Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
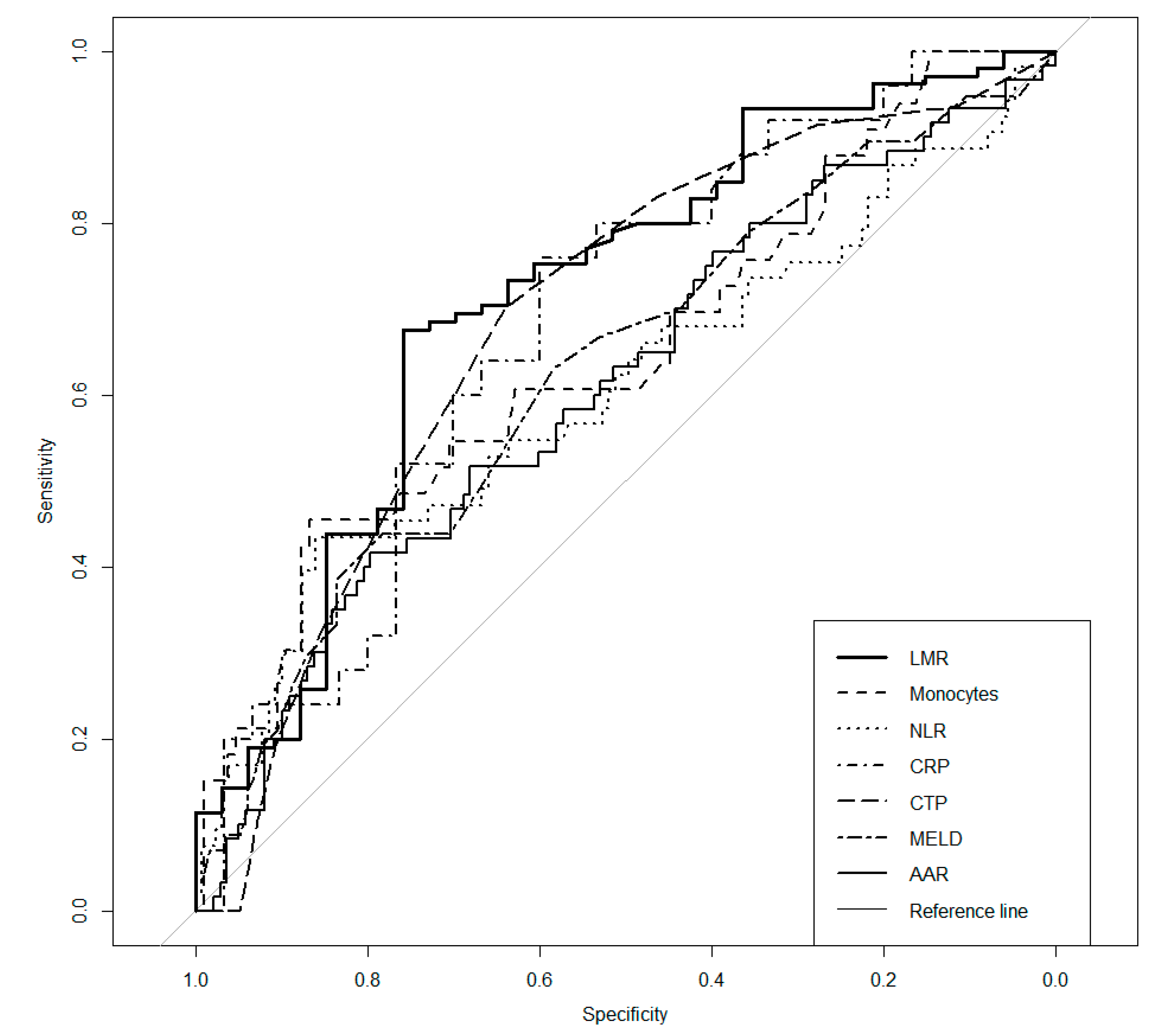
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piotrowski, D.; Boroń-Kaczmarska, A. Bacterial infections and hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis—Prophylaxis and treatment. Adv. Med. Sci. 2017, 62, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalan, R.; Fernandez, J.; Wiest, R.; Schnabl, B.; Moreau, R.; Angeli, P.; Stadlbauer, V.; Gustot, T.; Bernardi, M.; Canton, R.; et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: A position statement based on the EASL Special Conference 2013. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 1310–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, J.; Gustot, T. Management of bacterial infections in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, S1–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, J.; Acevedo, J.; Castro, M.; Garcia, O.; De Lope, C.R.; Roca, D.; Pavesi, M.; Sola, E.; Moreira, L.; Silva, A.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors of infections by multiresistant bacteria in cirrhosis: A prospective study. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.J.; Dong, J.J.; Dong, J.Z.; Yang, N.B.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Lin, Z.; Shi, K.Q. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts hospital-acquired bacterial infections in decompensated cirrhosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 469, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elalfy, H.; Besheer, T.; El-Maksoud, M.A.; Farid, K.; Elegezy, M.; El Nakib, A.M.; El-Aziz, M.A.; El-Khalek, A.A.; El-Morsy, A.; Elmokadem, A.; et al. Monocyte/granulocyte to lymphocyte ratio and the MELD score as predictors for early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after trans-arterial chemoembolization. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 75, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Yu, J.; Tan, L.; Wu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Q.; Duan, X.; Yu, L. Noninvasive indices for monitoring disease course in Chinese patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 486, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts-rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Merekoulias, G.; Alexopoulos, E.C.; Belezos, T.; Panagiotopoulou, E.; Jelastopulu, D.M. Lymphocyte to monocyte ratio as a screening tool for influenza. PLoS Curr. 2010, 2, RRN1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkmen, K.; Erdur, F.H.; Ozcicek, F.; Ozcicek, A.; Akbas, E.M.; Ozbicer, A.; Demirtas, L.; Turk, S.; Tonbul, H.Z. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio better predicts inflammation than neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in end-stage renal disease patients. Hemodial. Int. 2013, 17, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihan, Y.B.; Arslan, A.; Ergul, M.A. Subtypes of white blood cells in patients with prostate cancer or benign prostatic hyperplasia and healthy individuals. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 4779–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bambha, K.; Kim, W.R.; Kremers, K.; Therneau, T.M.; Kamath, P.S.; Wiesner, R.; Rosen, C.B.; Thostenson, J.; Benson, J.T.; Dickson, E.R. Predicting survival among patients listed for liver transplantation: An assessment of serial MELD measurements. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 1798–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.L.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Ratio of serum aspartate to alanine aminotransferase in chronic hepatitis. Relationship to cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1988, 95, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fix, O.K.; Horsburgh, C.R.; Heeren, T.C.; Reinus, J.F.; Garcia, E.; Mishkin, D.S.; Graham, C.S.; Koziel, M.J.; Nunes, D.P. The performance of APRI for the diagnosis of significant hepatic fibrosis is improved by a simple modification. In Proceedings of the Conference Report—AASLD, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 November 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.S.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Lou, J.; Yan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Sun, G.; Li, N. The role of the neutrophil Fcg receptor I (CD64) index in diagnosing spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhotic patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 49, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bal, C.K.; Daman, R.; Bhatia, V. Predictors of fifty days in-hospital mortality in decompensated cirrhosis patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidelines on Urological Infections. European Association of Urology. Available online: http://uroweb.org/wp-content/uploads/19-Urological-infections_2017_web.pdf (accessed on 15 June 2018).
- Mandell, L.A.; Wunderink, R.G.; Anzueto, A.; Bartlett, J.G.; Campbell, G.D.; Dean, N.C.; Dowell, S.F.; File, T.M., Jr.; Musher, D.M.; Niederman, M.S.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, S27–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderink, R.G.; Waterer, G.W. Clinical practice. Community-acquired pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, M.; Lucidi, C.; Giannelli, V.; Giusto, M.; Riggio, O.; Falcone, M.; Ridola, L.; Attili, A.F.; Venditti, M. Cirrhotic Patients Are at Risk for Health Care-Associated Bacterial Infections. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, A.Y.; Hooper, D.C. Hospital-acquired infections due to gram-negative bacteria. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- StatSoft, Inc. STATISTICA (Data Analysis Software System), Version 12; StatSoft, Inc.: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015; Available online: http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 June 2018).
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Lumley, T.; Johnson, R.C. Gmodels: Various R Programming Tools for Model Fitting. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/gmodels/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2018).
- Lopez-Raton, M.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.X. OptimalCutpoints: Computing Optimal Cutpoints in Diagnostic Tests. 2015. Available online: https://cran.rproject.org/web/packages/OptimalCutpoints/index.html (accessed on 4 June 2018).
- NCAR—Research Applications Laboratory. Verification: Weather Forecast Verification Utilities. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/verification/index.html (accessed on 6 June 2018).
