Associations Between School Characteristics and Classroom Radon Concentrations in Utah’s Public Schools: A Project Completed by University Environmental Health Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
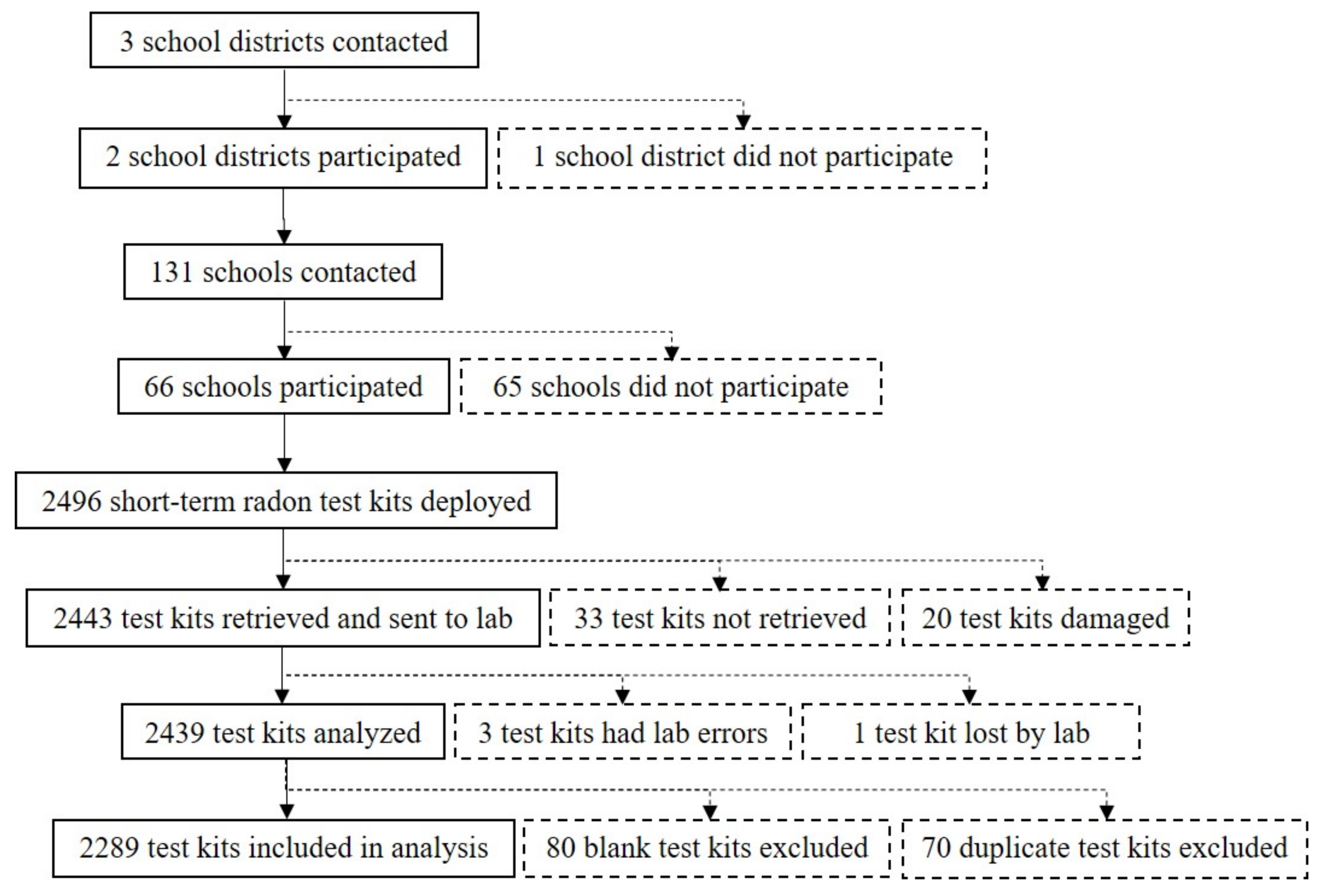
2.1. Study Design and Population
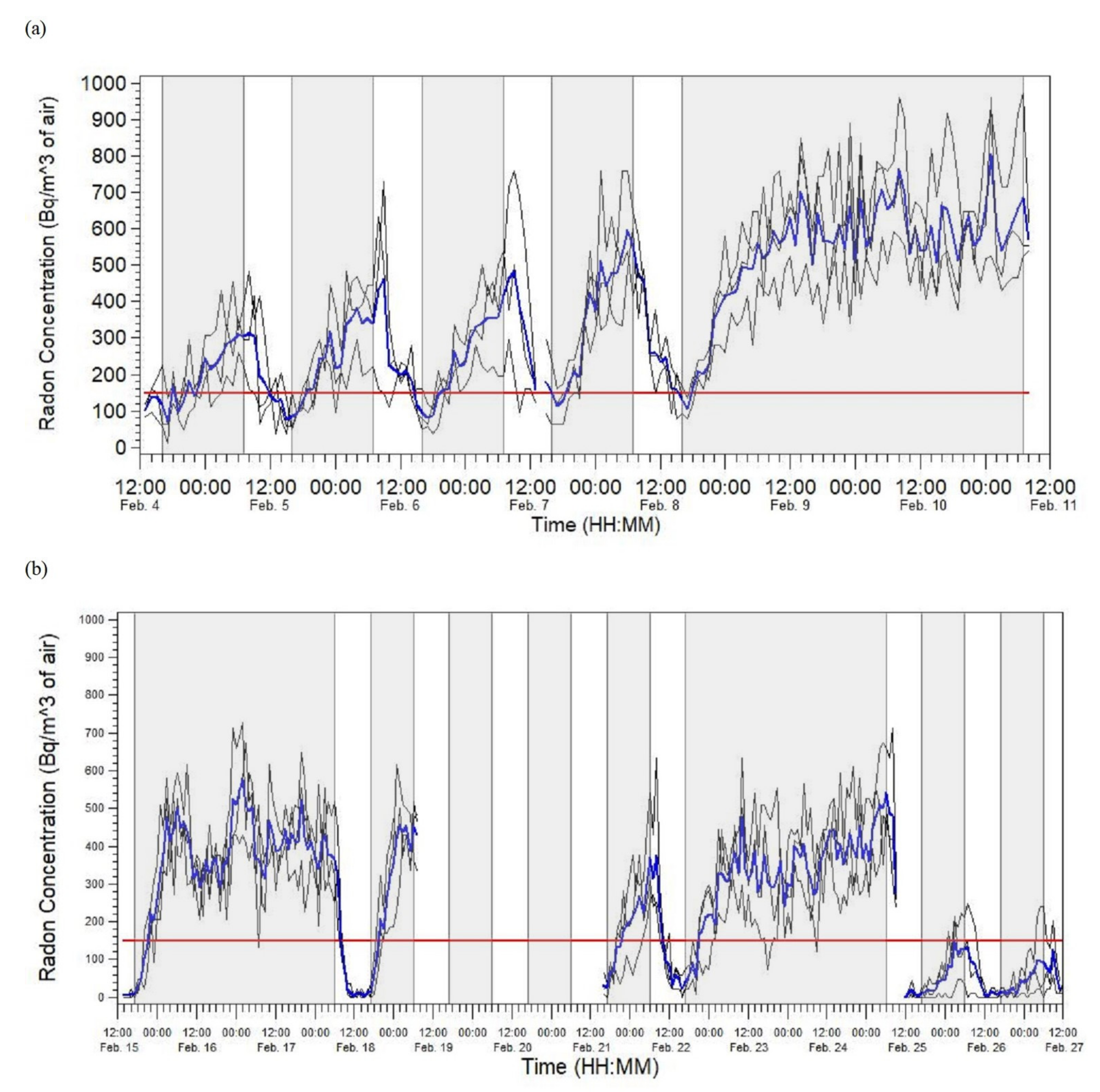
2.2. Exposure Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Radon in the Home. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/radiation/brochure/profile_radon.htm (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Basic Radon Facts; EPA 402/F-12/005; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Indoor Air Quality: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2016-08/documents/july_2016_radon_factsheet.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Toxicological Profile for Radon; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp145.pdf (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current Cigarette Smoking Among Adults in the United States. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/fact_sheets/adult_data/cig_smoking/ (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Utah Cancer Registry. Utah Cancer Registry Cancer Statistics. Available online: https://uofuhealth.utah.edu/utah-cancer-registry/cancer-statistics.php (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Radon Measurements in Schools; EPA402R92014; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air and Radiation: Washington, DC, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, J.Y.; Fowler, B.; Ding, Q.; Kirchhoff, A.C.; Pappas, L.; Boucher, K.; Akerley, W.; Wu, Y.; Kaphingst, K.; Harding, G.; et al. A statewide investigation of geographic lung cancer incidence patterns and radon exposure in a low-smoking population. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utah Department of Environmental Quality. Radon Program Homepage. Available online: https://deq.utah.gov/waste-management-and-radiation-control/radon/radon-program (accessed on 14 July 2020).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Technical Support. Document for the 1992 Citizen’s Guide to Radon; EPA 400-R-92-011; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air and Radiation: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Indoor Radon and Radon Decay Product Measurement Device Protocols; EPA 402-R-92-004; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Air and Radiation: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- DrHomeAir. DrHomeAir Homepage. Available online: https://www.doctorhomeair.com/ (accessed on 30 May 2020).
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. What is EPA’s Action Level for Radon and What Does it Mean? Available online: https://www.epa.gov/radon/what-epas-action-level-radon-and-what-does-it-mean (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Jin, Y.; Hein, M.J.; Deddens, J.A.; Hines, C.J. Analysis of lognormally distributed exposure data with repeated measures and values below the limit of detection using SAS. Ann. Occup. Hyg. 2011, 55, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W. Akaike’s information criterion in generalized estimating equations. Biometrics 2001, 57, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.J.; Cole, S.R.; Westreich, D.J.; Greenland, S.; Napravnik, S.; Eron, J.J., Jr. Splines for trend analysis and continuous confounder control. Epidemiology 2011, 22, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, S. Introduction to regression models. In Modern Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Rothman, K.J., Greenland, S., Lash, T.L., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008; pp. 381–417. [Google Scholar]
- Levesque, B.; Gauvin, D.; McGregor, R.G.; Martel, R.; Gingras, S.; Dontigny, A.; Walker, W.B.; Lajoie, P.; Letourneau, E. Radon in residences: Influences of geological and housing characteristics. Health Phys. 1997, 72, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.J.; Field, R.W. Effect of housing factors and surficial uranium on the spatial prediction of residential radon in Iowa. Environmetrics 2007, 18, 481–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovsky, M.; Vasilyev, A.; Onishchenko, A.; Yarmoshenko, I. Review of indoor radon concentrations in schools and kindergartens. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2018, 181, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J. Radon-hazard Potential of the Central Sevier Valley, Sevier County, Utah; Utah Department of Natural Resources, Utah Geological Survey, Special Study 89: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1996. Available online: https://ugspub.nr.utah.gov/publications/special_studies/ss-89.pdf (accessed on 24 June 2020).
