Comparison between Two Different Device Models 18 Hz GPS Used for Time–Motion Analyses in Ecological Testing of Football
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
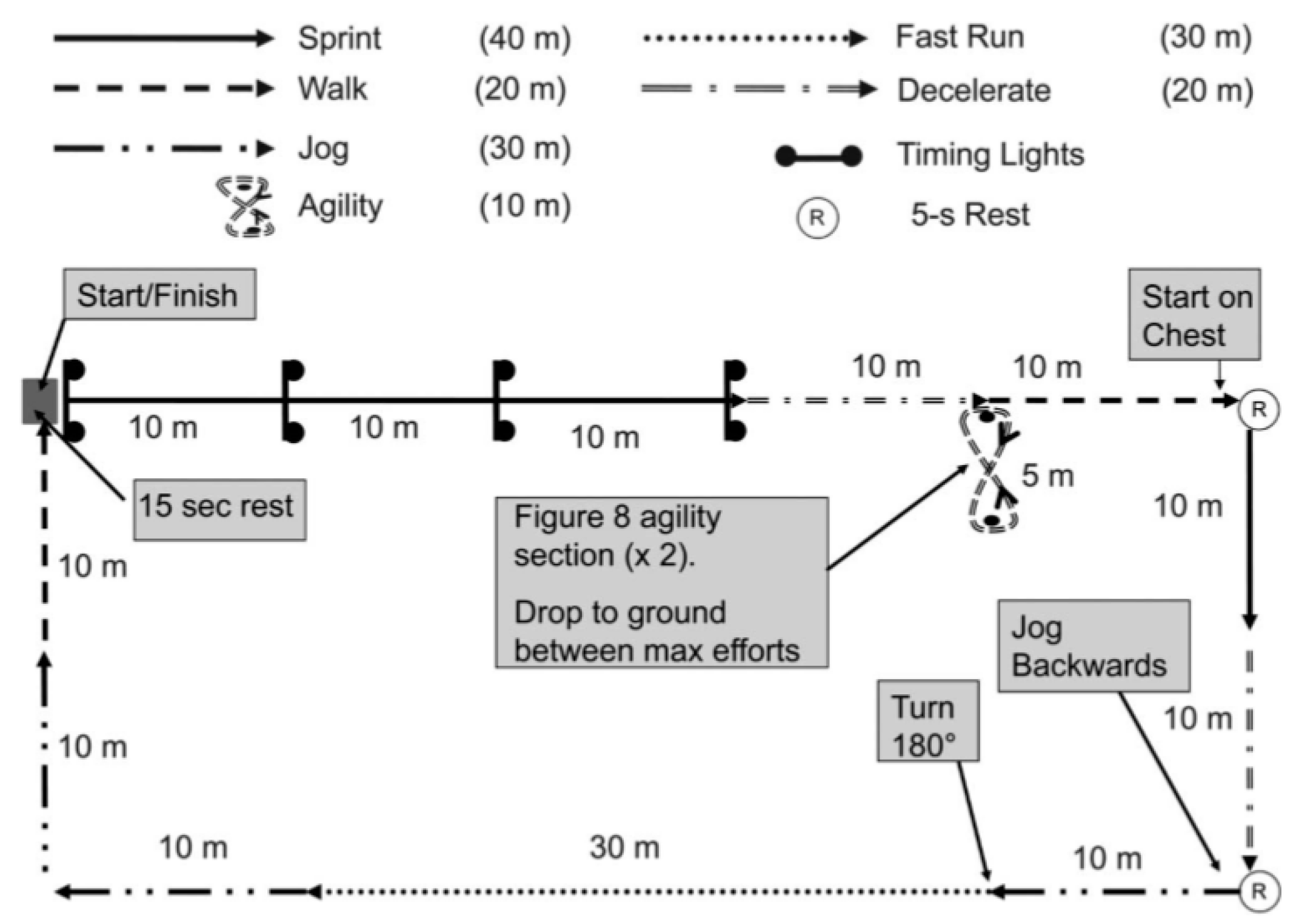
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cummins, C.; Orr, R.; O’Connor, H.; West, C. Global positioning systems (GPS) and microtechnology sensors in team sports: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2013, 43, 1025–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutz, Y.; Chambaz, A. Could a satellite-based navigation system (GPS) be used to assess the physical activity of individuals on earth? Eur. J. Clin. Nutrition 1997, 51, 338–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aughey, R.J. Applications of GPS technologies to field sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2011, 6, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casamichana, D.; Castellano, J.; Calleja-Gonzalez, J.; San Román, J.; Castagna, C. Relationship between indicators of training load in soccer players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutts, A.J.; Duffield, R. Validity and reliability of GPS devices for measuring movement demands of team sports. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, M.W.; Baumgart, C.; Polglaze, T.; Freiwald, J. Validity and reliability of GPS and LPS for measuring distances covered and sprint mechanical properties in team sports. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, J.J.; Lovell, R.; Varley, M.C.; Coutts, A.J. Unpacking the black box: Applications and considerations for using GPS devices in sport. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, C.P.; Lovell, D.I.; Gass, G.C. Performance analysis of elite rugby league match play using global positioning systems. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, J.; Maçãs, V. Measuring tactical behaviour in football. Int. J. Sport Med. 2012, 33, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, D.; Ortega, E.; Gómez-Ruano, M.Á.; Weigelt, M.; Nikolic, B.; Sainz de Baranda, P. Physical and Tactical Demands of the Goalkeeper in Football in Different Small-Sided Games. Sensors 2019, 19, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Allen, A.; Poon, T.K.; Modonutti, M.; Gregson, W.; Di Salvo, V. Integrating different tracking systems in football: Multiple camera semi-automatic system, local position measurement and GPS technologies. J. Sports Sci. 2014, 32, 1844–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbett, T.J. Sprinting patterns of national rugby league competition. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2012, 26, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampinini, E.; Alberti, G.; Fiorenza, M.; Riggio, M.; Sassi, R.; Borges, T.; Coutts, A. Accuracy of GPS devices for measuring high-intensity running in field-based team sports. Int. J. Sport Med. 2015, 36, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldron, M.; Worsfold, P.; Twist, C.; Lamb, K. Concurrent validity and test–retest reliability of a global positioning system (GPS) and timing gates to assess sprint performance variables. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, M.; Beaver, T.; Turczyn, D.; Cornish, S. Validity and Reliability of 15 Hz Global Positioning System Units for Assessing the Activity Profiles of University Football Players. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beato, M.; Coratella, G.; Stiff, A.; Iacono, A.D. The validity and between-unit variability of GNSS units (STATSports Apex 10 and 18 Hz) for measuring distance and peak speed in team sports. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato, M.; de Keijzer, K.L. The inter-unit and inter-model reliability of GNSS STATSports Apex and Viper units in measuring peak speed over 5, 10, 15, 20 and 30 meters. Biol. Sport 2019, 36, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carling, C.; Le Gall, F.; Dupont, G. Analysis of repeated high-intensity running performance in professional soccer. J. Sport Sci. 2012, 30, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampinini, E.; Sassi, A.; Morelli, A.; Mazzoni, S.; Fanchini, M.; Coutts, A.J. Repeated-sprint ability in professional and amateur soccer players. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 34, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, J.L.; Garcia-Unanue, J.; Viejo-Romero, D.; Navandar, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J. Validation of a Video-Based Performance Analysis System (Mediacoach®) to Analyze the Physical Demands during Matches in LaLiga. Sensors 2019, 19, 4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrzejewski, M.; Chmura, J.; Pluta, B.; Konarski, J.M. Sprinting activities and distance covered by top level Europa league soccer players. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 2015, 10, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, D.; Cormack, S.; Coutts, A.J.; Boyd, L.; Aughey, R.J. The validity and reliability of GPS units for measuring distance in team sport specific running patterns. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2010, 5, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Pine, M.J.; Spurrs, R.W.; Murphy, A.; Pruyn, E.C. Movement demands and match performance in professional Australian football. Int. J. Sport Med. 2012, 33, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellano, J.; Casamichana, D.; Calleja-González, J.; San Román, J.; Ostojic, S.M. Reliability and accuracy of 10 Hz GPS devices for short-distance exercise. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Johnston, R.J.; Watsford, M.L.; Kelly, S.J.; Pine, M.J.; Spurrs, R.W. Validity and interunit reliability of 10 Hz and 15 Hz GPS units for assessing athlete movement demands. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellaserra, C.L.; Gao, Y.; Ransdell, L. Use of integrated technology in team sports: A review of opportunities, challenges, and future directions for athletes. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 556–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida Castillo, A.; Gómez Carmona, C.D.; De la Cruz Sánchez, E.; Pino Ortega, J. Accuracy, intra-and inter-unit reliability, and comparison between GPS and UWB-based position-tracking systems used for time–motion analyses in soccer. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, G.; Alderson, J.; Hiscock, D.; Smith, M.; Alicea, A.; Donnelly, C.J. The effect of fatigue induced from a simulated hockey match on biomechanical ACL injury risk factors in elite female field hockey players. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference of the International Society of Biomechanics in Sports, Cologne, Germany, 14–18 June 2017; Volume 35, pp. 468–471. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, R.; Watsford, M.; Austin, D.; Pine, M.; Spurrs, R. Player acceleration and deceleration profiles in professional Australian football. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 55, 931–939. [Google Scholar]
- Edgecomb, S.; Norton, K. Comparison of global positioning and computer-based tracking systems for measuring player movement distance during Australian football. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2006, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisbey, B.; Montgomery, P.G.; Pyne, D.B.; Rattray, B. Quantifying movement demands of AFL football using GPS tracking. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero-Álvarez, J.C.; Coutts, A.; Granda, J.; Barbero-Álvarez, V.; Castagna, C. The validity and reliability of a global positioning satellite system device to assess speed and repeated sprint ability (RSA) in athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2010, 13, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugen, T.A.; Tønnessen, E.; Svendsen, I.S.; Seiler, S. Sprint time differences between single-and dual-beam timing systems. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 2376–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, W.G.; Marshall, S.W.; Batterham, A.M.