Five Predictors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Odontogenic Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment
2.2. Patient Management
2.3. Data Collection
- (1)
- Socio-demographic data: age, sex, associate medical condition (penicillin allergy, smoking status, consumption of alcohol, diabetes, asthma, psychiatric disorder);
- (2)
- Clinical symptoms of severity;
- (3)
- Number and type of space involved by the infection;
- (4)
- Treatment on admission: ongoing antibiotic (family and duration of treatment) and/or anti-inflammatory treatment (corticosteroids or Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, NSAIDs);
- (5)
- Duration of hospital stay and number of surgeries;
- (6)
- Bacteriological results, results of culture and sensitivity, antibiotics adaptation;
- (7)
- Complications [10].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Which Are the Risk Factors to Have Complex Evolution?
3.3. Are Complications Liked to the Antibiotics Taken before Hospitalization?
3.4. Which Are the Predictors of Multiple Surgeries to Treat Severe Odontogenic Infection?
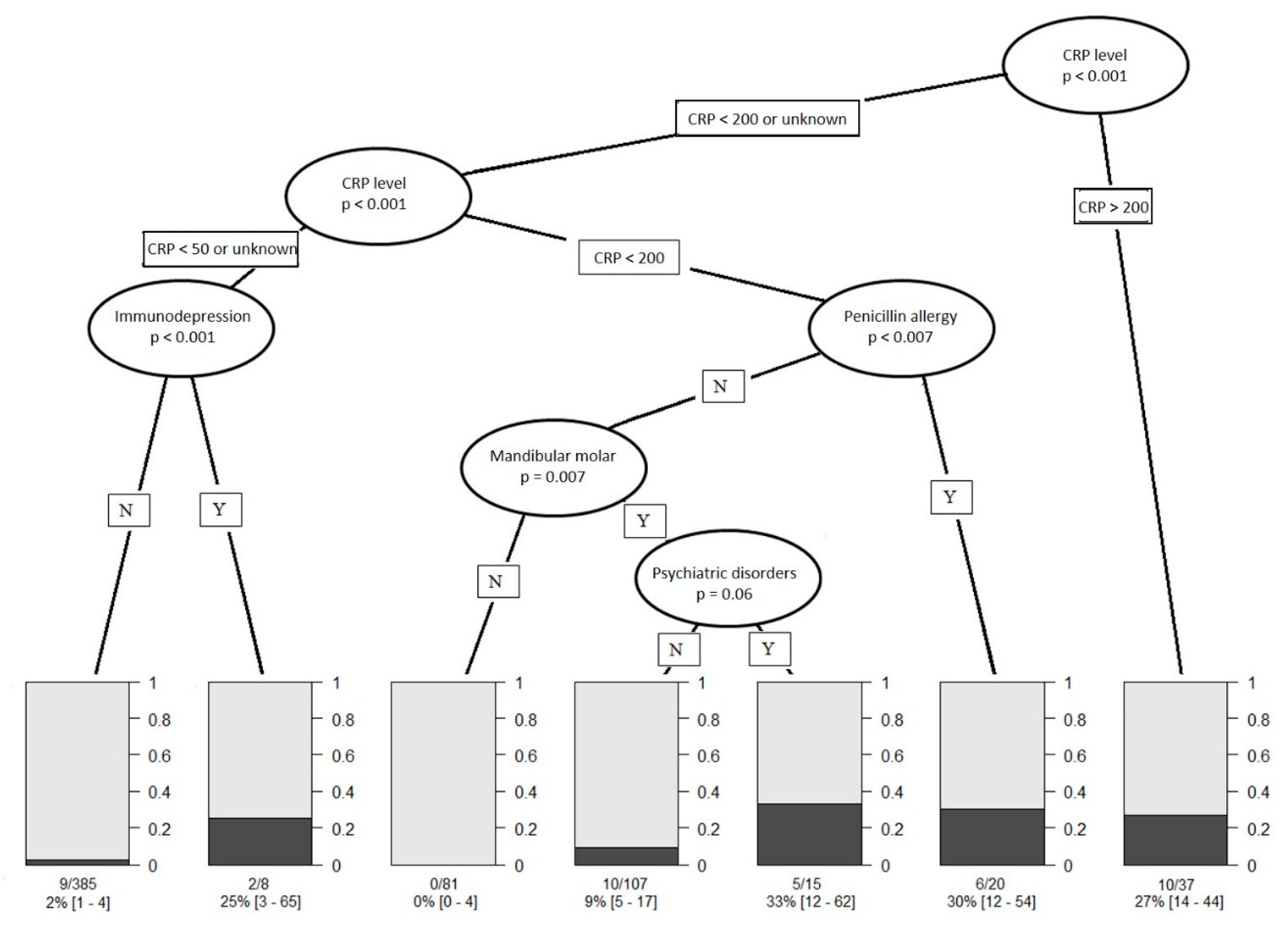
3.5. Conditional Inference Tree (CTREE) Construction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Consent for Publication
References
- Ylijoki, S.; Suuronen, R.; Jousimies-Somer, H.; Meurman, J.H.; Lindqvist, C. Differences between patients with or without the need for intensive care due to severe odontogenic infections. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluibau, I.C.; Jaunay, T.; Goss, A.N. Severe odontogenic infections. Aust. Dent. J. 2005, 50, S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.R.; Shanti, R.M.; Levi, M.H.; Adamo, A.K.; Kraut, R.A.; Trieger, N. Severe odontogenic infections, part 1: Prospective report. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, R.; Mirada, E.; Arias, J.; Paño, J.-R.; Burgueño, M. Severe odontogenic infections: Epidemiological, microbiological and therapeutic factors. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2011, 16, e670–e676. [Google Scholar]
- Jundt, J.S.; Gutta, R. Characteristics and cost impact of severe odontogenic infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012, 114, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T.R.; Shanti, R.M.; Hayes, C. Severe Odontogenic Infections, Part 2: Prospective Outcomes Study. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, D.; Camerer, C.; Camerer, D.-M.; Raguse, J.-D.; Menneking, H.; Hoffmeister, B.; Adolphs, N. Incidence and management of severe odontogenic infections—A retrospective analysis from 2004 to 2011. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppänen, L.; Lauhio, A.; Lindqvist, C.; Suuronen, R.; Rautemaa, R. Analysis of systemic and local odontogenic infection complications requiring hospital care. J. Infect. 2008, 57, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French Health Products Safety Agency. Prescribing antibiotics in odontology and stomatology. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 17, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, R.K.; Sharma, P.; Gaba, S.; Kaur, A.; Ghanghas, P. A review of complications of odontogenic infections. Natl. J. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 6, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E.; Lee, K.L.; Califf, R.M.; Pryor, D.B.; Rosati, R.A. Regression modelling strategies for improved prognostic prediction. Stat. Med. 1984, 3, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoumas, K.; Anterriotis, D.; Fyrgiola, M.; Lianou, V.; Triantafylou, D.; Dimopoulos, I. Epidemiological analysis of management of severe odontogenic infections before referral to the emergency department. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 47, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storoe, W.; Haug, R.H.; Lillich, T.T. The changing face of odontogenic infections. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2001, 59, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ahani, A.; Pogrel, M. A five-year retrospective study of odontogenic maxillofacial infections in a large urban public hospital. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2005, 34, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, R.; Sandhu, S.; Sahai, N.; Gupta, M.; Singh, K. Odontogenic infections: Microbiology and management. Contemp. Clin. Dent. 2014, 5, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmahan, S.; Tuopar, D.; Ameerally, P.J. The clinical relevance of microbiology specimens in head and neck space infections of odontogenic origin. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2014, 52, 629–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastenienė, R.; Pūrienė, A.; Aleksejūnienė, J.; Pečiulienė, V.; Zaleckas, L. Odontogenic Maxillofacial Infections: A Ten-Year Retrospective Analysis. Surg. Infect. 2015, 16, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, F.R.L.; Hajala, F.A.C.; Filho, F.W.V.F.; Moreira, R.W.F.; De Moraes, M. Eight-Year Retrospective Study of Odontogenic Origin Infections in a Postgraduation Program on Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009, 67, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zirk, M.; Buller, J.; Goeddertz, P.; Rothamel, D.; Dreiseidler, T.; Zöller, J.E.; Kreppel, M. Empiric systemic antibiotics for hospitalized patients with severe odontogenic infections. