) | 28.2 | 27 | 36 | 0.26 |
| Fibrates (%) | 4.3 | 4 | 10 | 0.05 |
| Risk Factors | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSP by Monofilament | |||
| Male sex | 1.05 | 0.58–1.90 | 0.864 |
| Age | 0.99 | 0.96–1.02 | 0.734 |
| Diabetes duration | 1.05 | 1.02–1.08 | 0.0003 |
| HbA1c | 1.07 | 0.94–1.21 | 0.275 |
| Arterial hypertension | 1.09 | 0.52–2.27 | 0.813 |
| Smoking | 0.77 | 0.28–2.10 | 0.601 |
| Cholesterol | 0.99 | 0.98–1.00 | 0.146 |
| Triglyceride | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.662 |
| HDL-Cholesterol | 0.99 | 0.97–1.01 | 0.643 |
| Waist circumference | 1.01 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.050 |
| CAN | |||
| Male sex | 0.89 | 0.39–2.04 | 0.796 |
| Age | 0.98 | 0.94–1.02 | 0.417 |
| Diabetes duration | 1.01 | 0.96 - 1.05 | 0.631 |
| HbA1c | 1.01 | 0.93–1.29 | 0.265 |
| Arterial hypertension | 3.25 | 1.12–9.39 | 0.016 |
| Smoking | 1.11 | 0.30–4.04 | 0.872 |
| Cholesterol | 1.01 | 1.0007–1.02 | 0.031 |
| Triglyceride | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.683 |
| HDL-Cholesterol | 0.99 | 0.96–1.02 | 0.687 |
| Waist circumference | 0.98 | 0.95–1.00 | 0.191 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis de Matos, M.; Santos-Bezerra, D.P.; Dias Cavalcante, C.d.G.; Xavier de Carvalho, J.; Leite, J.; Neves, J.A.J.; Admoni, S.N.; Passarelli, M.; Parisi, M.C.; Correa-Giannella, M.L. Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093232
Reis de Matos M, Santos-Bezerra DP, Dias Cavalcante CdG, Xavier de Carvalho J, Leite J, Neves JAJ, Admoni SN, Passarelli M, Parisi MC, Correa-Giannella ML. Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(9):3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093232
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis de Matos, Mozania, Daniele Pereira Santos-Bezerra, Cristiane das Graças Dias Cavalcante, Jacira Xavier de Carvalho, Juliana Leite, Jose Antonio Januario Neves, Sharon Nina Admoni, Marisa Passarelli, Maria Candida Parisi, and Maria Lucia Correa-Giannella. 2020. "Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 9: 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093232
APA StyleReis de Matos, M., Santos-Bezerra, D. P., Dias Cavalcante, C. d. G., Xavier de Carvalho, J., Leite, J., Neves, J. A. J., Admoni, S. N., Passarelli, M., Parisi, M. C., & Correa-Giannella, M. L. (2020). Distal Symmetric and Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathies in Brazilian Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Followed in a Primary Health Care Unit: A Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(9), 3232. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17093232




