Mental Health Disorders and Summer Temperature-Related Mortality: A Case Crossover Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and Population
- All subjects who had accessed the services of the MHD at least once (the MHD population);
- All subjects who had never accessed the services of the MHD (the non-MHD population).
2.2. Outcomes and Environmental Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
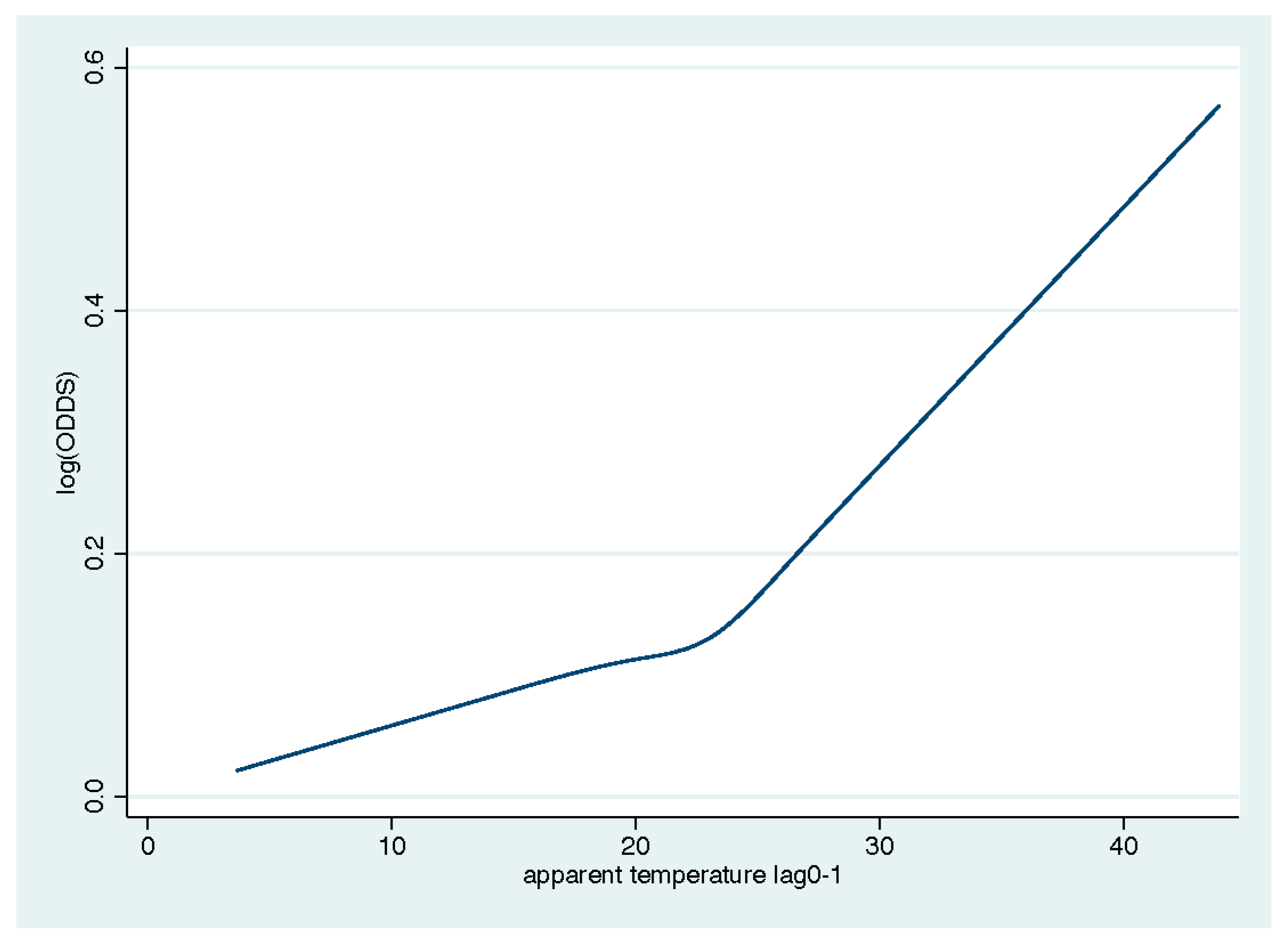
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Gasparrini, A.; Armstrong, B.; Li, S.; Tawatsupa, B.; Tobias, A.; Lavigne, E.; de Sousa Zanotti Stagliorio Coelho, M.; Leone, M.; Pan, X.; et al. Global variation in the effects of ambient temperature on mortality: A systematic evaluation. Epidemiology 2014, 25, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmarhnia, T.; Deguen, S.; Kaufman, J.S.; Smargiassi, A. Review Article: Vulnerability to Heat-related Mortality: A Systematic Review, Meta-analysis, and Meta-regression Analysis. Epidemiology 2015, 26, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunker, A.; Wildenhain, J.; Vandenbergh, A.; Henschke, N.; Rocklöv, J.; Hajat, S.; Sauerborn, R. Effects of Air Temperature on Climate-Sensitive Mortality and Morbidity Outcomes in the Elderly; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Evidence. EBioMedicine 2016, 6, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelozzi, P.; De’ Donato, F.K.; Bargagli, A.M.; D’Ippoliti, D.; De Sario, M.; Marino, C.; Schifano, P.; Cappai, G.; Leone, M.; Kirchmayer, U.; et al. Surveillance of Summer Mortality and Preparedness to Reduce the Health Impact of Heat Waves in Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2256–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, N.; Adger, W.N.; Agnolucci, P.; Blackstock, J.; Byass, P.; Cai, W.; Chaytor, S.; Colbourn, T.; Collins, M.; Cooper, A.; et al. Health and climate change: Policy responses to protect public health. Lancet 2015, 386, 1861–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, M.; De Sario, M.; de’Donato, F.K.; Davoli, M.; Michelozzi, P.; Stafoggia, M. Short-Term Effects of Heat on Mortality and Effect Modification by Air Pollution in 25 Italian Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.Y.; Liu, J.C.; Bell, M.L. Temperature-related mortality: A systematic review and investigation of effect modifiers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 073004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Regional Office for Europe. Improving Public Health Responses to Extreme Weather; Summary for Policy Makers; EuroHEAT: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Perčič, S.; Kukec, A.; Cegnar, T.; Hojs, A. Number of Heat Wave Deaths by Diagnosis, Sex, Age Groups, and Area, in Slovenia, 2015 vs. 2003. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirinhas, J.L.; Russo, A.; Libonati, R.; Trigo, R.M.; Castro, L.C.O.; Peres, L.F.; de Magalhães, A.F.M.M.; Nunes, B. Heat-related mortality at the beginning of the twenty-first century in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchama, A. Prognostic Factors in Heat Wave–Related Deaths A Meta-analysis. Arch. Int. Med. 2007, 167, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.; Bi, P.; Nitschke, M.; Ryan, P.; Pisaniello, D.; Tucker, G. The Effect of Heat Waves on Mental Health in a Temperate Australian City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, L.A.; Hajat, S.; Kovats, R.S.; Howard, L.M. Temperature-related