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppada, U.K.; Sinha, R. Outcome of Odontogenic Infections in Rural Setup: Our Experience in Management. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2020, 19, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, N.; Cloutier, L.; Khaldoun, E.; Bois, E.; Chirat, M.; Salvan, D. Criteria for admission of odontogenic infections at high risk of deep neck space infection. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2015, 132, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, P.; Almeida, E.; Moreira, P.; Fernandes, A.; Mealha, R.; Aragão, A.; Sabino, H. C-reactive protein as an indicator of sepsis. Intensiv. Care Med. 1998, 24, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Póvoa, P.; Teixeira-Pinto, A.; Carneiro, A.H. C-reactive protein, an early marker of community-acquired sepsis resolution: A multi-center prospective observational study. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, B.; Olshaker, J.S. The C-reactive protein1. J. Emerg. Med. 1999, 17, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, J.; Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Almeida, E.; Moreira, P.; Fernandes, A.; Mealha, R.; Sabino, H. Is C-reactive protein a good prognostic marker in septic patients? Intensiv. Care Med. 2009, 35, 909–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meili, M.; Kutz, A.; Briel, M.; Christ-Crain, M.; Bucher, H.C.; Mueller, B.; Schuetz, P. Infection biomarkers in primary care patients with acute respiratory tract infections-comparison of Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tung-Yiu, W.; Jehn-Shyun, H.; Ching-Hung, C.; Hung-An, C. Cervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin: A report of 11 cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2000, 58, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poeschl, P.W.; Spusta, L.; Russmueller, G.; Seemann, R.; Hirschl, A.; Poeschl, E.; Klug, C.; Ewers, R. Antibiotic susceptibility and resistance of the odontogenic microbiological spectrum and its clinical impact on severe deep space head and neck infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2010, 110, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariji, Y.; Gotoh, M.; Kimura, Y.; Naitoh, M.; Kurita, K.; Natsume, N.; Ariji, Y. Odontogenic infection pathway to the submandibular space: Imaging assessment. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2002, 31, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonetsu, K.; Izumi, M.; Nakamura, T. Deep facial infections of odontogenic origin: CT assessment of pathways of space involvement. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1998, 19, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, J.D.; Sadeghi, N.; Najam, F.; Margolis, M. Craniocervical necrotizing fasciitis of odontogenic origin with mediastinal extension. Ear Nose Throat J. 2004, 83, 579–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Aoki, T.; Kise, Y.; Watanabe, D.; Sasaki, J. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis due to odontogenic infections. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2000, 89, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matevosyan, N.R. Oral Health of Adults with Serious Mental Illnesses: A Review. Community Ment. Heal. J. 2009, 46, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, S.H.; Laugharne, J. The Impact of Lifestyle Factors on the Physical Health of People with a Mental Illness: A Brief Review. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2013, 21, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Number of Surgical Interventions = 1 N = 611 (%) | Number of Surgical Interventions > 1 N = 42 (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic outcomes | |||
| Gender male | 360 (59) | 26 (62) | 0.70 |
| Age | 36.8 ± 16.2 | 39.5 ± 15.6 | 0.30 |
| Medical history | |||
| Smoker | 349 (57) | 26 (62) | 0.54 |
| Drug abuse | 49 (8) | 5 (12) | 0.38 |
| Alcohol abuse | 67 (11) | 11 (26) | 0.003 * |
| Immunodepression | 15 (2) | 5 (12) | 0.001 * |
| Psychiatric disorder | 52 (9) | 10 (24) | 0.001 * |
| Penicillin allergy | 39 (6) | 8 (19) | 0.002 * |
| Pre-hospitalization management | |||
| Number of consultations | 1.7 +/− 0.9 | 2.3 +/− 1.5 | 0.02 * |
| Anti-inflammatory consummation | 297 (54) | 32 (78) | 0.003 * |
| Antibiotics consummation | 350 (63) | 28 (70) | 0.39 |
| Clinical symptoms at admission | |||
| Trismus | 352 (58) | 38 (90) | <0.001 * |
| No edema | 13 (2) | 0 (0) | <0.001 * |
| Facial edema | 214 (35) | 5 (12) | |
| Cervicofacial unilateral edema | 371 (61) | 32 (79) | |
| Cervical unilateral edema | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| Cervical bilateral edema | 11 (2) | 5 (12) | |
| Fever | 159 (26) | 23 (55) | <0.001 * |
| Dysphagia/odynophagia | 127 (21) | 27 (64) | <0.001 * |
| Dysphonia | 20 (3) | 8 (19) | <0.001 * |
| Dyspnea | 10 (2) | 6 (14) | <0.001 * |
| Anterior floor edema | 43 (7) | 19 (45) | <0.001 * |
| Tongue protraction limitation | 24 (4) | 6 (14) | 0.009 * |
| Oropharyngeal edema | 11 (2) | 7 (17) | <0.001 * |
| Biological samples | |||
| C-reactive protein level (mg/L) | 72.4 (±71.2) | 153.9 (±97.4) | <0.001 * |
| <50 | 224 (37) | 3 (7) | |
| 50–99 | 116 (19) | 9 (21) | |
| 100–199 | 86 (14) | 12 (29) | |
| ≥200 | 27 (4) | 10 (24) | |
