Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice and Related Factors in the AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects and Groups
2.2. Modeling Depression in Mice
2.3. Behavioral Assessment
2.4. Aerobic Exercise Plan
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. Diagnostic Assay
2.6.1. Western Blot
2.6.2. Realtime-PCR
2.6.3. Elisa
2.7. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Weight Results
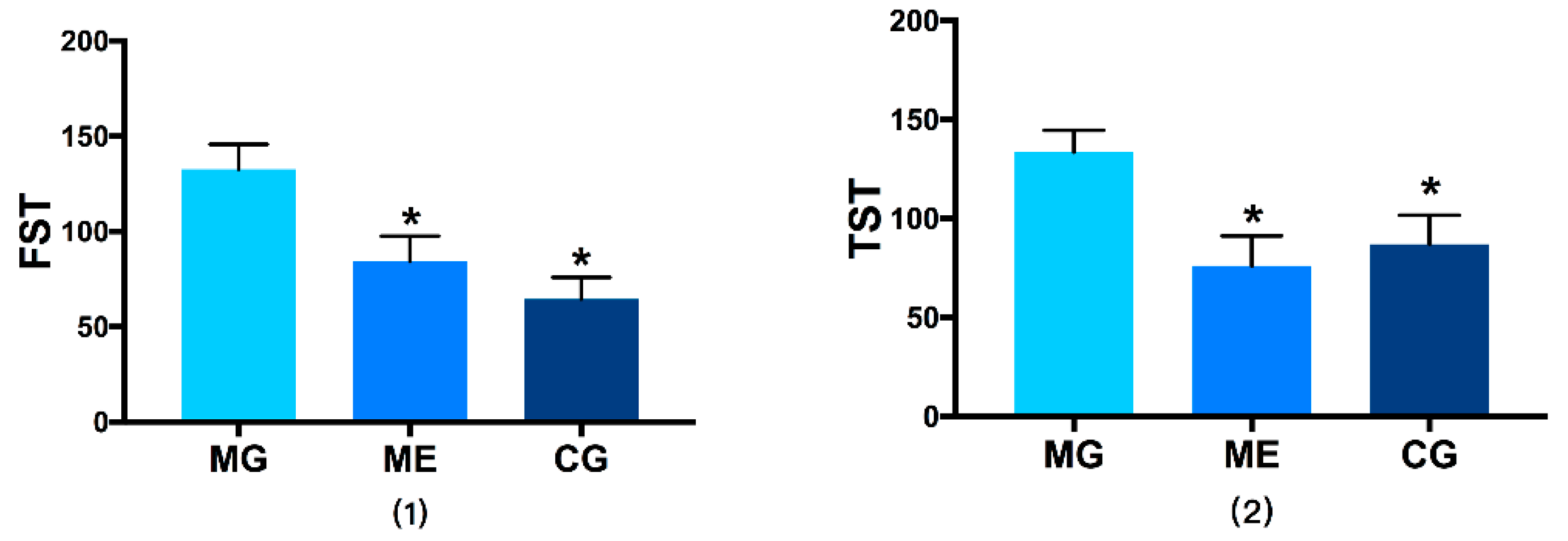
3.2. Behavioral Results
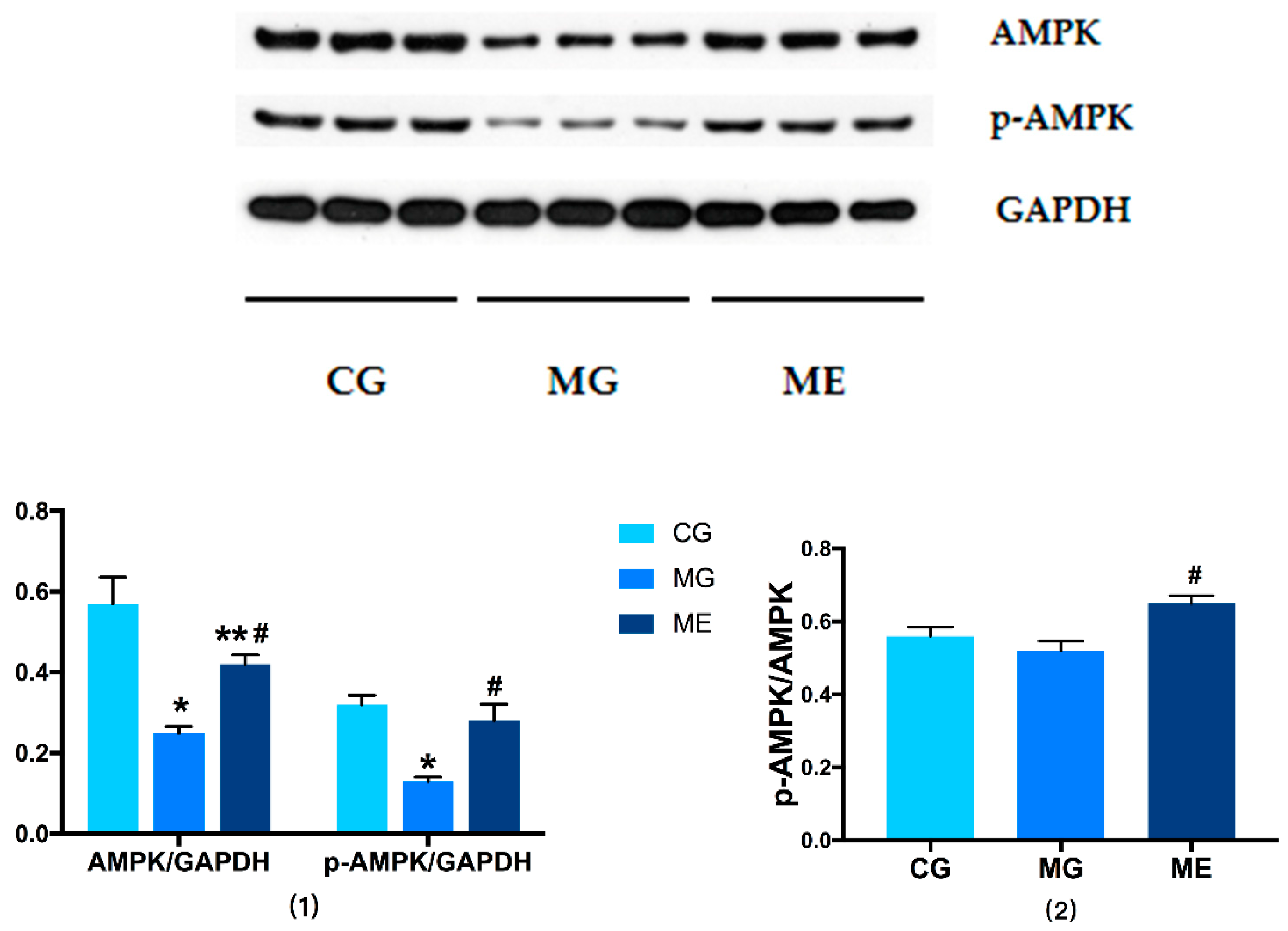
3.3. Western Blot Results
3.3.1. Changes in AMPK/p-AMPK Protein Expression
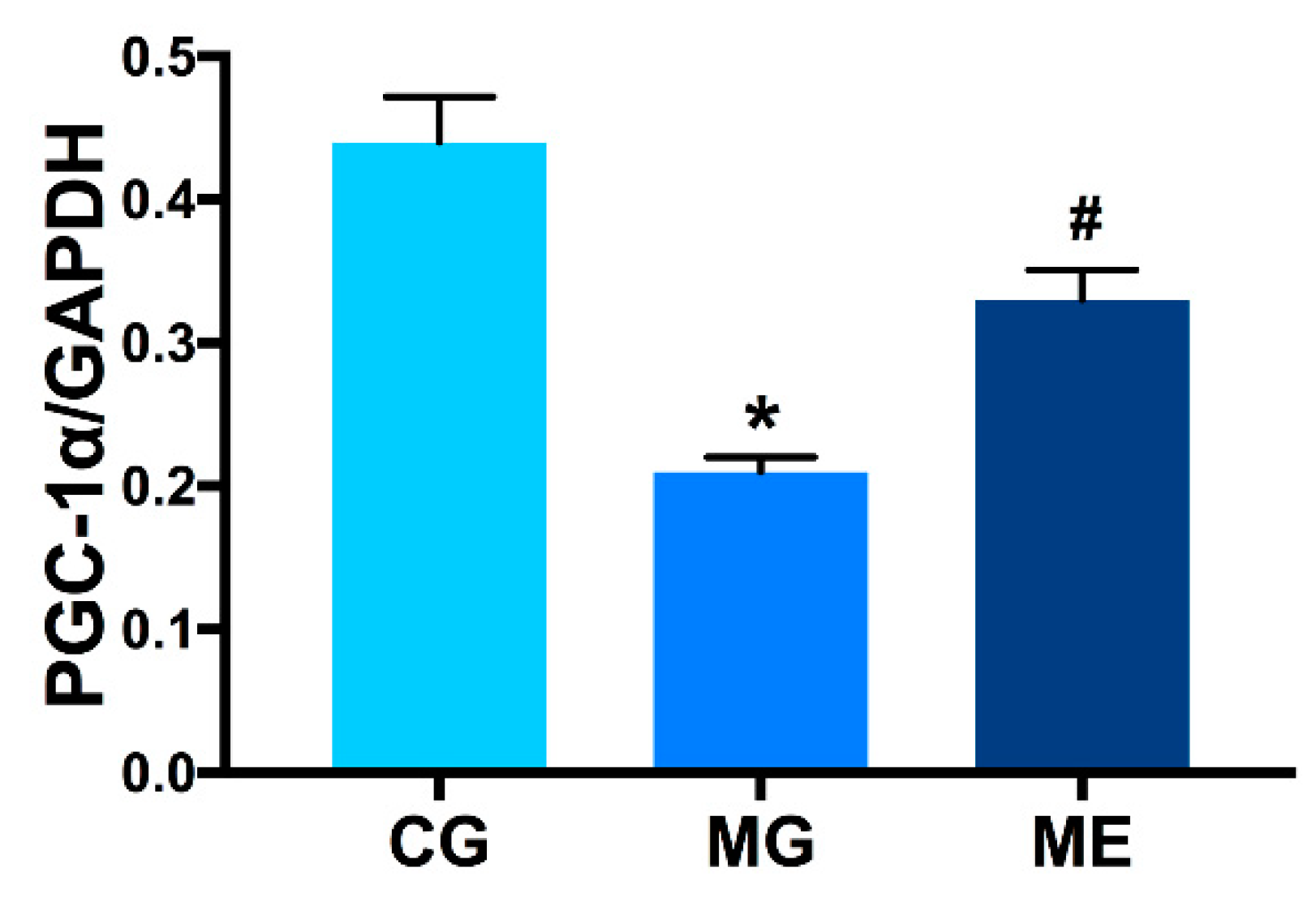
3.3.2. Changes in PGC-1α Protein Expression
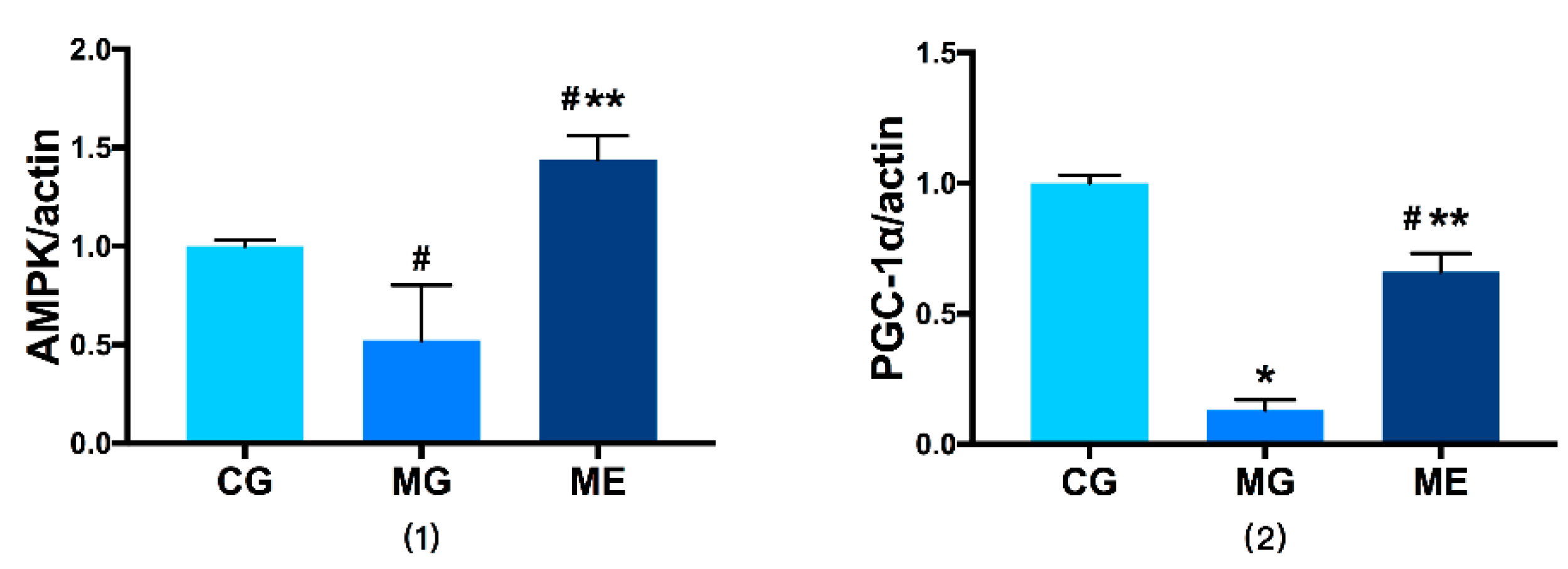
3.4. RT-PCR on AMPK and PGC-1αmRNA Expression
AMPK and PGC-1αmRNA Expression
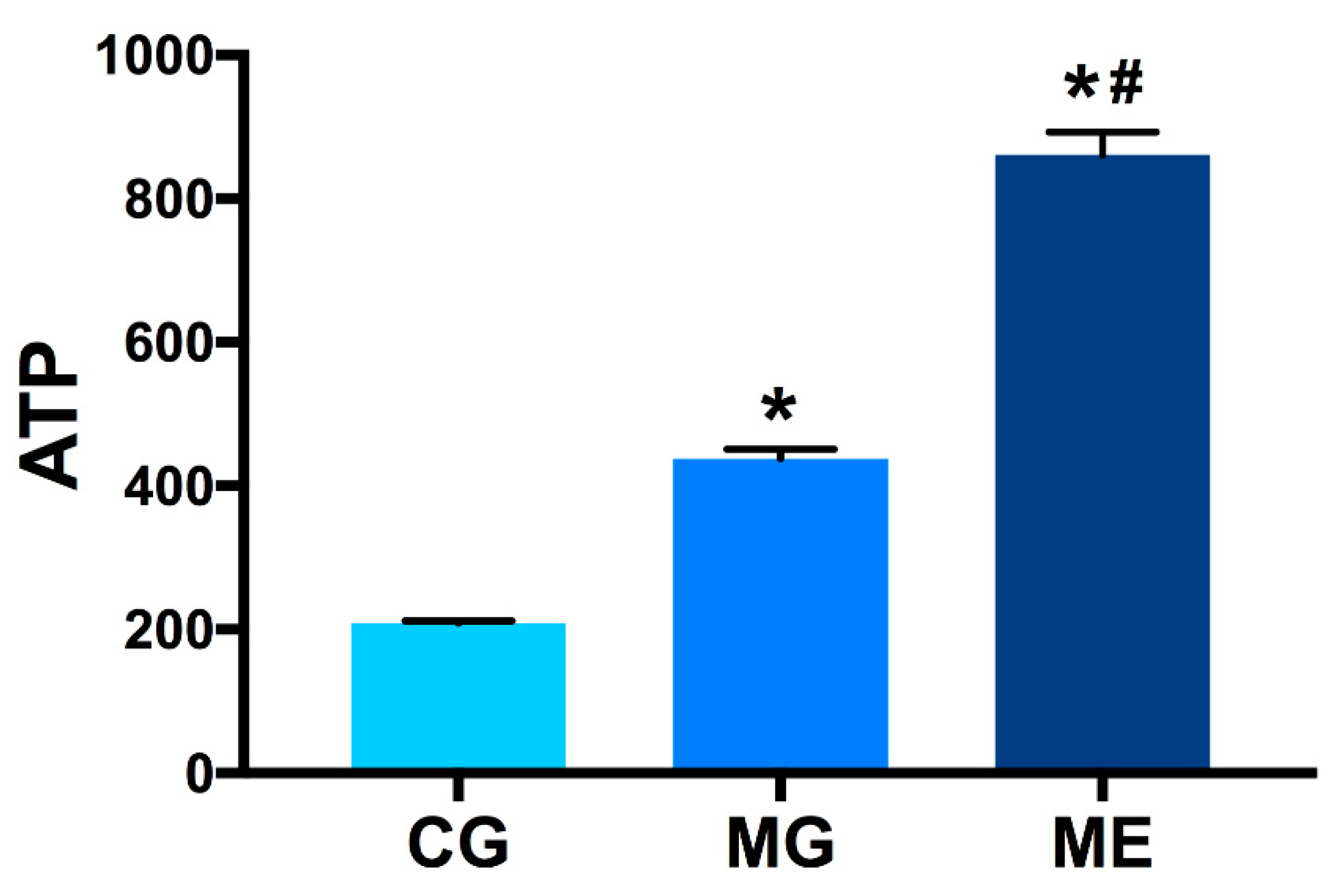
3.5. Elisa Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Discussion on Chronic Stress-Induced Depression Model in Mice
4.2. Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on the Behavior and Weight of Mice with CUMS-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors
4.3. Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on AMPK/PGC-1α of Mice with CUMS-Induced Depression-Like Behaviors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, Z.; Qin, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, G.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Sha, J.; Chen, J.; Xia, J.; et al. Longterm Exercise-Derived Exosomal miR-342-5p: A Novel Exerkine for Cardioprotection. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1386–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, Z. Swimming training affects apoptosis-related microRNAs and reduces cardiac apoptosis in mice. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2016, 35, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakil-Ur-Rehman, S.; Karimi, H.; Gillani, S.A. Effects of supervised structured aerobic exercise training program on fasting blood glucose level, plasma insulin level, glycemic control, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhi, N.; Geng, J.; Cao, W.; Yu, L.; Mi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wen, W.; et al. Structural brain network measures are superior to vascular burden scores in predicting early cognitive impairment in post stroke patients with small vessel disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2019, 22, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K. Mental health: A world of depression. Nat. J. 2014, 515, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.S.; Hattori, K.; Ogawa, S.; Sasayama, D.; Ota, M.; Teraishi, T.; Kunugi, H. Relationships of Cerebrospinal Fluid Monoamine Metabolite Levels with Clinical Variables in Major Depressive Disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2017, 78, e947–e956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukhalsky, A.L.; Shmarina, G.V.; Alioshkin, V.A.; Sabelnikov, A. HPA axis exhaustion and regulatory T cell accumulation in patients with a functional somatic syndrome: Recent view on the problem of Gulf War veterans. J. Neuroimmunol. 2008, 196, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.A.; Singhal, G.; Corrigan, F.; Jaehne, E.J.; Jawahar, M.C.; Baune, B.T. Exercise related anxiety-like behaviours are mediated by TNF receptor signaling, but not depression-like behaviours. Brain Res. 2018, 1695, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Zhan, Q.; Xiao, W.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Dong, H.; Sha, W.; Zhang, X. Altered serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor in first-episode drug-naive and chronic medicated schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2018, 264, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemili, H.; Mejri, M.A.; Bouhlel, E.; Amri, M. Biochemical status, oxidative and antioxidant responses after 3-month specific training in elite karate athletes. Physiol. Int. 2017, 104, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karabatsiakis, A.; Bock, C.; Salinas-Manrique, J.; Kolassa, S.; Calzia, E.; Dietrich, D.E.; Kolassa, I.T. Mitochondrial respiration in peripheral blood mononuclear cells correlates with depressive subsymptoms and severity of major depression. Transl. Psychiatry. 