deaths in people with psychosis, dementia and substance misuse. Br. J. Psychiatry 2012, 200, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.; Hornigold, R.; Page, L.; Waite, T. Associations between high ambient temperatures and heat waves with mental health outcomes: A systematic review. Public Health 2018, 161, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Barber, R.M.; Bell, B.; Bertozzi-Villa, A.; Biryukov, S.; Bolliger, I.; Charlson, F.; Davis, A.; Degenhardt, L.; Dicker, D.; et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 743–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.R.; McGee, R.E.; Druss, B.G. Mortality in Mental Disorders and Global Disease Burden Implications: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardi, D.; Pavarin, R.M.; Chierzi, F.; Terzi, L.; Manzo, V.; Piazza, A.; Menchetti, M.; Fioritti, A. Mortality Rates and Trends among Bologna Community Mental Health Service Users: A 13-Year Cohort Study. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2018, 206, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclure, M. The case-crossover design: A method for studying transient effects on the risk of acute events. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 133, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N.; Augustin, N.H. GAMs with integrated model selection using penalized regression splines and applications to environmental modelling. Ecol. Model. 2002, 157, 157–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafoggia, M.; Forastiere, F.; Agostini, D.; Biggeri, A.; Bisanti, L.; Cadum, E.; Caranci, N.; de’ Donato, F.; De Lisio, S.; De Maria, M.; et al. Vulnerability to heat-related mortality: A multicity, population-based, case-crossover analysis. Epidemiology. 2006, 17, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lora, A.; Barbato, A.; Cerati, G.; Erlicher, A.; Percudani, M. The mental health system in Lombardy, Italy: Access to services and patterns of care. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2012, 47, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, D.O.; Schifano, P.; Asta, F.; Lallo, A.; Michelozzi, P.; Rocklöv, J.; Forsberg, B. The effect of heat waves on mortality in susceptible groups: A cohort study of a mediterranean and a Northern European City. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DE Hert, M.; Correll, C.U.; Bobes, J.; Cetkovich-Bakmas, M.; Cohen, D.; Asai, I.; Detraux, J.; Gautam, S.; Möller, H.-J.; Ndetei, D.M.; et al. Physical illness in patients with severe mental disorders. I. Prevalence, impact of medications and disparities in health care. World Psychiatry 2011, 10, 52–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayerbe, L.; Forgnone, I.; Foguet-Boreu, Q.; González, E.; Addo, J.; Ayis, S. Disparities in the management of cardiovascular risk factors in patients with psychiatric disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2018, 48, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.S.S.; Chan, T.Y.K. Recurrent heat-related illnesses during antipsychotic treatment. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005, 39, 1940–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lõhmus, M. Possible Biological Mechanisms Linking Mental Health and Heat—A Contemplative Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profilo di Salute 2019. Available online: https://www.ausl.bologna.it/asl-bologna/dipartimenti-territoriali-1/dipartimento-di-sanita-pubblica/trasp/informazioni-ambientali/stato-della-salute-e-della-sicurezza-umana/profilo%20di%20salute%202019.pdf/attachment_download/file (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- Hartley, D. Rural disparities, population health, and rural culture. Am. J. Public Health 2004, 94, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, M.; Marmot, M. Neibourhood deprivation and health: Does it affect us all equally? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.H.; Zaitchik, B.F.; Gohlke, J.M. Heat waves and fatal traffic crashes in the continental United States. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2018, 119, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameezdeen, R.; Elmualim, A. The Impact of Heat Waves on Occurrence and Severity of Construction Accidents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Jang, S.Y.; Chun, S.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Han, K.T.; Park, E.C. Mortality in Schizophrenia and Other Psychoses: Data from the South Korea National Health Insurance Cohort, 2002–2013. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, M.; Mungai, F.; Miselli, M.; Shiers, D.; Curtis, J.; Starace, F. Strategies to implement physical health monitoring in people affected by severe mental illness: A literature review and introduction to the Italian adaptation of the Positive Cardiometabolic Health Algorithm. J. Psychopathol. 2015, 21, 269–280. [Google Scholar]
- Clifton, A.; Burgess, C.; Clement, S.; Ohlsen, R.; Ramluggun, P.; Sturt, J.; Walters, P.; Barley, E.A. Influnces on uptake of cancer screening in mental health service users: A qualitative study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2016, 16, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werneke, U.; Horn, O.; Maryon-Davis, A.; Wessely, S.; Donnan, S.; McPherson, K. Uptake of screening for breast cancer in patients with mental health problems. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2006, 60, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, R.; Wildgust, H.J.; Bushe, C.J. Cancer and schizophrenia: Is there a paradox? J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisely, S.; Crowe, E.; Lawrence, D. Cancer-related mortality in people with mental illness. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, C.L.; Hale, M.W.; Williams, L.E.; Wager, T.D.; Lowry, C.A. Somatic influences on subjective well-being and affective disorders: The convergence of thermosensory and central serotonergic systems. Front. Psychol. 2015, 5, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, M.W.; Raison, C.L.; Lowry, C.A. Integrative physiology of depression and antidepressant drug action: Implications for serotonergic mechanisms of action and novel therapeutic strategies for treatment of depression. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 137, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Apparent Temperature (°C) | Mean Temperature (°C) | Humidity | Ozone, mcg/m3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | 21.48 | 20.85 | 61.9 | 108.75 |
| sd | 4.57 | 4.03 | 11.47 | 26.02 |
| minimum | 6.75 | 4.63 | 18 | 10.5 |
| maximum | 31.9 | 34.02 | 100 | 229.62 |
| percentiles | ||||
| 25th | 18.27 | 17.75 | 52 | 84.75 |
| 50th | 21.65 | 21.02 | 62 | 104.88 |
| 75th | 25.09 | 24.19 | 71 | 126.38 |
| % missing | 9.15 | 0.66 | 9.15 | 8.86 |
| Non-MHD | MHD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Total | 45,278 | 100 | 3008 | 100 |
