Selecting Appropriate Words for Naming the Rows and Columns of Risk Assessment Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
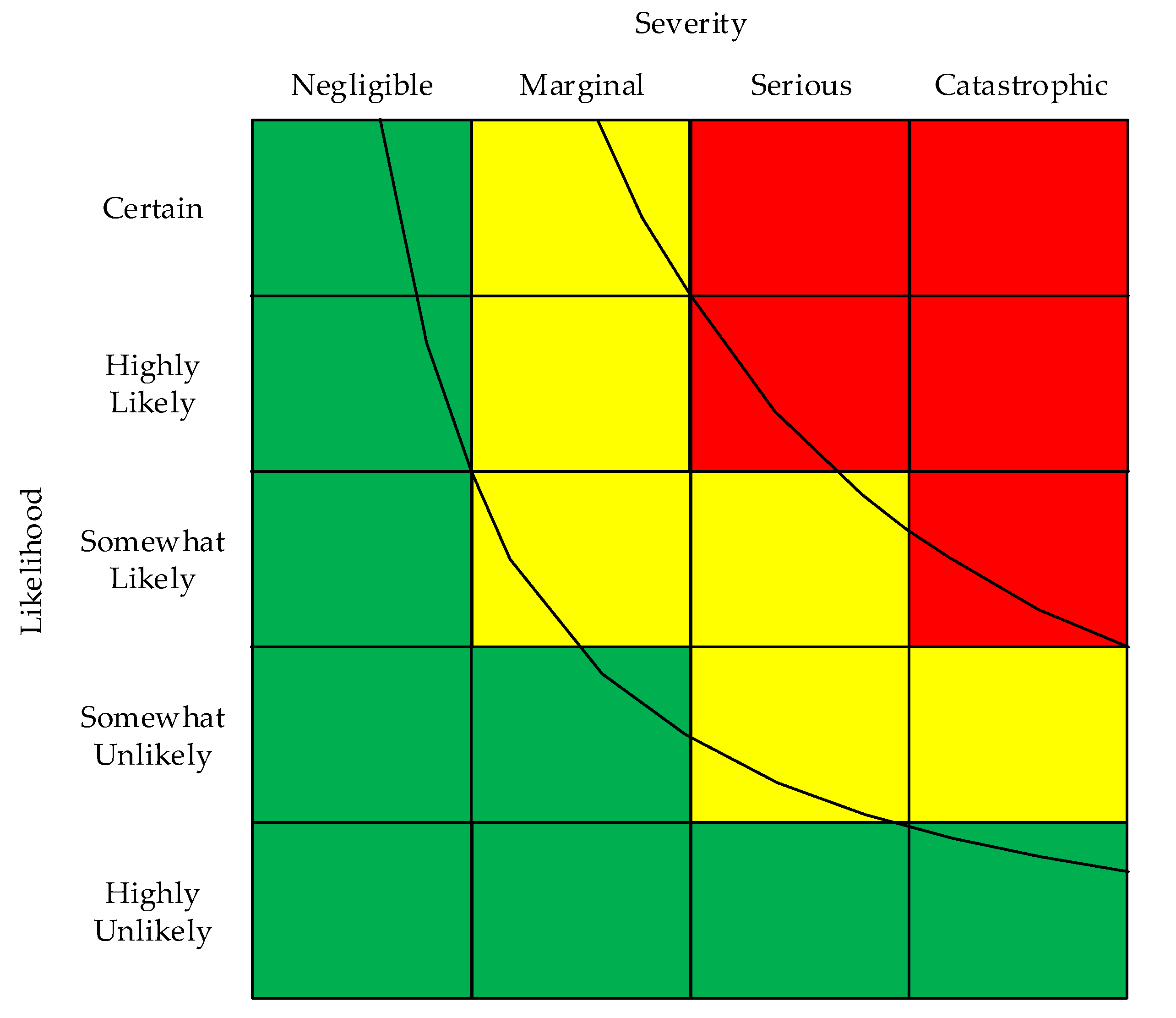
1.1. Formatting Options for RAMs
1.2. Assigning Risk Levels to Cells
1.3. Objective
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determine the Content of the Survey
2.2. Sampling Approach
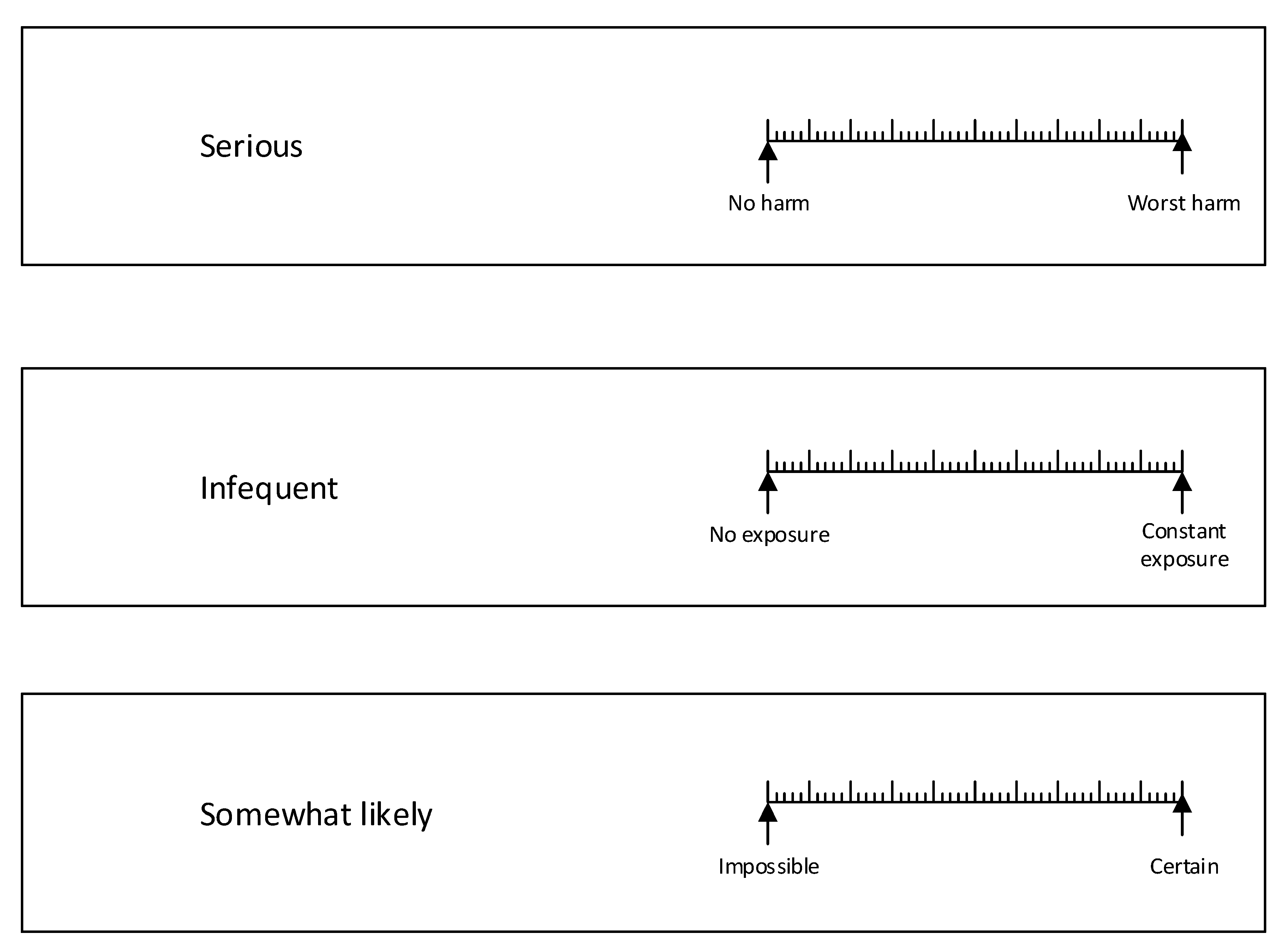
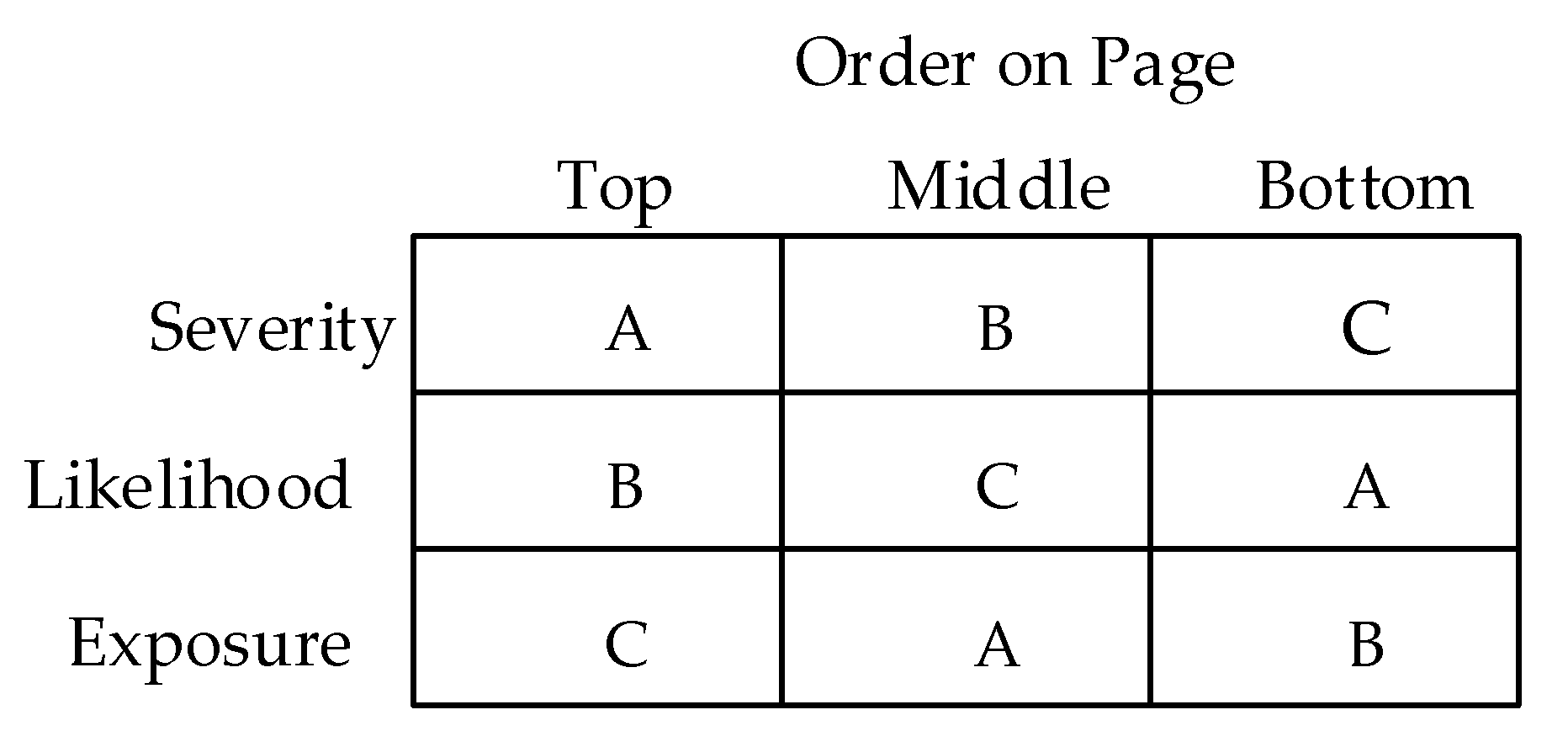
2.3. Survey Instrument
2.4. Procedures
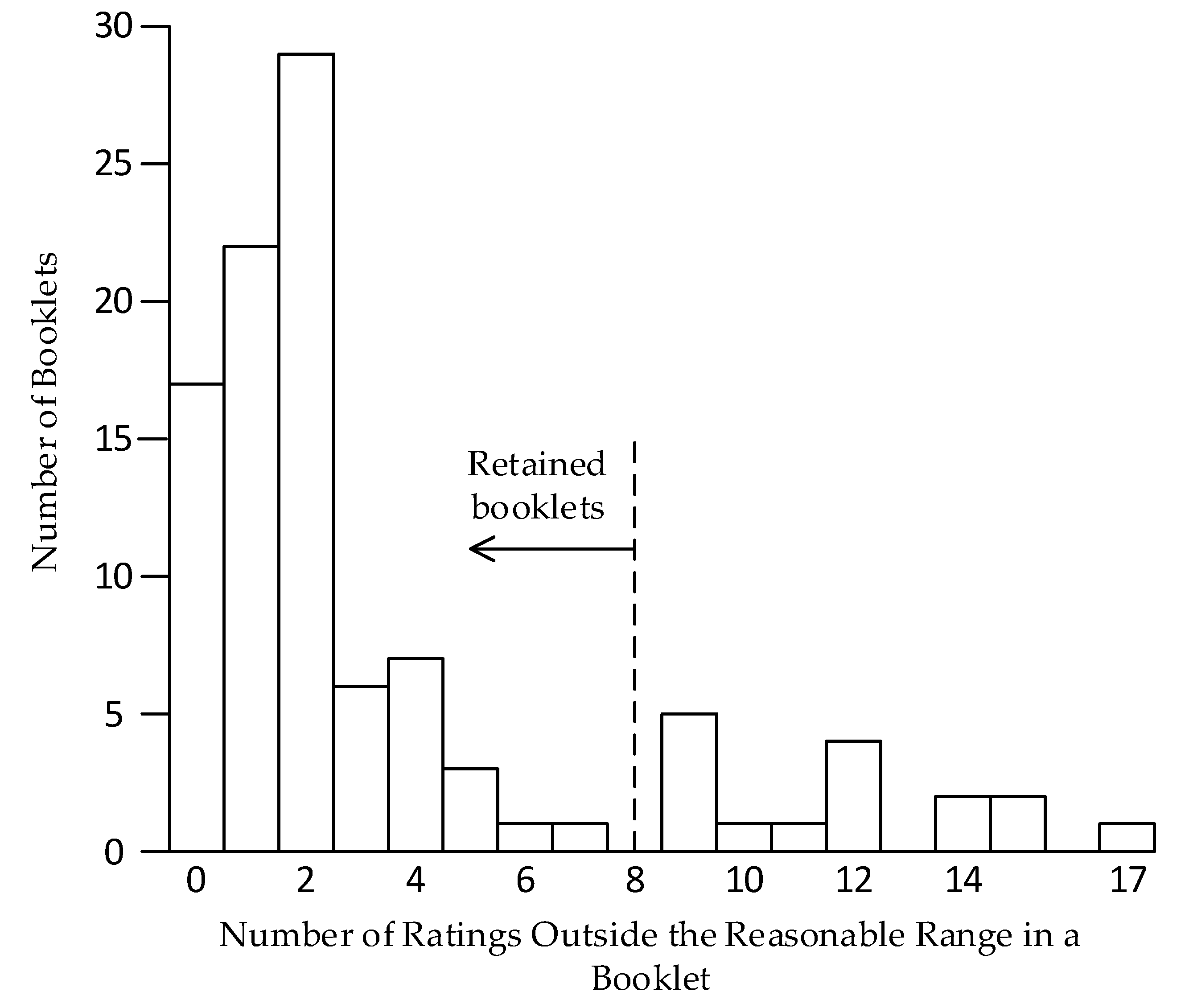
2.4.1. First Process—Remove Poor Booklets
2.4.2. Second Process—Identify Suitable Words and Phrases
3. Results
3.1. Findings of First Process
3.2. Findings of the Second Process
4. Evaluation
4.1. Severity Words and Phrases
4.2. Probability-Based Words and Phrases
4.3. Likelihood-Based Words and Phrases
4.4. Extent of Exposure Words and Phrases
5. Example Application
6. Conclusions
6.1. Limitations of the Project
6.2. Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ISO 45001. Occupational Health and Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use; International Organisation for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, R.C. Risk-Reduction Methods for Occupational Safety and Health, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 65–81. ISBN 978-1-1194-9399-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kjellén, U.; Albrechtsen, E. Prevention of Accidents and Unwanted Occurrences: Theory, Methods, and Tools in Safety Management, 2nd ed.