Self-Quantification Systems to Support Physical Activity: From Theory to Implementation Principles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characterization of the Quantified Self Movement
2.1. Self-Tracking Background
2.2. Modern Quantified Self and Personal Informatics
2.3. Goals of Quantified Selfers
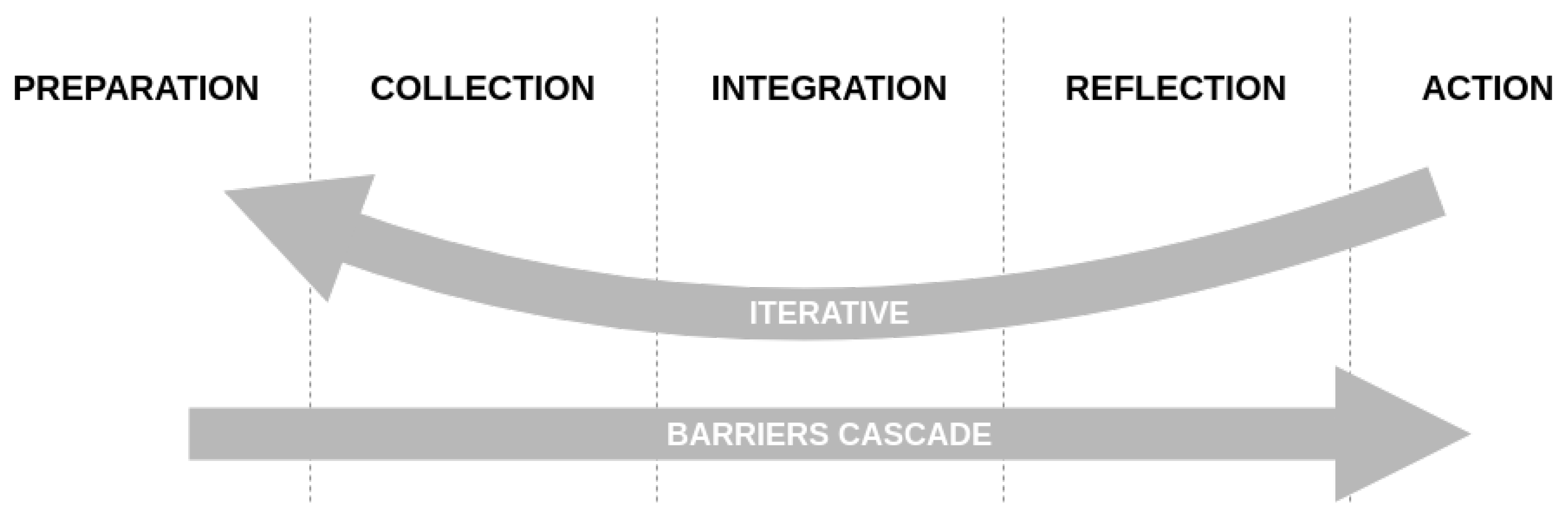
2.4. Barriers and Limits
2.5. Conceptual Models
2.5.1. Stage-Based Model
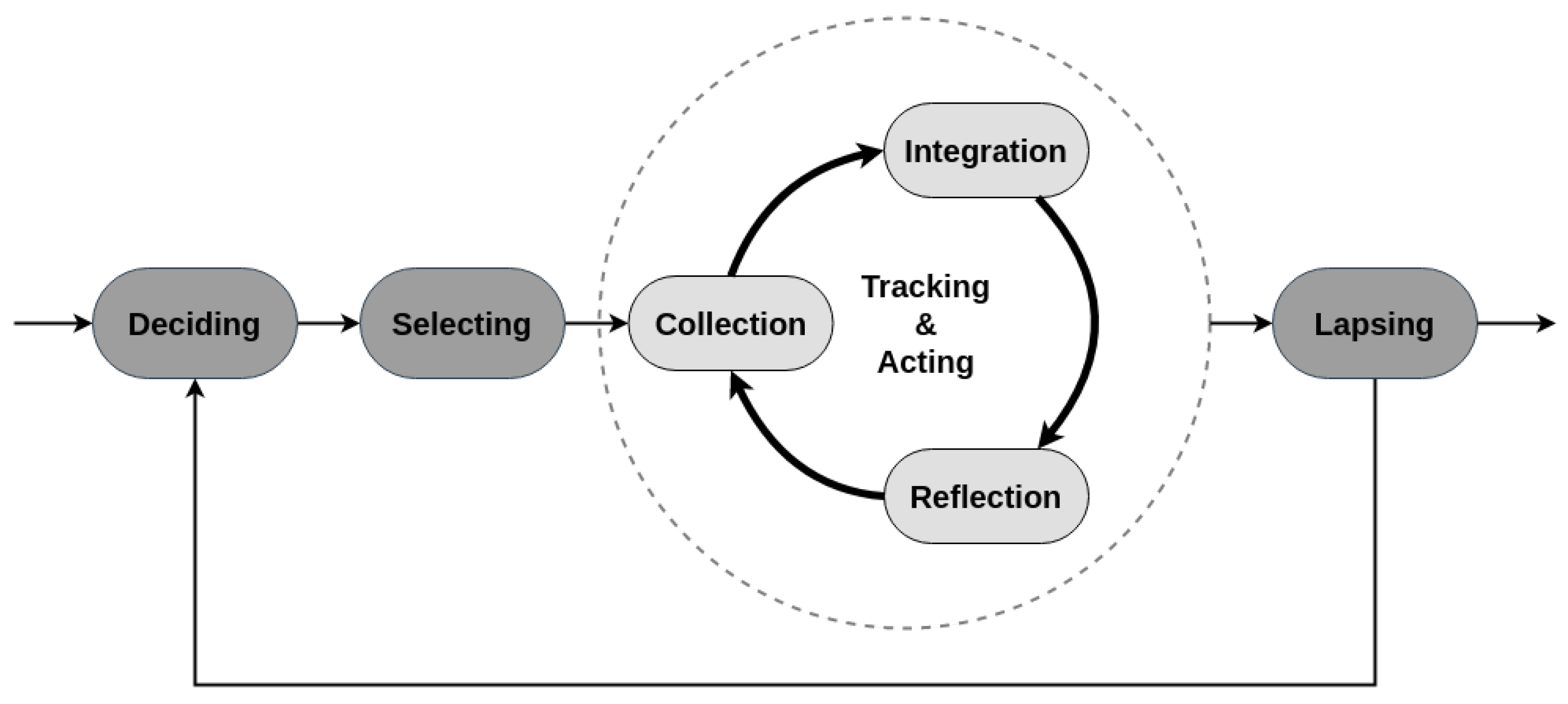
2.5.2. Lived Informatics Model
2.5.3. Conceptual Model of Shared Health Informatics
2.6. Existing Barriers and Guidelines for Design
2.6.1. Barriers
2.6.2. Guidelines
3. Criticism of Guidelines from the Literature
- Abstract and Reflective—use data abstraction, on Li’s integration stage for example, to encourage the user to reflect on his/her behaviors.
- Unobtrusive—collect and present data unobtrusively by limiting interruptions and making data available anytime.
- Public—present personal data to the user in a way that s.he is comfortable with if other people see it.
- Aesthetic—devices and displays must sustain interest, be comfortable and attractive to support the user’s personal style.
- Positive—use positive reinforcement to encourage change, reward the user for performing the desired behavior and attaining a goal.
- Controllable—permit the user to manipulate data so that it reflects the behavior he/she deems suitable.
- Trending/Historical—provide information about the user’s past behavior relating to his/her goals.
- Comprehensive—account for the range of behaviors contributing to the user’s desired lifestyle.
