Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source and Study Design
2.2. Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
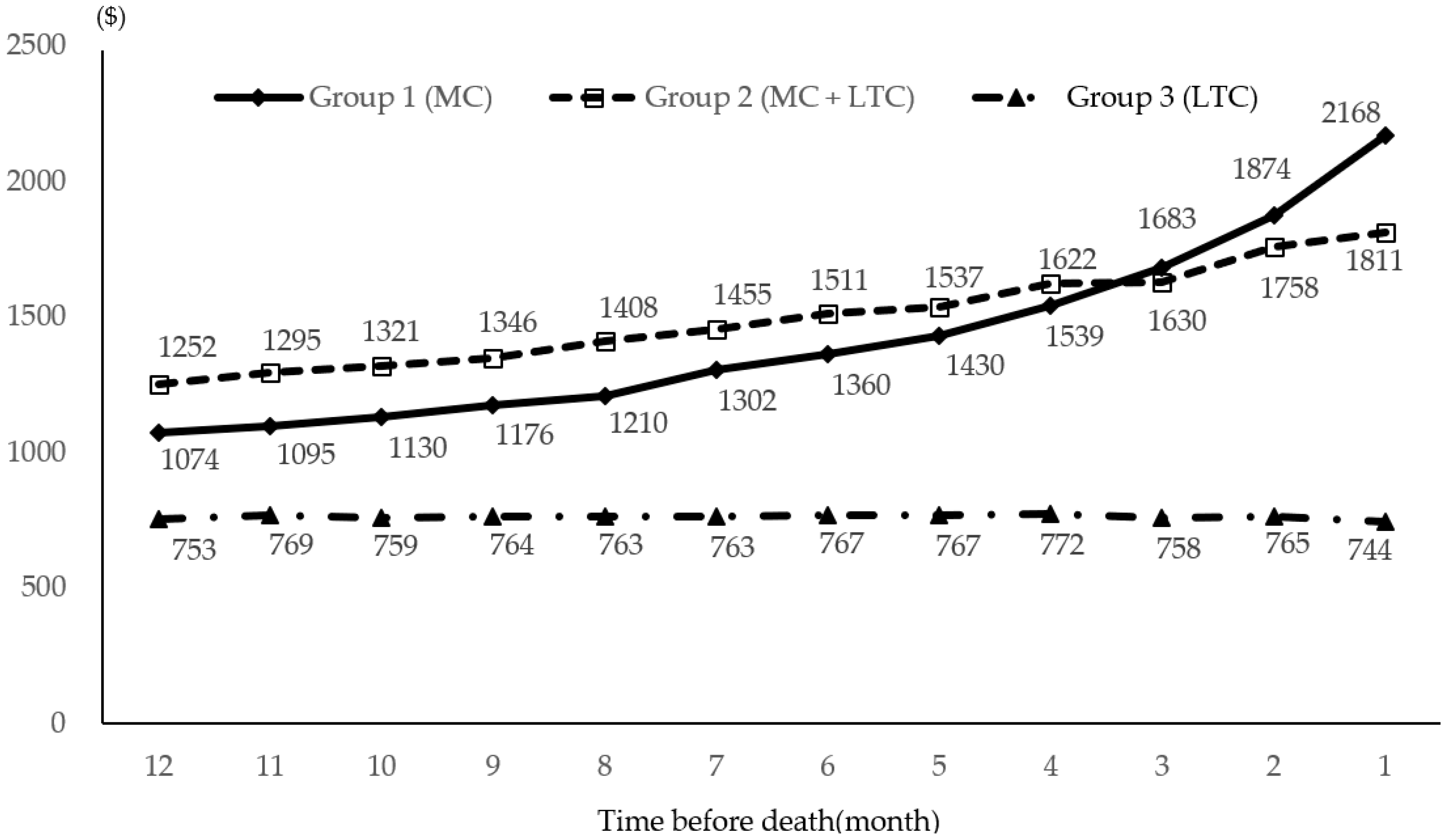
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Statistics Korea. Estimated Population by Age Group. 2019. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr (accessed on 29 September 2020).
- Kontis, V.; Bennett, J.E.; Mathers, C.D.; Li, G.; Foreman, K.; Ezzati, M. Future life expectancy in 35 industrialised countries: Projections with a Bayesian model ensemble. Lancet 2017, 389, 1323–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Corporation, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. 2018 National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook. 2019. Available online: http://www.hira.or.kr/bbsDummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA020045020000&brdScnBltNo=4&brdBltNo=2311&pageIndex=1#none (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Lee, G. Efficient Management Plan for Elderly Medical Expenses in Preparation for an Aging Society. 2017. Available online: https://www.nhis.or.kr/nhis/together/wbhaec07800m01.do?mode=view&articleNo=123576 (accessed on 3 July 2020).
