Analysis of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Disease Using Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Hospital Admissions
2.2. Air Pollution and Meteorological Data
2.3. Method of Analysis
- (1)
- The measurement error level: We modeled the air pollution data on the log scale because the pollution concentrations were nonnegative and often skewed to the right. The combination of true underlying process and spatial effect is linked with the observed pollution concentrations using a measurement error model, where the measurement errors are independent with zero mean and constant variance of
- (2)
- The underlying process level: The true levels were modeled by a first order autoregressive process which had variance and lag one correlation coefficient . The spatial structure was represented by a set of zero-mean Gaussian random effects , which had variance and correlation matrix . The latter was constructed using the Matern class of functions, with a smoothness parameter fixed at 0.5. This gave an exponential correlation structure , where denotes Euclidean distance.
- (3)
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases. Available online: http://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Yin, P.; Liu, S.; You, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, M. The disease burden of cardiovascular and circulatory diseases in China, 1990 and 2010. Chin. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 49, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Mathers, C. The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, G.; Zhao, D.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, M.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; et al. Relationship between fine particulate air pollution and ischaemic heart disease morbidity and mortality. Heart 2015, 101, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brook, R.D.; Rajagopalan, S.; Pope, C.A., III; Brook, J.R.; Bhatnagar, A.; Diez-Roux, A.V.; Holguin, F.; Hong, Y.; Luepker, R.V.; Mittleman, M.A.; et al. Particulate matter air pollution and cardiovascular disease: An update to the scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2010, 121, 2331–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, M.; Mannucci, P.M. Air pollution and cardiovascular disease. Thrombosis Res. 2012, 129, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stieb, D.M.; Judek, S.; Burnett, R.T. Meta-analysis of time-series studies of air pollution and mortality: Effects of gases and particles and the influence of cause of death, age, and season. