The Collective Leadership for Safety Culture (Co-Lead) Team Intervention to Promote Teamwork and Patient Safety
Abstract
1. Introduction
Teamwork and Collective Leadership
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Co-Lead
2.2. The Co-Lead Intervention: Overview and Module Descriptions
3. Results
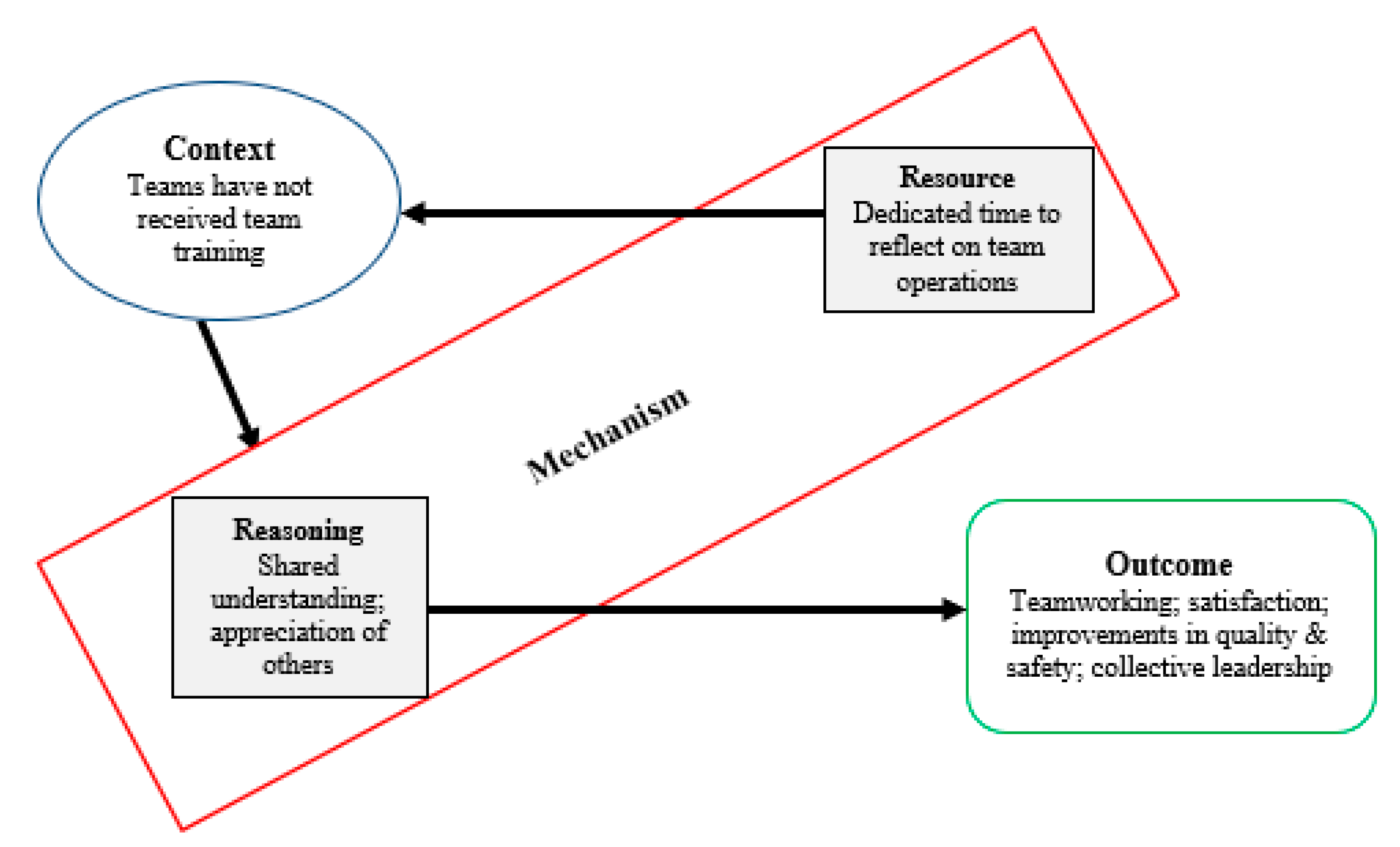
3.1. Intervention Mechanisms of Action
3.2. Realist Evaluation of Intervention
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Co-Lead Intervention Modules | Aim/Description | Resource Mechanisms Offered by Module | Reasoning Mechanisms Triggered by Module | Examples of Targeted Behaviours |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Team Values, Vision and Mission | The aim of this session is for the team to collectively establish and agree team values, team vision, and a team mission statement. These statements will guide and drive the work and goals of the team. | Enables team time and structured process to agree and make explicit a set of values, vision, and mission statements that represent the team’s goals and ways of working. |
| Collective action towards achievement of goals, e.g., monitoring, improvement efforts. |
| Team Goal Setting | The aim of this session is for the team to collectively establish the team’s goals and priorities for the coming months. These goals should align with the outputs from the previous session on creating the team’s vision and mission statements. | Opportunity to clarify and understand each other’s goals. Enabling team members to propose team goals and reach consensus on team targets, to establish a sense of ownership of team goals. |
| Collaborative goal setting. Implementation of action plan for sub-teams to work towards agreed goals and improvements. Implementation of new processes or ways of working. |
| Role Clarity | This session explores the concepts of role clarity, and the way that improved role clarity can enhance the work done by teams. Participants discuss and reflect on their perceptions and expectations of the roles of different team members. | Materials enhance learning on the importance of role clarity. Provides a structure that supports staff to reflect on their role and that of others on the team. |
| Explicitly recognising and appreciating skills of others. Collaboration across professional boundaries. |
| Collective Leadership for Safety Skills | This session focuses on collective leadership and responsibility for safety. The objective is to think about the team’s level of awareness of safety, and the safety skills that are strong in the team as well as those that need to be developed. | Materials provide evidence and learning about collective responsibility for patient care and offer the time to collectively reflect and prioritise the safety skills for improvement. |
| Adopting new roles and responsibilities in safety management. |
| Risk and Safety Management at the Team Level | The aim of this session is to create an understanding among all team members of the nature of risk and safety at the team level and how to understand if care has been safe in the past, is safe in the present, and will be safe in the future. | Materials provide learning around risk and safety and offer the time and structure to collectively focus on current safety measures and possible risks for the team. |
| Adopting new roles and responsibilities in safety management. Identifying risks and safety issues. |
| Monitoring and Communicating Safety at Team level | This module builds on the Risk and Safety Management module, to provide team members with a structured tool and overarching perspective on the ways in which they can track the team’s safety performance. | Time and opportunity for staff to collectively decide a wide range of performance and improvement measures specific to the team that would be meaningful for them to understand/improve performance. Materials provide a structure to drive improvement. |
| Adopting a role in data collection or analysis of safety metrics identified as important to the team. Providing feedback to team members on safety performance. |