4. Model for a Self-Quantification System for Physical Activity Support
4.1. Use Case Example
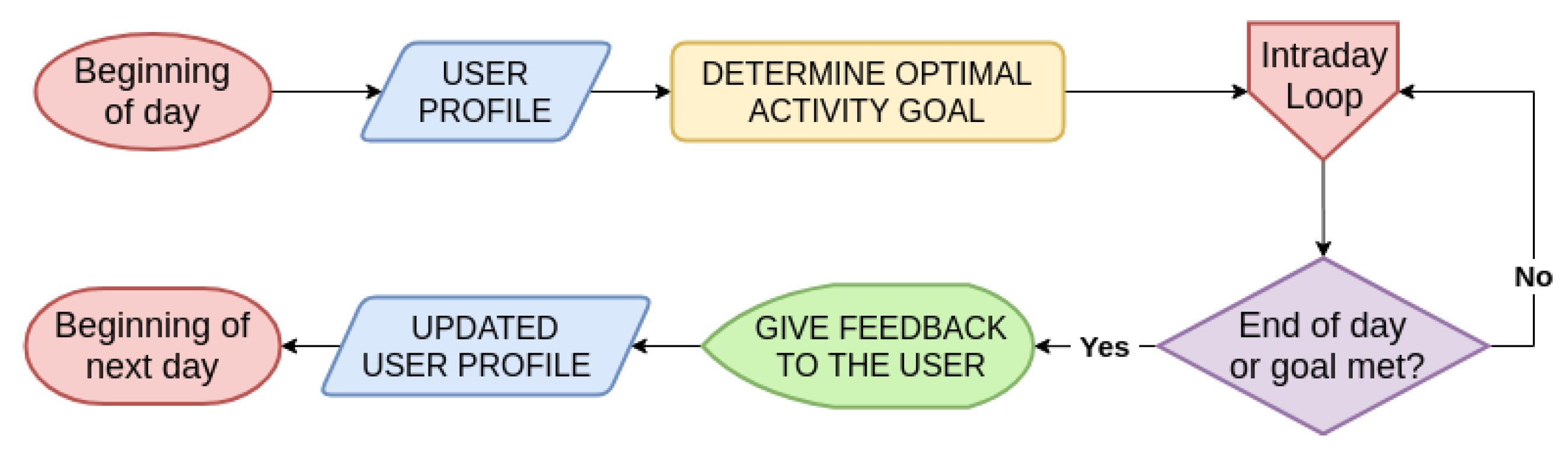
4.2. Learning Phase
4.3. Support Phase
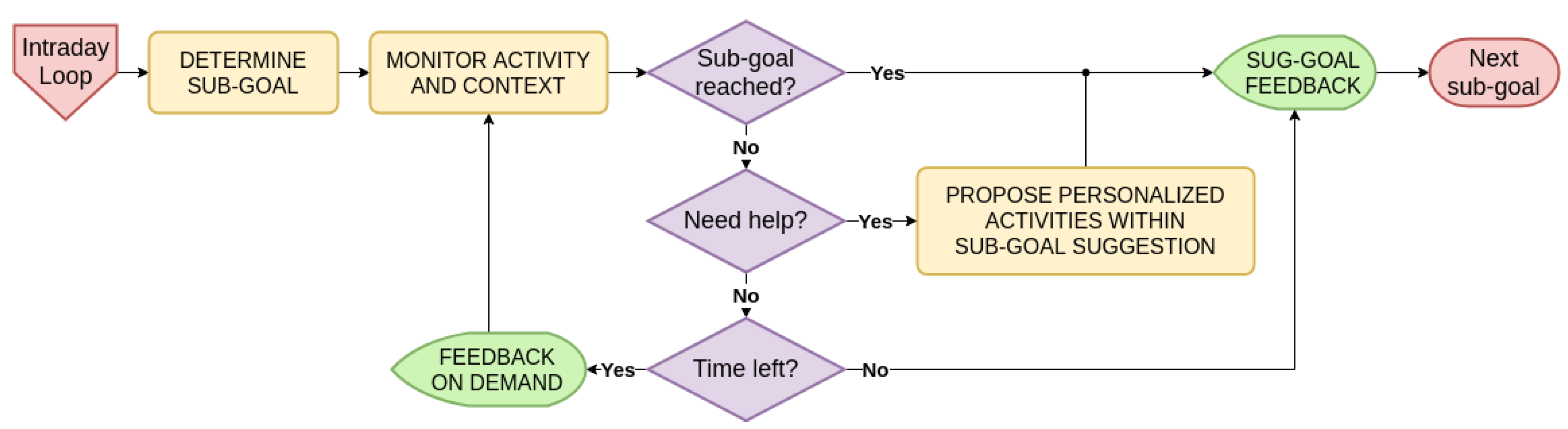
4.3.1. Daily Time Scale
4.3.2. Intraday Time Scale
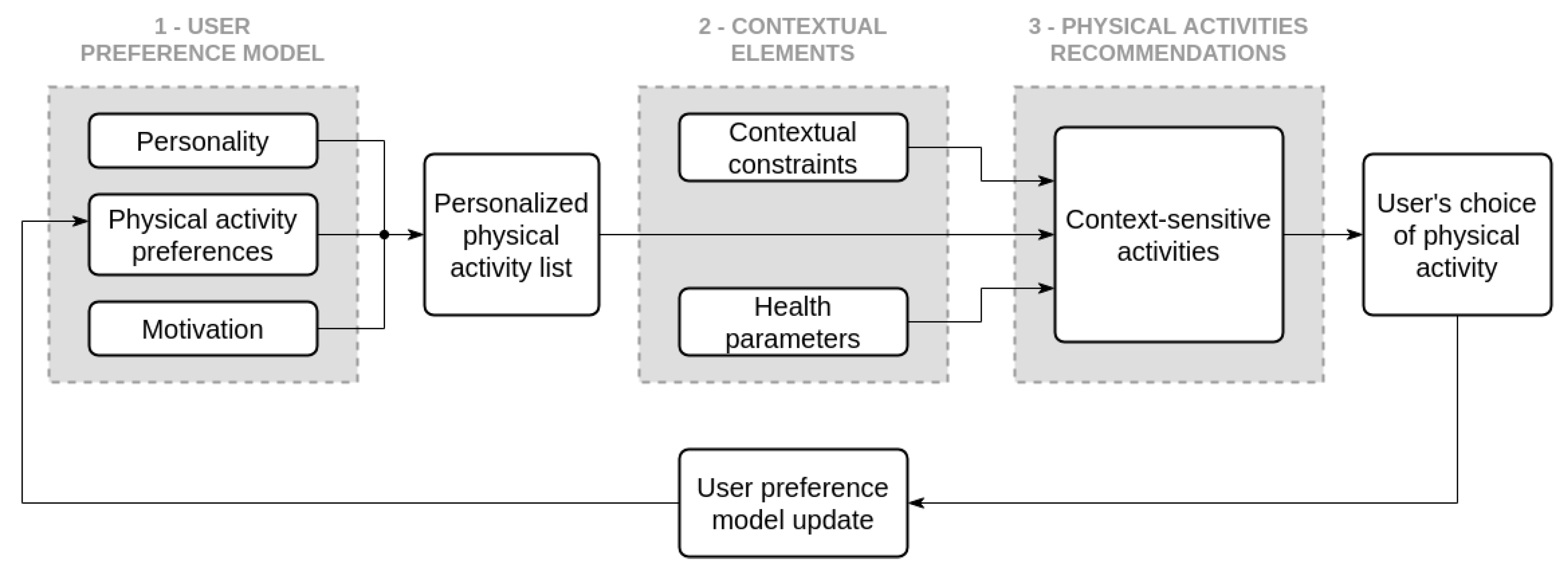
4.3.3. Personalized and Adapted Physical Activity Choice
4.4. Towards an Application of the Model: System Design and Development Challenges
5. Contributions and Limitations of the Model
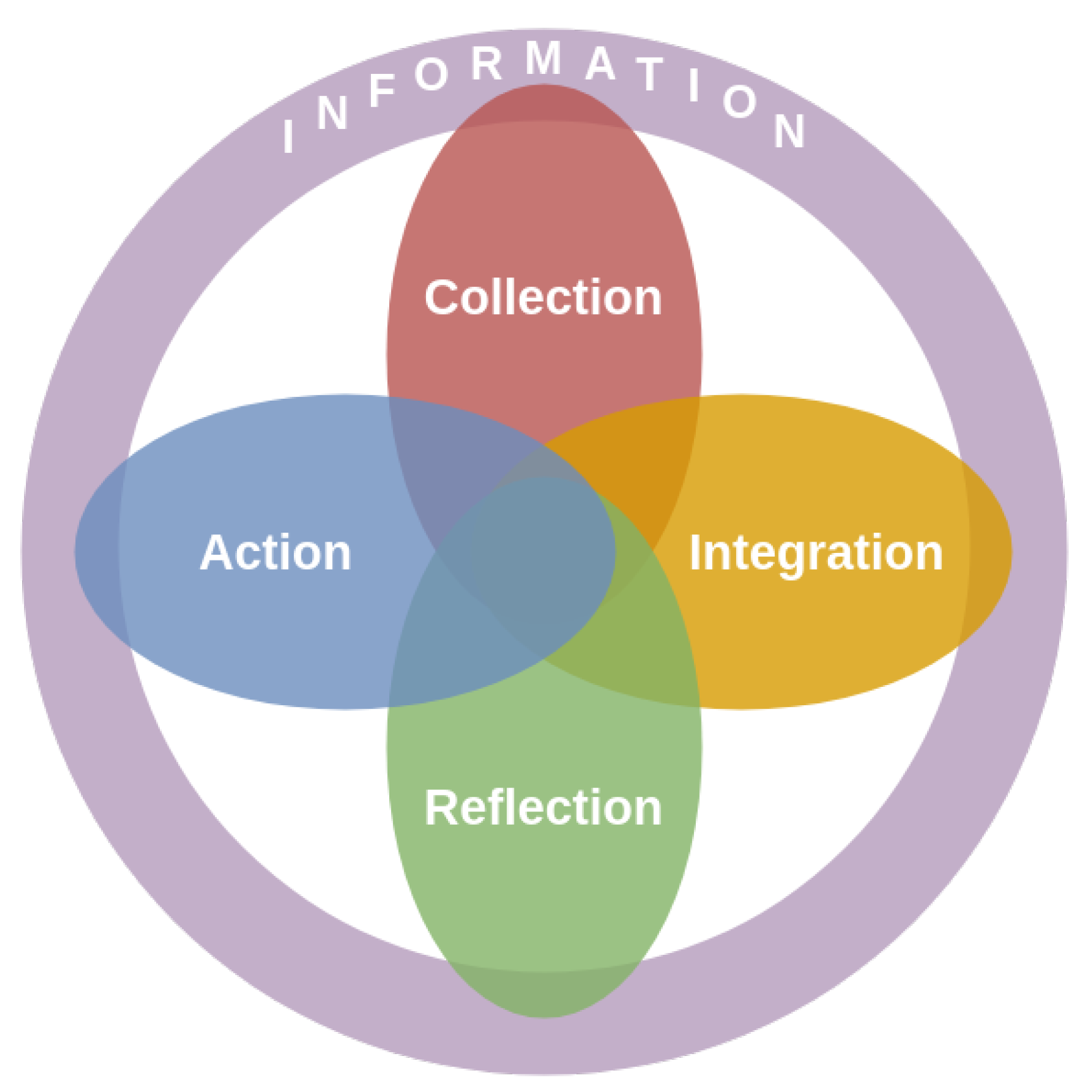
5.1. Summary of our Model’s Framework
5.2. Analysis and Results: Comparison of Our Applicative Model against the Previous Conceptual Ones
5.3. Contribution
5.4. Limitations and Future Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wolf, G.I.; De Groot, M. A Conceptual Framework for Personal Science. Front. Comput. Sci. 2020, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quantified Self. Quantified Self Blog. 2020. Available online: https://quantifiedself.com/ (accessed on 31 January 2020).