- Bossew, P.; Zunic, Z.S.; Stojanovska, Z.; Tollefsen, T.; Carpentieri, C.; Veselinovic, N.; Komatina, S.; Vaupotic, J.; Simovic, R.D.; Antignani, S.; et al. Geographical distribution of the annual mean radon concentrations in primary schools of Southern Serbia—Application of geostatistical methods. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 127, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunic, Z.S.; Bossew, P.; Bochicchio, F.; Veselinovic, N.; Carpentieri, C.; Venoso, G.; Antignani, S.; Simovic, R.; Curguz, Z.; Udovicic, V.; et al. The relation between radon in schools and in dwellings: A case study in a rural region of Southern Serbia. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 167, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitto, M. Radon testing in schools in New York State: A 20-year summary. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 137, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, S.; Dent, A.; Bryant, J.; Tencza, B.; Adams, E.; Dutton, N.D. Are schools safe from indoor radon? J. Environ. Health 2015, 77, 38–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bochicchio, F.; Zunic, Z.S.; Carpentieri, C.; Antignani, S.; Venoso, G.; Carelli, V.; Cordedda, C.; Veselinovic, N.; Tollefsen, T.; Bossew, P. Radon in indoor air of primary schools: A systematic survey to evaluate factors affecting radon concentration levels and their variability. Indoor Air 2014, 24, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madureira, J.; Paciencia, I.; Rufo, J.; Moreira, A.; de Oliveira Fernandes, E.; Pereira, A. Radon in indoor air of primary schools: Determinant factors, their variability and effective dose. Environ. Geochem. Health 2016, 38, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, K.; Stojanovska, Z.; Tsenova, M.; Badulin, V.; Kunovska, B. Measurement of indoor radon concentration in kindergartens in Sofia, Bulgaria. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 162, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishchenko, A.; Malinovsky, G.; Vasilyev, A.; Zhukovsky, M. Radon measurements in kindergartens in Ural Region (Russia). Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2017, 177, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubal, E.A.C.; Sheldon, L.S.; Burke, J.M.; McCurdy, T.R.; Berry, M.R.; Rigas, M.L.; Zartarian, V.G.; Freeman, N.C. Children’s exposure assessment: A review of factors influencing children’s exposure, and the data available to characterize and assess that exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalt, E.W.; Curl, C.L.; Allen, R.W.; Cohen, M.; Adar, S.D.; Stukovsky, K.H.; Avol, E.; Castro-Diehl, C.; Nunn, C.; Mancera-Cuevas, K.; et al. Time-location patterns of a diverse population of older adults: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Air Pollution (MESA Air). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2016, 26, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.; Terry, P.D.; Liu, X.; Harris, T.; Vowell, D.; Yard, B.; Chen, J. Radon in schools: A brief review of state laws and regulations in the United States. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Phillips, V.L. Primary Sources: 2012. America’s Teachers on the Teaching Profession; Scholastic and Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.scholastic.com/content/dam/corp-home/aboutscholastic/PrimarySources-2012-SecondEdition-Americas-Teachers-on-the-Teaching-Profession.pdf (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Leovic, K.W. Summary of EPA’s Radon-Reduction Research in Schools During 1989–90; EPA/600/S890/072; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Air and Energy Engineering Research Laboratory: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Saum, D.; Craig, A.B.; Leovic, K. Radon mitigation in schools. Case studies for radon mitigation systems installed by EPA in four Maryland schools are presented. ASHRAE J. 1990, 32, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Synnott, H.; Colgan, P.A.; Hanley, O.; Fenton, D. The effectiveness of radon remediation in Irish schools. Health Phys. 2007, 92, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denman, A.R.; Phillips, P.S. The cost-effectiveness of radon mitigation in schools in Northamptonshire. J. Radiol. Prot. 1998, 18, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucchini, R.G.; McDiarmid, M.; Van der Laan, G.; Rosen, M.; Placidi, D.; Radon, K.; Ruchirawat, M.; Kurtz, L.; Landrigan, P. Education and training: Key factors in global occupational and environmental health. Ann. Glob. Health 2018, 84, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, R.; Lange, S. Adjusting for multiple testing--when and how? J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2001, 54, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Radon and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health (accessed on 9 August 2020).
- Utah Geological Survey. Radon Gas Hazards. Available online: https://geology.utah.gov/hazards/problem-soils/radon/ (accessed on 9 August 2020).