- Jung, K.; Oh, Y.; Kang, E.; Kim, K.; Lee, Y.; Oh, M.; Hwang, N.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; et al. 2017 Elderly Status Survey Ministry of Health and Welfare & Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. 2017. Available online: http://www.mohw.go.kr/react/jb/sjb030301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=03&MENU_ID=032901&page=1&CONT_SEQ=344953 (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- National Health Insurance Corporation. 2018 First Half Long-Term Care Insurance Statistics. 2019. Available online: https://www.nhis.or.kr/bbs7/boards/B0163/27635?boardKey=36&sort=sequence&order=desc&rows=10&messageCategoryKey=&pageNumber=1&viewType=generic&targetType=12&targetKey=36&status=&period=&startdt=&enddt=&queryField=&query= (accessed on 13 August 2020).
- Kim, H.; Kwon, S.; Yoon, N.; Hyun, K. Utilization of long-term care services under the public long-term care insurance program in Korea: Implications of a subsidy policy. Health Policy 2013, 111, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y. Potentially avoidable hospitalization among long-term care insurance beneficiaries with dementia. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2020, 41, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Boo, S.; Hwang, S. Remodeling the Frame of Standard Utilization Plan in Long-Term Care Insurance. National Health Insurance Corporation. 2016. Available online: http://lib.nhis.or.kr/search/detail/CATXBZ000000031346 (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Hwang, I.; Shin, D.; Kang, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, S. Medical costs and healthcare utilization among cancer decedents in the last year of life in 2009. Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 4, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forder, J. Long-term care and hospital utilization by older people: An analysis of substitution rates. Health Econ. 2009, 18, 1322–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.G. Needs for Role Establishment of Geriatric Hospital and Long-Term Care Facilities for Long-Term Care for Elderly. Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Policy Trend. 2011. Available online: http://www.hira.or.kr/bbsDummy.do?pgmid=HIRAA030096000000 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Teno, J.M.; Gozalo, P.; Trivedi, A.N.; Bunker, J.; Lima, J.; Ogarek, J.; Mor, V. Site of death, place of care, and health care transitions among US Medicare beneficiaries, 2000–2015. JAMA 2018, 320, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Jung, Y.; Kwon, S. Delivery of institutional long-term care under two social insurances: Lessons from the Korean experience. Health Policy 2015, 119, 1330–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.; Hwang, R.; Lee, J. Utilization and expenditure of health care and long-term care at the end of life-evidence from Korea. Korea Soc. Policy Rev. 2018, 25, 99–123. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, J.; Won, J.; Ha, S. Cohort profile: The national health insurance service–senior (NHIS-senior) cohort in Korea. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e024344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, Y. The expansion of the Korean welfare state and its results—Focusing on long-term care insurance for the Elderly. Soc. Policy Adm. 2014, 48, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Song, Y.; Lee, K. Aging and health care expenditure. Korean J. Health Econ. Policy 2007, 13, 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hogan, C.; Lunney, J.; Gabel, J.; Lynn, J. Medicare beneficiaries’ costs of care in the last year of life. J. Health Aff. 2001, 20, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.A.; Keating, N.L.; Balboni, T.A.; Matulonis, U.A.; Block, S.D.; Prigerson, H.G. Place of death: Correlations with quality of life of patients with cancer and predictors of bereaved caregivers’ mental health. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kardamanidis, K.; Lim, K.; Da Cunha, C.; Taylor, L.K.; Jorm, L.R. Hospital costs of older people in New South Wales in the last year of life. Med. J. Aust. 2007, 187, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.; Kim, H. Impact of community health care resources on the place of death of older persons with dementia in South Korea using public administrative big data. Health Policy Manag. 2017, 27, 167–176. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, P.; Williams, H.; Maharaj, I. Patterns of end-of-life care: Place of death and terminal hospitalization among long-term-care residents. J. Hosp. Palliat. Nurs. 2015, 17, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.; Long, S.; Vincent, C. How can we keep patients with dementia safe in our acute hospitals? A review of challenges and solutions. J. R. Soc. Med. 2013, 106, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Park, J.K.; Park, Y.; Choi, W.S. End-of-life care needs for noncancer patients who want to die at home in South Korea. Int. J. Nutr. Pract. 2020, 26, e12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezaki, S.; Ikegami, N. Predictors of dying at home for patients receiving nursing services in Japan: A retrospective study comparing cancer and non-cancer deaths. BMC Palliat. Care 2011, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, M.; Carusone, S.; Goeree, R.; Walter, S.D.; Brazil, K.; Krueger, P. Effect of a clinical pathway to reduce hospitalizations in nursing home residents with pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Kim, E.; Lee, J. Factors relating to the quality of care for nursing home residents in Korea: Using the Delphi method. J. Korean Acad. Nurs. 2019, 49, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.B.; Lee, H.K.; Sok, S. Activities of daily living and nursing needs of the elderly in nursing home. J. Korean Acad. Community Health Nurs. 2009, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, D.H., Jr.; Ostermann, J.; Van Houtven, C.H.; Tulsky, J.A.; Steinhauser, K. What length of hospice use maximizes reduction in medical expenditures near death in the US Medicare program? Soc. Sci. Med. 2007, 65, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, S.R.; Pyenson, B.; Fitch, K.; Spence, C.; Iwasaki, K. Comparing hospice and nonhospice patient survival among patients who die within a three-year window. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2007, 33, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Planning and Implementing Palliative Care Services: A Guide for Programme Managers. 2016. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250584/9789241565417-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 29 September 2020).
