Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
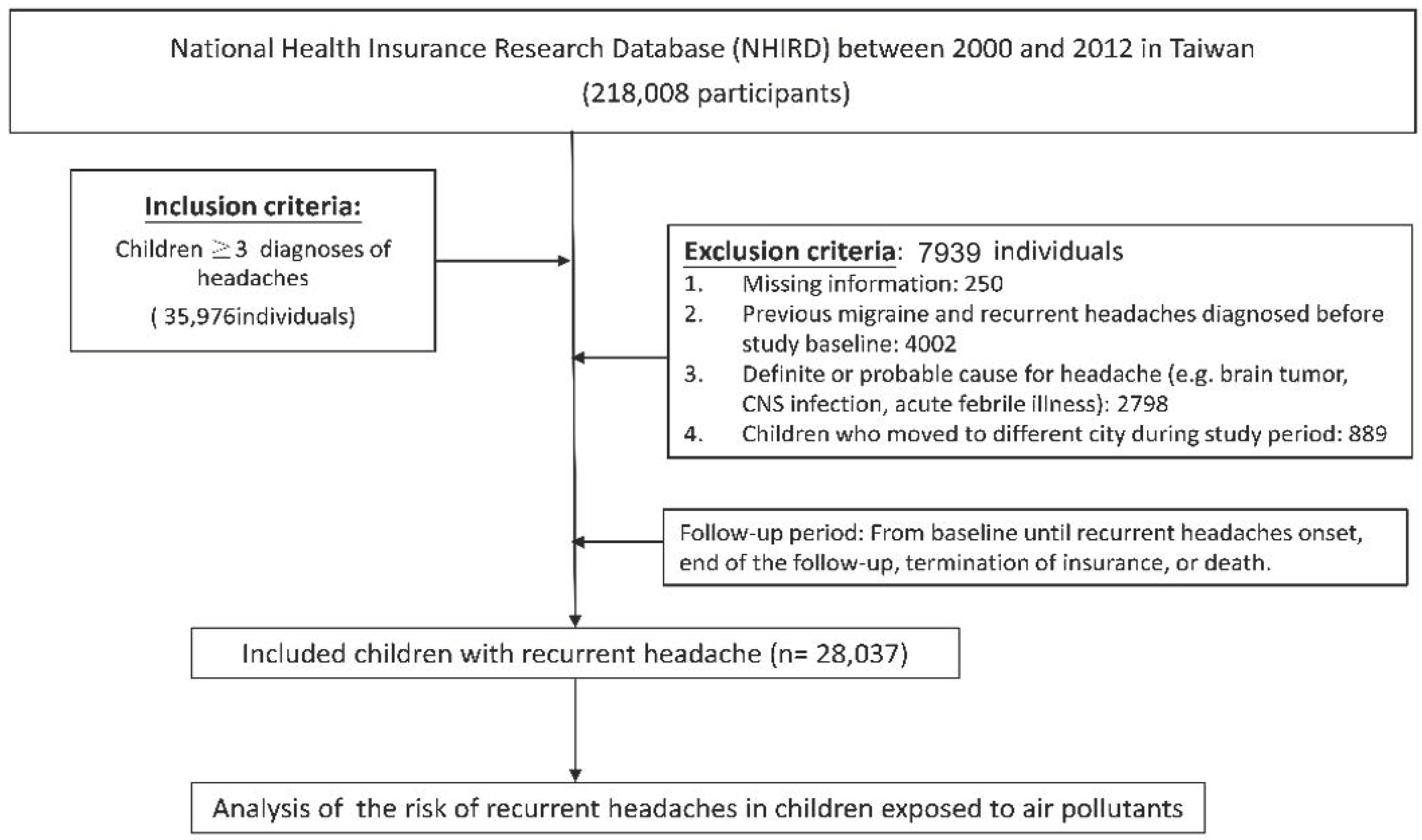
2.2. Study Population, Outcome of Interest, Endpoints, and Confounding Factors
2.3. Exposure Measurement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
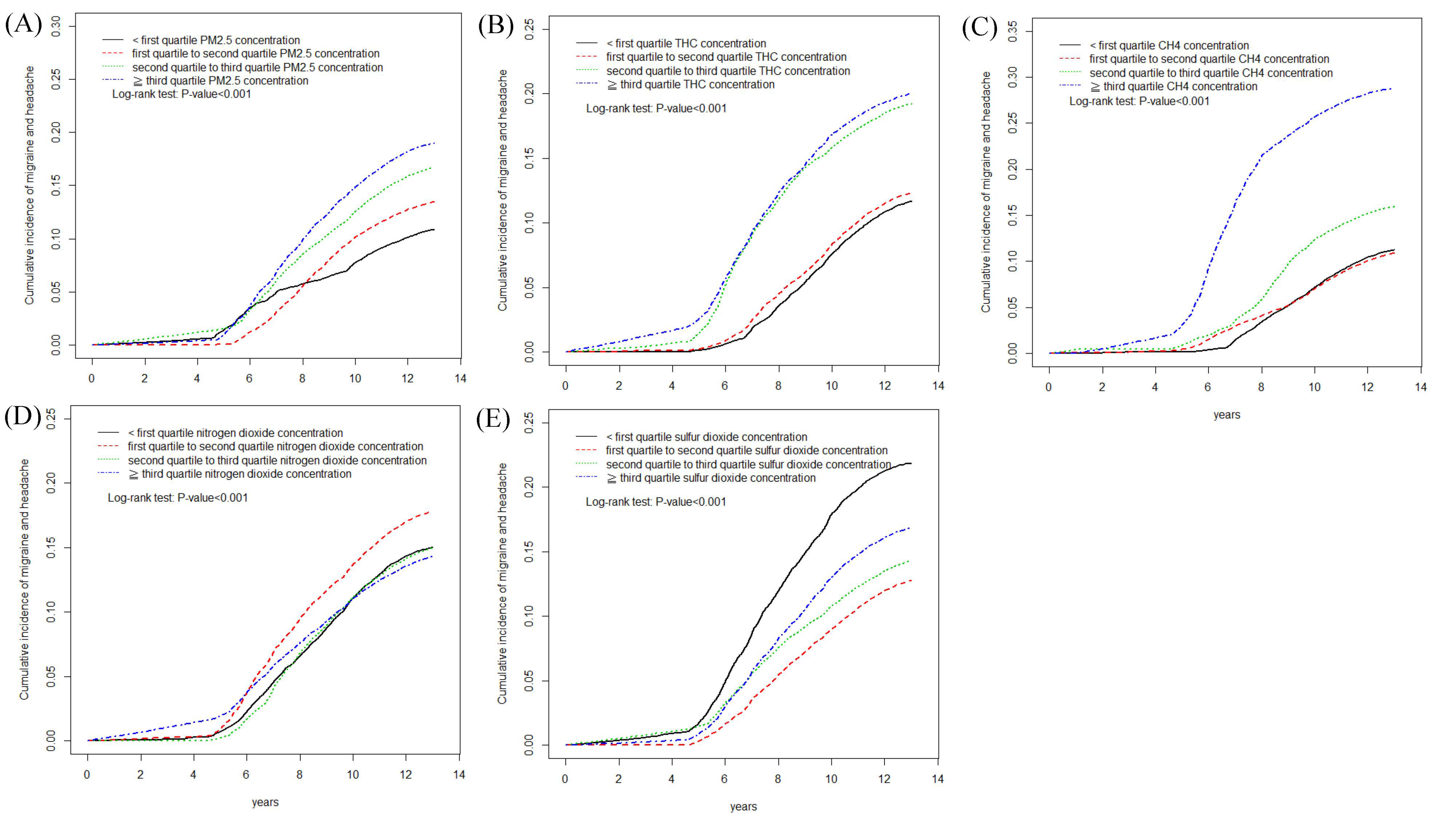
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| IR | cHR | (95%CI) | aHR † | (95%CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) | ||||||
| Quartile 1, 27.8 < μg/m3 | 4.75 | Reference group | Reference group | |||
| Quartile 2, 27.8–32.7 μg/m3 | 14.9 | 3.50 | (3.36–3.65) * | 3.52 | (3.37–3.67) * | |
| Quartile 3, 32.7–39.2 μg/m3 | 9.12 | 1.99 | (1.90–3.65) * | 1.94 | (1.86–2.03) * | |
| Quartile 4, 39.2 > μg/m3 | 21.7 | 5.29 | (5.08–5.50) * | 5.31 | (5.11–5.53) * | |
| Total hydrocarbons (THC) | ||||||
| Quartile 1, 11.2 < ppm | 11.5 | Reference group | Reference group | |||
| Quartile 2, 11.2–18.1 ppm | 20.6 | 2.03 | (1.97–2.10) * | 2.02 | (1.96–2.08) * | |
| Quartile 3, 18.1–25.9 ppm | 14.2 | 1.29 | (1.25–1.33) * | 1.30 | (1.26–1.34) * | |
| Quartile 4, 25.9 > ppm | 4.21 | 0.34 | (0.33–0.36) * | 0.34 | (0.33–0.36) * | |
| Methane (CH4) | ||||||
| Quartile 1, 8.59 < ppm | 11.6 | Reference group | Reference group | |||
| Quartile 2, 8.59–16.0 ppm | 21.8 | 2.18 | (2.11–2.24) * | 2.19 | (2.13–2.26) * | |
| Quartile 3, 16.0–22.6 ppm | 13.4 | 1.19 | (1.15–1.23) * | 1.19 | (1.15–1.23) * | |
| Quartile 4, 22.6 > ppm | 3.99 | 0.32 | (0.31–0.33) * | 0.32 | (0.31–0.84) * | |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | ||||||
| Quartile 1, 3.45 < ppb | 5.86 | Reference group | Reference group | |||
| Quartile 2, 3.45–4.24 ppb | 11.1 | 1.97 | (1.90–2.05) * | 2.14 | (2.06–2.23) * | |
| Quartile 3, 4.24–5.64 ppb | 16.5 | 3.17 | (3.05–3.29) * | 3.59 | (3.45–3.73) * | |
| Quartile 4, 5.64 > ppb | 16.2 | 3.03 | (3.03–2.92) * | 3.46 | (3.33–3.60) * | |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | ||||||
| Quartile 1, 18.4 < ppb | 10.5 | Reference group | Reference group | |||
| Quartile 2, 18.4–22.1 ppb | 10.4 | 0.98 | (0.95–1.02) | 1.39 | (1.33–1.45) * | |
| Quartile 3, 22.1–25.1 ppb | 10.5 | 1.00 | (0.97–1.02) | 1.67 | (1.60–1.75) * | |
| Quartile 4, 25.1 > ppb | 16.9 | 1.75 | (1.69–1.80) * | 3.29 | (3.15–3.44) * | |
References