- Pijls, K.E.; Koek, G.H.; Elamin, E.E.; de Vries, H.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E. Large intestine permeability is increased in patients with compensated liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2014, 306, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, K.; Garcio-Tsao, G. Novel prevention strategies for bacterial infections in cirrhosis. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2016, 17, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirchwolf, M.; Podhorzer, A.; Marino, M.; Shulman, C.; Cartier, M.; Zunino, M.; Paz, S.; Muñoz, A.; Bocassi, A.; Gimenez, J.; et al. Immune dysfunction in cirrhosis: Distinct cytokines phenotypes according to cirrhosis severity. Cytokine 2016, 77, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmuth, H.E.; Kunz, D.; Yagmur, E.; Timmer-Stranghöner, A.; Vidacek, D.; Siewert, E.; Bach, J.; Geier, A.; Purucker, E.A.; Gressner, A.M.; et al. Patients with acute on chronic liver failure display ‘sepsis-like’ immune paralysis. J. Hepatol. 2005, 42, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, C.L.; Silva, R.V.; Carrola, P.; Presa, J. Bacterial Infections in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis in an Internal Medicine Department. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 26, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamhane, U.U.; Aneja, S.; Montgomery, D.; Rogers, E.K.; Eagle, K.A.; Gurm, H.S. Association between admission neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 102, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, J.; Nunez, E.; Bodi, V.; Sanchis, J.; Miñana, G.; Mainar, L.; Santas, E.; Merlos, P.; Rumiz, E.; Darmofal, H.; et al. Usefulness of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in predicting long-term mortality in ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2008, 101, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.R.; Cook, E.J.; Goulder, F.; Justin, T.A.; Keeling, N.J. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2005, 91, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartal, O.; Kartal, A.T. Value of neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in pneumonia. Bratisl. Med. J. 2017, 118, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, A.U.; Küçük, A.; Şahin, A.; Ugan, Y.; Yilmaz, R.; Güngör, T.; Bağcacı, S.; Küçükşen, S. Two new inflammatory markers associated with Disease Activity Score-28 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, B.B.; Rifaioglu, E.N.; Ekiz, O.; Inan, M.U.; Sen, T.; Sen, N. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as a measure of systemic inflammation in psoriasis. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makay, B.; Gücenmez, Ö.A.; Duman, M.; Ünsal, E. The relationship of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with gastrointestinal bleeding in Henoch–Schonlein purpura. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akboga, M.K.; Canpolat, U.; Yayla, C.; Ozcan, F.; Ozeke, O.; Topaloglu, S.; Aras, D. Association of Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio With Inflammation and Severity of Coronary Atherosclerosis in Patients With Stable Coronary Artery Disease. Angiology 2016, 67, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, H.J.; Wu, Z.J.; Xiao, Z.M.; Xiang, B.D. The lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio is a superior predictor of overall survival compared to established biomarkers in HCC patients undergoing liver resection. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X. Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte-to-Monocyte Ratio Predicts Mortality in Patients with HBV-Related Decompensated Cirrhosis. Clin. Lab. 2019, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, Z.; Durrani, A.A. Assessing the outcome of patients with liver cirrhosis during hospital stay: A comparison of lymphocyte/monocyte ratio with MELD and Child-Pugh scores. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 29, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.J.; Dong, J.J.; Dong, J.Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Z.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Shi, K.Q.; Zhou, M.T. A nomogram for predicting prognostic value of inflammatory response biomarkers in decompensated cirrhotic patients without acute-on-chronic liver failure. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1413–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraja, B.; Sina, M.; Mone, I.; Pupuleku, F.; Babameto, A.; Prifti, S.; Burazeri, G. Predictive Value of the Model of End-Stage Liver Disease in Cirrhotic Patients with and without Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2012, 2012, 539059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.P.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Meng, F.K.; Xu, B.; Yu, H.W.; Meng, Q.H.; Liu, Y.M.; Zhang, S.B.; Meng, S.; et al. Comparison of the ability of the PDD-ICG clearance test, CTP, MELD, and MELD-Na to predict short-term and medium-term mortality in patients with decompensated hepatitis B cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Calculated Indices | First Publication | Required Parameters | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAR | Williams, Hoofnagle (1988) [14] | AST, ALT | |