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 339–351. ISBN 978-1-4987-3659-6. [Google Scholar]
- Main, B.W. Risk assessment: A review of the fundamental principles. Prof. Saf. 2004, 49, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Main, B.W. Risk Assessment: Challenges and Opportunities; Design Safety Engineering: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2012; pp. 4–13. ISBN 978-0-9741248-2-7. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, B.K.; Popov, G. Communicating and managing risk: The key result of risk assessment. Prof. Saf. 2017, 62, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Manuele, F.A. On the Practice of Safety, 4th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 116–119. ISBN 978-1-118-47894-3. [Google Scholar]
- Piampiano, J.M.; Rizzo, S.M. Safety or safe enough? Measuring risk and its variables objectively. Prof. Saf. 2012, 57, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- USA Department of Defense. Standard Practice for System Safety, MIL-STD-882E. Available online: https://www.dau.edu/cop/armyesoh/DAU%20Sponsored%20Documents/MIL-STD-882E.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Rausand, M. Risk Assessment: Theory, Methods, and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 99–102, 388–397. ISBN 978-1-4398-0684-5. [Google Scholar]
- Powlowka, Z. Occupational risk assessment. In Handbook of Occupational Safety and Health; Koradecka, D., Ed.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 473–481. ISBN 978-1-4398-0684-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pons, D.J. Alignment of the safety method with New Zealand legislative responsibilities. Safety 2019, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, G.K.; Ward, J.; Clarkson, J. A review of risk matrices used in acute hospitals in England. Risk Anal. 2019, 39, 1060–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunaryo; Hamka, M.A. Safety risk assessment on container terminal using hazard identification and risk assessment and fault tree analysis methods. Procedia Manuf. 2017, 194, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, P.L.; Pfitzer, T.; Simmons, R.J.; Dwyer, S.; Frost, J.; Olsen, E. The RAC matrix: A universal tool or toolkit? J. Syst. Saf. 2005, 41, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Viner, D. Occupational Risk Control: Predicting and Preventing the Unwanted, 2nd ed.; Gower Publishing: Burlington, VT, USA, 2015; pp. 88–91. ISBN 978-1-4724-1970-7. [Google Scholar]
