A Parent-Implemented Language Intervention for Late Talkers: An Exploratory Study on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Parent-Implemented Language Interventions in Late Talkers
1.2. Parent-Implemented Language Interventions in Other Populations with Language Delay
1.3. Objectives of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
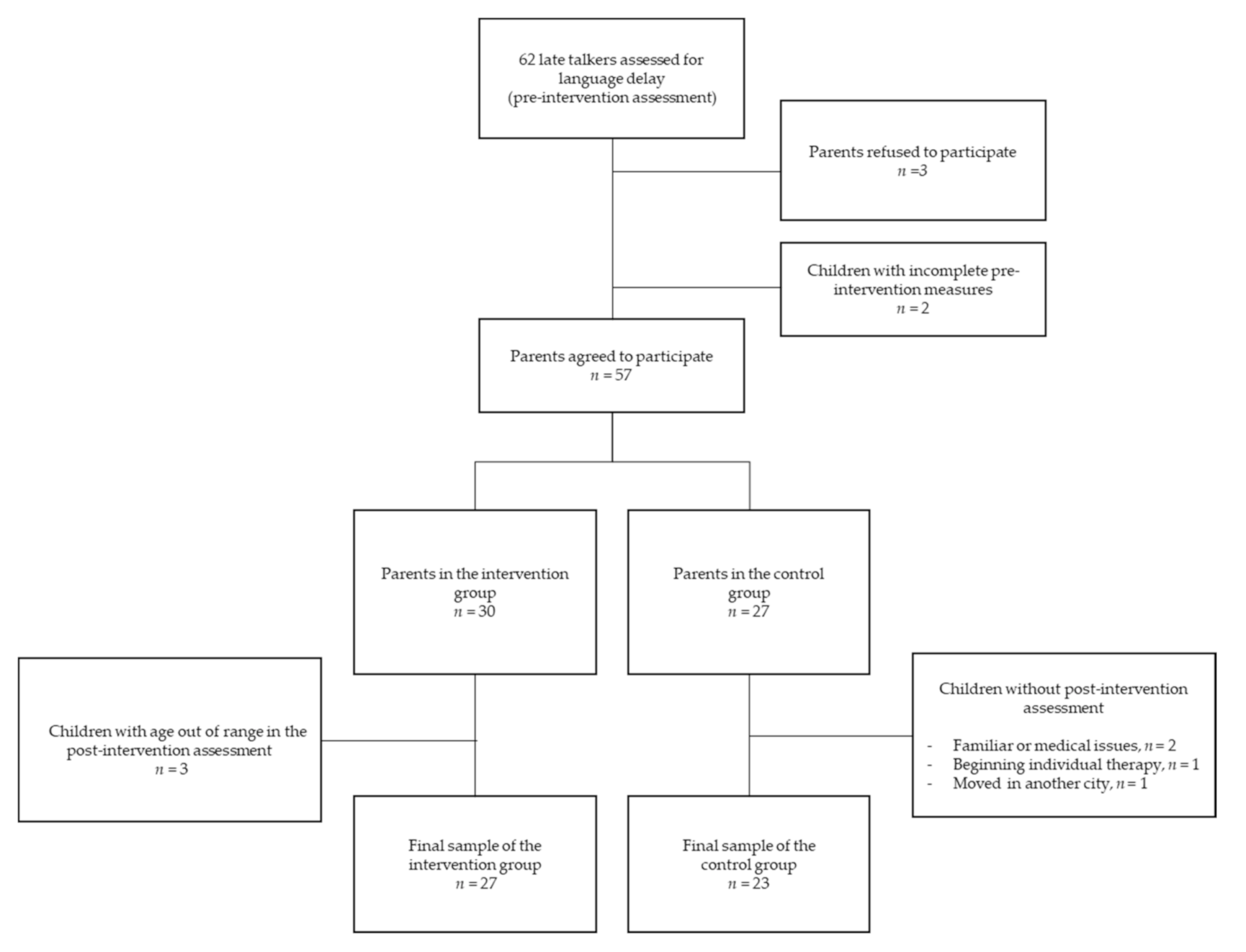
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure and Study Design
2.3. Tools
2.4. Parent-Administered Intervention Program
2.5. Ethics
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pre-Intervention Assessment
3.2. Effects of the Parent-Implemented Intervention on Late Talkers’ Expressive Lexical and Syntactic Skills
3.3. Effects of the Parent-Implemented Intervention on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Late Talkers’ Expressive Lexical and Syntactic Skills
4. Discussion
4.1. The Efficacy of the Parent-Implemented Intervention in Late Talkers
4.2. The Efficacy of Parent-Implemented Intervention in Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Late Talkers
4.3. Limitations and Strengths of the Study
4.4. Implications for Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A: Clinical and Perinatal Characteristics of Low-Risk Preterm Children
| Clinical and Perinatal Characteristics | Low-Risk Preterm Children (n = 23) |
|---|---|
| n (%) | |
| Caesarean Section | 22 (95.65) |
| SGA | 6 (26.08) |
| IVH I/II | 0 (0) |
| MV | 1 (4.35) |
| RDS | 12 (52.17) |
| Apnea | 1 (4.35) |
| BDP | 0 (0) |
| Sepsis | 1 (4.35) |
| ROP I/II | 0 (0) |
| Hyperbilirubinemia with Phototherapy, n (%) | 15 (65.22) |
References
- Bello, A.; Remi, L.; Olioso, G.; Anghinoni, E.; Galavotti, M.; Caselli, M.C. Un’esperienza di screening per l’identificazione di bambini con ritardo di linguaggio nella provincia di Mantova: Primi risultati e prospettive future. Psicol. Clin. Dello Svilupp. 2014, 18, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collisson, B.A.; Graham, S.A.; Preston, J.L.; Rose, M.S.; McDonald, S.; Tough, S. Risk and protective factors for late talking: An epidemiologic investigation. J. Pediatr. 2016, 172, 168–174.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpilahti, P.; Kaljonen, A.; Jansson-Verkasalo, E. Population-Based Screening for Language Delay: Let’s Talk STEPS Study. Psychology 2016, 7, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubrick, S.R.; Taylor, C.L.; Rice, M.L.; Slegers, D.W. Late language emergence at 24 months: An epidemiological study of prevalence, predictors, and covariates. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2007, 50, 1562–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, P.S.; Price, T.S.; Bishop, D.V.M.; Plomin, R. Outcomes of Early Language Delay: I. Predicting Persistent and Transient Language Difficulties at 3 and 4 Years. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2003, 46, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmarais, C.; Sylvestre, A.; Meyer, F.; Bairati, I.; Rouleau, N. Systematic review of the literature on characteristics of late-talking toddlers. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2008, 43, 361–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenson, L.; Marchman, V.; Thal, D.; Dale, P.; Reznick, J. The MacArthur–Bates Communicative Development Inventories: User’s Guide and Technical Manual; Paul Brookes: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla, L.; Dale, P. Late Talkers: Language Development, Interventions, and Outcomes; Paul Brookes: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rescorla, L. The Language Development Survey: A screening tool for delayed language in toddlers. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1989, 54, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, A.; Onofrio, D.; Remi, L.; Caselli, C. Prediction and persistence of late talking: A study of Italian toddlers at 29 and 34 months. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 75, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawa, V.V.; Spanoudis, G. Toddlers with delayed expressive language: An overview of the characteristics, risk factors and language outcomes. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rescorla, L. Late talkers: Do good predictors of outcome exist? Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2011, 17, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansavini, A.; Guarini, A.; Justice, L.M.; Savini, S.; Broccoli, S.; Alessandroni, R.; Faldella, G. Does preterm birth increase a child’s risk for language impairment? Early Hum. Dev. 2010, 86, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charkaluk, M.L.; Rousseau, J.; Benhammou, V.; Datin-Dorrière, V.; Flamant, C.; Gire, C.; Kern, S.; Pierrat, V.; Kaminski, M.; Marret, S. Association of Language Skills with Other Developmental Domains in Extremely, Very, and Moderately Preterm Children: EPIPAGE 2 Cohort Study. J. Pediatr. 2019, 208, 114–120.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Pereira, M.; Fernández, P.; Gómez-Taibo, M.L.; Resches, M. Language development of low risk preterm infants up to the age of 30months. Early Hum. Dev. 2014, 90, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrana, I.M.; Vollrath, M.E.; Jacobsson, B.; Sengpiel, V.; Ystrom, E. Preterm birth and risk for language delays before school entry: A sibling-control study. Dev. Psychopathol. 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilosi, A.M.; Pfanner, L.; Pecini, C.; Salvadorini, R.; Casalini, C.; Brizzolara, D.; Cipriani, P. Which linguistic measures distinguish transient from persistent language problems in Late Talkers from 2 to 4 years? A study on Italian speaking children. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2019, 89, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, K.; Fujiki, M.; Brinton, B.; Hart, C. The Relationship Between Social Behavior and Severity of Language Development. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2004, 47, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmond, S.M.; Rice, M.L. The socioemotional behaviors of children with SLI: Social adaptation or social deviance? J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1998, 41, 688–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidlage, J.K.; Cunningham, J.E.; Kaiser, A.P.; Trivette, C.M.; Barton, E.E.; Frey, J.R.; Roberts, M.Y. The effects of parent-implemented language interventions on child linguistic outcomes: A meta-analysis. Early Child. Res. Q. 2020, 50, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.; Dennis, J.A.; Charlton, J.J.V. Speech and language therapy interventions for children with primary speech and/or language disorders. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosh, R.; Arnott, W.; Scarinci, N. Parent-implemented home therapy programmes for speech and language: A systematic review. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2017, 52, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.Y.; Kaiser, A.P. The effectiveness of parent-implemented language interventions: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2011, 20, 180–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolametto, L.; Pearce, P.S.; Weitzman, E. Interactive focused stimulation for toddlers with expressive vocabulary delays. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 1996, 39, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buschmann, A.; Jooss, B.; Rupp, A.; Feldhusen, F.; Pietz, J.; Philippi, H. Parent based language intervention for 2-year-old children with specific expressive language delay: A randomised controlled trial. Arch. Dis. Child. 2009, 94, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.; Multhauf, B.; Hasselhorn, M.; Pietz, J. Long-Term Effects of a Parent-Based Language Intervention on Language Outcomes and Working Memory for Late-Talking Toddlers. J. Early Interv. 2015, 37, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConachie, H.; Diggle, T. Parent implemented early intervention for young children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2007, 13, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Kaat-van den Os, D.J.A.; Jongmans, M.J.; Volman, M.J.M.; Lauteslager, P.E.M. Parent-Implemented Language Interventions for Children with a Developmental Delay: A Systematic Review. J. Policy Pract. Intellect. Disabil. 2017, 14, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.Y.; Kaiser, A.P. Assessing the effects of a parent-implemented language intervention for children with language impairments using empirical benchmarks: A pilot study. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2012, 55, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girolametto, L.; Bello, A.; Onofrio, D.; Remi, L.; Caselli, M.C. Parent-coaching per l’intervento precoce sul linguaggio. Percorsi di lettura dialogica nel programma “Oltre il Libro”.; Erickson: Trento, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, A.; Onofrio, D.; Remi, L.; Caselli, M.C.; Girolametto, L. La lettura dialogica per genitori di bambini con ritardo di linguaggio di 2–3 anni. Psicol. Clin. Dello Svilupp. 