- Stovner, L.; Hagen, K.; Jensen, R.; Katsarava, Z.; Lipton, R.; Scher, A.; Steiner, T.; Zwart, J.A. The Global Burden of Headache: A Documentation of Headache Prevalence and Disability Worldwide. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2007, 27, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, T.J.; Birbeck, G.L.; Jensen, R.H.; Katsarava, Z.; Stovner, L.J.; Martelletti, P. Headache Disorders are Third Cause of Disability Worldwide. J. Headache Pain 2015, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frare, M.; Axia, G.; Battistella, P.A. Quality of Life, Coping Strategies, and Family Routines in Children with Headache. Headache 2002, 42, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D.I.; De ver Dye, T. Migraine and the Environment. Headache 2009, 49, 941–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J. Air Pollution and Children’s Health. Pediatrics 2004, 113, 1037–1043. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, A.J.; Ross Anderson, H.; Ostro, B.; Pandey, K.D.; Krzyzanowski, M.; Kunzli, N.; Gutschmidt, K.; Pope, A.; Romieu, I.; Samet, J.M.; et al. The Global Burden of Disease Due to Outdoor Air Pollution. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2005, 68, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervin, T.; Gerdtham, U.G.; Lyttkens, C.H. Societal Costs of Air Pollution-related Health Hazards: A Review of Methods and Results. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. C/E 2008, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dentener, F.; van Dingenen, R.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Tsai, S.S.; Yang, C.Y. Association Between Fine Particulate Air Pollution and Daily Clinic Visits for Migraine in a Subtropical City: Taipei, Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 4697–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meggs, W.J. Neurogenic Switching: A Hypothesis for a Mechanism for Shifting the Site of Inflammation in Allergy and Chemical Sensitivity. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Stieb, D.M.; Rowe, B.H. Air Pollution and Daily ED Visits for Migraine and Headache in Edmonton, Canada. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dales, R.E.; Cakmak, S.; Vidal, C.B. Air Pollution and Hospitalization for Headache in Chile. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukamal, K.J.; Wellenius, G.A.; Suh, H.H.; Mittleman, M.A. Weather and Air Pollution as Triggers of Severe Headaches. Neurology 2009, 72, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, R.; World Health Organization. Fuel for Life: Household Energy and Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.; Huang, A.T. Learning from Taiwan: Experience with Universal Health Insurance. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 313–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.M. Taiwan’s National Health Insurance System: High Value for the Dollar. In Six Countries, Six Reform Models: The Healthcare Reform Experience of Israel, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Singapore, Switzerland and Taiwan; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 171–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.S.; Lai, M.S.; Gau, S.S.; Wang, S.C.; Tsai, H.J. Concordance Between Patient Self-reports and Claims Data on Clinical Diagnoses, Medication Use, and Health System Utilization in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.C.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H.; Liao, Y.H.; Shen, T.C.; Tsai, J.D.; Chang, Y.J.; Li, T.C. Increased Risk of Kawasaki Disease in Children with Common Allergic Diseases. Ann. Epidemiol. 2014, 24, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Hung, Y.T.; Chuang, Y.L. Incorporating Development Stratification of Taiwan Townships into Sampling Design of Large Scale Health Interview Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2006, 4, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Air Quality Guidelines for Particulate Matter, Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide and Sulfur Dioxide: Global Update 2005: Summary of Risk Assessment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Fuh, J.L.; Juang, K.D.; Lu, S.R. Rising Prevalence of Migraine in Taiwanese Adolescents Aged 13–15 Years. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2005, 25, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wober-Bingol, C. Epidemiology of Migraine and Headache in Children and Adolescents. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2013, 17, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.W. Pediatric Migraine. Neurol. Clin. 2009, 27, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bille, B. A 40-year Follow-up of School Children with Migraine. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 1997, 17, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrer, F.M. Pathophysiology of Migraine. Semin. Neurol. 2006, 26, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gervil, M.; Ulrich, V.; Kaprio, J.; Olesen, J.; Russell, M.B. The Relative Role of Genetic and Environmental Factors in Migraine without Aura. Neurology 1999, 53, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducros, A.; Tournier-Lasserve, E.; Bousser, M.G. The Genetics of Migraine. Lancet Neurol. 2002, 1, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenroot, R.K.; Giedd, J.N. The Changing Impact of Genes and Environment on Brain Development During Childhood and Adolescence: Initial Findings from a Neuroimaging Study of Pediatric Twins. Dev. Psychopathol. 