2014, 4, e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattal, O.; Budur, K.; Vaughan, A.J.; Franco, K. Review of the literature on major mental disorders in adult patients with mitochondrial diseases. Psychosomatics 2006, 47, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, D. AMPK signalling in health and disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Sun, R.; Tao, X.; Wang, X.; Kang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. SIRT5 deficiency suppresses mitochondrial ATP production and promotes AMPK activation in response to energy stress. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Feige, J.N.; Lagouge, M.; Noriega, L.; Milne, J.C.; Elliott, P.J.; Auwerx, P.P.J. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 2009, 458, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, C.A.; Nelson, O.L.; Jansen, H.T.; Robbins, C.T.; Jensen, A.E.; Constantinescu, S.; Abbott, M.J.; Turcotte, L.P. Regulation of metabolism during hibernation in brown bears (Ursus arctos): Involvement of cortisol, PGC-1alpha and AMPK in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2020, 240, 110591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, P.; Towell, A.; Sampson, D.; Sophokleous, S.; Muscat, R. Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharm. Acology 1987, 93, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, X.; Caichuan, W. Study of chronic stress stimulation on behavior of depression model mice. J. Med. Sci. Yan Bian Univ. 2017, 40, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bedford, T.G.; Tipton, C.M.; Wilson, N.C.; Oppliger, R.A.; Gisolfi, C.V. Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1979, 47, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Nestler, E.J. The molecular neurobiology of depression. Nat. J. 2008, 7215, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, L. MiR-124 suppression in the prefrontal cortex reduces depression-like behavior in mice. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, B.; Pochwat, B.; Muszynska, B.; Opoka, W.; Krakowska, A.; Rafalo-Ulinska, A.; Friedland, K.; Nowak, G. Antidepressant-like activity of hyperforin and changes in BDNF and zinc levels in mice exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 372, 112045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, A.; Magaji, M.G.; Yau, J.; Ahmed, A. Methanol stem bark extract of Adansonia digitata ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior: Involvement of the HPA axis, BDNF, and stress biomarkers pathways. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.J.; Roth, K.A.; Carroll, B.J. Acute and chronic stress effects on open field activity in the rat: Implications for a model of depression. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1981, 5, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren-ling, W.; Qi, P. Neural immune change in depression model mice. Acta Anat. Sin. 2018, 49, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao-ling, H.; Hua-li, W. Comparison between two animal models of depression induced by corticosterone repeated injection and chronic unpredictable mild stress. Acta Anat. Sin. 2017, 48, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pan, W.; Hou, J. Avicularin Relieves Depressive-Like Behaviors Induced by Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Mice. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Lin-Xi, F. Antidepressant effects of the extract of Dendrobium nobile Lindl on chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive mice. Acta Physiol. Sin. J. 2017, 69, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.X.; Fang, Z.T. Effects of refined Xiaoyao Powder on ethology and expressions of P450scc in hippocampus of the depression rat. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. 2013, 28, 1253. [Google Scholar]