2019, 23, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansavini, A.; Guarini, A.; Savini, S.; Broccoli, S.; Justice, L.; Alessandroni, R.; Faldella, G. Longitudinal trajectories of gestural and linguistic abilities in very preterm infants in the second year of life. Neuropsychologia 2011, 49, 3677–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, M.C.; Bello, A.; Rinaldi, P.; Stefanini, S.; Pasqualetti, P. Il Primo Vocabolario del Bambino: Gesti, Parole e Frasi. Forme Lunghe e Forme Brevi del Questionario e Valori di Riferimento per la Fascia 8–36 Mesi; Franco Angeli: Milano, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bayley, N. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, Third Edition: Screening Test Manual; Pearson Clinical Assessment PsychCorp: San Antonio, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, R.; Orsini, A.; Rea, M.; Stoppa, E.; Mascellani, F. Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development, 3rd ed.; Giunti, O.S., Ed.; Manuale Dell’Adattamento Italiano, Italian Adaptation: Firenze, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tsybina, I.; Eriks-Brophy, A. Bilingual dialogic book-reading intervention for preschoolers with slow expressive vocabulary development. J. Commun. Disord. 2010, 43, 538–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehurst, G.J.; Falco, F.L.; Lonigan, C.J.; Fischel, J.E.; DeBaryshe, B.D.; Valdez-Menchaca, M.C.; Caulfield, M. Accelerating language development through picture book reading. Dev. Psychol. 1988, 24, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdall, N.; Melendez-Torres, G.J.; Murray, L.; Gardner, F.; Hartford, L.; Cooper, P.J. Shared Picture Book Reading Interventions for Child Language Development: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Child Dev. 2020, 91, e383–e399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, P.S.; Crain-Thoreson, C.; Notari-Syverson, A.; Cole, K. Parent-Child Book Reading as an Intervention Technique for Young Children with Language Delays. Top. Early Child. Spec. Educ. 1996, 16, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, A.C.; Sénéchal, M. A book reading intervention with preschool children who have limited vocabularies: The benefits of regular reading and dialogic reading. Early Child. Res. Q. 2000, 15, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, A.; Jooss, B.; Rupp, A.; Dockter, S.; Blaschtikowitz, H.; Heggen, I.; Pietz, J. Children with developmental language delay at 24 months of age: Results of a diagnostic work-up. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmarais, C.; Sylvestre, A.; Meyer, F.; Bairati, I.; Rouleau, N. Three profiles of language abilities in toddlers with an expressive vocabulary delay: Variations on a theme. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2010, 53, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, J.M.; Braddock, B.A. Gesture and Motor Skill in Relation to Language in Children With Language Impairment. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2011, 54, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caselli, C.; Casadio, P.; Bates, E. A comparison of the transition from first words to grammar in English and Italian. J. Child Lang. 1999, 26, 69–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, E.; Marchman, V.; Thal, D.; Fenson, L.; Dale, P.; Reznick, J.S.; Reilly, J.; Hartung, J. Developmental and stylistic variation in the composition of early vocabulary. J. Child Lang. 1994, 21, 85–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.; Garrett, Z.; Nye, C. The efficacy of treatment for children with developmental speech and language delay/disorder: A meta-analysis. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2004, 47, 924–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, S.; Wake, M.; Bavin, E.L.; Prior, M.; Williams, J.; Bretherton, L.; Eadie, P.; Barrett, Y.; Ukoumunne, O.C. Predicting language at 2 years of age: A prospective community study. Pediatrics 2007, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomella, T.L.; Cunningham, M.D.; Eyal, F.G.; Zenk, K.E. Neonatology: Management, Procedures, on-Call Problems, Diseases, and Drugs, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
| Participants’ Characteristics | Intervention | Control | χ2/t (df) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 27) | (n = 23) | |||
| Gestational Age (weeks), Mean (SD) | 36.29 (3.39) | 37.81 (2.86) | 1.70 (48) | 0.096 |
| Birthweight (grams), Mean (SD) | 2464.37 (888.11) | 2915.26 (696.13) | 1.97 (48) | 0.054 |
| Length of Stay in Hospital (days), Mean (SD) | 15.96 (33.92) | 5.09 (6.50) | −1.51 (48) | 0.137 |
| Gender (Female), n (%) | 10 (37.0) | 7 (30.4) | 0.24 (1, 50) | 0.623 |
| Firstborn, n (%) | 14 (51.8) | 9 (39.1) | 2.09 (1, 50) | 0.393 |
| Twins, n (%) | 9 (33.3) | 5 (21.7) | 0.83 (1, 50) | 0.363 |
| Otitis Media, n (%) | 1 (3.7) | 2 (8.7) | 0.55 (1, 50) | 0.459 |
| Family History of Language and/or Learning Disorders (LLD), n (%) | 6 (22.2) | 4 (17.4) | 0.18 (1, 50) | 0.670 |
| Nursery School Attendance, n (%) | 23 (85.2) | 15 (65.2) | 2.72 (1, 50) | 0.099 |
| Other Parent Input Besides Italian, n (%) | 6 (22.2) | 1 (4.3) | 3.30 (1, 50) | 0.107 |
| Mother’s Age (years), Mean (SD) | 40.67 (4.82) | 36.26 (4.80) | −3.23 (48) | 0.002 |
| Father’s Age (years), Mean (SD) | 42.67 (4.98) | 39.14 (5.82) | −2.19 (48) | 0.034 |
| Mothers with High Educational Level (>13 years), n (%) | 17 (63.0) | 13 (56.5) | 1.23 (1, 50) | 0.767 |
| Fathers with High Educational Level (>13 years), n (%) | 12 (44.4) | 9 (39.1) | 1.06 (1, 50) | 0.601 |
| Mother’s Nationality (Italian), n (%) | 22 (81.5) | 22 (95.6) | 2.36 (1, 50) | 0.124 |
| Father’s Nationality (Italian), n (%) | 23 (85.2) | 22 (95.6) | 1.51 (1, 50) | 0.219 |
