A Longitudinal Analysis of Gambling Predictors among Adolescents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Measures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrie, E.K.; Tzavara, C.K.; Tzavela, E.; Richardson, C.; Greydanus, D.; Tsolia, M.; Tsitsika, A.K. Gambling involvement and problem gambling correlates among European adolescents: Results from the European Network for Addictive Behavior study. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2019, 54, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESPAD Group. ESPAD Report 2019: Results from the European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen, S.G.; Jensen, S.M. Prevalence and correlates of problematic gambling among Danish adolescents. Int. J. Soc. Welf. 2014, 23, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chóliz, M.; Lamas, J. Place your bets, children! The frequency of gambling among minors and their relationship with gambling addiction indicators. Rev. Esp. Drogodepend. 2017, 42, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Caselles, P.; Cabrera, V.; Lloret, D. Prevalencia del juego de apuestas en adolescentes. Un análisis de los factores asociados. Health Addict. 2018, 18, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Observatorio Español de las Drogas y las Adicciones. Informe Sobre Adicciones Comportamentales. Madrid; 2019. Available online: http://www.pnsd.mscbs.gob.es (accessed on 26 August 2019).
- ESPAD Group. Results from the European School Survey Project on Alcohol and Other Drugs; ESPAD Report 2015; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Observatorio Español Sobre Adicciones. ESTUDES 2018/19. 2019. Available online: https://pnsd.sanidad.gob.es/fr/profesionales/sistemasInformacion/sistemaInformacion/pdf/ESTUDES_2018-19_Informe.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- McCormack, A.; Shorter, G.W.; Griffiths, M.D. Characteristics and Predictors of Problem Gambling on the Internet. Int. J. Mental Health Add. 2013, 11, 634–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newall, P.W.S. Dark nudges in gambling. Add. Res. Theory 2019, 27, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chóliz, M.; Marcos, M.; Lázaro-Mateo, J. The Risk of Online Gambling: A Study of Gambling Disorder Prevalence Rates in Spain. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirección General de Ordenación del Juego. Estudio Sobre la Prevalencia, Comportamiento y Características de los Usuarios de Juegos de Azar en España 2015; Ministerio de Hacienda y Administraciones Públicas: Madrid, Spain, 2015.
- Canale, N.; Griffiths, M.D.; Vieno, A.; Siciliano, V.; Molinaro, S. Impact of Internet gambling on problem gambling among adolescents in Italy: Findings from a large-scale nationally representative survey. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 57, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M. Internet Gambling: Issues, Concerns, and Recommendations. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2003, 6, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, H.J.; Shaffer, P.M. Psychiatric epidemiology, nosology, and treatment: Considering internet gambling. Psychiatr. Annals. 2014, 44, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calado, F.; Alexandre, J.; Rosenfeld, L.; Pereira, R.; Griffiths, M.D. The Efficacy of a Gambling Prevention Program among High-School Students. J. Gamb. Stud. 2020, 36, 573–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Roz, A.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R.; Weidberg, S.; Martínez-Loredo, V.; Secades-Villa, R. Prevalence of Problem Gambling Among Adolescents: A Comparison Across Modes of Access, Gambling Activities, and Levels of Severity. J. Gamb. Stud. 2016, 33, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, F.; Griffiths, M.D. Problem gambling worldwide: An update and systematic review of empirical research (2000–2015). J. Behav. Add. 2016, 5, 592–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, N.A.; Merkouris, S.S.; Greenwood, C.J.; Oldenhof, E.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Youssef, G.J. Early risk and protective factors for problem gambling: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 51, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floros, G.D. Gambling disorder in adolescents: Prevalence, new developments and treatment challenges. Adolesc. Health Med. Ther. 2018, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calado, F.; Alexandre, J.; Griffiths, M.D. Prevalence of Adolescent Problem Gambling: A Systematic Review of Recent Research. J. Gamb. Stud. 2017, 33, 397–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Guebaly, N.; Casey, D.M.; Currie, S.R.; Hodgins, D.C.; Schopflocher, D.P.; Smith, G.J.; Williams, R.J. The Leisure, Lifestyle, & Lifecycle Project (LLLP): A Longitudinal Study of Gambling in Alberta; Final Report for the Alberta Gambling Research Institute; Alberta Gambling Research Institute: Banff, AB, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.J.; Hann, R.G.; Schopflocher, D.P.; West, B.L.; McLaughlin, P.; White, N.; King, K.; Flexhaug, T. Quinte Longitudinal Study of Gambling and Problem Gambling. Ontario. 2015. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10133/3641 (accessed on 29 February 2020).