- Honglin, Q.; Jun, X.; Jiaqin, C. Aerobic Training Inhibits Hippocampal Inflammation by Activating the Hippocampus TLR4/miR223/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway Axis in Mice with CUMS Depression. China Sport Sci. J. 2019, 39, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Jin, Y.; Li, L.; Sun, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Svenningsson, P. Exercise prevents raphe nucleus mitochondrial overactivity in a rat depression model. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 132, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, P.C.; Tan, Z.N.; Jia, Z.Y.; Wang, B.; Grady, J.J.; Ma, X.M. Treadmill Exercise Reverses Depression Model-Induced Alteration of Dendritic Spines in the Brain Areas of Mood Circuit. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangasser, D.A.; Curtis, A.; Reyes, B.A.; Bethea, T.T.; Parastatidis, I.; Ischiropoulos, H.; van Bockstaele, E.J.; Valentino, R.J. Sex differences in corticotropin-releasing factor receptor signaling and trafficking: Potential role in female vulnerability to stress-related psychopathology. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 877, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Li, J.M.; Su, W.J.; Wang, B.; Jiang, C.L. Sex differences in depressive-like behaviour may relate to imbalance of microglia activation in the hippocampus. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 81, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozet, P.; Margalha, L.; Confraria, A.; Rodrigues, A.; Martinho, C.; Adamo, M.; Elias, C.A.; Baena-González, E. Mechanisms of regulation of SNF1/AMPK/SnRK1 protein kinases. Front Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. Sensing of energy and nutrients by AMP-activated protein kinase. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. J. 2011, 93, 891S–896S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakhill, J.S.; Scott, J.W.; Kemp, B.E. AMPK functions as an adenylate charge-regulated protein kinase. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinovitch, R.C.; Samborska, B.; Faubert, B.; Ma, E.H.; Gravel, S.P.; Andrzejewski, S.; Raissi, T.C.; Pause, A.; St-Pierre, J.; Jones, R.G. AMPK Maintains Cellular Metabolic Homeostasis through Regulation of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jiang, Q.; Tuccitto, A.; Chan, D.; Alqawlaq, S.; Won, G.J.; Sivak, J.M. The AMPK-PGC-1alpha signaling axis regulates the astrocyte glutathione system to protect against oxidative and metabolic injury. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 113, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liang, X.C. Effects of Mitochondrial Dysfunction via AMPK/PGC-1 alpha Signal Pathway on Pathogenic Mechanism of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy and the Protective Effects of Chinese Medicine. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2019, 25, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Rongjuan, G.; Huawei, S. Mitochondrial energy metabolism disorder in depression. J. Beijing Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2019, 42, 602–606. [Google Scholar]
- Si-jun, Z.; Xiao-zhe, Z.; Huan, X. Regulation of seabuckthorn seed oil on metabolic pathway disturbances on rats exposed to chronic unpredictable mild stress. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs J. 2017, 48, 2682–2690. [Google Scholar]
- Jou, S.H.; Chiu, N.Y.; Liu, C.S. Mitochondrial dysfunction and psychiatric disorders. Chang. Gung Med. J. 2009, 32, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.; Boles, R.G. Mitochondrial energy depletion in depression with somatization. Psychother. Psychosom. 2008, 77, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, J.; Hong, L.; Huang, W.; Dai, X.; Ye, Q.; Chen, X. Metformin ameliorates stress-induced depression-like behaviors via enhancing the expression of BDNF by activating AMPK/CREB-mediated histone acetylation. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 260, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odaira, T.; Nakagawasai, O.; Takahashi, K.; Nemoto, W.; Sakuma, W.; Lin, J.R.; Tan-No, K. Mechanisms underpinning AMP-activated protein kinase-related effects on behavior and hippocampal neurogenesis in an animal model of depression. Neuropharmacology 2019, 150, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, L.Z.; Femenia, T.; Orhan, F.; Porsmyr-Palmertz, M.; Goiny, M.; Martinez-Redondo, V.; Correia, J.C.; Izadi, M.; Bhat, M.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; et al. Skeletal muscle PGC-1alpha1 modulates kynurenine metabolism and mediates resilience to stress-induced depression. Cell 2014, 159, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, L.P.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q.; Hu, H.H.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.J.; Xiong, W.C.; et al. Astrocyte-derived ATP modulates depressive-like behaviors. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkman, H.O. Novel Treatment Targets Based on Insights in the Etiology of Depression: Role of IL-6 Trans-Signaling and Stress-Induced Elevation of Glutamate and ATP. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Lu, W.; Zhou, H.Y.; Long, L.H.; Hu, Z.L.; Ni, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.G.; et al. AMPK Mediates Glucocorticoids Stress-Induced Downregulation of the Glucocorticoid Receptor in Cultured Rat Prefrontal Cortical Astrocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltai, E.; Hart, N.; Taylor, A.W.; Goto, S.; Ngo, J.K.; Davies, K.J.; Radak, Z. Age-associated declines in mitochondrial biogenesis and protein quality control factors are minimized by exercise training. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2012, 303, R127–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da-lei, W.; Tong, W. Research on the Mechanism of Long-term Aerobic Exercise Reducing Oxidative Stress in the Hippocampus of Aging Rats. J. Xi’an Phys. Educ. Univ. 2014, 31, 350–354, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Yangwenjie, W.; Zhaojie, L.; Xuan, H.; Ying, Z. Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training on apelin-mediated Expressing of UCP3 in Skeletal Muscles of Mice. Chin. J. Sports Med. 2018, 37, 772–778. [Google Scholar]
