Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Elderly Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Enrollment of Patients
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Polysomnographic Data
2.4. POSA Diagnosis and Classifications
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Results
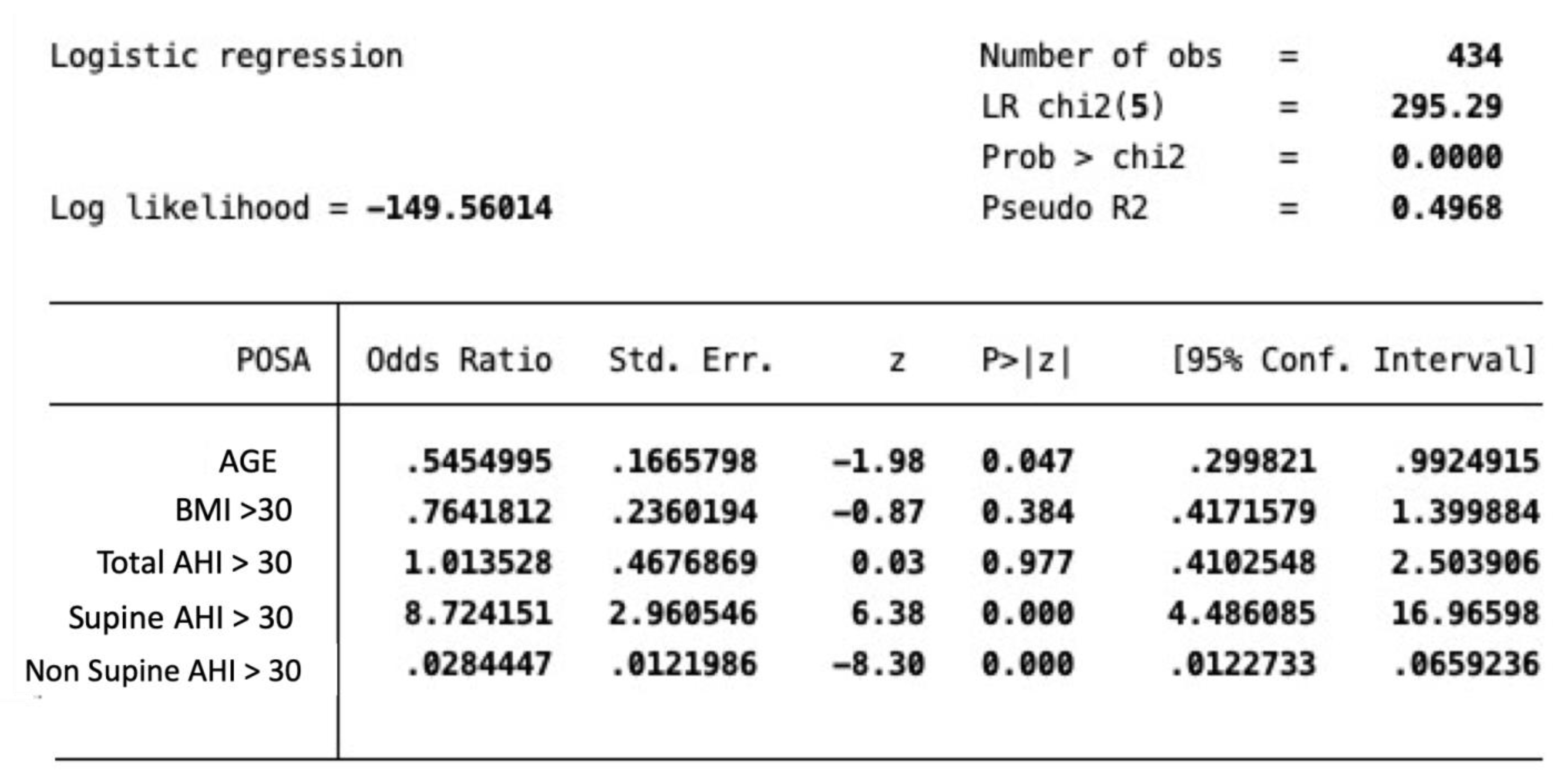
3.2. POSA Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, T.; Peppard, P.E.; Gottlieb, D.J. Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: A population health perspective. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufik, S.; Santos-Silva, R.; Taddei, J.A.; Bittencourt, L.R.A. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in the Sao Paulo Epidemiologic Sleep Study. Sleep Med. 2010, 11, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoff, R.J.; Cheong, T.H.; Olha, A.E.; Charbonneau, M.A.R.C.; Levy, R.D.; Cosio, M.G.; Gottfried, S.B. Mechanisms of apnea termination in obstructive sleep apnea: Role of chemoreceptor and mechanoreceptor stimuli. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1994, 149, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Schneider, H.; Schwartz, A.R.; Smith, P.L. Adult obstructive sleep apnea: Pathophysiology and diagnosis. Chest 2007, 132, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, R.B.; Gamaldo, C.; Harding, S.M.; Lloyd, R.M.; Quan, S.F.; Troester, M.T.; Vaughn, V.B. AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Darien, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Weinstein, M.D. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Shochat, T.; Pillar, G. Sleep apnoea in the older adult: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, consequences and management. Drugs Aging 2003, 20, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.; Shahar, E.; Nieto, F.J.; Redline, S.; Newman, A.B.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Samet, J.M. Predictors of sleep-disordered breathing in community-dwelling adults: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliulo, G.; De Vincentiis, M.; Iannella, G.; Ciofalo, A.; Pasquariello, B.; Manno, A.; Polimeni, A. Olfactory evaluation in obstructive sleep apnoea patients. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Miyamoto, M.; Hirata, K. Sleep disorders in the elderly: Diagnosis and management. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 2017, 18, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Srinivasan, K.; Naicker, T.R.; Moudgil, H. Sleep apnoea in the elderly. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppard, P.E.; Young, T.; Barnet, J.H.; Palta, M.; Hagen, E.W.; Hla, K.M. Increased incidence of sleep-disordered breathing in adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaremchuk, K. Sleep Disorders in the Elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 34, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, P.; Alehagen, U.; Ulander, M.; Svanborg, E.; Dahlström, U.; Broström, A. Sleep disordered breathing in community dwelling elderly: Associations with cardiovascular disease, impaired systolic function, and mortality after a six-year follow-up. Sleep Med. 2011, 12, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancoli-Israel, S.; Kripke, D.F.; Klauber, M.R.; Fell, R.; Stepnowsky, C.; Estline, E.; Chinn, A. Morbidity, mortality and sleep-disordered breathing in community dwelling elderly. Sleep 1996, 19, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Morrell, M.J.; Finn, L.; McMillan, A.; Peppard, P.E. The impact of ageing and sex on the association between sleepiness and sleep disordered breathing. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, A.; Morrell, M.J. Sleep disordered breathing at the extremes of age: The elderly. Breathe 2016, 12, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzer, R.; Petitpierre, N.J.; Marti-Soler, H.; Haba-Rubio, J. Incidence and characteristics of positional sleep apnea in the HypnoLaus population-based cohort. Sleep Med. 2018, 48, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, W.; Kox, D.; den Herder, C.; Laman, M.; van Tinteren, H.; de Vries, N. The role of sleep position in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 263, 946–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksenberg, A. Positional and non-positional obstructive sleep apnea patients. Sleep Med. 2005, 6, 377–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravesloot, M.J.L.; van Maanen, J.P.; Dun, L.; de Vries, N. The undervalued potential of positional therapy in position-dependent snoring and obstructive sleep apnea-a review of the literature. Sleep Breath. 2013, 17, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.H.; Ravesloot, M.J.L.; van Maanen, J.P.; Verhagen, E.; de Lange, J.; de Vries, N. Positional OSA part 1: Towards a clinical classification system for position-dependent obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravesloot, M.J.L.; Frank, M.H.; van Maanen, J.P.; Verhagen, E.A.; de Lange, J.; de Vries, N. Positional OSA part 2: Retrospective cohort analysis with a new classification system (APOC). Sleep Breath. 2016, 20, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duce, B.; Kulkas, A.; Langton, C.; Töyräs, J.; Hukins, C. Amsterdam positional OSA classification: The AASM 2012 recommended hypopnoea criteria increases the number of positional therapy candidates. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliven, A.; Carmi, N.; Coleman, R.; Odeh, M.; Silbermann, M. Age-related changes in upper airway muscles morphological and oxidative properties. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, Z.; Susarla, S.; Troulis, M.; Kaban, L. Age-related changes of the upper airway assessed by 3-dimensional computed tomography. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 1, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauter, E.; Leproult, R.; Plat, L. Age-related changes in slow wave sleep and REM sleep and relationship with growth hormone and cortisol levels in healthy men. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2000, 284, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, J.-P.; Pautex, S.; Hilleret, H.; Michel, J.-P. Sleep disordered breathing in the elderly. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2000, 12, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicini, C.; De Vito, A.; Iannella, G.; Gobbi, R.; Corso, R.M.; Montevecchi, F.; Cammaroto, G. The aging effect on upper airways collapse of patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 275, 2983–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Viana, A.; Ma, Y.; Capasso, R. The effect of aging on drug-induced sleep endoscopy findings. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 2644–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Budhiraja, R.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Gozal, D.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.K.; Redline, S. Rules for Scoring Respiratory Events in Sleep: Update of the 2007 AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2012, 8, 597–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudawara, N.K.; Bousoffara, L.; Ouaja, R.; Bouchareb, S.; Khalil, H.; Sakka, M.; Knani, J. Obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome in eldery patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, P2265. [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright, R.D. Effect of sleep position on sleep apnea severity. Sleep 1984, 7, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignold, J.J.; Mercer, J.D.; Antic, N.A.; McEvoy, R.D.; Catcheside, P.G. Accurate position monitoring andimproved supine-dependent obstructive sleep apnea with a new position recording and supine avoidance device. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2011, 7, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulhaj, A.; Al Dhaheri, S.; Su BBin Al-Houqani, M. Discriminating between positional and non-positional obstructive sleep apnea using some clinical characteristics. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-A.; Paek, J.-H.; Chung, Y.