| School Characteristic | N | % | Missing | Mean | SD | Min | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | 0 | |||||||||
| Elementary | 46 | 70 | ||||||||
| Junior high or middle | 12 | 18 | ||||||||
| High | 8 | 12 | ||||||||
| Age, years | 2 | 29.09 | 21.66 | 3.00 | 13.00 | 23.00 | 38.75 | 120.00 | ||
| Year HVAC system installed | 4 | 1999 | 14.22 | 1954 | 1994 | 2002 | 2009 | 2017 | ||
| Last year HVAC system maintained | 4 | |||||||||
| 2012–2018 | 38 | 61 | ||||||||
| 2019 | 24 | 39 | ||||||||
| Type of HVAC system | 3 | |||||||||
| Multizone system | 45 | 71 | ||||||||
| Single-zone or hydronic system | 6 | 10 | ||||||||
| Variable air volume system | 6 | 10 | ||||||||
| Combination of systems | 6 | 10 | ||||||||
| Time HVAC system turned on/started each day, HH:MM:SS | 3 | 06:10:00 | 1:18:15 | 00:00:00 | 06:00:00 | 06:15:00 | 07:00:00 | 07:45:00 | ||
| Time HVAC system turned off/stopped each day, HH:MM:SS | 3 | 16:42:01 | 1:46:26 | 15:00:00 | 16:00:00 | 16:00:00 | 16:30:00 | 23:59:59 | ||
| Total number of hours HVAC system on/running each day | 2 | 10.51 | 2.90 | 7.75 | 9.00 | 9.90 | 10.50 | 24.00 | ||
| HVAC system on/running during school hours | 1 | |||||||||
| No | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Yes | 65 | 100 | ||||||||
| Basement | 1 | |||||||||
| No | 45 | 69 | ||||||||
| Yes | 20 | 31 | ||||||||
| If basement, finished? | 1 | |||||||||
| No | 14 | 74 | ||||||||
| Yes | 5 | 26 | ||||||||
| Crawlspace or uncovered dirt floor | 5 | |||||||||
| No | 47 | 77 | ||||||||
| Yes | 14 | 23 | ||||||||
| Levels/Stories | 2 | |||||||||
| 1 | 48 | 75 | ||||||||
| 2–3 | 16 | 25 | ||||||||
| Classrooms | 4 | 43.61 | 21.11 | 19.00 | 32.00 | 38.00 | 49.00 | 148.00 | ||
| Students | 4 | 978.42 | 604.00 | 182.00 | 642.00 | 819.00 | 1200.00 | 3300.00 | ||
| Built using radon-resistant new construction | 17 | |||||||||
| No | 34 | 69 | ||||||||
| Yes | 15 | 31 |
| Classrooms | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radon Variable | N | % | GM a | 95% CI a | Min b | Max b |
| Below detection limits c | ||||||
| No | 1491 | 65 | ||||
| Yes | 798 | 35 | ||||
| Radon concentration, Bq/m3 | 31.39 | 27.16, 36.28 | 14.80 | 673.40 | ||
| Below EPA’s recommended action level d | ||||||
| No | 37 | 2 | ||||
| Yes | 2252 | 98 | ||||
| Radon Concentration, Bq/m3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| School Characteristic | GM a | 95% CI a | p-Value a |
| Grade | |||
| Elementary | 32.83 | 27.68, 38.94 | |
| Junior high or middle | 25.07 | 17.93, 35.06 | |
| High | 33.92 | 22.60, 50.92 | 0.34 |
| Age, 10 years | 1.02 b | 0.95, 1.09 b | 0.64 |
| Year HVAC system installed | |||
| 1954–1970 | 37.15 | 20.79, 66.35 | |
| 1971–1985 | 35.52 | 22.91, 55.07 | |
| 1986–2000 | 28.61 | 21.57, 37.94 | |
| 2001–2017 | 31.60 | 25.88, 38.60 | 0.78 |
| Last year HVAC system maintained | |||
| 2012 | 33.00 | 10.29, 105.86 | |
| 2018 | 32.89 | 27.11, 39.90 | |
| 2019 | 28.24 | 22.20, 35.93 | 0.61 |
| Type of HVAC system | |||
| Multi-zone system | 30.91 | 25.97, 36.78 | |
| Single-zone or hydronic system | 31.87 | 19.77, 51.39 | |
| Variable air volume system | 41.02 | 25.48, 66.04 | |