- Baybutt, P. Guidelines for designing risk matrices. Process Saf. Prog. 2018, 37, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Card, A.J.; Ward, J.R.; Clarkson, P.J. Trust-level risk evaluation and control guidance in the NHS east of England. Risk Anal. 2014, 34, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, L.A., Jr.; Babayev, D.; Huber, W. Some limitations of qualitative risk rating systems. Risk Anal. 2005, 25, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, L.A., Jr. What’s wrong with risk matrices? Risk Anal. 2008, 28, 497–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, C.; Wu, D.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Comparison of different methods to design risk matrices from the perspective of applicability. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 122, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.; Yin, Z.; Frangopol, D.M. Risk matrix integrating risk attitudes based on utility theory. Risk Anal. 2015, 35, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, B.; Fitts, D.J.; Woodson, W.E.; Rose-Sundholm, R.; Tillman, P. Human Factors and Ergonomics Design Handbook, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 4. ISBN 978-0-07-170287-4. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, R.J. Applied Biostatistics for the Health Sciences; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 76–77. ISBN 978-0-470-14764-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, M.A. Participative assessment. In Evaluation of Human Work, 3rd ed.; Wilson, J.R., Corlett, N., Eds.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 83–98. ISBN 0-415-26757-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, B.K.; Popov, G. Managing risk thorough layers of control. Prof. Saf. 2020, 65, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Occupational Health and Safety Management System; ANSI/ASSE Z10-2012 (Revision 2017); American Society of Safety Professionals: Park Ridge, IL, USA, 2017.
- Marling, G.; Horberry, T.; Harris, J. Development and validation of plain English interpretations of the seven elements of the risk management process. Safety 2019, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

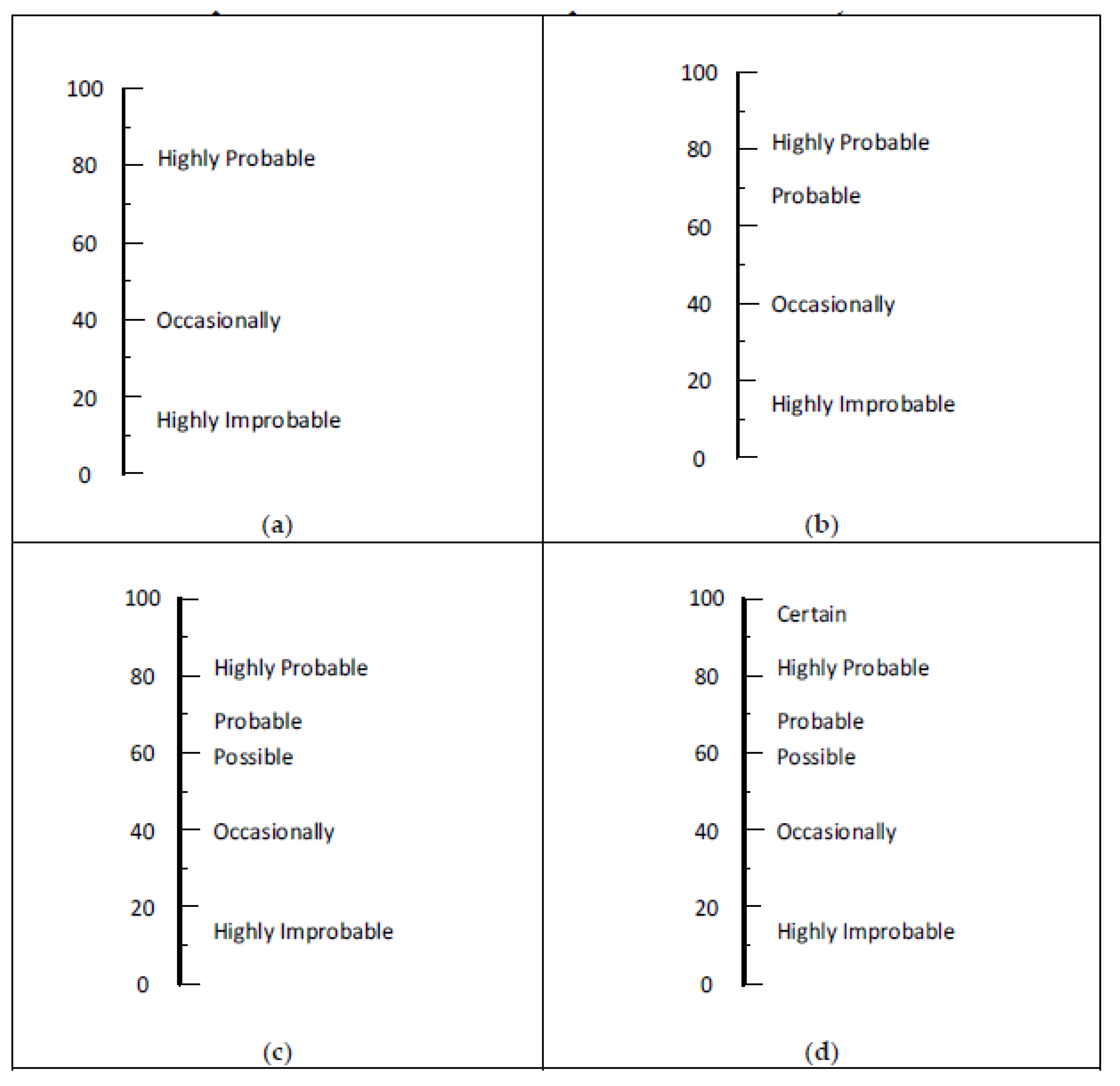

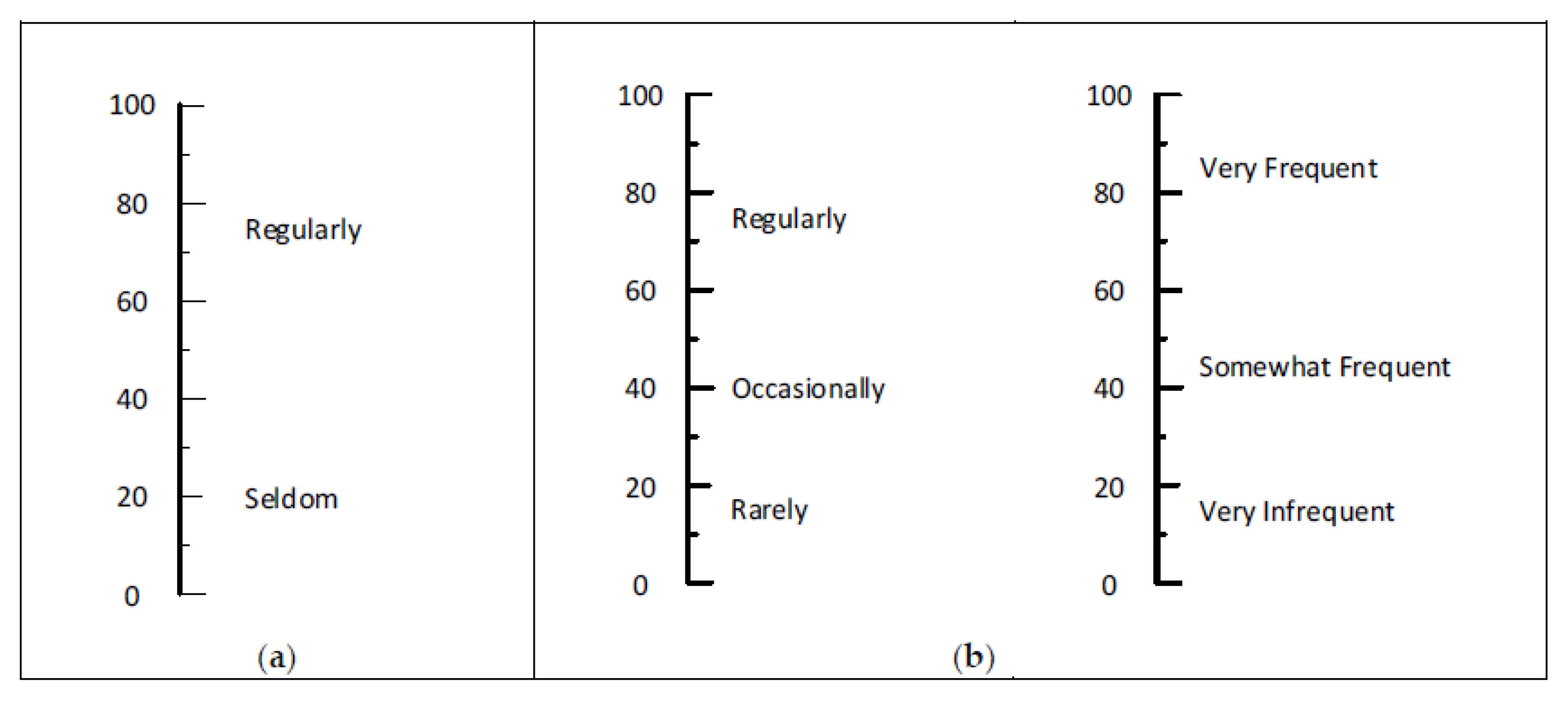
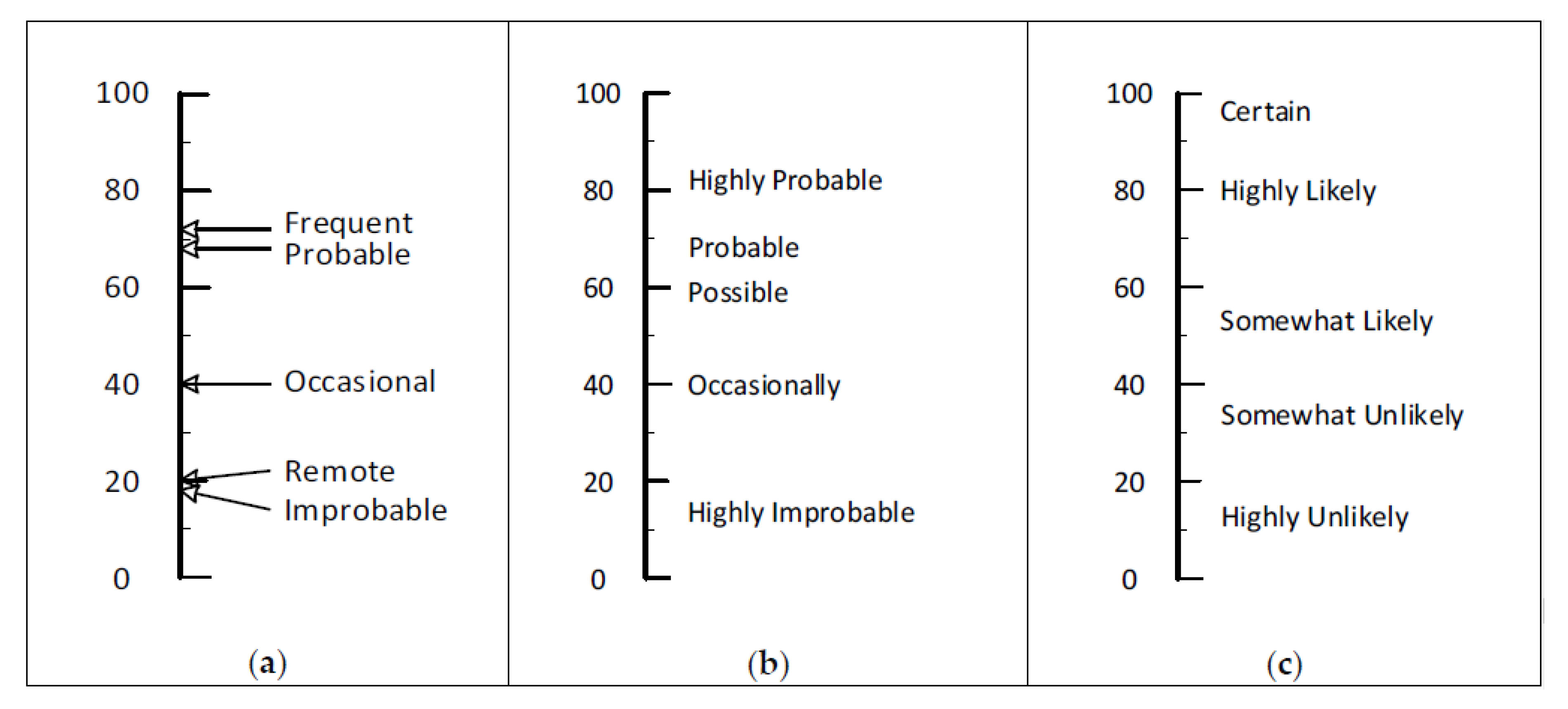
| Severity | Likelihood/Probability | Extent of Exposure |
|---|---|---|
| Catastrophic | Highly likely | Very frequent |
| Major damage | Very likely | Frequent |
| Critical | Likely | Somewhat frequent |
| Severe loss | Somewhat likely | Infrequent |
| Severe | Somewhat unlikely | Very infrequent |
| Serious | Unlikely | Regularly |
| Moderate | Very unlikely | Occasionally |
| Minor damage | Highly unlikely | Rarely |
| Marginal | Certain | Very rarely |
| Negligible | Almost certain | Seldom |
| Minor | Highly probable | Uncommon |