| age class | ||||
| 18–40 | 537 | 1.19 | 76 | 2.53 |
| 41–64 | 4005 | 8.85 | 557 | 18.52 |
| 65–74 | 6066 | 13.40 | 527 | 17.52 |
| 75–84 | 13,805 | 30.49 | 967 | 32.15 |
| >84 | 20,865 | 46.08 | 881 | 29.29 |
| gender | ||||
| male | 21,266 | 46.97 | 1312 | 43.62 |
| female | 24,012 | 53.03 | 1696 | 56.38 |
| cause of death | ||||
| Natural | 43,251 | 95.52 | 2741 | 91.12 |
| Certain infectious and parasitic diseases | 908 | 2.01 | 94 | 3.14 |
| Neoplasms | 14,712 | 32.61 | 693 | 23.14 |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 231 | 0.51 | 10 | 0.33 |
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | 1772 | 3.93 | 155 | 5.18 |
| Mental and behavioral disorders | 1781 | 3.95 | 212 | 7.08 |
| Diseases of the nervous system | 1404 | 3.11 | 153 | 5.11 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | 15,610 | 34.60 | 910 | 30.38 |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | 3271 | 7.25 | 261 | 8.71 |
| Diseases of the digestive system | 1650 | 3.66 | 112 | 3.74 |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | 69 | 0.15 | 9 | 0.30 |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 200 | 0.44 | 16 | 0.53 |
| Diseases of the genitourinary system | 831 | 1.84 | 63 | 2.10 |
| Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium | 4 | 0.01 | ||
| Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period | 2 | 0.00 | ||
| Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | 43 | 0.10 | 7 | 0.23 |
| Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified | 605 | 1.34 | 33 | 1.10 |
| External causes of morbidity and mortality | 2028 | 4.49 | 267 | 8.91 |
| residency | ||||
| urban | 26,562 | 58.66 | 1552 | 51.60 |
| rural | 18,716 | 41.34 | 1456 | 48.40 |
| psychiatric diagnosis | ||||
| Schizophrenia and other functional psychosis | 335 | 11.14 | ||
| Mania and bipolar affective disorders | 147 | 4.89 | ||
| Depression | 1039 | 34.54 | ||
| Neurotic disorders | 309 | 10.27 | ||
| Disorders of personality and behavior | 156 | 5.19 | ||
| Alcoholism and substance abuse | 49 | 1.63 | ||
| Dementia and cognitive decline | 939 | 31.22 | ||
| other | 34 | 1.13 | ||
| Non-MHD | MHD | z-Test | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | p | |||
| Total | 1.019 | 1.012 | 1.026 | <0.001 | 1.055 | 1.024 | 1.086 | <0.001 | 0.0255 |
| age class | |||||||||
| 18–40 | 1.039 | 0.969 | 1.113 | 0.283 | 1.063 | 0.865 | 1.307 | 0.562 | 0.834 |
| 41–64 | 0.99 | 0.963 | 1.018 | 0.476 | 1.072 | 0.997 | 1.152 | 0.059 | 0.044 |
| 65–74 | 1.007 | 0.985 | 1.029 | 0.531 | 1.065 | 0.992 | 1.142 | 0.081 | 0.137 |
| 75–84 | 1.024 | 1.009 | 1.039 | 0.001 | 1.048 | 0.995 | 1.104 | 0.074 | 0.393 |
| >84 | 1.023 | 1.011 | 1.035 | <0.001 | 1.046 | 0.992 | 1.103 | 0.094 | 0.415 |
| gender | |||||||||
| male | 1.017 | 1.006 | 1.029 | 0.004 | 1.083 | 1.036 | 1.132 | <0001 | 0.007 |
| female | 1.020 | 1.009 | 1.031 | 0.000 | 1.034 | 0.993 | 1.075 | 0.102 | 0.518 |
| cause of death | |||||||||
| Natural | 1.020 | 1.011 | 1.028 | 0.000 | 1.052 | 1.020 | 1.085 | 0.001 | 0.053 |
| Certain infectious and parasitic diseases | 1.020 | 0.973 | 1.068 | 0.410 | 0.974 | 0.839 | 1.130 | 0.727 | 0.563 |
| Neoplasms | 1.013 | 1.001 | 1.025 | 0.039 | 1.072 | 1.016 | 1.131 | 0.011 | 0.043 |
| Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | 1.055 | 0.988 | 1.203 | 0.086 | 1.176 | 0.770 | 1.797 | 0.452 | 0.731 |
| Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | 1.015 | 0.967 | 1.036 | 0.973 | 1.113 | 0.991 | 1.250 | 0.072 | 0.086 |