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hong, X.; Wold, L.E. Cardiovascular effects of ambient particulate air pollution exposure. Circulation 2010, 121, 2755–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; McDermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Burnett, R.T.; Turner, M.C.; Cohen, A.; Krewski, D.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Thun, M.J. Lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality associated with ambient air pollution and cigarette smoke: Shape of the exposure–response relationships. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Liu, E.; Verrier, R.L.; Schwartz, J.; Gold, D.R.; Mittleman, M.; Baliff, J.; Oh, J.A.; Allen, G.; Monahan, K.; et al. Air pollution and incidence of cardiac arrhythmia. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.K.; Yao, X. Air pollution in mega cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, R.A.; Muller, R.A. Air pollution in China: Mapping of concentrations and sources. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bozzetti, C.; Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Slowik, J.G.; Platt, S.M.; Canonaco, F.; et al. High secondary aerosol contribution to particulate pollution during haze events in China. Nature 2014, 514, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, H.; Chen, R.; Tong, S. Ambient air pollution, climate change, and population health in China. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matus, K.; Nam, K.M.; Selin, N.E.; Lamsal, L.N.; Reilly, J.M.; Paltsev, S. Health damages from air pollution in China. Glob. Environ.Chang. 2012, 22, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jin, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Jantunen, M.; Bi, J.; et al. Spatial and temporal trends in the mortality burden of air pollution in China: 2004–2012. Environ. Int. 2017, 98, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jia, Y.; Pan, X.; Liu, L.; Wichmann, H.E. The association between fine particulate air pollution and hospital emergency room visits for cardiovascular diseases in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 4826–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, H.; Huang, W.; Chen, B.; Zhao, N. Impact of outdoor air pollution on cardiovascular health in Mainland China. CVD Prev. Control. 