2008, 20, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, W.P. Headache and Facial Pain in Scuba Divers. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2004, 8, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, S. Influence of Different Weather Events on Concentrations of Particulate Matter with Different Sizes in Lanzhou, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabriat, H.; Danchot, J.; Michel, P.; Joire, J.E.; Henry, P. Precipitating Factors of Headache. A Prospective Study in a National Control-Matched Survey in Migraineurs and Nonmigraineurs. Headache 1999, 39, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S. Interactions Between Particulate Air Pollution and Temperature in Air Pollution Mortality Time Series Studies. Environ. Res. 2004, 96, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solotareff, L.; Cuvellier, J.C.; Duhamel, A.; Vallee, L.; Tich, S.N.T. Trigger Factors in Childhood Migraine: A Prospective Clinic-based Study from North of France. J. Child Neurol. 2017, 32, 754–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neut, D.; Fily, A.; Cuvellier, J.C.; Vallee, L. The Prevalence of Triggers in Paediatric Migraine: A Questionnaire Study in 102 Children and Adolescents. J. Headache Pain 2012, 13, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Roy, D. Trigger Factors in Childhood Migraine: A Clinic-based Study from Eastern India. J. Headache Pain 2009, 10, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelman, L. The Triggers or Precipitants of the Acute Migraine Attack. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2007, 27, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zebenholzer, K.; Rudel, E.; Frantal, S.; Brannath, W.; Schmidt, K.; Wober-Bingol, C.; Wober, C. Migraine and Weather: A Prospective Diary-based Analysis. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2011, 31, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyszkowicz, M.; Rowe, B.H.; Kaplan, G.G. Ambient Sulphur Dioxide Exposure and Emergency Department Visits for Migraine in Vancouver, Canada. Int. J. Occup Med. Environ. Health 2009, 22, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Myung, W.; Cheong, H.K.; Yi, S.M.; Hong, Y.C.; Cho, S.I.; Kim, H. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure and Risk of Migraine: Synergistic Effect with High Temperature. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.F.; Weng, Y.H.; Chiu, Y.W.; Yang, C.Y. Air Pollution and Daily Clinic Visits for Headache in a Subtropical City: Taipei, Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2015, 12, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N = 218,008 | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Boys | 113,364 | 52.0 |