| Missing values | 158 (26) | 8 (19) | |
| Surgical outcomes | |||
| Number of spaces involved | 1.2 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | <0.001 * |
| Tooth position | |||
| Quadrant 1 | 56 (9) | 0 (0) | 0.04 |
| Quadrant 2 | 69 (11) | 2 (5) | 0.30 |
| Quadrant 3 | 70 (11) | 2 (5) | 0.30 |
| Quadrant 4 | 24 (4) | 0 (0) | 0.39 |
| Quadrant 5 | 47 (8) | 5 (12) | 0.37 |
| Quadrant 6 | 360 (59) | 34 (81) | 0.005 * |
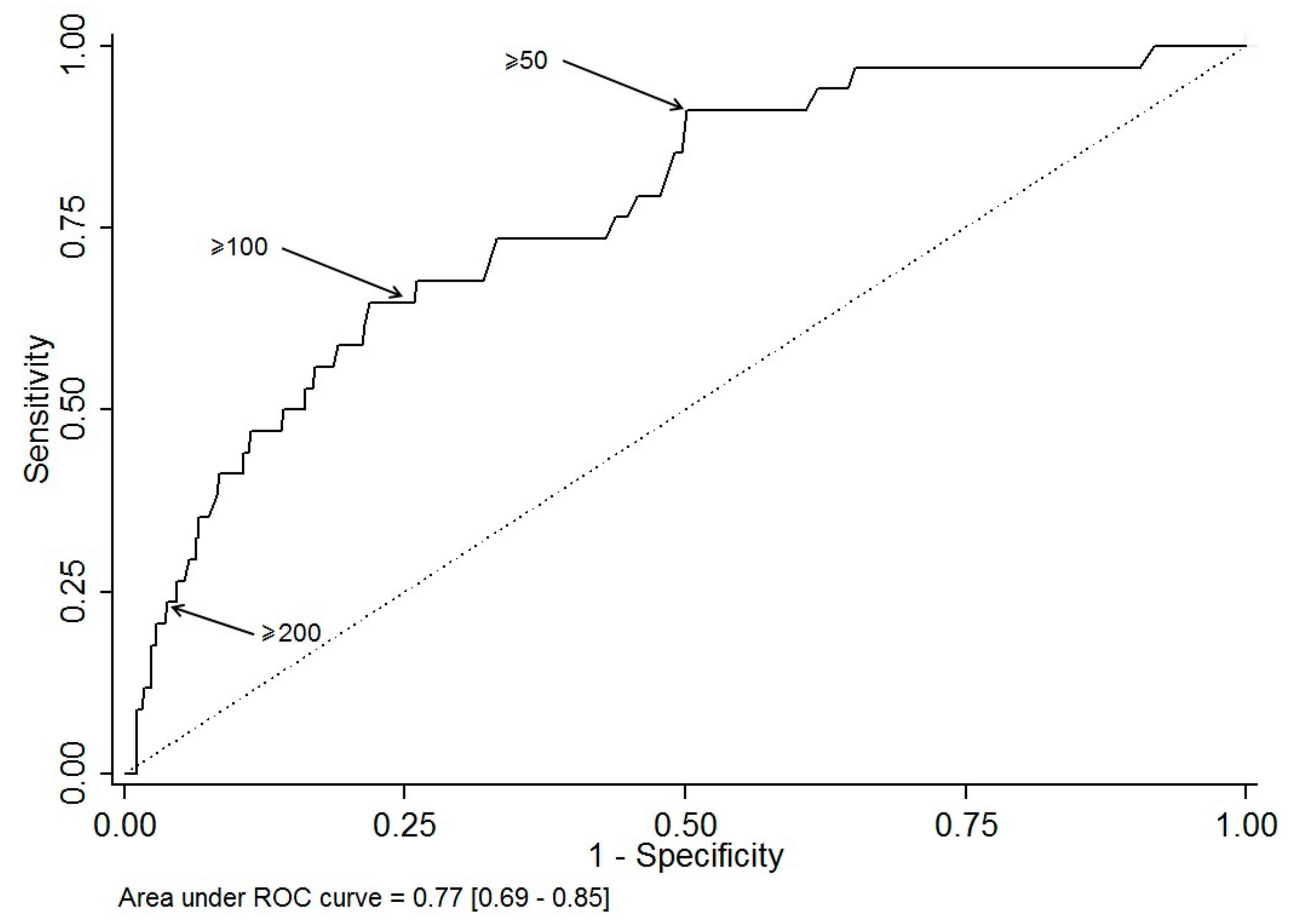
| Characteristics | Sensibility | Specificity | PPV | VPN | LR+ | LR− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP level | ||||||
| ≥50 | 91 | 49 | 12 | 99 | 1.80 | 0.18 |
| ≥100 | 65 | 75 | 16 | 97 | 2.59 | 0.47 |
| ≥200 | 29 | 94 | 27 | 95 | 4.93 | 0.75 |
| Characteristics | OR | CI 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical history | |||
| Alcohol abuse | 2.70 | 1.09–6.7 | 0.03 * |
| Immunodepression | 3.32 | 0.9–12.31 | 0.07 |
| Psychiatric disorder | 3.02 | 1.21–7.55 | 0.02 * |
| Penicillin allergy | 5.47 | 1.99–15.09 | 0.001 * |
| Pre-hospitalization management | |||
| Anti-inflammatory consummation | 2.20 | 0.97–4.99 | 0.06 |
| Tooth position | |||
| Quadrant 6 | 2.74 | 1.16–6.48 | 0.02 * |
| Biological samples C-reactive protein level (mg/L) | |||
| <50 | 0.18 | 0.05–0.72 | 0.02 * |
| 50–99 | 1 | - | |
| 100–200 | 1.55 | 0.59–4.13 | 0.38 |
| 200 | 4.12 | 1.33–12.72 | 0.01 * |
| Missing values | 0.79 | 0.27–2.34 | 0.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham Dang, N.; Delbet-Dupas, C.; Mulliez, A.; Devoize, L.; Dallel, R.; Barthélémy, I. Five Predictors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Odontogenic Infections. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238917
Pham Dang N, Delbet-Dupas C, Mulliez A, Devoize L, Dallel R, Barthélémy I. Five Predictors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Odontogenic Infections. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(23):8917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238917
Chicago/Turabian StylePham Dang, Nathalie, Candice Delbet-Dupas, Aurélien Mulliez, Laurent Devoize, Radhouane Dallel, and Isabelle Barthélémy. 2020. "Five Predictors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Odontogenic Infections" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 23: 8917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238917
APA StylePham Dang, N., Delbet-Dupas, C., Mulliez, A., Devoize, L., Dallel, R., & Barthélémy, I. (2020). Five Predictors Affecting the Prognosis of Patients with Severe Odontogenic Infections. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(23), 8917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17238917