| Effective Team Meetings | This module facilitates teams to collectively discuss and agree on the best structure to make the most effective use of meeting times. | Materials provide team members with tools to support effective team functioning. Time and opportunity to collectively decide how to support/improve future meetings. |
| Attendance at and contribution to team meetings. Information sharing. |
| Removing Frustrations/ Blockers | Build-up of frustrations and barriers in everyday work in healthcare can reduce team and individual efficiency and contribute to safety issues. This module helps teams identify and find possible solutions to the frustrations and barriers commonly occurring in their working practice. | Material provides structure to collectively reflect and identify problems and troubleshoot team specific operations. Provides safe space and dedicated time to discuss barriers, frustrations, blockers to team processes. |
| Collective action towards implementation or de-implementation of processes or ways of working. Problem solving as a team. |
| Building Trust | This module provides a space where team members can get to know each other better and build trust through creation of an environment where they can share concerns and provide mutual support during times of difficulty. | Providing a safe space and dedicated time to get to know team members, share ambitions and stories, identify strengths and weaknesses, and build mechanisms of support. |
| Seeking support and advice from other colleagues. Anticipating and supporting others’ needs. Learning from mistakes. |
| Structured Interdisciplinary Rounds | Structured interdisciplinary rounds (SIDRs) are a way for interdisciplinary teams to enhance their teamwork and collaboration, by strengthening communications between members around care plans for patients. | Materials provide the evidence and learning to heighten staff awareness of the benefits of inclusiveness. Provides time and opportunity for staff to collectively decide how to best implement the initiative and tailor it to their needs as a team. |
| Implementation of SIDRs. Attendance from all relevant professionals. Speaking up and providing input to collaborate towards development of patient care plans. |
| Challenging Unsafe Behaviours (CUSS) [14,31] | Staff may occasionally be concerned when they witness unconventional or unsafe practices in the workplace but may lack the structure and tools to raise the issue with colleagues. This module provides a standardised method to support interdisciplinary communication which can be used to speak about safety concerns when they arise and encourage all staff to challenge unsafe behaviour. | Group exposure and practice of graded assertiveness method for communicating safety concerns. Agreement on a standard method for raising concerns within the team to ensure team members will be heard/understood. |
| Speaking up and voicing safety concerns. Seeking input from others. Using agreed CUSS terms when communicating about safety. Effective communication between team members. |
| Communication at Safety Critical Moments (ISBAR3) [32] # | Safety-critical moments regularly arise during clinical practice, for example during staff handovers. In this module, teams become familiarised with a structured and focused tool to enhance communication of important information during such times. | Group exposure to tools that facilitate focused communication between team members to deliver information in a structured and effective way. Understanding of the importance of clear, standardised communication |
| Use of ISBAR communication tool in daily practice. |
| Talking about Safety (PlayDecide serious game) [33] | In this module, team members engage in structured discussions on patient safety and error reporting, using a "serious game" learning tool that has been co-designed with input from health professionals, patients, and researchers. The game creates a safe space to encourage deep discussion about patient safety to develop a shared understanding of the importance of error reporting in strengthening patient safety culture. | Offers staff a safe structure to learn through other people’s real experiences and acknowledge challenges inherent in safety management and reporting. |
