Assessment of Relative Asthma Risk in Populations Living near Incineration Facilities in Seoul, Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
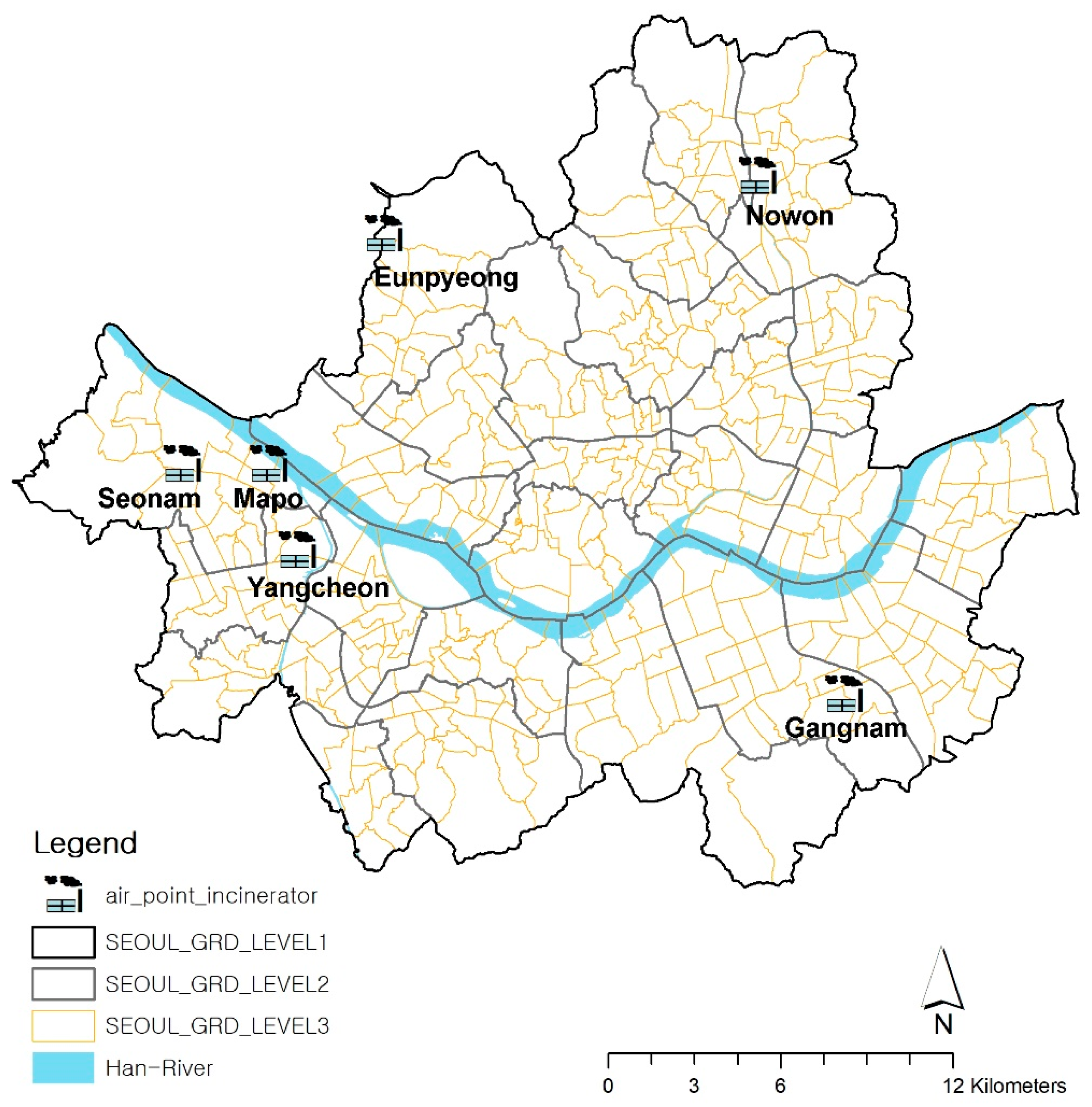
2.1. Study Area and Incinerators
2.2. Data
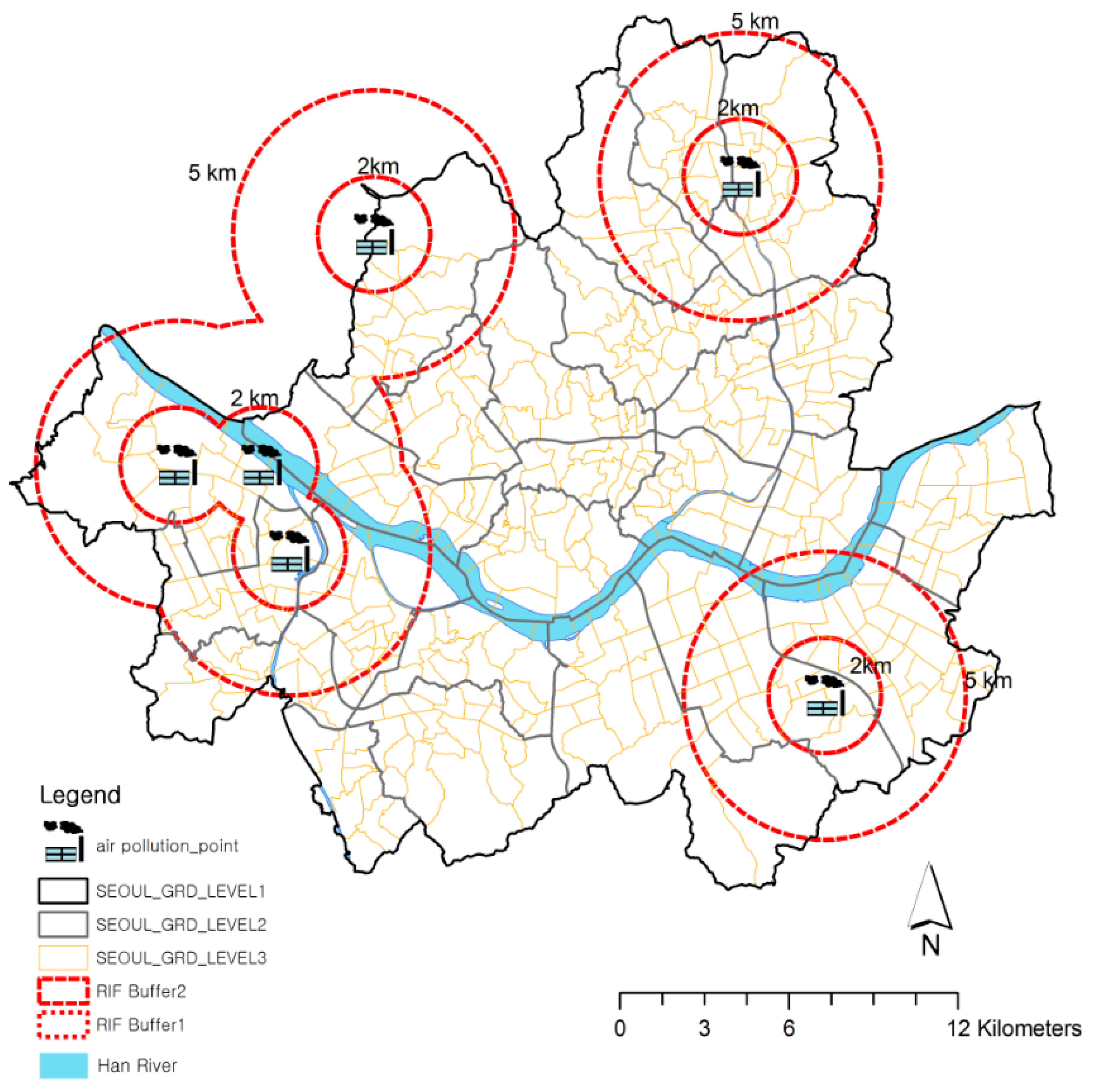
2.3. Disease Mapping and Risk Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Area
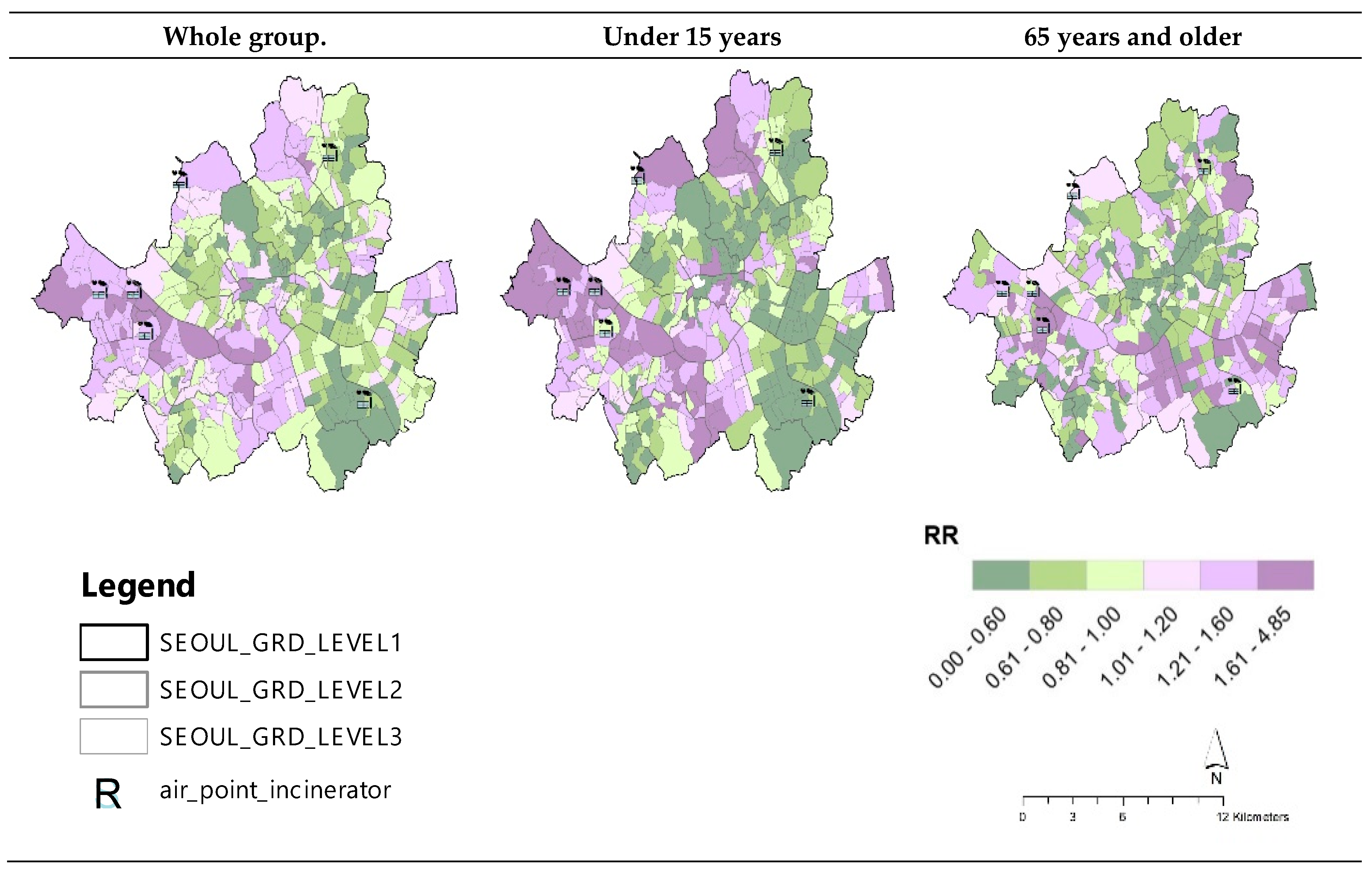
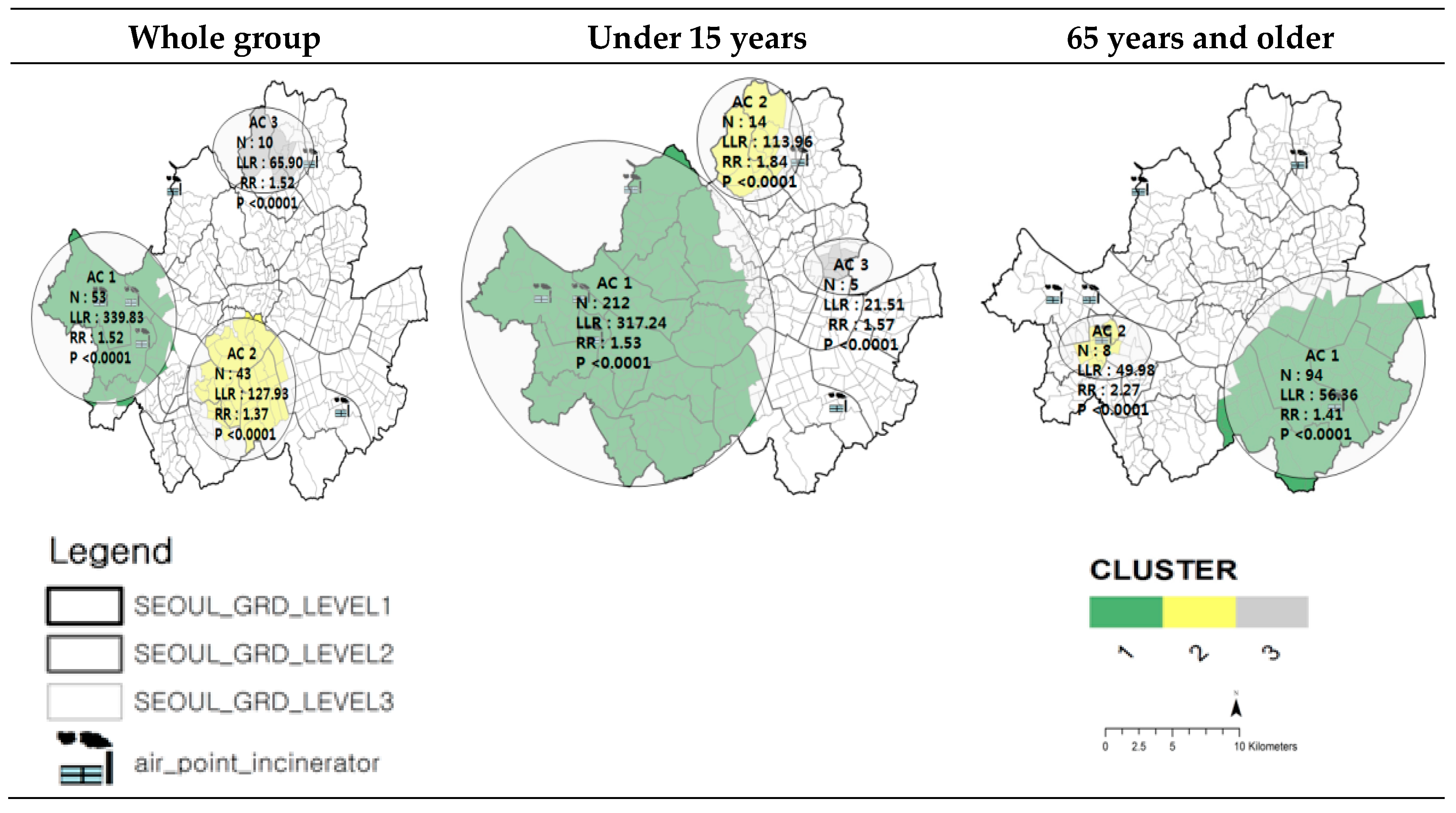
3.2. Asthma-Related Hospitalization Mapping and Cluster Analysis by Age Group in Seoul
3.3. Risk Analysis of Asthma-Related Hospitalization
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crowley, D.; Staines, A.; Collins, C.; Bracken, J.; Bruen, M.; Fry, J.; Hrymak, V.; Malone, D.; Magette, B.; Ryan, M. Health and Environmental Effects of Landfilling and Incineration of Waste-A Literature Review. Reports 2003, Paper 3. Available online: http://arrow.dit.ie/schfsehrep/3 (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Vilavert, L.; Nadal, M.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Long-term monitoring of dioxins and furans near a municipal solid waste incinerator: Human health risks. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-W.; Shy, C.M. Health effects of waste incineration: A review of epidemiologic studies. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2001, 51, 1100–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashworth, D.C.; Elliott, P.; Toledano, M.B. Waste incineration and adverse birth and neonatal outcomes: A systematic review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forastiere, F.; Badaloni, C.; de Hoogh, K.; von Kraus, M.K.; Martuzzi, M.; Mitis, F.; Palkovicova, L.; Porta, D.; Preiss, P.; Ranzi, A. Health impact assessment of waste management facilities in three European countries. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordioli, M.; Ranzi, A.; De Leo, G.A.; Lauriola, P. A review of exposure assessment methods in epidemiological studies on incinerators. J. Environ. Public Health 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, P.; Shaddick, G.; Kleinschmidt, I.; Jolley, D.; Walls, P.; Beresford, J.; Grundy, C. Cancer incidence near municipal solid waste incinerators in Great Britain. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 73, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, D.; Milani, S.; Lazzarino, A.I.; Perucci, C.A.; Forastiere, F. Systematic review of epidemiological studies on health effects associated with management of solid waste. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, T.; Stanojevic, S.; Moores, G.; Gershon, A.S.; Bateman, E.D.; Cruz, A.A.; Boulet, L.P. Global asthma prevalence in adults: Findings from the cross-sectional world health survey. BMC Public Health 2012, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Health Insurance Corporation; Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. National Health Insurance Statistical Yearbook; National Health Insurance Corporation: Seoul, Korea, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.-H.; Park, H.-W.; Rosenberg, D.M. The current status of asthma in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2006, 21, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R.J.; Staimer, N.; Gillen, D.; Tjoa, T.; Sioutas, C.; Fung, K.; George, S.C.; Kleinman, M.T. Personal and ambient air pollution is associated with increased exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma. Environ. Health Perspec. 2006, 114, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aylin, P.; Maheswaran, R.; Wakefield, J.; Cockings, S.; Jarup, L.; Arnold, R.; Wheeler, G.; Elliott, P. A national facility for small area disease mapping and rapid initial assessment of apparent disease clusters around a point source: The UK Small Area Health Statistics Unit. J. Public Health Med. 1999, 21, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, L.; Hodgson, S.; Abellan, J.J.; LeFevre, S.; Jarup, L. Evaluation of spatial relationships between health and the environment: The rapid inquiry facility. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1306–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, P.; Wartenberg, D. Spatial epidemiology: Current approaches and future challenges. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 112, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulldorff, M. A spatial scan statistic. Commun. Stat. Theory. 1997, 26, 1481–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, C. A Study on Range of Environmental Impact Assessment for Cumulative Effect Assessment—A Review on Living Environment Sector; Korea Environment Institute: Sejong, Korea, 2006; pp. 61–62. [Google Scholar]
- Piel, F.B.; Parkes, B.; Hambly, P.; Roca-Barcelo, A.; McCallion, M.; Leonardi, G.; Strosnider, H.; Yip, F.; Elliott, P.; Hansell, A.L. Sofeware application profile: The Rapid Inquiry Facility 4.0: An open access tool for environmental public health tracking. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, i38–i48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Lee, S.; Choo, J.; Shin, J.; Lim, J.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Chang, M.; Huh, C.; Kang, D. Development of composite deprivation index for Korea: The correlation with standardized mortality ratio. J. Peve Med. Public Health 2009, 42, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Umezaki, M.; Nakamura, K.; Takano, T. Variations in societal characteristics of spatial disease clusters: Examples of colon, lung and breast cancer in Japan. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2005, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.C.; Kanarek, N.; Fox, M.G.; Guseynova, A.; Crow, S.; Piantadosi, S. Spatial analyses identify the geographic source of patients at a National Cancer Institute Comprehensive Cancer Center. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, Y.S. Practical guideline of asthma management-Korean guideline for Asthma 2015-. Korean J. Med. 2016, 90, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Viel, J.-F.; Clément, M.