-S.; Kim, W.S. Clinical features in patients with positional obstructive sleep apnea according to its subtypes. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Cho Yw Kim, D.E.; Hwang, S.H.; Song, M.L.; Motamedi, G.K. Two subtypes of positional obstructive sleep apnea: Supine-predominant and supine-isolated. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2015, 127, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mador, M.J.; Kufel, T.J.; Magalang, U.J.; Rajesh, S.K.; Watwe, V.; Grant, B.J.B. Incidence of positional sleep apnea in patients undergoing polysomnography. Chest 2005, 128, 2130–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinzer, R.; Vat, S.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Marti-Soler, H.; Andries, D.; Tobback, N.; Vollenweider, P. Incidence of sleep-disordered breathing in the general population: The HypnoLaus study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Allgar, V.; Elliott, M.W. Identifying poor compliance with CPAP in obstructive sleep apnoea: A simple prediction equation using data after a two week trial. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guralnick, A.S.; Balachandran, J.S.; Szutenbach, S.; Adley, K.; Emami, L.; Mohammadi, M.; Mokhlesi, B. Educational video to improve CPAP use in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea at risk for poor adherence: A randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2017, 72, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannella, G.; Vicini, C.; Polimeni, A.; Greco, A.; Gobbi, R.; Montevecchi, F.; Pace, A. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux Diagnosis in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients Using the Pepsin Salivary Test. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, C.J.; Cramer, J.D.; Liu, S.Y.C.; Capasso, R. Sleep Surgery in the Elderly: Lessons from the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, N.; Ravesloot, M.; Van Maanen, J.P. Positional Therapy in Obstructive Sleep Apnea; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mador, M.J.; Choi, Y.; Bhat, A.; Dmochowski, J.; Braun, M.; Gottumukkala, V.A.; Grant, B.J. Are the adverse effects of body position in patients with obstructive sleep apnea dependent on sleep stage? Sleep Breath. 2010, 14, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzel, T.; Möller, M.; Becker, H.F.; Knaack, L.; Peter, J.H. Effect of sleep position and sleep stage on the collapsibility of the upper airways in patients with sleep apnea. Sleep 2001, 24, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| <65 | >65 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TOTAL NUMBER OF PATIENTS | 288 | 146 | |
| M | 207 (71%) | 100 (68.4%) | chi square = 0.38 degree of freedom = 1 p = 0.5 |
| F | 81 (28.1%) | 46 (31.5%) | |
| MIDDLE AGE | 51.4 | 72.41 | Student’s t-test t = −25.5 p = 0.0001 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| BMI | Mean = 31.1 CI: 30.29–31.82 SD = 6.55 Hi = 41.1 Low = 20.0 Median = 29.8 | Mean = 29.9 CI: 28.86–30.89 SD = 4.49 Hi = 42.6 Low = 20.4 Median = 29.2 | Student’s t-test p = 0.06 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| AHI | Mean = 27.4 CI: 24.92–29.95 SD = 21.6 Hi = 103 Low = 5.00 Median = 20.1 | Mean = 28.3 CI: 24.80–31.86 SD = 22.0 Hi = 109 Low = 5.10 Median = 20.9 | Student’s t-test t = -0.4 p = 0.6 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| AHI supine position | Mean = 38.0 CI: 35.04–40.89 SD = 25.3 Hi = 110 Low = 0.00 Median = 30.4 | Mean = 37.7 CI: 33.54–41.76 SD = 25.2 Hi = 118 Low = 2.00 Median = 33.1 | Student’s t-test t = 0.1 p = 0.9 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| AHI non-supine position | Mean = 19.9 CI: 17.31–22.41 SD = 21.9 Hi = 93.0 Low = 0.00 Median = 11.4 | Mean = 21.7 CI: 18.16–25.33 SD = 22.4 Hi = 116. Low = 0.00 Median = 12.8 | Student’s t-test t = -0.8 p = 0.4 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| Percentage of time in supine position | Mean = 44.8 CI: 41.99–47.70 SD = 23.2 Hi = 100. Low = 5.70 Median = 42.5 | Mean = 44.8 CI: 41.99–47.70 SD = 23.2 Hi = 