| Girls | 104,644 | 48.0 | |
| Age, years | mean, SD | 6.01 | 2.98 |
| Monthly income (NTD) † | <15,000 | 187,199 | 85.9 |
| 15,000−19,999 | 23,668 | 10.9 | |
| ≥20,000 | 7141 | 3.28 | |
| Urbanization level | 1 (highest) | 74,591 | 34.2 |
| 2 | 69,003 | 31.7 | |
| 3 | 40,924 | 18.8 | |
| 4 (lowest) | 33,490 | 15.4 | |
| Outcome | |||
| recurrent headaches | Yes | 28,037 | 12.9 |
| Follow-up time, years | mean, SD | 10.7 | 2.60 |
| IR | cHR | (95%CI) | aHR † | (95%CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) | |||||
| Quartile 1, <11,120 μg/m3 | 8.62 | Reference group | Reference group | ||
| Quartile 2, 11,120–12,652 μg/m3 | 11.0 | 1.30 | (1.26, 1.35) ** | 1.29 | (1.25, 1.34) ** |
| Quartile 3, 12,652–15,056 μg/m3 | 13.5 | 1.59 | (1.54, 1.65) ** | 1.57 | (1.51, 1.62) ** |
| Quartile 4, >15,056 μg/m3 | 15.0 | 1.78 | (1.72, 1.84) ** | 1.75 | (1.69, 1.81) ** |
| Total hydrocarbons (THC) | |||||
| Quartile 1, <835 ppm | 8.06 | Reference group | Reference group | ||
| Quartile 2, 835–877 ppm | 8.40 | 1.05 | (1.01, 1.09) * | 1.08 | (1.04, 1.12) ** |
| Quartile 3, 877–949 ppm | 16.9 | 2.26 | (2.18, 2.34) ** | 2.41 | (2.33, 2.49) ** |
| Quartile 4, >949 ppm | 16.3 | 2.25 | (2.17, 2.33) ** | 2.50 | (2.41, 2.59) ** |
| Methane (CH4) | |||||
| Quartile 1, <735 ppm | 8.93 | Reference group | Reference group | ||
| Quartile 2, 735–754 ppm | 6.82 | 0.76 | (0.73, 0.79) ** | 0.78 | (0.75, 0.81) ** |
| Quartile 3, 754–770 ppm | 11.0 | 1.27 | (1.22, 1.32) ** | 1.29 | (1.24, 1.33) ** |
| Quartile 4, >770 ppm | 24.1 | 3.16 | (3.06, 3.26) ** | 3.22 | (3.11, 3.33) ** |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | |||||
| Quartile 1, <1346 ppb | 13.7 | Reference group | Reference group | ||
| Quartile 2, 1346–1914 ppb | 10.4 | 0.75 | (0.72, 0.77) ** | 0.79 | (0.76, 0.81) ** |
| Quartile 3, 1914–2338 ppb | 11.7 | 0.87 | (0.84, 0.90) ** | 0.89 | (0.86, 0.92) ** |
| Quartile 4, >2338 ppb | 12.3 | 0.90 | (0.87, 0.92) ** | 0.93 | (0.90, 0.96) ** |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | |||||
| Quartile 1, <7896 ppb | 11.8 | Reference group | Reference group | ||
| Quartile 2, 7896–8894 ppb | 12.0 | 1.02 | (0.99, 1.05) | 1.07 | (1.03, 1.10) ** |
| Quartile 3, 8894–10,214 ppb | 11.5 | 0.99 | (0.96, 1.02) | 1.05 | (1.01, 1.09) * |
| Quartile 4, >10,214 ppb | 12.9 | 1.13 | (1.10, 1.17) ** | 1.23 | (1.19, 1.27) ** |
| Variables | Boys | Girls | Age ≤ 6 | Age > 6 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aHR † | (95%CI) | aHR † | (95%CI) | aHR † | (95%CI) | aHR † | (95%CI) | |
| Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) | ||||||||