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, E.; Garcia-Calvo, T.; Resta, R.; Blanco, H.; del Campo, R.L.; Garcia, J.D.; Pulido, J.J. A comparison of a GPS device and a multi-camera video technology during official soccer matches: Agreement between systems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, M.; Al Haddad, H.; Simpson, B.M.; Palazzi, D.; Bourdon, P.C.; Di Salvo, V.; Mendez-Villanueva, A. Monitoring accelerations with GPS in football: Time to slow down? Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.G.; de Ruiter, C.J.; van Niel, C.; van de Rhee, R.; Beek, P.J.; Savelsbergh, G.J. Measuring acceleration and deceleration in soccer-specific movements using a local position measurement (LPM) system. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.T.; Scott, T.J.; Kelly, V.G. The validity and reliability of global positioning systems in team sport: A brief review. J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1470–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato, M.; Bartolini, D.; Ghia, G.; Zamparo, P. Accuracy of a 10 Hz GPS unit in measuring shuttle velocity performed at different speeds and distances (5–20 m). J. Hum. Kinetics 2016, 54, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, J.; Beato, M.; Hulton, A.T. Manipulation of exercise to rest ratio within set duration on physical and technical outcomes during small-sided games in elite youth soccer players. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2016, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Villanueva, A.; Buchheit, M.; Simpson, B.; Peltola, E.; Bourdon, P. Does on-field sprinting performance in young soccer players depend on how fast they can run or how fast they do run? J. Strenght Cond. Res. 2011, 25, 2634–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varley, M.C.; Fairweather, I.H.; Aughey, R.J. Validity and reliability of GPS for measuring instantaneous velocity during acceleration, deceleration, and constant motion. J. Sport Sci. 2012, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pino, J.; Martinez-Santos, R.; Moreno, M.I.; Padilla, C. Automatic analysis of football games using GPS on real time. J. Sport Sci. Med. 2007, 6, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Randers, M.B.; Mujika, I.; Hewitt, A.; Santisteban, J.; Bischoff, R.; Solano, R.; Zubillaga, A.; Peltola, E.; Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M. Application of four different football match analysis systems: A comparative study. J. Sports Sci. 2010, 28, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Apex | Wimu | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | Diff | SD | MAE | RMSE | SWC | Corr | ICC | SEE | |
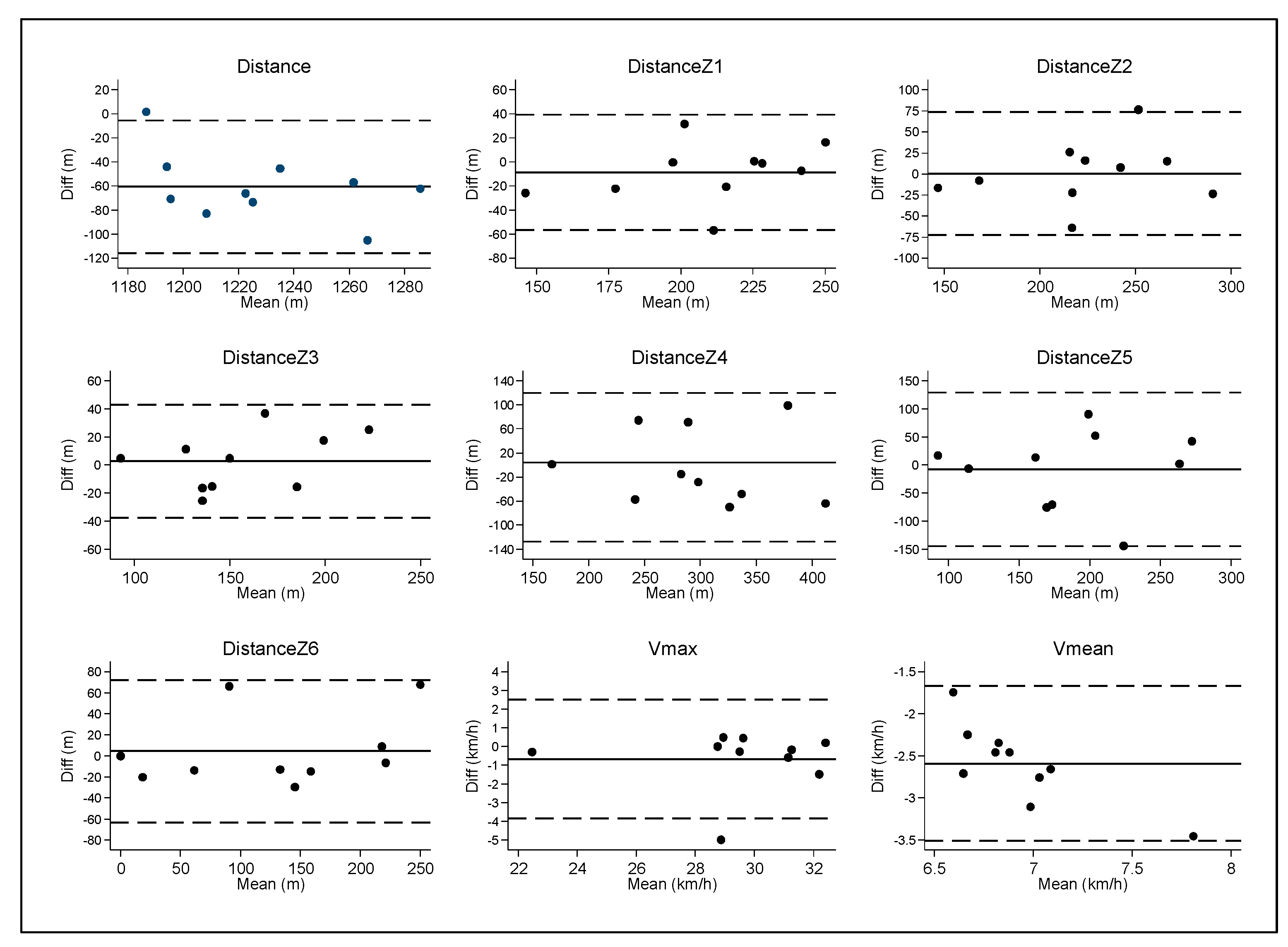