| Age at Pre-Intervention (months), Mean (SD) | 31.09 (1.06) | 31.34 (1.02) | 0.87 (48) | 0.389 |
| Age at Post-Intervention (months), Mean (SD) | 36.72 (1.38) | 37.18 (1.12) | 1.27 (48) | 0.210 |
| Pre and Post-Intervention Interval (days), Mean (SD) | 173.48 (34.96) | 177.26 (39.90) | 0.35 (48) | 0.723 |
| Participants’ Characteristics | Low-Risk Preterm Children | Full-Term Children | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | χ2/t (df) | p | Intervention | Control | χ2/t (df) | p | |
| (n = 17) | (n = 6) | (n = 10) | (n = 17) | |||||
| Gestational Age (weeks), Mean (SD) | 34.23 (2.30) | 33.59 (1.73) | −0.61 (21) | 0.548 | 39.80 (1.46) | 39.30 (1.12) | −0.99 (25) | 0.329 |
| Birthweight (grams), Mean (SD) | 1876.65 (468.12) | 2031.17 (254.60) | 0.76 (21) | 0.455 | 3463.50 (356.17) | 3227.29 (499.50) | −1.31 (25) | 0.203 |
| Length of Stay in Hospital (days), Mean (SD) | 23.88 (41.09) | 11.17 (10.81) | −0.74 (21) | 0.468 | 2.50 (1.78) | 2.94 (0.41) | 0.65 (25) | 0.524 |
| Gender (Female), n (%) | 4 (23.5) | 2 (33.3) | 0.22 (1, 23) | 0.632 | 6 (60.0) | 5 (29.4) | 2.44 (1, 27) | 0.224 |
| Firstborn, n (%) | 10 (58.8) | 1 (16.7) | 3.44 (1, 23) | 0.171 | 4 (40.0) | 8 (47.1) | 1.69 (1, 27) | 0.636 |
| Twins, n (%) | 9 (52.9) | 5 (83.3) | 1.72 (1, 23) | 0.340 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | - | - |
| Otitis Media, n (%) | 1 (5.9) | 0 (0.0) | 0.37 (1, 23) | 1.000 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (11.8) | 1.27 (1, 27) | 0.516 |
| Family History of Language and/or Learning Disorders (LLD), n (%) | 2 (11.8) | 2 (33.3) | 1.44 (1, 23) | 0.231 | 4 (40.0) | 2 (11.8) | 2.90 (1, 27) | 0.153 |
| Nursery School Attendance, n (%) | 14 (82.4) | 2 (33.3) | 5.03 (1, 23) | 0.045 | 9 (90.0) | 13 (76.5) | 0.76 (1, 27) | 0.621 |
| Other Parent Input Besides Italian, n (%) | 4 (23.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1.71 (1, 23) | 0.539 | 2 (20.0) | 1 (5.9) | 1.27 (1, 27) | 0.535 |
| Mother’s Age (years), Mean (SD) | 41.41 (5.50) | 36.67 (3.20) | −2.12 (21) | 0.046 | 39.40 (4.25) | 36.12 (5.32) | −1.66 (25) | 0.110 |
| Father’s Age (years), Mean (SD) | 43.33 (5.02) | 40.60 (5.50) | −1.08 (19) | 0.293 | 41.13 (4.85) | 38.69 (6.01) | −0.99 (22) | 0.331 |
| Mothers with High Educational Level (>13 years), n (%) | 8 (47.1) | 4 (66.7) | 0.68 (1, 23) | 0.640 | 9 (90.0) | 9 (52.9) | 3.72 (1, 27) | 0.133 |
| Fathers with High Educational Level (>13 years), n (%) | 5 (29.4) | 2 (33.3) | 3.07 (1, 23) | 0.246 | 7 (70.0) | 7 (41.2) | 2.20 (1, 27) | 0.389 |
| Mother’s Nationality (Italian), n (%) | 13 (76.5) | 6 (100.0) | 1.71 (1, 23) | 0.539 | 1 (10.0) | 16 (94.1) | 0.16 (1, 27) | 1.000 |
| Father’s Nationality (Italian), n (%) | 14 (82.4) | 6 (100.0) | 1.22 (1, 23) | 0.539 | 1 (10.0) | 16 (94.1) | 0.16 (1, 27) | 1.000 |
| Age at Pre-Intervention (months), Mean (SD) | 30.87 (0.66) | 31.94 (0.91) | 3.08 (21) | 0.006 | 31.45 (1.50) | 31.13 (1.00) | −0.65 (25) | 0.520 |