- Motti, V.G.; Caine, K. Human Factors Considerations in the Design of Wearable Devices. Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 2014, 58, 1820–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakurel, J. Enhancing the Adoption of Quantified Self-Tracking Devices; Lappeenranta University of Technology: Lappeenranta, Finland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vizer, L.M.; Eschler, J.; Koo, B.M.; Ralston, J.; Pratt, W.; Munson, S. “It’s Not Just Technology, It’s People”: Constructing a Conceptual Model of Shared Health Informatics for Tracking in Chronic Illness Management. J. Med. Internet Res. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, I.; Dey, A.; Forlizzi, J. A stage-based model of personal informatics systems. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems-CHI ’10, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–15 April 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, I.; Dey, A.K.; Forlizzi, J. Understanding my data, myself. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing-UbiComp’11, Beijing, China, 17–21 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, E.K.; Lee, N.B.; Lee, B.; Pratt, W.; Kientz, J.A. Understanding Quantified-Selfers’ Practices in Collecting and Exploring Personal Data. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26 April–1 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Clavel, C. Tailored, Multimodal and Opportune Interactions on a Wearable Sport Coach: The WE-nner Framework. In Global Thoughts, Local Designs; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, G. Know Thyself: Tracking Every Facet of Life, From Sleep To Mood To Pain. WIRED 2009, 17, 95. [Google Scholar]
- Yau, N.; Schneider, J. Self-Surveillance. Bull. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2009, 35, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, D. Understanding the Human Machine [commentary]. IEEE Technol. Soc. Mag. 2013, 32, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, N.G. The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin; University of Pennsylvania Press: Pennsylvania, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dymaxion Chronofile-Wikipedia, 2020. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dymaxion_Chronofile (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Driver, D. Designing with Data: Nicholas Felton|Create, 2020. Available online: http://feltron.com/ (accessed on 12 February 2020).