- Dussault, F.; Dufour, M.; Brunelle, N.; Tremblay, J.; Rousseau, M.; Leclerc, D.; Cousineau, M.M.; Berbiche, D. Consistency of Adolescents’ Self-Report of Gambling Age of Onset: A Longitudinal Study. J. Gamb. Stud. 2019, 35, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chóliz, M. The Challenge of Online Gambling: The Effect of Legalization on the Increase in Online Gambling Addiction. J. Gamb. Stud. 2016, 32, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, L.M.; Derevensky, J.L.; Gupta, R. The prevention of gambling problems in youth: A conceptual framework. J. Gamb. Stud. 2002, 18, 97–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson-Gillespie, L.; Rugle, L.; Rosenthal, R.; Fong, T. Preventing the incidence and harm of gambling problems. J. Prim. Prev. 2008, 29, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huic, A.; Kranzelic, V.; Dodig Hundric, D.; Ricijas, N. Who Really Wins? Efficacy of a Croatian Youth Gambling Prevention Program. J. Gamb. Stud. 2017, 33, 1011–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevensky, J.L. Youth Gambling: Some Current Misconceptions. Austin J. Psychiatr. Behav. Sci. 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gilbeau, L. Preventing adolescent gambling problems. In Gambling Disorder; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 297–311. [Google Scholar]
- St-Pierre, R.; Derevensky, J.L. Youth Gambling Behavior: Novel Approaches to Prevention and Intervention; Current Addiction Reports; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, B.C.; Ong, Y.J.; Loo, J.M.Y. A review of educational-based gambling prevention programs for adolescents. Asian J. Gamb. Issues Public Health 2017, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, K.M.; Pilling, M.; Foxcroft, D.R. Alcohol-related affordances and group subjectivities: A Q-Methodology study. Drugs Educ. Prev. Policy 2018, 25, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, G. Confiamos demasiado en el valor de la cognición y de la educación en la prevención? Rev. Esp. Drogodepend. 2015, 40, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- UNODC. International Standards on Drug Use Prevention Second Updated Edition; UNODC and WHO: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Harden, K.P.; Tucker-Drob, E.M. Individual differences in the development of sensation seeking and impulsivity during adolescence: Further evidence for a dual systems model. Dev. Psychol. 2011, 47, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, D. Adolescent risk taking, impulsivity, and brain development: Implications for prevention. Dev. Psychobiol. 2010, 52, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, M.; Nigro, G. Wagering the future: Cognitive distortions, impulsivity, delay discounting, and time perspective in adolescent gambling. J. Adolesc. 