| Combination of systems | 25.59 | 15.87, 41.28 | 0.57 |
| Time HVAC system turned on/started each day, one hour | 1.00 b | 0.88, 1.13 b | 0.97 |
| Time HVAC system turned off/stopped each day, HH:MM:SS c | |||
| 15:00:00–16:00:00 | 28.44 | 23.66, 34.20 | |
| 16:00:01–16:30:00 | 43.27 | 30.10, 62.19 | |
| 16:30:01–18:00:00 | 29.38 | 18.35, 47.02 | |
| 18:00:01–23:59:59 | 33.68 | 22.47, 50.48 | 0.23 |
| Total number of hours HVAC system on/running each day, one hour | 1.01 b | 0.96, 1.06 b | 0.76 |
| Basement | |||
| No | 30.16 | 25.32, 35.91 | |
| Yes | 33.01 | 25.44, 42.85 | 0.57 |
| If basement, finished? | |||
| No | 35.10 | 25.43, 48.44 | |
| Yes | 27.33 | 15.96, 46.80 | 0.41 |
| Crawlspace or uncovered dirt floor | |||
| No | 30.28 | 25.46, 36.01 | |
| Yes | 33.18 | 24.19, 45.51 | 0.61 |
| Levels/Stories | |||
| 1 | 31.26 | 26.37, 37.06 | |
| 2 | 29.89 | 21.24, 42.08 | |
| 3 | 33.48 | 18.65, 60.10 | 0.94 |
| Classrooms | |||
| 19–30 | 42.60 | 30.95, 58.64 | |
| 31–40 | 29.42 | 24.24, 35.69 | |
| 41–50 | 23.02 | 15.84, 33.46 | |
| 51–60 | 22.98 | 15.36, 34.37 | |
| 61–70 | 24.22 | 11.52, 50.92 | |
| 71–80 | 57.12 | 20.13, 162.13 | |
| 81–148 | 58.59 | 32.03, 107.18 | 0.03 d |
| Students, 100 students | 1.00 b | 0.97, 1.02 b | 0.78 |
| Built using radon resistant new construction | |||
| No | 31.28 | 26.01, 37.61 | |
| Yes | 35.31 | 26.78, 46.56 | 0.47 |
| Mitigated for radon previously | |||
| No | 32.30 | 27.61, 37.80 | |
| Yes | 36.16 | 20.67, 63.28 | 0.70 |
| Classrooms ≥ EPA’s RAL | Classrooms < EPA’s RAL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| School Characteristic | Median | N | % | N | % | OR b | 95% CI b |
| Grade | |||||||
| Elementary | 26 | 70 | 1330 | 59 | 1.00 | Reference | |
| Junior high, middle, or high | 11 | 30 | 922 | 41 | 0.61 | 0.17, 2.19 | |
| Age, 10 years | 1.20 | 0.95, 1.51 | |||||
| Missing | 0 | 57 | |||||
| Year HVAC system installed, 10 years | 0.72 | 0.53, 0.99 | |||||
| Missing | 0 | 136 | |||||
| Last year HVAC system maintained | |||||||
| 2012–2018 | 2018 | 20 | 61 | 1368 | 66 | 1.00 | Reference |
| 2019 | 2019 | 13 | 39 | 710 | 34 | 1.25 | 0.24, 6.40 |
| Missing | 4 | 174 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 1 year | 1.25 | 0.24, 6.40 | ||||
| Type of HVAC system | |||||||
| Multi-zone, variable air volume, or combination of systems | 28 | 76 | 1979 | 93 | 1.00 | Reference | |
| Single-zone or hydronic system | 9 | 24 | 150 | 7 | 4.24 | 0.56, 32.40 | |
| Missing | 0 | 123 | |||||
| Time HVAC system turned on/started each day, one hour | 1.15 | 0.79, 1.67 | |||||
| Missing | 0 | 127 | |||||
| Time HVAC system turned off/stopped each day, HH:MM:SS | |||||||
| 15:00:00–16:00:00 | 16:00:00 | 9 | 24 | 1266 | 60 | 1.00 | Reference |
| 16:00:01–17:00:00 | 16:30:00 | 21 | 57 | 431 | 20 | 6.85 | 1.38, 34.14 |
| 17:00:01–23:59:59 | 19:15:00 | 7 | 19 | 428 | 20 | 2.30 | 0.54, 9.72 |
| Missing | 0 | 127 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 1 h | 1.09 | 0.81, 1.45 | ||||
| Total number of hours HVAC system on/running each day | |||||||
| 7.75–10 | 9.0 | 12 | 32 | 1328 | 61 | 1.00 | Reference |
| >10–11 | 10.5 | 18 | 49 | 423 | 19 | 4.71 | 0.92, 24.09 |