| Age at Post-Intervention (months), Mean (SD) | 36.32 (1.31) | 37.13 (1.41) | 1.27 (21) | 0.219 | 37.40 (1.29) | 37.20 (1.05) | −0.44 (25) | 0.661 |
| Pre and Post-Intervention Interval (days), Mean (SD) | 168.94 (29.61) | 156.50 (38.17) | −0.82 (21) | 0.419 | 181.20 (43.21) | 184.59 (38.93) | −0.21 (25) | 0.836 |
| All Children (n = 50) | Low-Risk Preterm Children (n = 23) | Full-Term Children (n = 27) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention (n = 27) | Control (n = 23) | Intervention (n = 17) | Control (n = 6) | Intervention (n = 10) | Control (n = 17) | |||||||
| M (SD) | M (SD) | U | p | M (SD) | M (SD) | U | p | M (SD) | M (SD) | U | p | |
| MB-CDI Language Measures | ||||||||||||
| Word Production | 139.37 (106.90) | 102.61 (97.70) | 235.00 | 0.142 | 145.82 (122.09) | 133.83 (64.35) | 49.00 | 0.919 | 128.40 (79.38) | 91.60 (106.47) | 56.50 | 0.155 |
| Social Words | 30.33 (9.61) | 23.35 (11.24) | 201.50 | 0.034 | 29.59 (10.09) | 28.83 (5.81) | 50.00 | 0.973 | 31.60 (9.09) | 21.41 (12.16) | 44.00 | 0.040 |
| Nouns | 77.22 (66.21) | 58.74 (65.78) | 260.00 | 0.325 | 83.88 (75.12) | 79.83 (51.57) | 48.00 | 0.865 | 65.90 (49.03) | 51.29 (69.96) | 63.50 | 0.286 |
| Predicates | 19.04 (25.60) | 12.57 (16.56) | 252.50 | 0.256 | 20.59 (31.00) | 16.50 (13.03) | 41.50 | 0.516 | 16.40 (13.18) | 11.18 (17.78) | 53.50 | 0.115 |
| Function Words | 7.67 (6.72) | 5.35 (6.38) | 221.00 | 0.080 | 7.06 (6.67) | 5.17 (3.97) | 45.00 | 0.708 | 8.70 (7.04) | 5.41 (7.14) | 53.00 | 0.115 |
| Incomplete Sentences | 7.78 (11.73) | 4.78 (7.03) | 290.00 | 0.672 | 5.76 (9.62) | 6.67 (11.65) | 46.50 | 0.759 | 11.20 (14.57) | 4.12 (4.86) | 64.50 | 0.309 |
| Complete Sentences | 0.33 (1.21) | 1.22 (3.34) | 264.00 | 0.176 | 0.47 (1.50) | 1.50 (2.59) | 25.50 | 0.074 | 0.10 (0.32) | 1.12 (3.71) | 82.50 | 0.902 |
| Total Sentences | 8.11 (12.08) | 6.00 (8.54) | 301.00 | 0.844 | 6.24 (10.41) | 8.17 (11.79) | 42.00 | 0.562 | 11.30 (14.52) | 5.24 (7.39) | 66.50 | 0.359 |
| Bayley-III Cognitive Measure | ||||||||||||
| Cognitive Composite Score | 90.93 (10.10) | 85.65 (8.57) | 216.50 | 0.064 | 89.12 (10.34) | 84.17 (7.36) | 37.00 | 0.354 | 94.00 (9.37) | 86.17 (9.10) | 46.50 | 0.052 |
| All Children (n = 50) | Low-Risk Preterm Children (n = 23) | Full-Term Children (n = 27) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Children’s Change from Pre- to Post-Intervention | Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | ||||
| (n = 27) | (n = 23) | χ2 | p | (n = 17) | (n = 6) | Fisher’s p | (n = 10) | (n = 17) | Fisher’s p | |
| Expressive lexical delay | 3.94 | 0.047 | 0.371 | 0.120 | ||||||
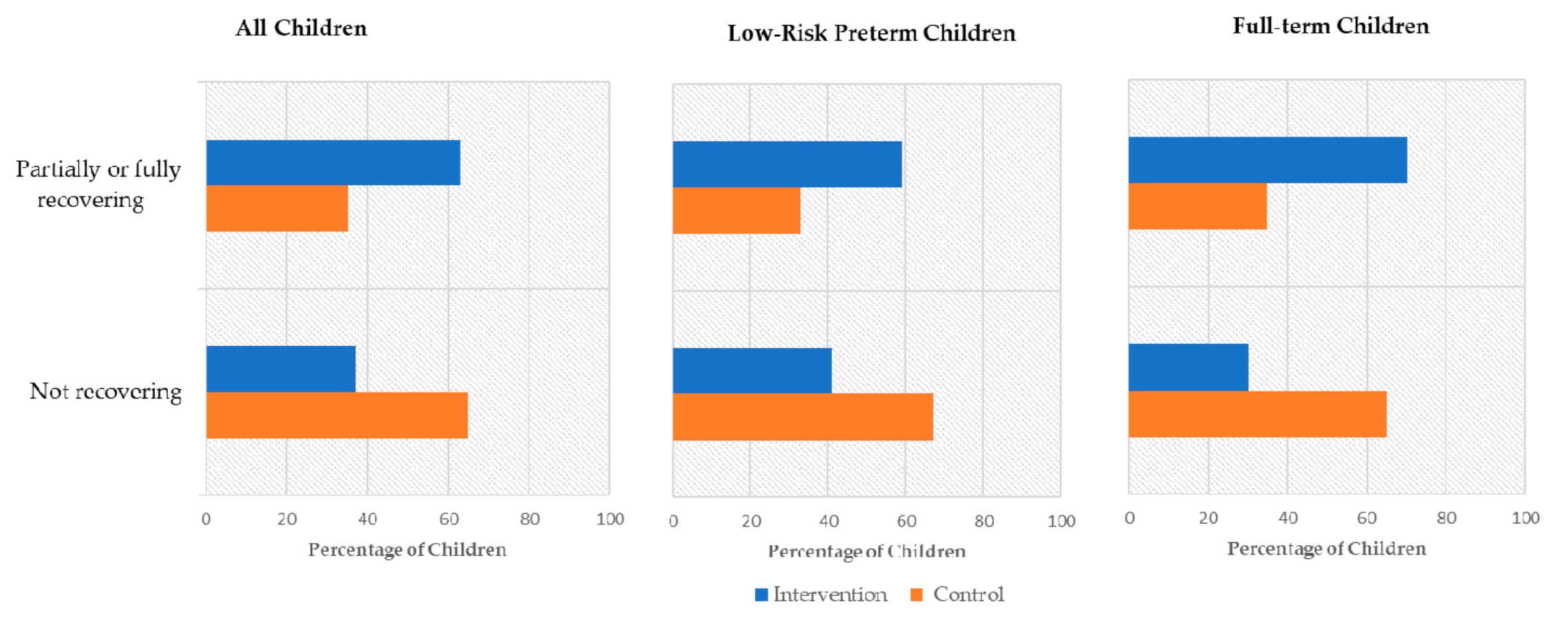
| Children partially or fully recovering, n (%) | 17 (63) | 8 (35) | 10 (59) | 2 (33) | 7 (70) | 6 (35) | ||||
| Children not recovering, n (%) | 10 (37) | 15 (65) | 7 (41) | 4 (67) | 3 (30) | 11 (65) | ||||
| Expressive syntactic skills | 8.60 | 0.013 | 0.010 | 0.018 | ||||||
| Children with stable complete sentences, n (%) | 3 (11) | 6 (26) | 2 (12) | 4 (67) | 1 (10) | 2 (12) | ||||