2009, 4, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, G.; Sun, B.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Ma, N.; Yu, F.; Guo, H.; Huang, H.; Lee, Y.L.; et al. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution and mortality due to cardiovascular disease and cerebrovascular disease in Shenyang, China. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.W.; Tam, W.S.; Yu, T.S.; Wong, A.H. Associations between daily mortalities from respiratory and cardiovascular diseases and air pollution in Hong Kong, China. Occ. Environ. Med. 2002, 59, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Kan, H. Short-term exposure to ambient air pollution and coronary heart disease mortality in 8 Chinese cities. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 197, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Peng, L.; Kan, H.; Wang, W.; Geng, F.; Mu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, D. Acute effects of particulate air pollution on the incidence of coronary heart disease in Shanghai, China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Westerdahl, D.; Mo, Y.; Liang, F.; Pan, X. Spatiotemporal analysis of particulate air pollution and ischemic heart disease mortality in Beijing, China. Environ. Health 2014, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; He, G.; Fan, M.; Chiu, K.Y.; Fan, M.; Liu, C.; Xue, A.; Liu, T.; Pan, Y.; Mu, Q.; et al. Particulate air pollution and mortality in 38 of China’s largest cities: Time series analysis. Br. Med. J. 2017, 356, j667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Shaddick, G. Spatial modeling of air pollution in studies of its short-term health effects. Biometrics 2010, 66, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H. Heritage Tourism in China: Modernity, Identity and Sustainability; Channel View Publications: Bristol, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Diggle, P.J.; Tawn, J.A.; Moyeed, R.A. Model-based geostatistics. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C App. Stat. 1998, 47, 299–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A. Prior distributions for variance parameters in hierarchical models (comment on article by Browne and Draper). Bayesian Anal. 2006, 1, 515–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.J. Generalized additive models. In Statistical Models in S; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 249–307. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Akaike, H. Factor analysis and AIC. In Selected Papers of Hirotugu Akaike; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1987; pp. 371–386. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. China’s Ambient air Quality Secondary Standards. Available online: http://kjs.mep.gov.cn/hjbhbz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/t20120302_224165.shtml (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Cohen, A.J.; Ross Anderson, H.; Ostro, B.; Pandey, K.D.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Künzli, N.; Gutschmidt, K.; Pope, A.; Romieu, I.; Samet, J.M.; et al. The global burden of disease due to outdoor air pollution. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2005, 68, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, J.N.; Ma, G.X.; Zhang, Y.S. China tackles the health effects of air pollution. Lancet 2013, 382, 1959–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Dockery, D.W. Health effects of fine particulate air pollution: Lines that connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlin, B.P.; Xia, H.; Devine, O.; Tolbert, P.; Mulholland, J. Spatio-temporal hierarchical models for analyzing Atlanta pediatric asthma ER visit rates. In Case Studies in Bayesian Statistics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 303–320. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Carlin, B.P.; Gelfand, A.E. Hierarchical regression with misaligned spatial data: Relating ambient ozone and pediatric asthma ER visits in Atlanta. Environ. Off. J. Int. Environ. Soc. 2003, 14, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.; Peng, R.D.; Dominici, F. Estimating the acute health effects of coarse particulate matter accounting for exposure measurement error. Biostatistics 2011, 12, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L. Spatial misalignment in time series studies of air pollution and health data. Biostatistics 2010, 11, 720–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Gou, Y.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Yuan, Z.; Kong, L.; Xue, F. A Multicity Analysis of the Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Hospital Admissions in Shandong, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Kan, H.; Chen, B.; Huang, W.; Bai, Z.; Song, G.; Pan, G. Association of particulate air pollution with daily mortality: The China Air Pollution and Health Effects Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