| >11–24 | 13.5 | 7 | 19 | 444 | 20 | 1.74 | 0.47, 6.47 |
| Missing | 0 | 57 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 1 h | 1.12 | 0.93, 1.35 | ||||
| Basement | |||||||
| No | 20 | 54 | 1495 | 67 | 1.00 | Reference | |
| Yes | 17 | 46 | 724 | 33 | 1.76 | 0.42, 7.41 | |
| Missing | 0 | 29 | |||||
| Crawlspace or uncovered dirt floor | |||||||
| No | 21 | 58 | 1451 | 70 | 1.00 | Reference | |
| Yes | 15 | 42 | 611 | 30 | 1.69 | 0.36, 7.92 | |
| Missing | 1 | 186 | |||||
| Levels/Stories | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | 25 | 68 | 1621 | 74 | 1.00 | Reference |
| 2 | 2 | 7 | 19 | 376 | 17 | 1.21 | 0.23, 6.37 |
| 3 | 3 | 5 | 14 | 198 | 9 | 1.64 | 0.39, 6.79 |
| Missing | 0 | 57 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 1 level | 1.26 | 0.58, 2.75 | ||||
| Classrooms | |||||||
| 19–30 | 26 | 22 | 61 | 259 | 12 | 19.40 | 4.59, 81.99 |
| 31–70 | 40 | 7 | 19 | 1599 | 76 | 1.00 | Reference |
| 71–148 | 95 | 7 | 19 | 245 | 12 | 6.53 | 2.04, 20.84 |
| Missing | 1 | 149 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 10 classrooms | 0.92 | 0.53, 1.60 | ||||
| Students e | |||||||
| 182–650 | 530 | 23 | 64 | 484 | 23 | 9.32 | 2.23, 38.99 |
| 651–1500 | 1000 | 7 | 19 | 1373 | 65 | 1.00 | Reference |
| 1501–3300 | 2400 | 6 | 17 | 246 | 12 | 4.78 | 1.33, 17.24 |
| Missing | 1 | 149 | |||||
| Trend c, d | Scaling factor: 100 students | 0.95 | 0.75, 1.19 | ||||
| Built using radon resistant new construction | |||||||
| No | 30 | 81 | 1171 | 68 | 1.00 | Reference | |
| Yes | 7 | 19 | 546 | 32 | 0.50 | 0.10, 2.50 | |
| Missing | 0 | 535 | |||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, E.A.; Ou, J.Y.; Chausow, C.; Verdeja, M.A.; Divver, E.; Johnston, J.D.; Beard, J.D. Associations Between School Characteristics and Classroom Radon Concentrations in Utah’s Public Schools: A Project Completed by University Environmental Health Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165839
Davis EA, Ou JY, Chausow C, Verdeja MA, Divver E, Johnston JD, Beard JD. Associations Between School Characteristics and Classroom Radon Concentrations in Utah’s Public Schools: A Project Completed by University Environmental Health Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(16):5839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165839
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Elizabeth A., Judy Y. Ou, Cheyenne Chausow, Marco A. Verdeja, Eleanor Divver, James D. Johnston, and John D. Beard. 2020. "Associations Between School Characteristics and Classroom Radon Concentrations in Utah’s Public Schools: A Project Completed by University Environmental Health Students" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 16: 5839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165839
APA StyleDavis, E. A., Ou, J. Y., Chausow, C., Verdeja, M. A., Divver, E., Johnston, J. D., & Beard, J. D. (2020). Associations Between School Characteristics and Classroom Radon Concentrations in Utah’s Public Schools: A Project Completed by University Environmental Health Students. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(16), 5839. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17165839