2015, 45, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, M.A.; Chiesi, F.; Iozzi, A.; Manfredi, A.; Fagni, F.; Primi, C. Gambling-Related Distortions and Problem Gambling in Adolescents: A Model to Explain Mechanisms and Develop Interventions. Front. Psychol. 2018, 8, 2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secades-Villa, R.; Martínez-Loredo, V.; Grande-Gosende, A.; Fernández-Hermida, J.R. The Relationship between Impulsivity and Problem Gambling in Adolescence. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, M.A.; Chiesi, F.; Primi, C. A model to explain at-risk/problem gambling among male and female adolescents: Gender similarities and differences. J. Adolesc. 2013, 36, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenassa, E.D.; Paradis, A.D.; Dolan, S.L.; Wilhelm, C.S.; Buka, S.L. Childhood impulsive behavior and problem gambling by adulthood: A 30-year prospective community-based study. Addiction 2012, 107, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevensky, J.L.; Gilbeau, L. Adolescent Gambling: Twenty-five Years of Research. Can. J. Add. 2015, 6, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Zhou, K.; Sun, Y.; Rao, L.-L.; Zheng, R.; Liang, Z.-Y. Anticipated Regret, Risk Perception, or Both: Which is Most Likely Responsible for Our Intention to Gamble? J. Gamb. Stud. 2010, 26, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canale, N.; Vieno, A.; ter Bogt, T.; Pastore, M.; Siciliano, V.; Molinaro, S. Adolescent Gambling-Oriented Attitudes Mediate the Relationship between Perceived Parental Knowledge and Adolescent Gambling: Implications for Prevention. Prev. Sci. 2016, 17, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Jariego, J.C.; Parrado-González, A.; Ojea-Rodríguez, F.J. Behavioral Intention to Gamble among Adolescents: Differences between Gamblers and Non-gamblers—Prevention Recommendations. J. Gamb. Stud. 2019, 36, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, R.; Michie, S. A brief introduction to the COM-B Model of behaviour and the PRIME Theory of motivation. Qeios 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishbein, M.; Ajzen, I. Predicting and Changing Behavior: The Reasoned Action Approach; Psychology Press (Taylor & Francis): New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, R.W.; Youssef, G.J.; Hasking, P.; Yücel, M.; Jackson, A.C.; Dowling, N.A. The relationship between gambling attitudes, involvement, and problems in adolescence: Examining the moderating role of coping strategies and parenting styles. Addict. Behav. 2016, 58, 42–46. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0306460316300363 (accessed on 30 September 2019). [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.A.; King, D.L.; Delfabbro, P.H. Family factors in adolescent problematic Internet gaming: A systematic review. J. Behav. Add. 2017, 6, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allami, Y.; Vitaro, F.; Brendgen, M.; Carbonneau, R.; Tremblay, R.E. Identifying at-risk profiles and protective factors for problem gambling: A longitudinal study across adolescence and early adulthood. Psychol. Add. Behav. 