| Modified APRI | Fix et al. (2005) [15] | albumin, AST, PLT, age | |
| FIB-4 | Sterling et al. (2006) [16] | ALT, AST, PLT, age | |
| NLR | Zahorec R (2001) [8] | neutrophil, lymphocyte | |
| LMR | Merekoulias G et al. (2010) [9] | lymphocyte, monocyte | |
| PLR | Turkmen K et al. (2013) [10] | PLT, lymphocyte | |
| NMR | Cihan YB et al. (2013) [11] | neutrophil, monocyte | |
| CTP | Pugh et al. (1973) [12] | bilirubin, albumin, prothrombin time, ascites, encephalopathy | a |
| MELD | Bambha K et al. (2004) [13] | creatinine, bilirubin, INR | b |
| Infection Type | Infectious Agent | Number of Cases (% of All Infections) |
|---|---|---|
| UTI | Escherichia coli Klebsiella pneumoniae Enterococcus faecalis | 32 (53.3%) 16 (26.7%) 4 (6.7%) |
| Pneumonia | Mycobacterium tuberculosis Citrobacter freundi Candida albicans | 1 (1.7%) 1 (1.7%) 1 (1.7%) |
| Sepsis | Staphylococcus aureus Coagulase-negative staphylococci Escherichia coli Streptococcus group B | 3 (5.0%) 2 (3.3%) 1 (1.7%) 1 (1.7%) |
| SBP | Escherichia coli Enterobacter faecalis | 1 (1.7%) 1 (1.7%) |
| Infected post-operative wound | Staphylococcus epidermidis | 1 (1.7%) |
| Abscess of subcutaneous tissue | Escherichia coli | 2 (3.3%) |
| Parameter | Presence of Infection (n = 60) | Lack of Infection (n = 149) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | 2.45 (1.45–6.00) | 1.85 (1.30–3.01) | 0.024 a |
| LMR | 1.43 (1.06–2.01) | 2.59 (1.73–3.84) | <0.001 c |
| PLR | 91.5 (58.8–118.6) | 73.2 (50.8–99.6) | 0.047 a |
| NMR | 5.00 (3.64–7.52) | 4.87 (3.72–7.33) | 0.988 |
| Monocytes [G/L] | 0.70 (0.42–1.02) | 0.54 (0.36–0.75) | 0.011 a |
| AAR | 1.88 (1.41–2.49) | 1.57 (0.98–2.01) | 0.014 a |
| Modified APRI | 15.86 (7.82–30.85) | 12.18 (6.58–31.76) | 0.755 |
| FIB-4 | 6.25 (2.99–10.72) | 6.37 (3.30–12.03) | 0.960 |
| CRP [mg/L] | 30.7 (9.2–40.6) | 6.5 (2.1–29.6) | 0.020 a |
| CTP | 10 (8–11) | 8 (6–9) | <0.001 c |
| MELD | 15 (12–22) | 13 (10–17) | 0.006 b |
| Parameter | AUC | p | Cut-Off | Se | Sp | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | 0.606 | 0.033 a | 3.96 | 0.434 | 0.860 | 0.561 | 0.787 |
| LMR | 0.715 | <0.001 c | 2.06 | 0.676 | 0.758 | 0.899 | 0.424 |
| Monocytes | 0.648 | 0.010 a | 0.91 | 0.455 | 0.867 | 0.517 | 0.835 |
| AAR | 0.610 | 0.013 a | 2.11 | 0.417 | 0.797 | 0.472 | 0.759 |
| CRP | 0.685 | 0.010 a | 9.2 | 0.760 | 0.600 | 0.613 | 0.750 |
| CTP | 0.687 | <0.001 c | 9.0 | 0.702 | 0.639 | 0.485 | 0.816 |
| MELD | 0.629 | 0.005 b | 18 | 0.439 | 0.783 | 0.500 | 0.738 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predictor | Odds Ratio | CI | p | Nagelkerke’s R2 | Odds Ratio | CI | p | Nagelkerke’s R2 |
| LMR | 0.15 | 0.06–0.37 | <0.001 c | 0.199 | 0.22 | 0.08–0.64 | 0.005 b | 0.251 |
| MONO | 5.42 | 2.23–13.15 | <0.001 c | 0.144 | ||||
| NLR | 4.38 | 2.09–9.17 | <0.001 c | 0.116 | ||||
| CRP | 3.86 | 1.24–12.04 | 0.020 a | 0.133 | ||||
| CTP | 3.17 | 1.52–6.62 | 0.002 b | 0.090 | 2.77 | 1.01–7.60 | 0.048 a | |
| MELD | 3.18 | 1.54–6.56 | 0.002 b | 0.077 | ||||
| AAR | 2.68 | 1.39–5.18 | 0.003 b | 0.060 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piotrowski, D.; Sączewska-Piotrowska, A.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Boroń-Kaczmarska, A. Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051727
Piotrowski D, Sączewska-Piotrowska A, Jaroszewicz J, Boroń-Kaczmarska A. Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(5):1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051727
Chicago/Turabian StylePiotrowski, Damian, Anna Sączewska-Piotrowska, Jerzy Jaroszewicz, and Anna Boroń-Kaczmarska. 2020. "Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 5: 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051727
APA StylePiotrowski, D., Sączewska-Piotrowska, A., Jaroszewicz, J., & Boroń-Kaczmarska, A. (2020). Lymphocyte-To-Monocyte Ratio as the Best Simple Predictor of Bacterial Infection in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5), 1727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051727