-C.; Hägi, M.; Grandjean, S.; Challier, B.; Danzon, A. Dioxin emissions from a municipal solid waste incinerator and risk of invasive breast cancer: A population-based case-control study with GIS-derived exposure. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2008, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, M.; Pirani, M.; Rashid, I.; Caranci, N.; Cirilli, C. Cancer incidence in people with residential exposure to a municipal waste incinerator: An ecological study in Modena (Italy), 1991–2005. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 1362–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazucha, M.J.; Rhodes, V.; Boehlecke, B.A.; Southwick, K.; Degnan, D.; Shy, C.M. Characterization of spirometric function in residents of three comparison communities and of three communities located near waste incinerators in North Carolina. Arch. Environ. Health 2002, 57, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-T.; Shy, C.M. Respiratory function as measured by peak expiratory flow rate and PM10: Six communities study. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1998, 9, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gray, E.; Peat, J.; Mellis, C.; Harrington, J.; Woolcock, A. Asthma severity and morbidity in a population sample of Sydney school children: Part I–Prevalence and effect of air pollutants in coastal regions. Aust. N. Z. J. Med. 1994, 24, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranzi, A.; Fano, V.; Erspamer, L.; Lauriola, P.; Perucci, C.A.; Forastiere, F. Mortality and morbidity among people living close to incinerators: A cohort study based on dispersion modeling for exposure assessment. Environ. Health 2011, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyake, Y.; Yura, A.; Misaki, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Usui, T.; Iki, M.; Shimizu, T. Relationship between distance of schools from the nearest municipal waste incineration plant and child health in Japan. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 20, 1023–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holowaty, E.J.; Norwood, T.A.; Wanigaratne, S.; Abellan, J.J.; Beale, L. Feasibility and utility of mapping disease risk at the neighborhood level within a Canadian public health unit: An ecological study. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2010, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesaroni, G.; Farchi, S.; Davoli, M.; Forastiere, F.; Perucci, C.A. Individual and area-based indicators of socioeconomic status and childhood asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 22, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Percentiles | Mean | Std. Deviation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 25 | Median | 75 | Max | |||
| Population number (2009–2011, average) | |||||||
| Whole group | 1218 | 18,500 | 23,700 | 30,500 | 51,631 | 24,200 | 8882 |
| Children group (under 15 years) | 56 | 1170 | 1639 | 2147 | 4572 | 1693 | 785 |
| Senior group (65 years and older) | 141 | 1750 | 2270 | 2812 | 5240 | 2345 | 859 |
| Asthma-related admissions (2009–2011, accumulated) | |||||||
| Whole group | 2 | 37 | 56 | 81.50 | 211 | 60.85 | 34.00 |
| Children group (under 15 years) | 1 | 17 | 28 | 47 | 144 | 33.84 | 22.54 |
| Senior group (65 years and older) | 1 | 10 | 13 | 17 | 19 | 13.95 | 6.88 |
| Age/Gender | ISRR | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed Value | Expected Value | ISRR (95% Confidence Interval) | ||
| Whole age group | Male | 12,969 | 13,093.51 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) |
| Female | 12,649 | 12,803.44 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) | |
| Total | 25,618 | 25,896.96 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) | |
| Children group (under 15 years) | Male | 8108 | 8213.42 | 0.99 (0.97–1.01) |
| Female | 5977 | 6055.49 | 0.99 (0.96–1.01) | |
| Total | 14,085 | 14,268.91 | 0.99 (0.97–1.00) | |
| Senior group (65 years and older) | Male | 2289 | 2305.73 | 0.99 (0.95–1.03) |
| Female | 3044 | 3113.83 | 0.98 (0.94–1.01) | |
| Total | 5333 | 5419.55 | 0.98 (0.96–1.01) | |