2018, 32, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisone, F.; Settineri, S.; Sicari, F.; Merlo, E.M. Gambling in adolescence: A narrative review of the last 20 years. J. Add. Dis. 2020, 38, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, A.; Langham, E.; Hing, N. Social influences normalize gambling-related harm among higher risk gamblers. J. Behav. Add. 2018, 4, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hing, N.; Cherney, L.; Blaszczynski, A.; Gainsbury, S.M.; Lubman, D.I. International Gambling Studies Do advertising and promotions for online gambling increase gambling consumption? An exploratory study. Int. Gamb. Stud. 2014, 14, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloret, D.; Perona, V.; Castaños, A.; Segura-Heras, J.V.; Antón-Esclápez, M.A.; Caselles, P. Estudio Longitudinal del Juego de Apuestas Entre Adolescentes y Sus Factores de Riesgo. Alicante 2016–2017; Diputación Provincial de Alicante: Alicante, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, H.; Thomas, S.L.; Bestman, A.; Randle, M.; Daube, M. Do betting advertisements contain attention strategies that may appeal to children? An interpretative content analysis. Health Promot. J. Aust. 2018, 29, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyemcsok, C.; Thomas, S.L.; Bestman, A.; Pitt, H.; Daube, M.; Cassidy, R. Young people’s recall and perceptions of gambling advertising and intentions to gamble on sport. J. Behav. Add. 2018, 7, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.; Delfabbro, P.; Griffiths, M. The Convergence of Gambling and Digital Media: Implications for Gambling in Young People. J. Gamb. Stud. 2010, 26, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricijas, N.; Dodig Hundric, D.; Huic, A. Predictors of adverse gambling related consequences among adolescent boys. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2016, 67, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurrier, M.; Blaszczynski, A. Risk Perception in Gambling: A Systematic Review. J. Gamb. Stud. 2014, 30, 253–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes-Balog, K.E.; Hemphill, S.A.; Toumbourou, J.W.; Dowling, N.A. Problem gambling and internalising symptoms: A longitudinal analysis of common and specific social environmental protective factors. Add. Behav. 2015, 46, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Chambers, T.; Abbott, M.; Signal, L. High Stakes: Children’s Exposure to Gambling and Gambling Marketing Using Wearable Cameras. Int. J. Ment. Health Add. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayer, T.; Kalke, J.; Meyer, G.; Brosowski, T. Do simulated gambling activities predict gambling with real money during adolescence? Empirical findings from a longitudinal study. J. Gamb. Stud. 2018, 34, 929–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dussault, F.; Brunelle, N.; Kairouz, S.; Rousseau, M.; Leclerc, D.; Tremblay, J.; Cousineau, M.M.; Dufour, M. Transition from playing with simulated gambling games to gambling with real money: A longitudinal study in adolescence. Int. Gamb. Stud. 2017, 17, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Mills, D.; Nower, L. The relationship of loot box purchases to problem video gaming and problem gambling. Add. Behav. 2019, 97, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlberg, L.L.; Krug, E.G. Violence: A global public health problem. In World Report on Violence and Health; Krug, E.G., Dahlberg, L.L., Mercy, J.A., Zwi, A.B., Lozano, R., Eds.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar]
- Delfabbro, P.; King, D.; Griffiths, M.D. From adolescent to adult gambling: An analysis of longitudinal gambling patterns in South Australia. J. Gamb. Stud. 2014, 30, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussault, F.; Brendgen, M.; Vitaro, F.; Wanner, B.; Tremblay, R.E. Longitudinal links between impulsivity, gambling problems and depressive symptoms: A transactional model from adolescence to early adulthood. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatr. 2011, 52, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgerton, J.; Melnyk, T.; Roberts, L. Problem Gambling and the Youth-to-Adulthood Transition: Assessing Problem Gambling Severity Trajectories in a Sample of Young Adults. J. Gamb. Stud. 2015, 31, 1463–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keen, B.; Blaszczynski, A.; Anjoul, F. Systematic Review of Empirically Evaluated School-Based Gambling Education Programs. J. Gamb. Stud. 2017, 33, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladouceur, R.; Goulet, A.; Vitaro, F. Prevention programmes for youth gambling: A review of the empirical evidence. Int. Gamb. Stud. 2013, 13, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegni, N.; Melchiori, F.M.; D’Ardia, C.; Prestano, C.; Canu, M.; Piergiovanni, G.; Di Filippo, G. Gambling Behavior and Risk Factors in Preadolescent Students: A Cross Sectional Study. Front. Psychol. 2019, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, J.D.; Willett, J.B. Applied Longitudinal Data Analysis: Modeling Change and Event Occurrence; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Winters, K.C.; Stinchfield, R.D.; Fulkerson, J. Toward the development of an adolescent gambling problem severity scale. J. Gamb. Stud. 1993, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becoña, E. Pathological gambling in Spanish children and adolescents: An emerging problem. Psychol. Rep. 1997, 81, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plutchik, R.; van Praag, H. The measurement of suicidality, aggressivity and impulsivity. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatr. 1989, 13, S23–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, G.; Montero, I.; Jáuregui, J.; Martínez, M.L.; Álvarez, S.; Marín, J.J. Validación de la Escala de Impulsividad de Plutchik en población española. Arch. Neurobiol. 