| Total Distance (m) | 1197.85 | 30.23 | 1258.51 | 42.12 | −60.66 | 28.17 | 60.94 | 66.28 | 9.47 | 0.74 * | 0.30 * | 0.90 |
| DistanceZ1 (m) | 205.16 | 36.86 | 213.92 | 29.19 | −8.76 | 24.45 | 18.29 | 24.79 | 6.53 | 0.75 * | 0.72 * | 0.88 |
| DistanceZ2 (m) | 224.24 | 50.74 | 223.70 | 42.52 | 0.54 | 37.30 | 27.52 | 35.39 | 9.11 | 0.69 * | 0.71 * | 0.69 |
| DistanceZ3 (m) | 157.16 | 43.59 | 154.49 | 35.56 | 2.67 | 20.49 | 17.29 | 19.62 | 7.75 | 0.89 * | 0.88 * | 0.53 |
| DistanceZ4 (m) | 295.76 | 74.30 | 299.71 | 80.85 | −3.95 | 63.11 | 52.92 | 60.01 | 15.12 | 0.67 * | 0.69 * | 1.10 |
| DistanceZ5 (m) | 183.46 | 68.74 | 191.66 | 66.74 | −8.21 | 69.88 | 51.21 | 66.8 | 13.22 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 1.89 |
| DistanceZ6 (m) | 132.08 | 92.98 | 127.58 | 82.85 | 4.50 | 34.53 | 24.08 | 33.06 | 17.15 | 0.93 * | 0.93 * | 0.40 |
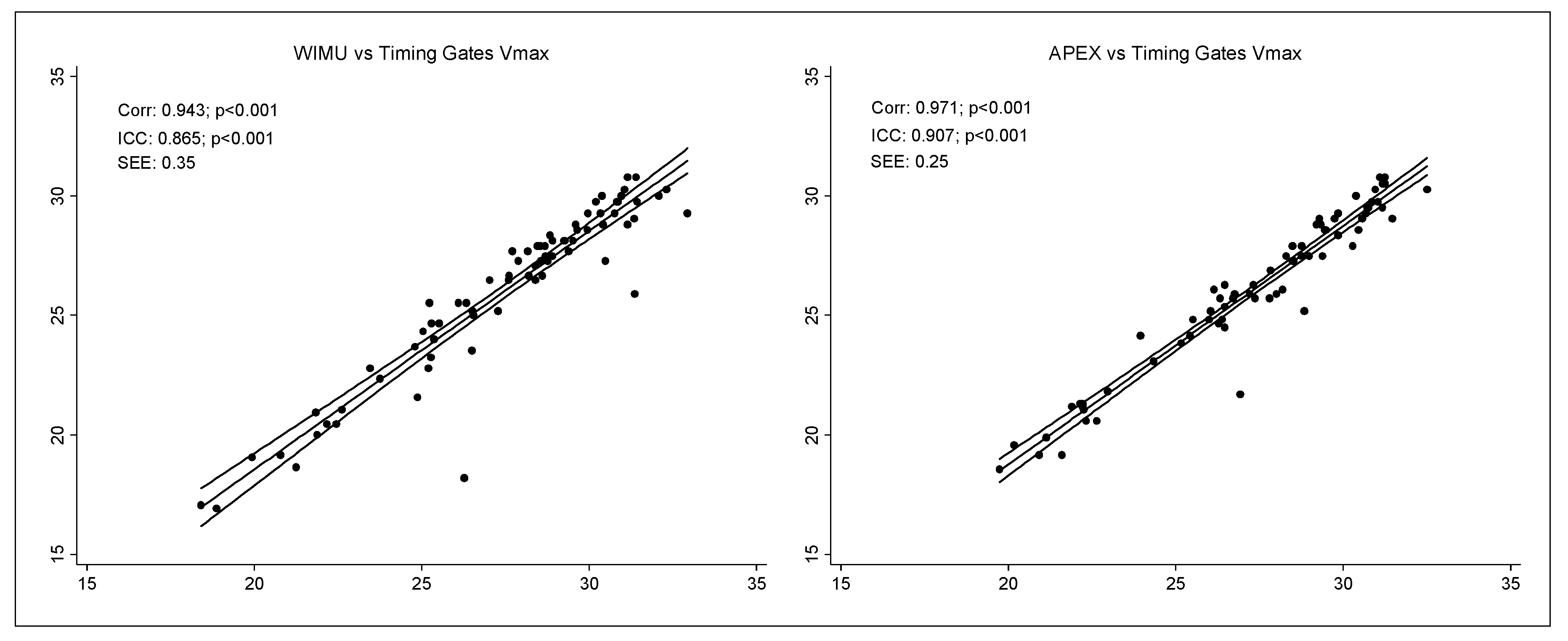
| Vmax (km·h−1) | 29.19 | 2.95 | 29.85 | 2.94 | −0.66 | 1.62 | 0.89 | 1.67 | 0.58 | 0.85 * | 0.84 * | 0.62 |
| Vmean (km·h−1) | 5.64 | 0.21 | 8.23 | 0.56 | −2.59 | 0.47 | 2.59 | 2.63 | 0.28 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 1.41 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gimenez, J.V.; Garcia-Unanue, J.; Navandar, A.; Viejo-Romero, D.; Sanchez-Sanchez, J.; Gallardo, L.; Hernandez-Martin, A.; Felipe, J.L. Comparison between Two Different Device Models 18 Hz GPS Used for Time–Motion Analyses in Ecological Testing of Football. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17061912
Gimenez JV, Garcia-Unanue J, Navandar A, Viejo-Romero D, Sanchez-Sanchez J, Gallardo L, Hernandez-Martin A, Felipe JL. Comparison between Two Different Device Models 18 Hz GPS Used for Time–Motion Analyses in Ecological Testing of Football. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(6):1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17061912
Chicago/Turabian StyleGimenez, Jesus Vicente, Jorge Garcia-Unanue, Archit Navandar, David Viejo-Romero, Javier Sanchez-Sanchez, Leonor Gallardo, Antonio Hernandez-Martin, and Jose Luis Felipe. 2020. "Comparison between Two Different Device Models 18 Hz GPS Used for Time–Motion Analyses in Ecological Testing of Football" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 6: 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17061912
APA StyleGimenez, J. V., Garcia-Unanue, J., Navandar, A., Viejo-Romero, D., Sanchez-Sanchez, J., Gallardo, L., Hernandez-Martin, A., & Felipe, J. L. (2020). Comparison between Two Different Device Models 18 Hz GPS Used for Time–Motion Analyses in Ecological Testing of Football. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(6), 1912. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17061912