| Quartile 1, <11,120 μg/m3 | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | ||||
| Quartile 2, 11,120–12,652 μg/m3 | 1.31 | (1.24, 1.39) ** | 1.28 | (1.22, 1.35) ** | 1.35 | (1.29,1.42) ** | 1.21 | (1.14, 1.29) ** |
| Quartile 3, 12,652–15,056 μg/m3 | 1.59 | (1.51, 1.68) ** | 1.55 | (1.47, 1.62) ** | 1.61 | (1.54, 1.68) ** | 1.50 | (*1.41, 1.59) ** |
| Quartile 4, >15,056 μg/m3 | 1.75 | (1.67, 1.84) ** | 1.75 | (1.67, 1.84) ** | 1.78 | (1.70, 1.85) ** | 1.72 | (1.62, 1.82) ** |
| Total hydrocarbons (THC) | ||||||||
| Quartile 1, <835 ppm | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | ||||
| Quartile 2, 835–877 ppm | 1.09 | (1.03, 1.16) ** | 1.06 | (1.01, 1.12) * | 1.10 | (1.05, 1.16) ** | 1.02 | (0.95, 1.09) |
| Quartile 3, 877–949 ppm | 2.60 | (2.47, 2.74) ** | 2.24 | (2.14, 2.35) ** | 2.38 | (2.29, 2.48) ** | 2.48 | (2.34, 2.63) ** |
| Quartile 4, >949 ppm | 2.77 | (2.63, 2.93) ** | 2.27 | 2.16, 2.39) ** | 2.52 | (2.41, 2.64) ** | 2.50 | (2.35, 2.66) ** |
| Methane (CH4) | ||||||||
| Quartile 1, <735 ppm | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | ||||
| Quartile 2, 735–754 ppm | 0.78 | (0.74, 0.83) ** | 0.77 | (0.73, 0.81) ** | 0.76 | (0.73, 0.80) ** | 0.81 | (0.75, 0.87) ** |
| Quartile 3, 754–770 ppm | 1.35 | (1.28, 1.42) ** | 1.23 | (1.17, 1.30) ** | 1.31 | (1.25, 1.37) ** | 1.25 | (1.17, 1.34) ** |
| Quartile 4, >770 ppm | 3.50 | (3.33, 3.67) ** | 2.98 | (2.85, 3.12) ** | 3.15 | (3.03, 3.28) ** | 3.37 | (3.19, 3.57) ** |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | ||||||||
| Quartile 1, <1346 ppb | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | ||||
| Quartile 2, 1346–1914 ppb | 0.80 | (0.77, 0.85) ** | 0.77 | (0.73, 0.81) ** | 0.77 | (0.74, 0.81) ** | 0.81 | (0.76, 0.86) ** |
| Quartile 3, 1914–2338 ppb | 0.91 | (0.87, 0.96) ** | 0.87 | (0.83, 0.91) ** | 0.87 | (0.83, 0.91) ** | 0.93 | (0.88, 0.99) ** |
| Quartile 4, >2338 ppb | 0.94 | (0.90, 0.98) ** | 0.92 | (0.88, 0.96) ** | 0.93 | (0.89,0.97) * | 0.92 | (0.88, 0.97) ** |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | ||||||||
| Quartile 1, <7896 ppb | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | Reference group | ||||
| Quartile 2, 7896–8894 ppb | 1.06 | (1.01, 1.12) * | 1.07 | (1.02, 1.12) ** | 1.15 | (1.10, 1.20) ** | 0.94 | (0.88, 0.99) * |
| Quartile 3, 8894–10,214 ppb | 1.11 | (1.05, 1.17) ** | 1.00 | (0.95, 1.05) | 1.16 | (1.11, 1.21) ** | 0.90 | (0.85, 0.96) ** |
| Quartile 4, >10,214 ppb | 1.28 | (1.22, 1.35) ** | 1.18 | (1.12, 1.24) ** | 1.21 | (1.15, 1.26) ** | 1.26 | (1.20, 1.34) ** |