| Insignificant | Probable | Remote |
| Death of one person | Improbable | Daily |
| Permanent injury/illness | Highly improbable | Weekly |
| Medical treatment case | Possible | Monthly |
| First aid only case | Almost incredible | Annually |
| Severity | Likelihood/Probability | Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Catastrophe | <70 | Highly likely | <70 | Very frequent | <70 |
| Major damage | <70 | Highly probable | <70 | Regularly | <70 |
| Severe loss | <70 | Certain | <70 | Daily | <70 |
| Death of one person | <70 | Very unlikely | >30 | Very infrequent | >30 |
| Minor damage | >30 | Highly unlikely | >30 | Very rarely | >30 |
| Negligible | >30 | Highly improbable | >30 | Uncommon | >30 |
| Minor | >30 | ||||
| Severity | Likelihood/Probability | Extent of Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word or Phrase | Ave | Word or Phrase | Ave | Word or Phrase | Ave |
| Death of one person | 96.9 | Certain | 96.0 | Daily | 88.1 |
| Catastrophic | 96.8 | Highly probable | 81.7 | Very frequent | 85.0 |
| Permanent injury/illness | 94.4 | Almost certain | 81.4 | Regularly | 74.1 |
| Severe loss | 86.9 | Highly likely | 80.7 | Frequent | 72.0 |
| Critical | 84.5 | Very likely | 79.1 | Weekly | 66.7 |
| Severe | 83.8 | Probable | 68.2 | Somewhat frequent | 54.7 |
| Major damage | 81.7 | Likely | 66.0 | Monthly | 49.9 |