| Reporting of safety events. Team reflexivity and learning from safety events and near misses (time for reflection and learning). |
| Safety Pause Huddles [34] | This module familiarises team members with the Safety Pause, which is designed to facilitate the sharing of critical information among teams to maximise patient safety following clinical handovers, with the goal of adopting it for use in everyday practice. | Offers the evidence and learning to support the Safety Pause Huddle. Provides a tool to identify and highlight safety concerns to the team. Time and a structure to collectively decide how to use the tool as a team. Demonstrates importance of regular, focused communication |
| Implementation of huddles into practice (e.g., during clinical handover). Improved MDT communication. |
| High Reliability at the Team Level | This module focuses on building high reliability among teams, to ensure delivery of high-quality care in a consistent manner, and with minimal errors, despite healthcare’s complex and challenging work environment. | Provides staff with evidence and learning to achieve higher collective safety awareness through reflecting individually and collectively on the reliability of the team, the factors that impact this reliability of the team and how to improve. |
| Collaboration to ensure reliability in care processes. Identify opportunities for improvement. Adapting to challenges. |
| Developing a positive work environment | This module focuses on engaging the whole team to find solutions that will help foster a positive work environment which will in turn provide the support necessary to reduce stress, avoid burnout, and improve job satisfaction among staff members. | Provides affirmation of the importance of caring for self and team and a structure that enables the team time to reflect and collectively develop improvements. |
| Implementation of initiatives to develop positivity and improve experience for staff and patients. |
| Emotional Support in Teams | This module focuses on the ways in which team members can create an environment of support during challenging times, and introduces a tool which can be used by line managers, colleagues, and peers to hold meaningful and supportive conversations with staff after an adverse event has occurred. | Provides practical guidance to support colleagues after a traumatic event, time to practice using the model and an opportunity to collectively reflect and agree on how to best support each other. |
| Showing support and concern for others. Role blurring and task sharing behaviours. |
| Enhancing Person-Centred Care | This module focuses on developing awareness among health professionals of the importance of featuring the patient as the focal point in the care that they provide and working collectively to build a person-centred environment in their workplace. | Emphasising humanity in care and offers teams the time to reflect on their own care, providing a structure that encourages team members to incorporate person-centred thinking into their daily practice |
| Implementation of initiatives to develop positivity and improve experience for staff and patients. |
| Sustaining Improvements | This module focuses on the next steps after teams have taken part in the Co-Lead intervention, and wish to carry forward any useful tools, information, and lessons learned. | Offers team time and structure to reflect on achievements, progress, and enables the team to collectively plan for and ensure sustainability of changes. |
| Putting plan or processes in place to support the team to sustain improvements. Successful maintenance of new ways of working. |
References
- Institute of Medicine. Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; p. 360. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, R. Report of the Mid Staffordshire NHS Foundation Trust public Inquiry: Executive Summary; The Stationery Office: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- West, M.; Armit, K.; Loewenthal, L.; Eckert, R.; West, T.; Lee, A. Leadership and Leadership Development in Healthcare: The Evidence Base; The Kings Fund: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Day, D.V.; Fleenor, J.W.; Atwater, L.E.; Sturm, R.E.; McKee, R.A. Advances in leader and leadership development: A review of 25 years of research and theory. Leadersh. Q. 2014, 25, 63–82. [Google Scholar]