| Base Sequence | |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | F ACAGCAACAGGGTGGTGGAC R TTTGAGGGTGCAGCGAACTT |
| PGC-1α | F TGATGTGAATGACTTGGATACAGACA R GCTCATTGTTGTACTGGTTGGATATG |
| AMPK | F AAACCCACAGAAATCCAAACAC R CCTTCCATTCATAGTCCAACTG |
| Group | Before Experiment | After Modelling | After Exercise Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|
| CG | 41.68 ± 1.3503 | 53.47 ± 2.8909 | 61.37 ± 2.5877 |
| MG | 41.54 ± 1.4773 | 49.86 ± 1.4607 | 55.56 ± 1.2855 |
| ME | 42.13 ± 1.2811 | 49.16 ± 1.0023 | 58.4 ± 1.5269 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, J.; Tang, C.; Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Qu, H.; Chen, R.; Tong, Z. Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice and Related Factors in the AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062042
Luo J, Tang C, Chen X, Ren Z, Qu H, Chen R, Tong Z. Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice and Related Factors in the AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(6):2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062042
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Jia, Changfa Tang, Xiaobin Chen, Zhanbing Ren, Honglin Qu, Rong Chen, and Zhen Tong. 2020. "Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice and Related Factors in the AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 6: 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062042
APA StyleLuo, J., Tang, C., Chen, X., Ren, Z., Qu, H., Chen, R., & Tong, Z. (2020). Impacts of Aerobic Exercise on Depression-Like Behaviors in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Mice and Related Factors in the AMPK/PGC-1α Pathway. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(6), 2042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17062042