- Kopp, J. Self-Monitoring: A Literature Review of Research and Practice. Soc. Work Res. Abstr. 1988, 24, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotitsch, W.J.; Nelson-Gray, R.O. An Overview of Self-Monitoring Research in Assessment and Treatment. Psychol. Assess. 1999, 11, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasnja, P.; Pratt, W. Healthcare in the Pocket: Mapping the Space of Mobile-Phone Health Interventions. J. Biomed. Inform. 2012, 45, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, M.; Gray, K.; Sanchez, F.M. The Use of Self-Quantification Systems for Personal Health Information: Big Data Management Activities and Prospects. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 2015, 3, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.A.; Hossain, S.M.; Hovsepian, K.; Rahman, M.M.; Plarre, K.; Kumar, S. mPuff: Automated detection of cigarette smoking puffs from respiration measurements. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM/IEEE 11th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks (IPSN), Beijing, China, 16–19 April 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, H.; Lorig, K. Patient Self-Management: A Key To Effectiveness and Efficiency in Care of Chronic Disease. Public Health Rep. 2004, 119, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.; Duggan, M. Tracking for Health; Pew Research Center’s Internet & American Life Project: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, D.A.; Caraway, M.; Johnston, C.; Ping, A.; Fogarty, J.; Munson, S.A. Beyond Abandonment to Next Steps. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murnane, E.L.; Walker, T.G.; Tench, B.; Voida, S.; Snyder, J. Personal Informatics in Interpersonal Contexts. Proc. ACM Hum. Comput. Interact. 2018, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, M. Emerging Patient-Driven Health Care Models: An Examination of Health Social Networks, Consumer Personalized Medicine and Quantified Self-Tracking. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 492–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, M.C.; Caldeira, C.; Reynolds, T.L.; Victory, S.; Zheng, K.; Chen, Y. Self-Tracking for Fertility Care. Proc. ACM Hum. Comput. Interact. 2017, 1, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooksby, J.; Rost, M.; Morrison, A.; Chalmers, M.C. Personal tracking as lived informatics. In Proceedings of the 32nd annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems-CHI’14, Toronto, ON, Canada, 26 April–1 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, R.S.; Brennan, P.F. Exploring Patients’ Health Information Communication Practices with Social Network Members As a Foundation for Consumer Health It Design. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2015, 84, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.R.; Miller, A.D.; Haldar, S.; Khelifi, M.; Eschler, J.; Elera, R.G.; Pollack, A.H.; Pratt, W. Supporting Collaborative Health Tracking in the Hospital. In Proceedings of the 2018 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems-CHI’18, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–26 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, D.A.; Ping, A.; Fogarty, J.; Munson, S.A. A lived informatics model of personal informatics. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing-UbiComp’15, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consolvo, S.; McDonald, D.W.; Landay, J.A. Theory-driven design strategies for technologies that support behavior change in everyday life. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems-CHI 09, Boston, MA, USA, 4–9 April 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiClemente, C.C.; Marinilli, A.S.; Singh, M.; Bellino, L.E. The Role of Feedback in the Process of Health Behavior Change. Am. J. Health Behav. 2001, 25, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froehlich, J.; Dillahunt, T.; Klasnja, P.; Mankoff, J.; Consolvo, S.; Harrison, B.; Landay, J.A. UbiGreen: Investigating a mobile tool for tracking and supporting green transportation habits. In Proceedings of the Sigchi Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Boston, MA, USA, 4–9 April 2009; pp. 1043–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Locke, E.A.; Latham, G.P. Building a Practically Useful Theory of Goal Setting and Task Motivation: A 35-year Odyssey. Am. Psychol. 2002, 57, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.O.; DiClemente, C.C.; Norcross, J.C. In Search of How People Change: Applications To Addictive Behaviors. Am. Psychol. 1992, 47, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S. Erving Goffman, the Presentation of Self in Everyday Life (1959). Public Cult. 2020, 32, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festinger, L. A Theory of Cognitive Dissonance; Stanford University Press: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1957; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.J.; Mamykina, L.; Lindtner, S.; Delajoux, G.; Strub, H.B. Fish’n’Steps: Encouraging Physical Activity with an Interactive Computer Game. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarinaimi, N.; Forlizzi, J.; Hurst, A.; Zimmerman, J. Breakaway: An ambient display designed to change human behavior. In Proceedings of the CHI’05 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Portland, OR, USA, 22–27 April 2005; pp. 1945–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Berlin, J.E.; Storti, K.L.; Brach, J.S. Using Activity Monitors To Measure Physical Activity in Free-Living Conditions. Phys. Ther. 2006, 86, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudorlocke, C.; Burkett, L.; Reis, J.; Ainsworth, B.; Macera, C.; Wilson, D. How Many Days of Pedometer Monitoring Predict Weekly Physical Activity in Adults? Prev. Med. 2005, 40, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheers, T.; Philippaerts, R.; Lefevre, J. Variability in Physical Activity Patterns As Measured by the Sensewear Armband: How Many Days Are Needed? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 112, 1653–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, T.L.; Swartz, A.M.; Cashin, S.E.; Strath, S.J. How Many Days of Monitoring Predict Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Older Adults? Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.B.; Ryan, D.A.; Tudor-Locke, C. Relationship Between Objective Measures of Physical Activity and Weather: A Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2006, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.; Ruiz, C.; Wilson, V.; Strong, D.; Djamasbi, S. Using personality traits and chronotype to support personalization and feedback in a sleep health behavior change support system. In Proceedings of the 51st Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, R.A.J.; Truong, K.P.; Zaga, C.; Li, J.; Evers, V. A Word of Advice: How To Tailor Motivational Text Messages Based on Behavior Change Theory To Personality and Gender. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2017, 21, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.; Seki, N.; Umeda, K.; Tanabe, N.; Shinoda, K.; Konishi, I.; Sekiya, A.; Sekii, A.; Ohta, T. Relationship Between Exercise Adherence and Personality Characteristics in Persons Experienced in the Medical Fitness Program. [Nihon Koshu Eisei Zasshi] Jpn. J. Public Health 2017, 64, 664–671. [Google Scholar]
- Axelsson, M.; Lötvall, J.; Cliffordson, C.; Lundgren, J.; Brink, E. Self-Efficacy and Adherence As Mediating Factors Between Personality Traits and Health-Related Quality of Life. Qual. Life Res. 2012, 22, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Patrick, H.; Deci, E.L.; Williams, G.C. Facilitating health behaviour change and its maintenance: Interventions based on Self-Determination Theory. Eur. Health Psychol. 2008, 10, 2–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, R.B.; Zyzanski, S.J.; Alemagno, S.A. Prediction of Motivation and Behavior Change Following Health Promotion: Role of Health Beliefs, Social Support, and Self-Efficacy. Soc. Sci. Med. 1991, 32, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.; Smith, B.K. Visualizing health: Imagery in diabetes education. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference on Designing for User Experiences, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–7 June 2003; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Akizuki, K.; Ohashi, Y. Measurement of Functional Task Difficulty During Motor Learning: What Level of Difficulty Corresponds To the Optimal Challenge Point? Hum. Mov. Sci. 2015, 43, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrosch, C.; Sabiston, C.M. Goal Adjustment, Physical and Sedentary Activity, and Well-Being and Health Among Breast Cancer Survivors. Psycho-Oncology 2012, 22, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandigo, J.; Holt, N.L.; Mandigo, J. The Inclusion of Optimal Challenge in Teaching Games for Understanding. Phys. Health Educ. J. 2000, 66, 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Pesce, C.; Crova, C.; Marchetti, R.; Struzzolino, I.; Masci, I.; Vannozzi, G.; Forte, R. Searching for Cognitively Optimal Challenge Point in Physical Activity for Children With Typical and Atypical Motor Development. Ment. Health Phys. Act. 2013, 6, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onla-or, S.; Winstein, C.J. Determining the Optimal Challenge Point for Motor Skill Learning in Adults With Moderately Severe Parkinson’s Disease. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2007, 22, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, M.; Aung, M.H.; Zhang, M.; Choudhury, T. MyBehavior. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing-UbiComp’15, Osaka, Japan, 7–11 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, E.E.; Robertson-Wilson, J. Behavior Change Techniques and Physical Activity Using the Fitbit Flex®. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, M.; Christina, M.F.; Deborah, L.S.; Rubio, N.; Kennon, M.S. Intrinsic Motivation and Exercise Adherence. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 1997, 28, 335–354. [Google Scholar]