| Children with emergent complete sentences, n (%) | 17 (63) | 5 (22) | 9 (53) | 0 (0) | 8 (80) | 5 (30) | ||||
| Children with stable incomplete sentences, n (%) | 7 (26) | 12 (52) | 6 (35) | 2 (33) | 1 (10) | 10 (59) | ||||
| Daily Growth Rate | All Children (n = 50) | Low-Risk Preterm Children (n = 23) | Full-Term Children (n = 27) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | Intervention | Control | |||||||
| (n = 27) | (n = 23) | U | p | (n = 17) | (n = 6) | U | p | (n = 10) | (n = 17) | U | p | |
| Total words | 1.20 (0.77) | 0.84 (0.88) | 225.00 | 0.096 | 0.95 (0.62) | 0.94 (0.90) | 50.00 | 0.944 | 1.61 (0.85) | 0.81 (0.90) | 44.00 | 0.040 |
| Social words | 0.07 (0.05) | 0.08 (0.08) | 271.00 | 0.442 | 0.07 (0.03) | 0.06 (0.10) | 37.00 | 0.327 | 0.07 (0.06) | 0.08 (0.07) | 85.00 | 1.000 |
| Nouns | 0.67 (0.43) | 0.45 (0.48) | 219.00 | 0.075 | 0.57 (0.42) | 0.53 (0.49) | 46.00 | 0.795 | 0.82 (0.43) | 0.42 (0.49) | 44.00 | 0.040 |
| Predicates | 0.29 (0.25) | 0.22 (0.26) | 250.00 | 0.239 | 0.21 (0.16) | 0.23 (0.23) | 46.00 | 0.726 | 0.44 (0.30) | 0.22 (0.28) | 49.00 | 0.071 |
| Function words | 0.09 (0.07) | 0.06 (0.06) | 222.50 | 0.087 | 0.06 (0.07) | 0.07 (0.06) | 49.00 | 0.889 | 0.14 (0.06) | 0.05 (0.07) | 30.00 | 0.005 |
| Complete sentences | 0.06 (0.07) | 0.03 (0.06) | 227.00 | 0.093 | 0.04 (0.07) | 0.04 (0.07) | 44.00 | 0.617 | 0.09 (0.08) | 0.03 (0.06) | 45.00 | 0.046 |
| Total sentences | 0.12 (0.09) | 0.09 (0.09) | 241.00 | 0.175 | 0.13 (0.10) | 0.13 (0.12) | 50.50 | 0.973 | 0.10 (0.08) | 0.07 (0.07) | 65.00 | 0.334 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuccarini, M.; Suttora, C.; Bello, A.; Aceti, A.; Corvaglia, L.; Caselli, M.C.; Guarini, A.; Sansavini, A. A Parent-Implemented Language Intervention for Late Talkers: An Exploratory Study on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239123
Zuccarini M, Suttora C, Bello A, Aceti A, Corvaglia L, Caselli MC, Guarini A, Sansavini A. A Parent-Implemented Language Intervention for Late Talkers: An Exploratory Study on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Children. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239123
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuccarini, Mariagrazia, Chiara Suttora, Arianna Bello, Arianna Aceti, Luigi Corvaglia, Maria Cristina Caselli, Annalisa Guarini, and Alessandra Sansavini. 2020. "A Parent-Implemented Language Intervention for Late Talkers: An Exploratory Study on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Children" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239123
APA StyleZuccarini, M., Suttora, C., Bello, A., Aceti, A., Corvaglia, L., Caselli, M. C., Guarini, A., & Sansavini, A. (2020). A Parent-Implemented Language Intervention for Late Talkers: An Exploratory Study on Low-Risk Preterm and Full-Term Children. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9123. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239123