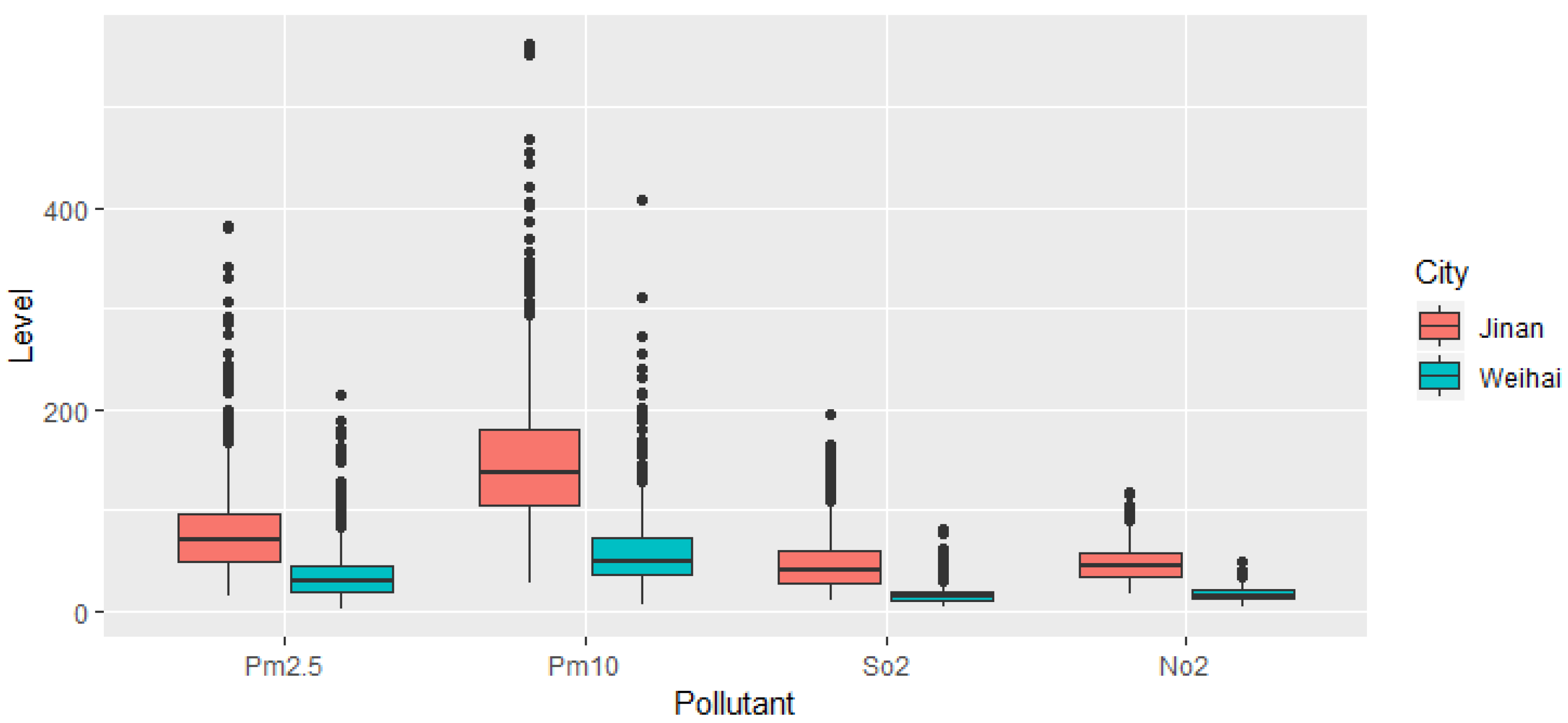
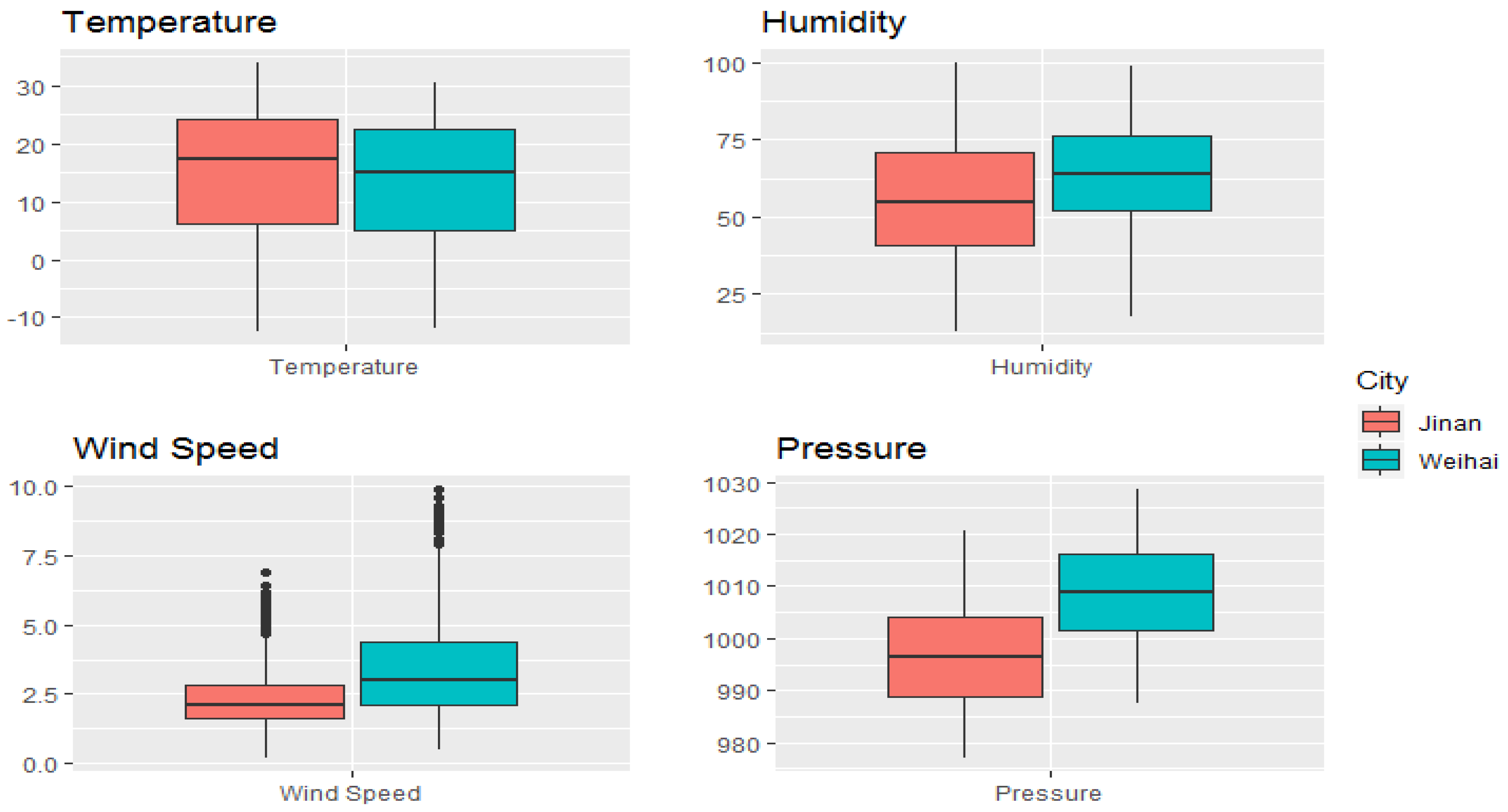
| City | Hospitalization (Cases/Per Day) | Min | P25 | P50 | P75 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 8 | 195 | 291 | 346 | 580 | |
| Male | 5 | 106 | 158 | 191 | 308 | |
| Jinan | Female | 3 | 89 | 131 | 157 | 274 |
| ≥65 | 3 | 103 | 148 | 180 | 361 | |
| <65 | 5 | 92 | 138 | 169 | 296 | |
| Total | 1 | 67 | 80 | 96 | 200 | |
| Male | 0 | 37 | 45 | 54 | 113 | |
| Weihai | Female | 1 | 29 | 36 | 43 | 89 |
| ≥65 | 0 | 37 | 45 | 54 | 109 | |
| <65 | 1 | 28 | 35 | 44 | 104 |
| Jinan | |||||||
| PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | ||||
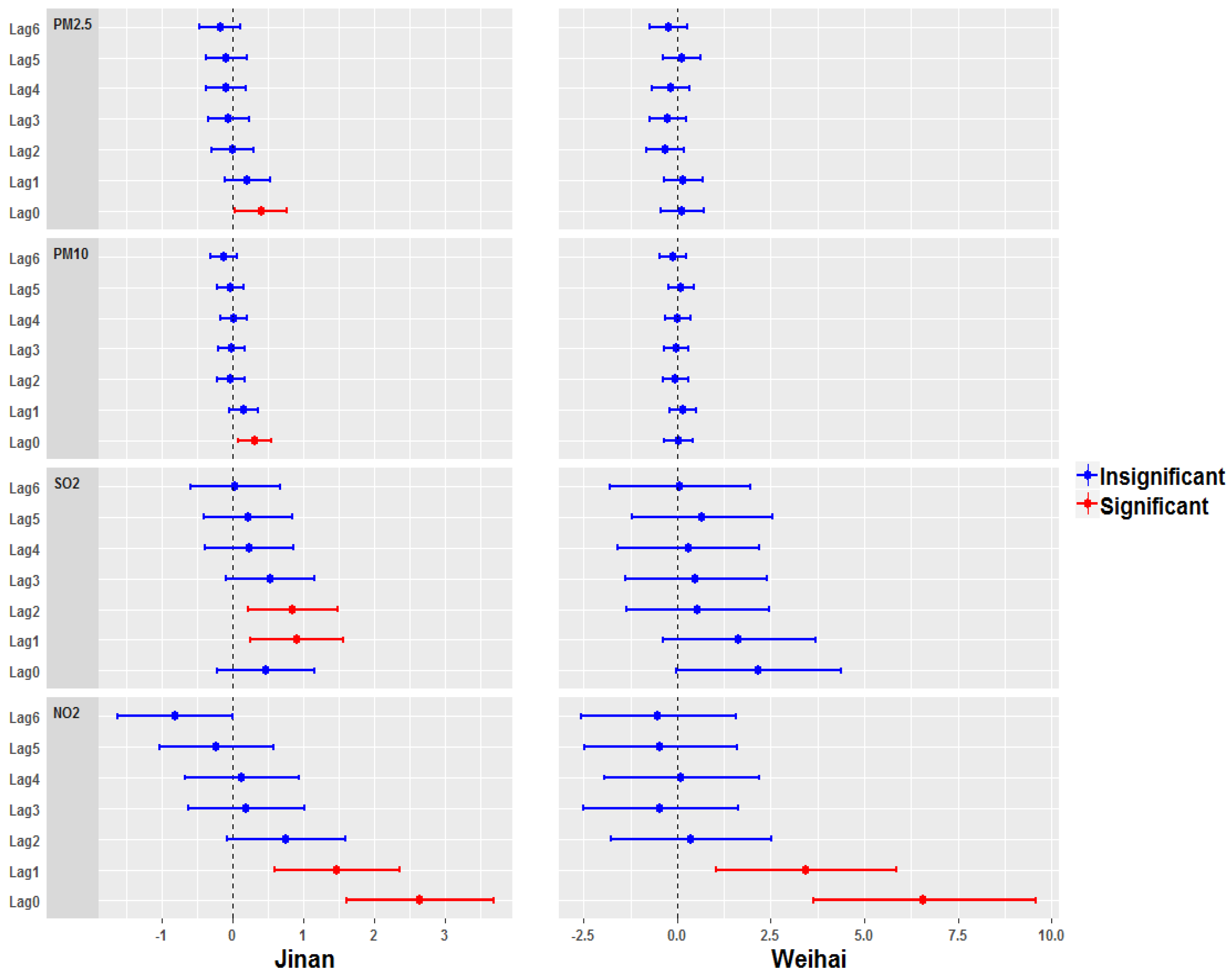
| Single pollutant | 0.401 (0.029, 0.775) * | Single pollutant | 0.316 (0.086, 0.547) * | Single pollutant | 0.903 (0.252, 1.559) * | Single pollutant | 2.647 (1.607, 3.697) * |
| +PM10 | −0.279 (−1.106, 0.555) | +PM2.5 | 0.472 (−0.045, 0.992) | +PM2.5 | 0.889 (0.156, 1.628) * | + PM2.5 | 3.164 (1.835, 4.509) * |
| +SO2 | 0.360 (−0.057, 0.778) | +SO2 | 0.307 (0.050, 0.565) * | +PM10 | 0.859 (0.115, 1.609) * | + PM10 | 3.018 (1.631, 4.423) * |
| +NO2 | −0.295 (−0.764, 0.177) | +NO2 | −0.124 (−0.429, 0.183) | +NO2 | 0.298 (−0.584, 1.188) | + SO2 | 3.879 (2.483, 5.295) * |
| +All | −0.342 (−1.181, 0.504) | +All | 0.071 (−0.475, 0.620) | +All | 0.316 (−0.568, 1.208) | +All | 4.229 (2.564, 5.922) * |
| Weihai | |||||||
| PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 | NO2 | ||||
| Single pollutant | 0.161 (−0.356, 0.680) | Single pollutant | 0.143 (−0.210, 0.497) | Single pollutant | 2.149 (−0.031, 4.377) | Single pollutant | 6.568 (3.636, 9.584) * |
| +PM10 | −0.001 (−0.808, 0.812) | +PM2.5 | 0.144 (−0.409, 0.699) | +PM2.5 | 3.580 (0.472, 6.785) * | +PM2.5 | 9.606 (5.887, 13.456) * |
| +SO2 | −0.239 (−0.949, 0.477) | +SO2 | −0.021 (−0.447, 0.407) | + PM10 | 2.875 (0.264, 5.554) * | +PM10 | 8.453 (5.048, 11.970) * |
| +NO2 | −0.536 (−1.204, 0.136) | +NO2 | −0.167 (−0.582, 0.249) | +NO2 | −1.980 (−4.767, 0.887) * | +SO2 | 8.415 (4.448, 12.532) * |