1999, 61, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. Dimensions of sensation seeking. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1971, 36, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyle, R.H.; Stephenson, M.T.; Palmgreen, P.; Lorch, E.P.; Donohew, R.L. Reliability and validity of a brief measure of sensation seeking. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2002, 32, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, J.R. Propiedades psicométricas del inventario de búsqueda de sensaciones para adolescentes en México (IBS-Mx). Int. J. Psychol. Res. 2015, 8, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lloret, D.; Cabrera, V.; Núñez, R. Diseño y validación de la escala EDGAR-A (Early Detection of Gambling Abuse Risk—Adolescents). In IV International Congress of Clinical and Health Psychology on Children and Adolescents; Ediciones Pirámide: Madrid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- García Ruiz, P.; Buil, P.; Solé Moratilla, M.J. Consumos de riesgo: Menores y juegos de azar online. El problema del “juego responsable”. Política Soc. 2016, 53, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.; Tsai, J.; Pilver, C.E.; Tan, H.S.; Hoff, R.A.; Cavallo, D.A.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Steinberg, M.A.; Rugle, L.; Potenza, M.N. Differences in gambling problem severity and gambling and health/functioning characteristics among Asian-American and Caucasian high-school students. Psychiatry Res. 2013, 210, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barnes, G.M.; Welte, J.W.; Hoffman, J.H.; Tidwell, M.C. The Co-occurrence of Gambling with Substance Use and Conduct Disorder among Youth in the United States. Am. J. Add. 2011, 20, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, P.D.L.; Vargas-Sáenz, A.; Hulbert, C.A.; Boldero, J.M. Predictors of gambling and problem gambling in Victoria, Australia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hing, N.; Russell, A.; Tolchard, B.; Nower, L. Risk factors for gambling problems: An analysis by gender. J. Gamb. Stud. 2016, 32, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeman, R.F.; Patock-Peckham, J.A.; Hoff, R.A.; Krishnan-Sarin, S.; Steinberg, M.A.; Rugle, L.J.; Potenza, M.N. Perceived parental permissiveness toward gambling and risky behaviors in adolescents. J. Behav. Add. 2014, 3, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Situ, J.; Mo, Z. Risk Propensity, Gambling Cognition and Gambling Behavior: The Role of Family and Peer Influences. J. Educ. Dev. Psychol. 2016, 6, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisarska, A.; Ostaszewski, K. Factors associated with youth gambling: Longitudinal study among high school students. Public Health 2020, 184, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, M. A “components” model of addiction within a biopsychosocial framework. J. Subst. Use 2005, 10, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, H.; Thomas, S.L.; Bestman, A.; Stoneham, M.; Daube, M. “It’s just everywhere!” Children and parents discuss the marketing of sports wagering in Australia. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2016, 40, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapthiang, S.; van Gordon, W.; Shonin, E.; Griffiths, M.D. Adolescent problem gambling requires community-level health promotion approaches. Add. Res. Theory 2019, 28, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chóliz, M.; Marcos, M. Adicción al Juego en la Juventud de la Comunitat Valenciana; Consell Valencià de la Joventut: Valencia, Spain, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wagenaar, A.C.; Holder, H.D. Effects of Alcoholic Beverage Server Liability on Traffic Crash Injuries. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1991, 15, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
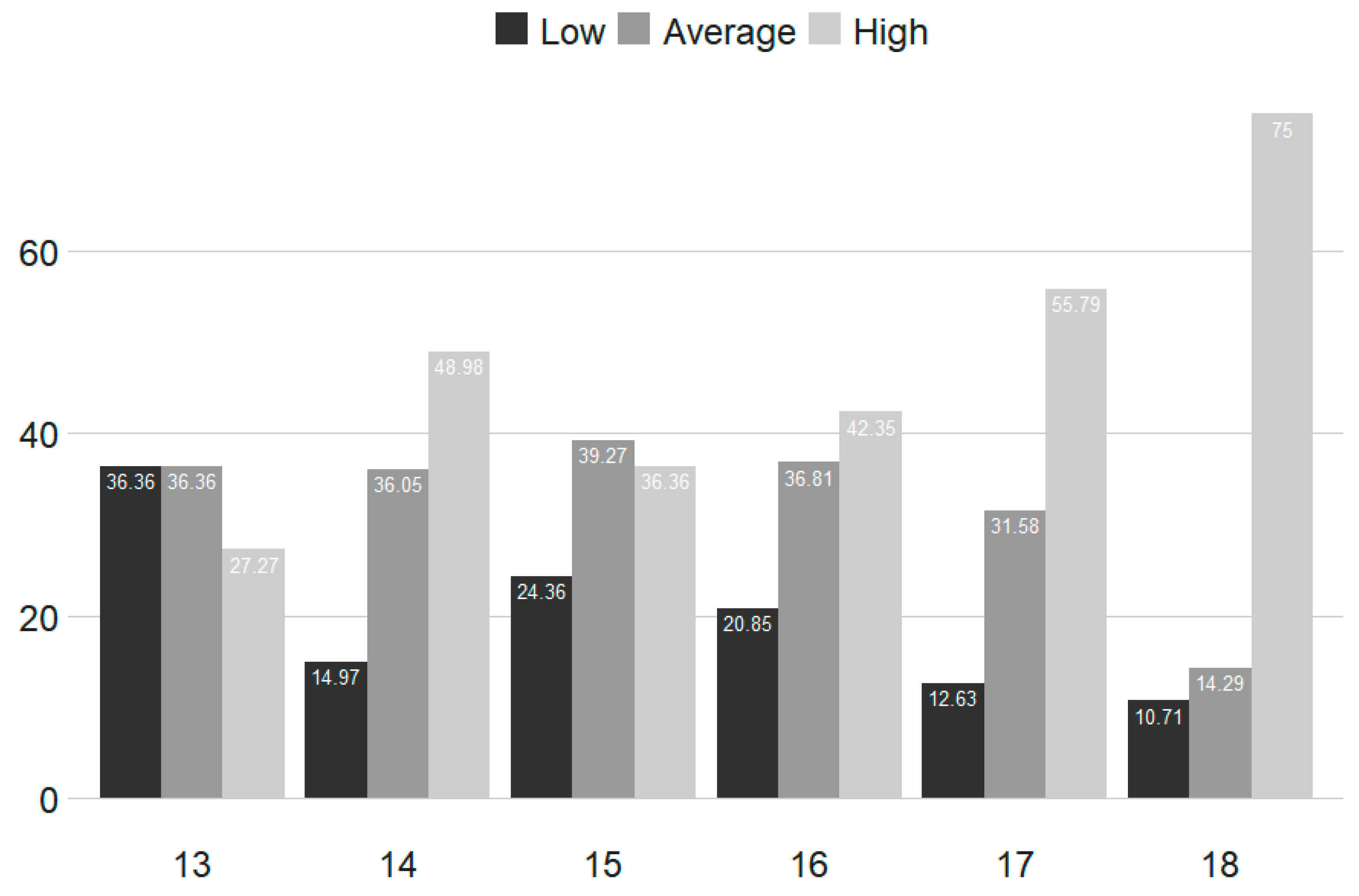

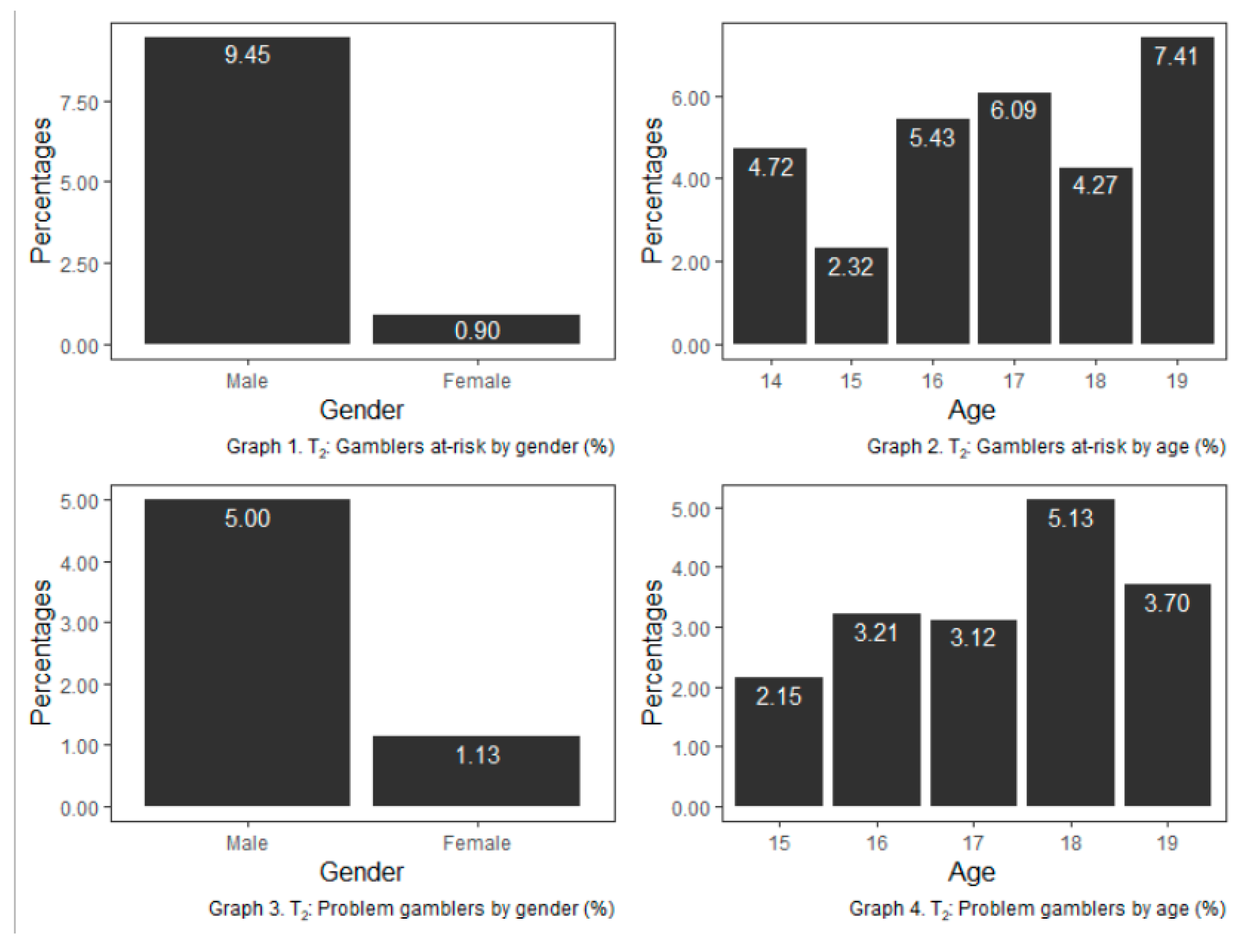

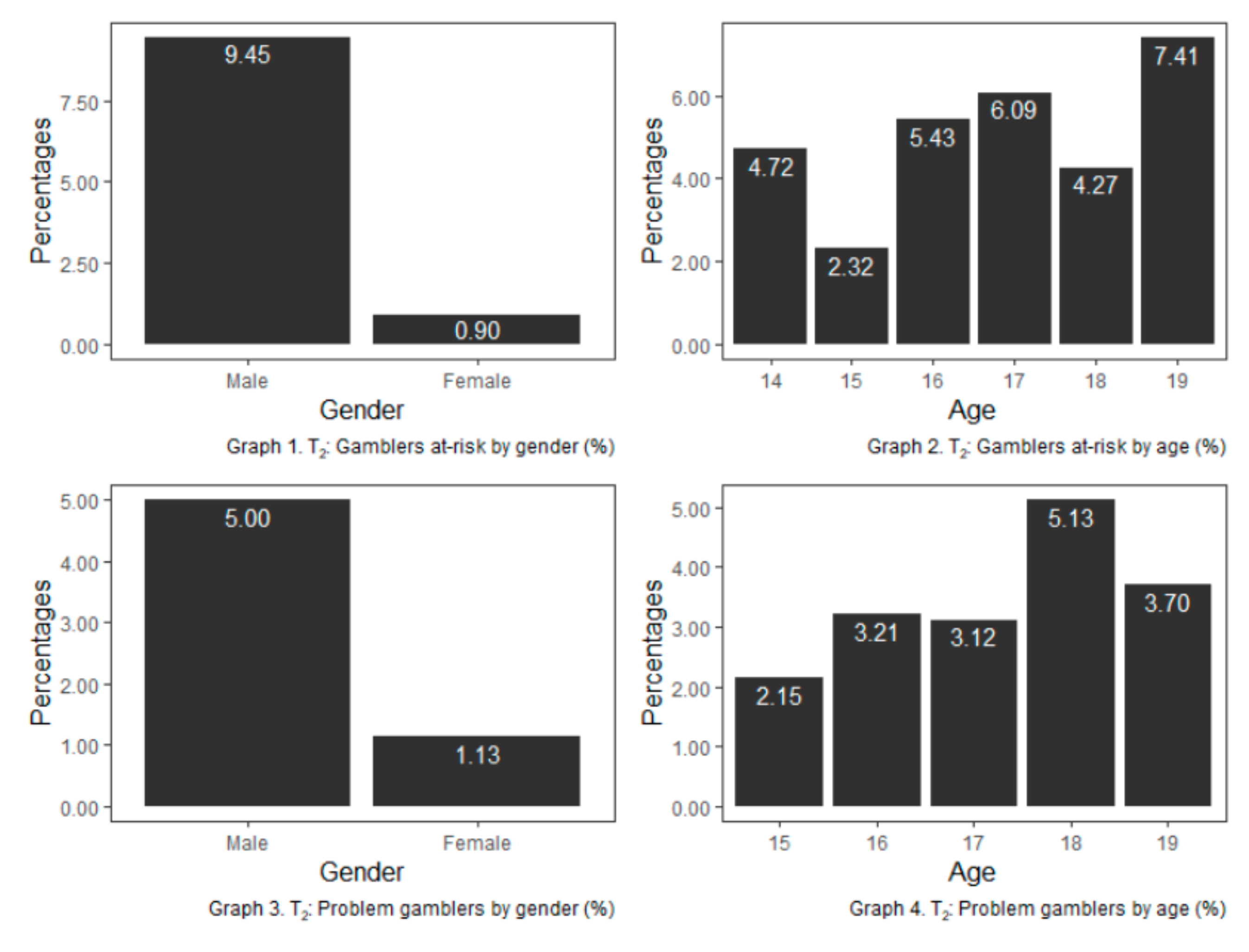

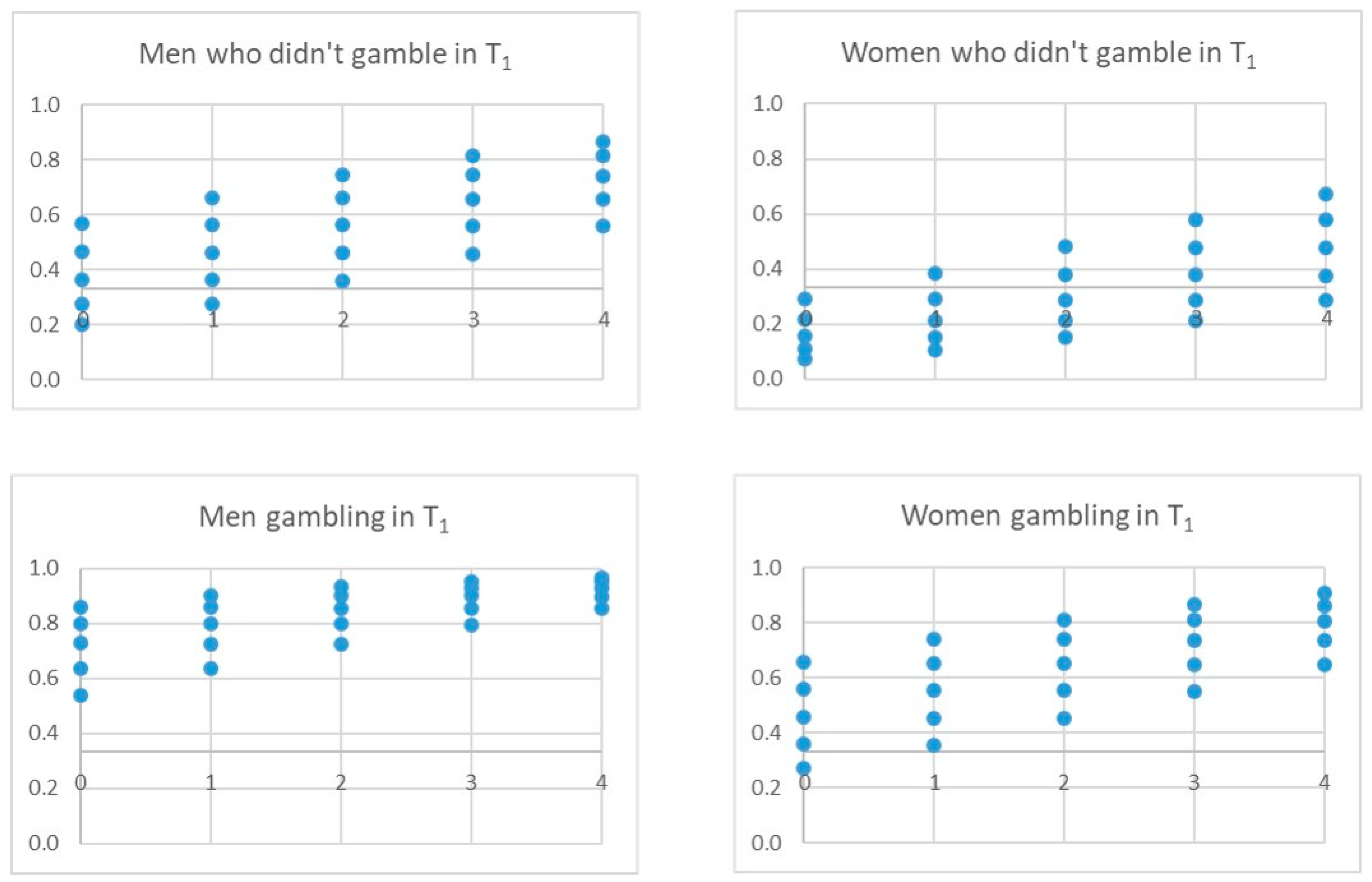
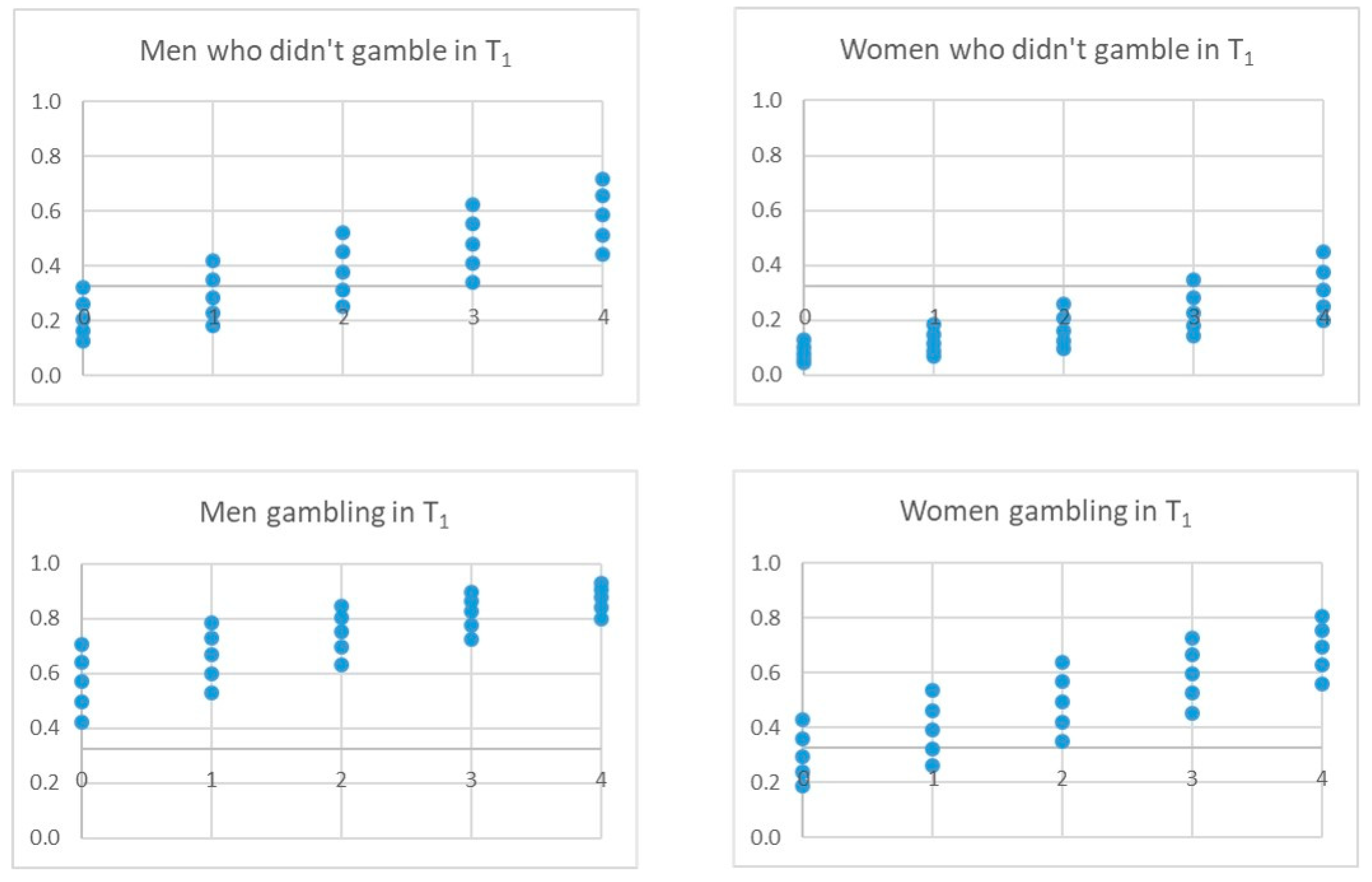
| T1 (n = 2716) | T2 (n = 2430) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |
| Never | 53.6 | 81.4 | 71.5 | 39.27 | 73.3 | 57.9 |
| Low | 7.5 | 5.5 | 10.7 | 4.27 | 5.9 | 5.2 |
| Average | 14.8 | 8.6 | 4.5 | 9.82 | 9.6 | 9.7 |
| High | 24.1 | 4.5 | 13.3 | 46.6 | 11.2 | 27.2 |
| Gambling Behavior for T2 | 95% CI | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Infrequent Gambling | Frequent Gambling | |||||
| n | Mean ± SD | n | Mean ± SD | |||
| Age | 707 | 14.99 ± 1.00 | 364 | 15.18 ± 1.02 | (−0.32, −0.06) | 0.003 |
| Sensation-seeking | 708 | 3.29 ± 0.77 | 366 | 3.42 ± 0.75 | (−0.23, −0.04) | 0.007 |
| impulsivity | 708 | 2.35 ± 0.36 | 366 | 2.39 ± 0.38 | (−0.08, 0.01) | 0.124 |
| Risk perception | 696 | 1.44 ± 0.64 | 362 | 1.73 ± 0.75 | (−0.38, −0.20) | <0.001 |
| Self-efficacy not to gamble | 693 | 3.49 ± 0.66 | 354 | 3.29 ± 0.79 | (0.11, 0.30) | <0.001 |
| Parents attitude | 677 | 0.87 ± 0.71 | 348 | 1.05 ± 0.87 | (−0.29, −0.08) | 0.001 |
| Group pressure (friends) | 678 | 0.44 ± 0.52 | 352 | 0.75 ± 0.68 | (−0.39, −0.23) | <0.001 |
| Subjective norm: parents | 702 | 4.83 ± 2.82 | 359 | 5.61 ± 3.46 | (−1.19, −0.36) | <0.001 |
| Subjective norm: friends | 701 | 7.20 ± 3.57 | 358 | 7.89 ± 4.16 | (−1.20, −0.19) | 0.007 |
| Subjective norm: peers | 699 | 5.17 ± 3.10 | 358 | 5.25 ± 3.42 | (−0.50, 0.35) | 0.721 |
| Subjective norm: teachers | 700 | 4.03 ± 2.60 | 359 | 3.68 ± 2.74 | (0.01, 0.69) | 0.041 |
| Subjective norm: partner | 686 | 6.04 ± 3.45 | 355 | 6.95 ± 4.00 | (−1.4, −0.42) | <0.001 |
| Exposure to publicity | 706 | 24.18 ± 6.36 | 366 | 26.3 ± 6.72 | (−2.94, −1.30) | <0.001 |
| Accessibility | 659 | 2.41 ± 0.68 | 345 | 2.63 ± 0.66 | (−0.31, −0.13) | <0.001 |
| Normative perception | 696 | 2.00 ± 0.75 | 353 | 2.31 ± 0.88 | (−0.41, −0.20) | <0.001 |