| Age/Gender | 0~2 km from the Incineration Facility | 2~5 km from the Incineration Facility | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Expected | ISRR (95% Confidence Interval) | Observed | Expected | ISRR (95% Confidence Interval) | |
| Whole group | ||||||
| Male | 2051 | 1806.97 | 1.14 (1.09–1.19) | 4712 | 4640.94 | 1.02 (0.88–1.04) |
| Female | 1979 | 1753.64 | 1.13 (1.08–1.18) | 4425 | 4482.29 | 0.99 (0.96–1.02) |
| Total | 4030 | 3560.61 | 1.13 (1.10–1.17) | 9137 | 9123.22 | 1.00 (0.98–1.02) |
| Under 15 years | ||||||
| Male | 1350 | 1217.02 | 1.11 (1.05–1.17) | 2974 | 2955.28 | 1.01 (0.97–1.04) |
| Female | 1014 | 884.95 | 1.15 (1.08–1.22) | 2121 | 2176.3 | 0.97 (0.93–1.02) |
| Total | 2364 | 2101.96 | 1.12 (1.08–1.17) | 5095 | 5131.58 | 0.99 (0.97–1.02) |
| 65 years and older | ||||||
| Male | 315 | 255.33 | 1.23 (1.10–1.38) | 820 | 799.41 | 1.03 (0.96–1.10) |
| Female | 441 | 383.7 | 1.15 (1.05–1.26) | 1058 | 1048.35 | 1.10 (0.95–1.07) |
| Total | 756 | 639.02 | 1.18 (1.10–1.27) | 1878 | 1847.76 | 1.02 (0.97–1.06) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, H.-J.; Kang, J.E.; Lim, Y.-R. Assessment of Relative Asthma Risk in Populations Living near Incineration Facilities in Seoul, Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207448
Bae H-J, Kang JE, Lim Y-R. Assessment of Relative Asthma Risk in Populations Living near Incineration Facilities in Seoul, Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(20):7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207448
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Hyun-Joo, Jung Eun Kang, and Yu-Ra Lim. 2020. "Assessment of Relative Asthma Risk in Populations Living near Incineration Facilities in Seoul, Korea" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 20: 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207448
APA StyleBae, H.-J., Kang, J. E., & Lim, Y.-R. (2020). Assessment of Relative Asthma Risk in Populations Living near Incineration Facilities in Seoul, Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(20), 7448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17207448