| +All | −0.654 (−1.597, 0.298) | +All | 0.098 (−0.457, 0.656) | +All | 0.035 (−3.277, 3.460) | +All | 9.648 (5.518, 13.940) * |
| Jinan | Weihai | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pollutant | Class | Estimate | Lag | Estimate | Lag |
| PM2.5 | Male | 0.404 (0.009, 0.801) * | 0 | −0.419 (−0.992, 0.157) | 2 |
| Female | 0.398 (0.013, 0.783) * | 0 | −0.420 (−1.010, 0.174) | 3 | |
| ≥65 | 0.323 (−0.056, 0.704) | 0 | 0.660 (0.109, 1.214) * | 5 | |
| <65 | 0.485 (0.074, 0.899) * | 0 | −0.577 (−1.198, 0.048) | 3 | |
| PM10 | Male | 0.308 (0.063, 0.553) * | 0 | 0.119 (−0.260, 0.499) | 3 |
| Female | 0.326 (0.088, 0.565) * | 0 | 0.283 (−0.138, 0.706) | 1 | |
| ≥65 | 0.279 (0.045, 0.514) * | 0 | 0.306 (−0.068, 0.682) | 5 | |
| <65 | 0.356 (0.100, 0.612) * | 0 | −0.257 (−0.684, 0.172) | 4 | |
| SO2 | Male | 0.749 (0.058, 1.445) * | 1 | 2.859 (0.340, 5.441) * | 0 |
| Female | 1.089 (0.415, 1.768) * | 1 | 1.281 (−1.292, 3.921) | 0 | |
| ≥65 | 0.709 (0.041, 1.381) * | 1 | 2.438 (0.344, 4.576) * | 5 | |
| <65 | 1.116 (0.398, 1.839) * | 1 | 1.924 (−0.807, 4.730) | 0 | |
| NO2 | Male | 2.516 (1.414, 3.630) * | 0 | 7.419 (4.031, 10.918) * | 0 |
| Female | 2.803 (1.725, 3.892) * | 0 | 5.535 (2.070, 9.119) * | 0 | |
| ≥65 | 2.284 (1.225, 3.355) * | 0 | 7.612 (4.321, 11.006) * | 0 | |
| <65 | 3.033 (1.880, 4.199) * | 0 | 5.236 (1.591, 9.011) * | 0 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Gou, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhang, D.; Xue, F. Analysis of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Disease Using Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Models. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030879
Liu Y, Sun J, Gou Y, Sun X, Zhang D, Xue F. Analysis of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Disease Using Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030879
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi, Jingjie Sun, Yannong Gou, Xiubin Sun, Dandan Zhang, and Fuzhong Xue. 2020. "Analysis of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Disease Using Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Models" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030879
APA StyleLiu, Y., Sun, J., Gou, Y., Sun, X., Zhang, D., & Xue, F. (2020). Analysis of Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Cardiovascular Disease Using Bayesian Spatio-Temporal Models. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030879