| Types of Medical Care Use | n | (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MC | 6713 | (22.06) | |
| MC + LTC | MC + LTC-home care | 12,280 | (40.35) |
| MC + LTC-facility care | 7921 | (26.03) | |
| MC + LTC-home & facility care | 2961 | (9.73) | |
| LTC | LTC-home care | 345 | (1.13) |
| LTC-facility care | 44 | (0.14) | |
| LTC-home & facility care | 12 | (0.04) | |
| Neither | 157 | (0.52) | |
| Characteristics | Total (N = 30,433) | MC (n = 6713) | MC + LTC (n = 23,162) | LTC (n = 401) | Neither (n = 157) | χ2 | p | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | ||||||||||||
| Gender | ||||||||||||
| Men | 11,305 | (37.15) | 2659 | (39.61) | 8496 | (36.68) | 102 | (25.44) | 48 | (30.57) | 46.05 | <0.001 |
| Women | 19,128 | (62.85) | 4054 | (60.39) | 14,666 | (63.32) | 299 | (74.56) | 109 | (69.43) | ||
| Age (yr) | ||||||||||||
| 65–69 | 454 | (1.49) | 112 | (1.67) | 340 | (1.47) | -- | -- | 2 | (1.27) | 298.52 | <0.001 |
| 70–74 | 3463 | (11.38) | 883 | (13.15) | 2556 | (11.04) | 13 | (3.24) | 11 | (7.01) | ||
| 75–79 | 5735 | (18.84) | 1441 | (21.47) | 4238 | (18.3) | 35 | (8.73) | 21 | (13.38) | ||
| 80–84 | 7270 | (23.89) | 1705 | (25.4) | 5488 | (23.69) | 50 | (12.47) | 27 | (17.20) | ||
| 85 or over | 13,511 | (44.40) | 2572 | (38.31) | 10,540 | (45.51) | 303 | (75.56) | 96 | (61.15) | ||
| Grade of LTCI (Level of benefit coverage) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | 6838 | (22.47) | 1760 | (26.22) | 4920 | (21.24) | 115 | (28.68) | 43 | (27.39) | 94.42 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 8384 | (27.55) | 1747 | (26.02) | 6466 | (27.92) | 119 | (29.68) | 52 | (33.12) | ||
| 3 | 15,211 | (49.98) | 3206 | (47.76) | 11,776 | (50.84) | 167 | (41.65) | 62 | (39.49) | ||
| Insurance type | ||||||||||||
| HI | 25,607 | (84.14) | 5757 | (85.76) | 19,336 | (83.48) | 377 | (94.01) | 137 | (87.26) | 51.16 | <0.001 |
| Medical aid | 4826 | (15.86) | 956 | (14.24) | 3826 | (16.52) | 24 | (5.99) | 20 | (12.74) | ||
| Household income level | ||||||||||||
| Low | 8004 | (26.30) | 1643 | (24.47) | 6244 | (26.96) | 77 | (19.2) | 40 | (25.48) | 65.36 | <0.001 |
| Mid-low | 7649 | (25.13) | 1697 | (25.28) | 5760 | (24.87) | 149 | (37.16) | 43 | (27.39) | ||
| Mid-high | 9069 | (29.80) | 2045 | (30.46) | 6852 | (29.58) | 111 | (27.68) | 61 | (38.85) | ||
| High | 5711 | (18.77) | 1328 | (19.78) | 4306 | (18.59) | 64 | (15.96) | 13 | (8.28) | ||
| Primary caregiver | ||||||||||||
| Spouse | 6349 | (20.86) | 1343 | (20.01) | 4936 | (21.31) | 41 | (10.22) | 29 | (18.47) | 1170.29 | <0.001 |
| Children | 11,214 | (36.85) | 2316 | (34.5) | 8504 | (36.72) | 295 | (73.57) | 99 | (63.06) | ||
| Care assistant | 7030 | (23.10) | 2348 | (34.98) | 4638 | (20.02) | 25 | (6.23) | 19 | (12.10) | ||
| None | 1034 | (3.40) | 157 | (2.34) | 874 | (3.77) | 3 | (0.75) | -- | -- | ||
| Else | 4806 | (15.79) | 549 | (8.18) | 4210 | (18.18) | 37 | (9.23) | 10 | (6.37) | ||
| Place of residence at applying for LTCI | ||||||||||||
| Home | 19,608 | (64.43) | 3781 | (56.32) | 15,344 | (66.25) | 353 | (88.03) | 130 | (82.8) | 3142.68 | <0.001 |
| LTC facility | 4810 | (15.81) | 290 | (4.32) | 4481 | (19.35) | 31 | (7.73) | 8 | (5.10) | ||