| Mental and behavioral disorders | 1.018 | 0.984 | 1.053 | 0.305 | 1.090 | 0.996 | 1.194 | 0.061 | 0.162 |
| Diseases of the nervous system | 1.062 | 1.024 | 1.102 | 0.001 | 1.088 | 0.973 | 1.217 | 0.138 | 0.683 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | 1.032 | 1.020 | 1.044 | <0.001 | 1.039 | 0.994 | 1.087 | 0.093 | 0.759 |
| Diseases of the respiratory system | 1.034 | 1.008 | 1.060 | 0.010 | 1.015 | 0.929 | 1.110 | 0.740 | 0.705 |
| Diseases of the digestive system | 0.999 | 0.963 | 1.036 | 0.966 | 1.011 | 0.891 | 1.147 | 0.864 | 0.806 |
| Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | 1.204 | 0.992 | 1.460 | 0.060 | 0.863 | 0.466 | 1.597 | 0.639 | 0.312 |
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | 1.024 | 0.925 | 1.133 | 0.653 | 1.262 | 0.891 | 1.787 | 0.190 | 0.739 |
| Diseases of the genitourinary system | 1.010 | 0.963 | 1.060 | 0.678 | 0.979 | 0.817 | 1.173 | 0.816 | 0.258 |
| Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium | 1.167 | 0.622 | 2.191 | 0.631 | |||||
| Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period | 0.000 | 0.998 | |||||||
| Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | 0.977 | 0.805 | 1.185 | 0.814 | 0.000 | 0.997 | 0.997 | ||
| Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified | 0.994 | 0.939 | 1.052 | 0.842 | 1.059 | 0.811 | 1.383 | 0.674 | 0.844 |
| External causes of morbidity and mortality | 0.993 | 0.962 | 1.025 | 0.671 | 1.096 | 1.007 | 1.194 | 0.034 | 0.273 |
| residency | |||||||||
| urban | 1.023 | 1.013 | 1.034 | <0.001 | 1.049 | 1.004 | 1.095 | 0.031 | 0.283 |
| rural | 1.012 | 1 | 1.024 | 0.057 | 1.057 | 1.015 | 1.101 | 0.008 | 0.044 |
| Psychiatric Diagnosis | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Schizophrenia and other functional psychosis | 1.048 | 0.951–1.156 | 0.343 |
| Mania and bipolar affective disorders | 1.027 | 0.881–1.197 | 0.731 |
| Depression | 1.083 | 1.030–1.138 | 0.002 |
| Neurotic disorders | 0.985 | 0.897–1.083 | 0.761 |
| Disorders of personality and behavior | 0.957 | 0.835–1.098 | 0.532 |
| Alcoholism and substance abuse | 0.960 | 0.715–1.290 | 0.788 |
| Dementia and cognitive decline | 1.074 | 1.022–1.129 | 0.005 |
| Other | 0.902 | 0.672–1.211 | 0.492 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stivanello, E.; Chierzi, F.; Marzaroli, P.; Zanella, S.; Miglio, R.; Biavati, P.; Perlangeli, V.; Berardi, D.; Fioritti, A.; Pandolfi, P. Mental Health Disorders and Summer Temperature-Related Mortality: A Case Crossover Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239122
Stivanello E, Chierzi F, Marzaroli P, Zanella S, Miglio R, Biavati P, Perlangeli V, Berardi D, Fioritti A, Pandolfi P. Mental Health Disorders and Summer Temperature-Related Mortality: A Case Crossover Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239122
Chicago/Turabian StyleStivanello, Elisa, Federico Chierzi, Paolo Marzaroli, Sara Zanella, Rossella Miglio, Patrizia Biavati, Vincenza Perlangeli, Domenico Berardi, Angelo Fioritti, and Paolo Pandolfi. 2020. "Mental Health Disorders and Summer Temperature-Related Mortality: A Case Crossover Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239122
APA StyleStivanello, E., Chierzi, F., Marzaroli, P., Zanella, S., Miglio, R., Biavati, P., Perlangeli, V., Berardi, D., Fioritti, A., & Pandolfi, P. (2020). Mental Health Disorders and Summer Temperature-Related Mortality: A Case Crossover Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239122