| Serious | 74.9 | Possible | 59.4 | Occasionally | 40.2 |
| Medical treatment case | 74.0 | Somewhat likely | 53.6 | Annually | 36.2 |
| Moderate | 48.9 | Almost incredible | 46.1 | Infrequent | 23.1 |
| First aid only case | 41.8 | Somewhat unlikely | 34.4 | Uncommon | 21.0 |
| Marginal | 32.9 | Unlikely | 24.6 | Seldom | 19.7 |
| Minor damage | 25.6 | Improbable | 18.7 | Remote | 16.9 |
| Minor | 21.8 | Very unlikely | 14.6 | Rarely | 15.8 |
| Negligible | 15.7 | Highly improbable | 14.3 | Very infrequent | 15.0 |
| Insignificant | 12.6 | Highly unlikely | 13.3 | Very rarely | 11.5 |
| Severity | Likelihood/Probability | Extent of Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Word or Phrase | SD | Word or Phrase | SD | Word or Phrase | SD |
| Permanent injury/illness | 7.0 | Very unlikely | 8.6 | Very rarely | 8.0 |
| Death of one person | 7.7 | Highly probable | 9.6 | Rarely | 8.6 |
| Moderate | 8.3 | Improbable | 11.1 | Uncommon | 11.2 |
| Insignificant | 9.3 | Highly unlikely | 11.4 | Very frequent | 12.2 |
| Catastrophic | 9.8 | Certain | 11.5 | Seldom | 13.0 |
| Serious | 10.9 | Likely | 12.9 | Infrequent | 13.1 |
| Severe | 11.8 | Somewhat unlikely | 12.6 | Remote | 13.4 |
| Minor | 14.5 | Probable | 13.1 | Daily | 13.8 |
| Severe loss | 15.0 | Highly likely | 13.3 | Very infrequent | 14.8 |
| Minor damage | 15.5 | Unlikely | 13.3 | Somewhat frequent | 14.9 |
| Major damage | 15.6 | Somewhat likely | 14.8 | Occasionally | 16.22 |
| Critical | 16.2 | Almost certain | 14.9 | Regularly | 16.2 |
| Medical treatment case | 17.1 | Highly improbable | 15.4 | Frequent | 16.4 |
| Marginal | 17.2 | Possible | 16.0 | Weekly | 20.4 |
| Negligible | 20.7 | Very likely | 16.3 | Monthly | 21.9 |
| First aid only case | 21.3 | Almost incredible | 31.6 | Annually | 26.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jensen, R.C.; Hansen, H. Selecting Appropriate Words for Naming the Rows and Columns of Risk Assessment Matrices. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155521
Jensen RC, Hansen H. Selecting Appropriate Words for Naming the Rows and Columns of Risk Assessment Matrices. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(15):5521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155521
Chicago/Turabian StyleJensen, Roger C., and Haley Hansen. 2020. "Selecting Appropriate Words for Naming the Rows and Columns of Risk Assessment Matrices" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 15: 5521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155521
APA StyleJensen, R. C., & Hansen, H. (2020). Selecting Appropriate Words for Naming the Rows and Columns of Risk Assessment Matrices. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(15), 5521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17155521