| Geriatric hospital | 4174 | (13.72) | 2180 | (32.47) | 1988 | (8.58) | 1 | (0.25) | 5 | (3.18) | ||
| Else | 1841 | (6.05) | 462 | (6.88) | 1349 | (5.82) | 16 | (3.99) | 14 | (8.92) | ||
| Cause of death | ||||||||||||
| Circulatory ds. | 8784 | (28.86) | 2089 | (31.12) | 6583 | (28.42) | 78 | (19.41) | 34 | (21.66) | 731.61 | <0.001 |
| Neoplasms | 4440 | (14.59) | 1303 | (19.41) | 3133 | (13.52) | 2 | (0.50) | 2 | (1.27) | ||
| Respiratory ds. | 3685 | (12.11) | 647 | (9.64) | 3012 | (13.02) | 18 | (4.48) | 8 | (5.10) | ||
| Endocrine, nutritional ds. | 1846 | (6.07) | 434 | (6.46) | 1402 | (6.05) | 7 | (1.74) | 3 | (1.91) | ||
| Nervous system ds. | 1659 | (5.45) | 488 | (7.28) | 1161 | (5.01) | 8 | (1.99) | 2 | (1.27) | ||
| Others | 10,019 | (32.92) | 1752 | (26.09) | 7871 | (33.98) | 288 | (71.64) | 108 | 68.79) | ||
| Group | Number of Admissions, n (%) | n (%) | Hospital Days, M ± SD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | ≥3 | ||||||
| MC Group (N = 6713) | ||||||||
| 90 days before death | 3187 | (54.80) | 1005 | (17.28) | 1624 | (27.92) | 5816 (86.64) | 66.77 ± 32.55 |
| 30 days before death | 4280 | (75.83) | 944 | (16.73) | 420 | (7.44) | 5644 (84.08) | 25.59 ± 9.14 |
| 10 days before death | 4849 | (89.58) | 465 | (8.59) | 99 | (1.83) | 5413 (80.63) | 9.43 ± 2.33 |
| 3 days before death | 5064 | (95.91) | 198 | (3.75) | 18 | (0.34) | 5280 (78.65) | 2.92 ± 0.76 |
| MC + LTC Group (N = 23,162) | ||||||||
| 90 days before death | 8344 | (52.93) | 3820 | (24.23) | 3599 | (22.83) | 15,763 (68.06) | 38.14 ± 32.26 |
| 30 days before death | 10,453 | (72.68) | 2848 | (19.80) | 1081 | (7.52) | 14,382 (62.09) | 18.98 ± 11.51 |
| 10 days before death | 11,637 | (87.04) | 1468 | (10.98) | 265 | (1.98) | 13,370 (57.72) | 8.19 ± 3.39 |
| 3 days before death | 12,074 | (94.63) | 634 | (4.97) | 51 | (0.40) | 12,759 (55.09) | 2.91 ± 1.01 |
| Place of Death | Year, n (%) | χ2 | p | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Total | |||||||||
| Hospital | 1534 | (52.97) | 3244 | (51.89) | 3272 | (47.83) | 3798 | (52.64) | 3897 | (53.91) | 15,745 | (51.74) | 456.78 | <0.001 |
| LTC facility | 377 | (13.02) | 1252 | (20.03) | 1627 | (23.78) | 1807 | (25.05) | 1881 | (26.02) | 6944 | (22.82) | ||
| Home | 985 | (34.01) | 1756 | (28.09) | 1942 | (28.39) | 1610 | (22.31) | 1451 | (20.07) | 7744 | (25.45) | ||
| Total | 2896 | (100.0) | 6252 | (100.0) | 6841 | (100.0) | 7215 | (100.0) | 7229 | (100.0) | 30,433 | (100.0) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boo, S.; Lee, J.; Oh, H. Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239078
Boo S, Lee J, Oh H. Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239078
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoo, Sunjoo, Jungah Lee, and Hyunjin Oh. 2020. "Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239078
APA StyleBoo, S., Lee, J., & Oh, H. (2020). Cost of Care and Pattern of Medical Care Use in the Last Year of Life among Long-Term Care Insurance Beneficiaries in South Korea: Using National Claims Data. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 9078. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17239078