| Ambient Air Pollutants | Ambient Temperature | IR | aHR † (95% CI) | p-Value for Interaction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) | <0.001 | |||
| <Median | <Median | 9.24 | 1.00 (Reference) | |
| <Median | ≥Median | 10.8 | 1.20 (1.15, 1.24) * | |
| ≥Median | <Median | 14.4 | 1.61 (1.53, 1.70) * | |
| ≥Median | ≥Median | 14.3 | 1.55 (1.51, 1.60) * | |
| Total hydrocarbons (THC) | <0.001 | |||
| <Median | <Median | 6.97 | 1.00 (Reference) | |
| <Median | ≥Median | 8.93 | 1.26 (1.21, 1.31) * | |
| ≥Median | <Median | 13.4 | 2.11 (2.02, 2.21) * | |
| ≥Median | ≥Median | 18.6 | 3.21 (3.08, 3.34) * | |
| Methane (CH4) | <0.001 | |||
| <Median | <Median | 7.5 | 1.00 (Reference) | |
| <Median | ≥Median | 7.97 | 1.04 (1.00, 1.08) | |
| ≥Median | <Median | 14.2 | 1.98 (1.90, 2.07) * | |
| ≥Median | ≥Median | 18.6 | 2.74 (2.65, 2.84) * | |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | <0.001 | |||
| <Median | <Median | 11 | 1.00 (Reference) | |
| <Median | ≥Median | 12.4 | 1.13 (1.09, 1.17) * | |
| ≥Median | <Median | 9.35 | 0.86 (0.82, 0.90) * | |
| ≥Median | ≥Median | 14.4 | 1.36 (1.31, 1.42) * | |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | <0.001 | |||
| <Median | <Median | 9.58 | 1.00 (Reference) | |
| <Median | ≥Median | 13.0 | 1.38 (1.33, 1.44) * | |
| ≥Median | <Median | 10.3 | 1.16 (1.11, 1.21) * | |
| ≥Median | ≥Median | 13.4 | 1.54 (1.48, 1.60) * |
| Pollutant Levels | cHR | 95%CI | aHR † | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.000) * | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.001) * |
| Total hydrocarbons (THC) | 1.003 | (1.003, 1.003) * | 1.004 | (1.004, 1.004) * |
| Methane (CH4) | 1.010 | (1.010, 1.010) * | 1.010 | (1.010, 1.010) * |
| Sulfur dioxide (SO2) | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.000) * | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.001) * |
| Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.000) * | 1.000 | (1.000, 1.001) * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-Y.; Wan, L.; Lin, H.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Wei, C.-C. Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239140
Hong S-Y, Wan L, Lin H-J, Lin C-L, Wei C-C. Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239140
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Syuan-Yu, Lei Wan, Hui-Ju Lin, Cheng-Li Lin, and Chang-Ching Wei. 2020. "Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239140
APA StyleHong, S.-Y., Wan, L., Lin, H.-J., Lin, C.-L., & Wei, C.-C. (2020). Long-Term Ambient Air Pollutant Exposure and Risk of Recurrent Headache in Children: A 12-Year Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239140