- West, M.; Eckert, R.; Steward, K.; Pasmore, B. Developing Collective Leadership for Health Care; The King’s Fund: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yammarino, F.J.; Salas, E.; Serban, A.; Shirreffs, K.; Shuffler, M.L. Collectivistic leadership approaches: Putting the “we” in leadership science and practice. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2012, 5, 382–402. [Google Scholar]
- D’Innocenzo, L.; Mathieu, J.E.; Kukenberger, M.R. A meta-analysis of different forms of shared leadership–team performance relations. J. Manag. 2016, 42, 1964–1991. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Cormican, K.; Chen, G. A meta-analysis of shared leadership: Antecedents, consequences, and moderators. J. Leadersh. Organ. Stud. 2020, 27, 49–64. [Google Scholar]
- De Brún, A.; O’Donovan, R.; McAuliffe, E. Interventions to develop collectivistic approaches to leadership in healthcare settings: A systematic review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.P.; Day, R.; Salas, E. Teamwork as an Essential Component of High-Reliability Organizations. Health Serv. Res. 2006, 41, 1576–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.; Diaz, G.D.; Salas, E.; Le, H.; Burke, C.S.; Lyons, R. Does team building work? Small Group Res. 2009, 40, 181–222. [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, M.A.; Diaz, G.D.; Dietz, A.S.; Benishek, L.E.; Thompson, D.; Pronovost, P.J. Teamwork in healthcare: Key discoveries enabling safer, high-quality care. Am. Psychol. 2018, 73, 433–450. [Google Scholar]
- Salas, E.; Diaz, G.D.; Weaver, S.J.; King, H. Does team training work? Principles for health care. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2008, 15, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar]
- King, H.B.; Battles, J.; Baker, D.P.; Alonso, A.; Salas, E.; Webster, J. TeamSTEPPS™: Team strategies and tools to enhance performance and patient safety. In Advances in Patient Safety: New Directions and Alternative Approaches (Performance and Tools); Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2008; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, B.; Rusin, L.; Kiesewetter, J.; Zottmann, J.M.; Fischer, M.R.; Prückner, S. Crew resource management training in healthcare: A systematic review of intervention design, training conditions and evaluation. BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e025247. [Google Scholar]
- Maynard, M.T.; Marshall, D.; Dean, M.D. Crew resource management and teamwork training in health care: A review of the literature and recommendations for how to leverage such interventions to enhance patient safety. In Annual Review of Health Care Management: Strategy and Policy Perspectives on Reforming Health Systems; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, C.W.; Meterko, M.; Rosen, A.K.; Zhao, S.; Shokeen, P.; Singer, S. Relationship of Hospital Organizational Culture to Patient Safety Climate in the Veterans Health Administration. Med. Care Res. Rev. 2009, 66, 320–338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Brún, A.; McAuliffe, E. Identifying the context, mechanisms and outcomes underlying collective leadership in teams: Building a realist programme theory. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Lega, F.; Prenestini, A.; Rosso, M. Leadership research in healthcare: A realist review. Health Serv. Manag. Res. 2017, 30, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Pawson, R.; Tilley, N. Realistic Evaluation; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.; De Brún, A.; Beirne, D.; Conway, C.; Cunningham, U.; English, A. Using Co-Design to Develop a Collective Leadership Intervention for Healthcare Teams to Improve Safety Culture. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1182. [Google Scholar]