| Gambling Behavior at T2 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrequent Gambling n (%) | Frequent Gambling n (%) | ||
| Gambling behavior at T1 | <0.001 | ||
| No gamble | 649(76.4) | 201(23.6) | |
| Yes gambles | 59(26.3) | 165(73.7) | |
| Gender | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 234(48.5) | 248(51.5) | |
| Female | 474(80.1) | 118(19.4) | |
| Gambling behavior of parents | 0.002 | ||
| Do not gamble | 574(68.3) | 266(31.7) | |
| At least one gambles | 134(57.3) | 100(42.7) | |
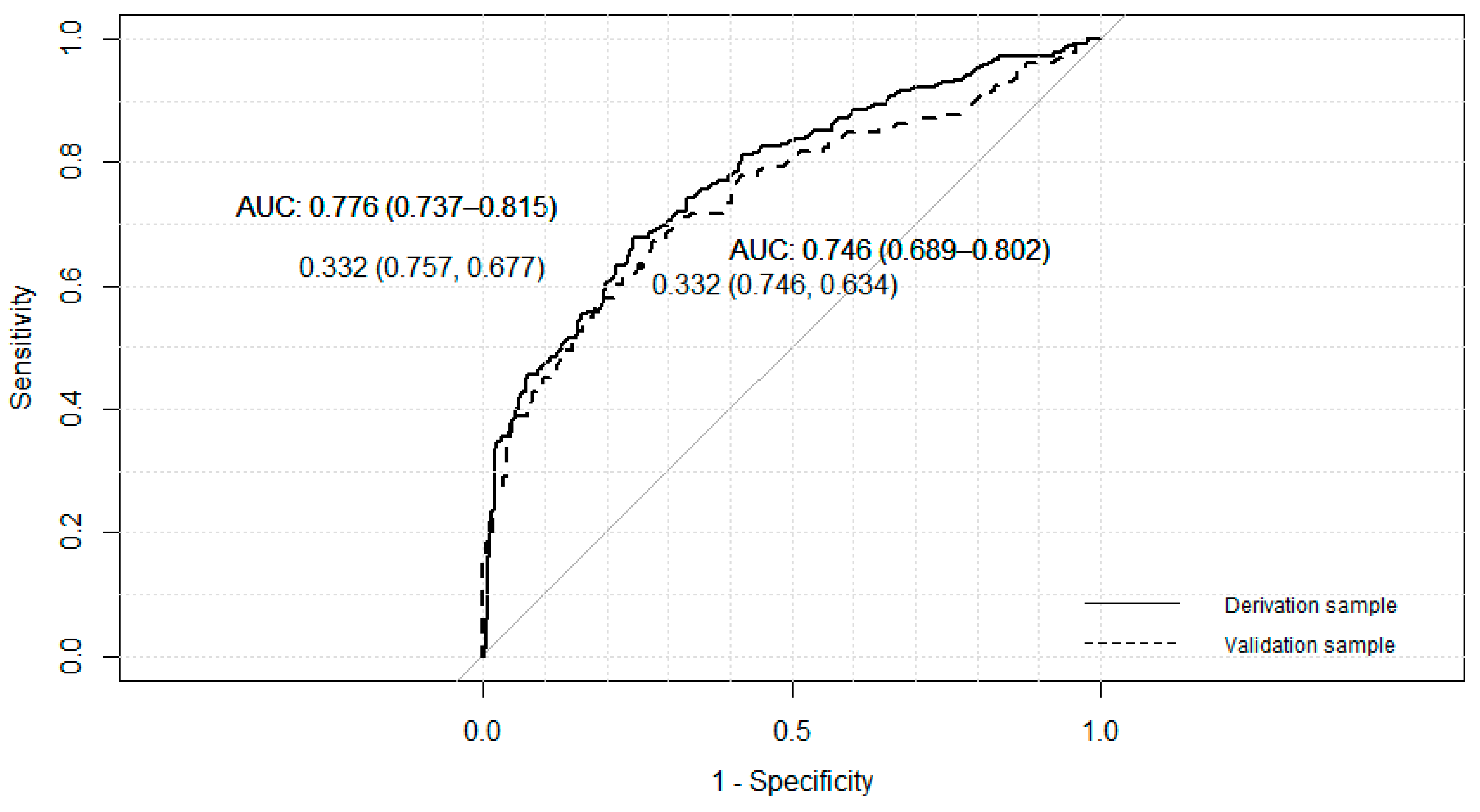
| Variable | Beta | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | VIF | AIC | R2 Nagelkerke | HL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | 725.36 | 0.308 | 0.933 | |||||
| Constant | −2.013 | |||||||
| Gambling behavior at T1 | 1.680 | <0.001 | 5.364 | 3.48–8.34 | 1.03 | |||
| Gender | −1.207 | <0.001 | 0.299 | 0.21–0.43 | 1.04 | |||
| Risk perception | 0.412 | 0.003 | 1.509 | 1.15–1.99 | 1.02 | |||
| Sensation-seeking | 0.252 | 0.046 | 1.287 | 1.01–1.65 | 1.03 | |||
| Model B | 693.14 | 0.302 | 0.776 | |||||
| Constant | −1.374 | |||||||
| Gambling behavior at T1 | 1.525 | <0.001 | 4.596 | 2.92–7.31 | 1.10 | |||
| Gender | −1.154 | <0.001 | 0.315 | 0.22–0.46 | 1.02 | |||
| Risk perception | 0.401 | 0.004 | 1.493 | 1.14–1.97 | 1.01 | |||
| Peer pressure (friends) | 0.412 | 0.018 | 1.510 | 1.07–2.13 | 1.08 | |||
| Model C | 684.45 | 0.302 | 0.669 | |||||
| Constant | −1.927 | |||||||
| Gambling behavior at T1 | 1.615 | <0.001 | 5.027 | 3.23–7.90 | 1.04 | |||
| Gender | −1.150 | <0.001 | 0.317 | 0.22–0.46 | 1.02 | |||
| Risk perception | 0.422 | 0.004 | 1.524 | 1.15–2.03 | 1.02 | |||
| Accessibility | 0.294 | 0.040 | 1.341 | 1.02–1.78 | 1.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botella-Guijarro, Á.; Lloret-Irles, D.; Segura-Heras, J.V.; Cabrera-Perona, V.; Moriano, J.A. A Longitudinal Analysis of Gambling Predictors among Adolescents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249266
Botella-Guijarro Á, Lloret-Irles D, Segura-Heras JV, Cabrera-Perona V, Moriano JA. A Longitudinal Analysis of Gambling Predictors among Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(24):9266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249266
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotella-Guijarro, Álvaro, Daniel Lloret-Irles, José Vicente Segura-Heras, Víctor Cabrera-Perona, and Juan Antonio Moriano. 2020. "A Longitudinal Analysis of Gambling Predictors among Adolescents" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 24: 9266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249266
APA StyleBotella-Guijarro, Á., Lloret-Irles, D., Segura-Heras, J. V., Cabrera-Perona, V., & Moriano, J. A. (2020). A Longitudinal Analysis of Gambling Predictors among Adolescents. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(24), 9266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249266