100 Low = 5.70 Median = 42.5 | Student’s t-test t = −0.1 p = 0.9 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| Percentage of time in non-supine position | Mean = 55.1 CI: 52.29–58.00 SD = 23.2 Hi = 94.3 Low = 0.00 Median = 57.5 | Mean = 54.9 CI: 50.88–58.90 SD = 27.3 Hi = 97.2 Low = 0.900 Median = 60.8 | Student’s t-test t = 0.7 p = 0.9 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| Mean SpO2 | Mean = 91.6 CI: 90.92–92.19 SD = 6.29 Hi = 97.0 Low = 67.5 Median = 92.4 | Mean = 91.2 CI: 90.33–92.11 SD = 3.34 Hi = 97.0 Low = 70.5 Median = 91.8 | Student’s t-test t = 0.6 p = 0.5 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| Total time of sleep(hours) | Mean = 7.03 SD = 0.837 Hi = 8.80 Low = 6.00 Median = 7.00 Average Absolute Deviation from Median = 0.677 | Mean = 7.10 SD = 0.789 Hi = 9.00 Low = 6.00 Median = 7.00 Average Absolute Deviation from Median = 0.580 | Student’s t-test t = -0.1 p = 0.4 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| ODI | Mean = 30.1 CI: 26.41–33.71 SD = 21.9 Hi = 109 Low = 4.40 Median = 22.9 | Mean = 30.1 CI: 26.41–33.71 SD = 21.9 Hi = 109 Low = 4.40 Median = 22.9 | Student’s t-test t = -0.5 p = 0.5 degrees of freedom = 432 |
| <65 288 Patients | >65 146 Patients | p-Value Chi Square Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild OSA | 106 (36.8%) | 47 (32.1%) | p = 0.3 degrees of freedom = 1 |
| Moderate OSA | 88 (30.5%) | 52 (35.6%) | p = 0.4 degrees of freedom = 1 |
| Severe OSA | 94 (32.6%) | 47 (32.1%) | p = 1 degrees of freedom = 1 |
| POSA CLASSIFICATION | <65 Years Old 288 Patients | >65 Years Old 146 Patients | Chi Square Test with Yates Correction p-Value Degrees of Freedom | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POSA + | POSA - | POSA + | POSA - | ||
| CARTRIGHT | 148 (51.3%) | 140 (48.6%) | 72 (49.3%) | 74 (50.7%) | Chi squared = 0.09 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.7 |
| BIGNOLD | 66 (22.9%) | 222 (77.1%) | 30 (20.5%) | 116 (79.4%) | Chi squared = 0.2 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.6 |
| APOC1 | 86 (29.8%) | 33 (22.6%) | Chi squared = 2.2 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.1 | ||
| APOC2 | 59 (20.4%) | 27 (38.9%) | Chi squared = 0.1 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.7 | ||
| APOC3 | 20 (6.9%) | 8 (5.4%) | Chi squared = 0.14 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.6 | ||
| NON APOC | 123 (42.7%) | 78 (53.4%) | Chi squared = 4.05 degrees of freedom = 1 p = 0.06 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannella, G.; Magliulo, G.; Lo Iacono, C.A.M.; Bianchi, G.; Polimeni, A.; Greco, A.; De Vito, A.; Meccariello, G.; Cammaroto, G.; Gobbi, R.; et al. Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Elderly Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031120
Iannella G, Magliulo G, Lo Iacono CAM, Bianchi G, Polimeni A, Greco A, De Vito A, Meccariello G, Cammaroto G, Gobbi R, et al. Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Elderly Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(3):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031120
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannella, Giannicola, Giuseppe Magliulo, Cristina Anna Maria Lo Iacono, Giulia Bianchi, Antonella Polimeni, Antonio Greco, Andrea De Vito, Giuseppe Meccariello, Giovanni Cammaroto, Riccardo Gobbi, and et al. 2020. "Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Elderly Patients" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 3: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031120
APA StyleIannella, G., Magliulo, G., Lo Iacono, C. A. M., Bianchi, G., Polimeni, A., Greco, A., De Vito, A., Meccariello, G., Cammaroto, G., Gobbi, R., Brunori, M., Di Luca, M., Montevecchi, F., Pace, A., Visconti, I. C., Milella, C., Solito, C., Pelucchi, S., Cerritelli, L., & Vicini, C. (2020). Positional Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in Elderly Patients. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(3), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17031120