- De Brun, A.; Rogers, L.; O’Shea, M.; McAuliffe, E. Understanding the impact of a collective leadership intervention on team working and safety culture in healthcare teams: A realist evaluation protocol. HRB Open Res. 2019, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Brún, A.; McAuliffe, E. “The hierarchical days aren’t going to work any longer”: A realist evaluation of a collective leadership intervention (Co-Lead) in healthcare teams. 2020. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Dalkin, S.M.; Greenhalgh, J.; Jones, D.; Cunningham, B.; Lhussier, M. What’s in a mechanism? Development of a key concept in realist evaluation. Implement. Sci. 2015, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, D.A. The Reflective Practitioner: How Professionals Think in Action; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, C.L.; Conger, J.A. Shared Leadership: Reframing the Hows and Whys of Leadership; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hoch, J.E. Shared leadership and innovation: The role of vertical leadership and employee integrity. J. Bus. Psychol. 2013, 28, 159–174. [Google Scholar]
- Carson, J.B.; Tesluk, P.E.; Marrone, J.A. Shared leadership in teams: An investigation of antecedent conditions and performance. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 1217–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Rycroft-Malone, J.; Burton, C.R.; Wilkinson, J.; Harvey, G.; McCormack, B.; Baker, R. Collecwtive action for implementation: A realist evaluation of organisational collaboration in healthcare. Implement. Sci. 2015, 11, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Venus, M.; Mao, C.; Lanaj, K.; Johnson, R.E. Collectivistic leadership requires a collective identity. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2012, 5, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- TeamSTEPPS 2.0 Curriculum [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. 2019. Available online: https://www.ahrq.gov/teamstepps/instructor/index.html (accessed on 25 July 2020).
- Powell, S.M.; Hill, R.K. My copilot is a nurse—Using crew resource management in the OR. AORN J. 2006, 83, 178–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.; Shé, É.N.; De Brún, A.; Korpos, C.; Hamza, M.; Burke, E. The co-design, implementation and evaluation of a serious board game ‘PlayDecide patient safety’ to educate junior doctors about patient safety and the importance of reporting safety concerns. BMC Med Educ. 2019, 19, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Health Service Executive (HSE) Quality and Patient Safety. The Safety Pause Information Sheet: Health Service Executive. Available online: https://www.lenus.ie/handle/10147/293915 (accessed on 2 April 2020).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Brún, A.; Anjara, S.; Cunningham, U.; Khurshid, Z.; Macdonald, S.; O’Donovan, R.; Rogers, L.; McAuliffe, E. The Collective Leadership for Safety Culture (Co-Lead) Team Intervention to Promote Teamwork and Patient Safety. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228673
De Brún A, Anjara S, Cunningham U, Khurshid Z, Macdonald S, O’Donovan R, Rogers L, McAuliffe E. The Collective Leadership for Safety Culture (Co-Lead) Team Intervention to Promote Teamwork and Patient Safety. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(22):8673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228673
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Brún, Aoife, Sabrina Anjara, Una Cunningham, Zuneera Khurshid, Steve Macdonald, Róisín O’Donovan, Lisa Rogers, and Eilish McAuliffe. 2020. "The Collective Leadership for Safety Culture (Co-Lead) Team Intervention to Promote Teamwork and Patient Safety" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 22: 8673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228673
APA StyleDe Brún, A., Anjara, S., Cunningham, U., Khurshid, Z., Macdonald, S., O’Donovan, R., Rogers, L., & McAuliffe, E. (2020). The Collective Leadership for Safety Culture (Co-Lead) Team Intervention to Promote Teamwork and Patient Safety. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(22), 8673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228673