- John, O.P.; Donahue, E.M.; Kentle, R.L. Big Five Inventory. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, M.; Brink, E.; Lundgren, J.; Lötvall, J. The Influence of Personality Traits on Reported Adherence To Medication in Individuals With Chronic Disease: An Epidemiological Study in West Sweden. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernigon, C.; Vallacher, R.R.; Nowak, A.; Conroy, D.E. Rethinking Approach and Avoidance in Achievement Contexts: The Perspective of Dynamical Systems. Rev. Gen. Psychol. 2015, 19, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teboul, A.; Klosek, C.; Montiny, C.; Gernigon, C. Development and Validation of the Approach-Avoidance System Questionnaire (AASQ). Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seligman, C.; Darley, J.M. Feedback As a Means of Decreasing Residential Energy Consumption. J. Appl. Psychol. 1977, 62, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Voorsluys, W.; Niu, S.; Khandoker, A.; Buyya, R. An Autonomic Cloud Environment for Hosting Ecg Data Analysis Services. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2012, 28, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.; Golle, P.; Jakobsson, M.; Shi, E.; Staddon, J.; Masuoka, R.; Molina, J. Controlling data in the cloud: Outsourcing computation without outsourcing control. In Proceedings of the 2009 ACM Workshop on Cloud Computing Security; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 85–90. [Google Scholar]
- Thilakanathan, D.; Chen, S.; Nepal, S.; Calvo, R.; Alem, L. A Platform for Secure Monitoring and Sharing of Generic Health Data in the Cloud. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2014, 35, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Lu, H.; Saunders, C.L.; Potoglou, D.; Robinson, N. Public Preferences for Electronic Health Data Storage, Access, and Sharing-Evidence From a Pan-European Survey. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2016, 23, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, B.; Li, J. The Policy Effect of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) on the Digital Public Health Sector in the European Union: An Empirical Investigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCrae, R.R. The Five-Factor Model of Personality Traits: Consensus and Controversy. Camb. Handb. Personal. Psychol. 2009, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayanan, E.A.; Bartlett, D.J.; Chapman, J.L.; Hoyos, C.M.; Phillips, C.L.; Grunstein, R.R. A Review of Psychosocial Factors and Personality in the Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnoea. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 190005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickhouser, J.E.; Zell, E.; Krizan, Z. Does Personality Predict Health and Well-Being? A Metasynthesis. Health Psychol. 2017, 36, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prochaska, J.O.; Velicer, W.F. The Transtheoretical Model of Health Behavior Change. Am. J. Health Promot. 1997, 12, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A.; Freeman, W.; Lightsey, R. Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control; W H Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
| Improving Health | Improving Other Aspects of Life | Finding New Life Experience |
|---|---|---|
| - to cure or manage a condition | - to maximize work performance | - to satisfy curiosity |
| - to find triggers | - to be mindful | - to have fun |
| - to answer a specific question | - to trigger events | - to discover new tools |
| - to identify relationship | - to learn something interesting | |
| - to execute a treatment plan | - suggestion from another person | |
| - to make better health decisions | ||
| - to find balance to improve health |
| Barriers | Guidelines |
|---|---|
| - not using the right tool | - adopting a holistic approach |
| - not collecting the right data | - designing an iterative and flexible system |
| - sparse data sets | - facilitating data management |
| - ineffective visualizations | - supporting user behavior change |
| Stage-Based Model of Personal Informatics (2010) | Lived InformaticsModel (2015) | Conceptual Model of Shared Health Informatics (2019) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics of the model | - Personal informatics framework. - Focused on behavior change. - Linear sequence of stages. - Barriers identification for each stage. | - Extension of the 2010 model. - Less focused on behavior change. - Circular sequence of stages. - Flexibility allowing interruption and resumption of use. | - Extension of the 2010 model. - Focused on chronic illness self-management. - Simultaneity of stages (no sequence). - Includes patient and therapists. |
| Absent from the model | - Explanation on how to account for identified barriers. - Precise guidelines for system design to account for the sequence of stages. | - Explanation on how to account for flexibility and human lapse. - Precise guidelines for system design to account for a circular sequence. | - Explanation on how to account for patient and therapists. - Precise guidelines for system design to account for simultaneous work. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dulaud, P.; Di Loreto, I.; Mottet, D. Self-Quantification Systems to Support Physical Activity: From Theory to Implementation Principles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249350
Dulaud P, Di Loreto I, Mottet D. Self-Quantification Systems to Support Physical Activity: From Theory to Implementation Principles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249350
Chicago/Turabian StyleDulaud, Paul, Ines Di Loreto, and Denis Mottet. 2020. "Self-Quantification Systems to Support Physical Activity: From Theory to Implementation Principles" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249350
APA StyleDulaud, P., Di Loreto, I., & Mottet, D. (2020). Self-Quantification Systems to Support Physical Activity: From Theory to Implementation Principles. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9350. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249350





