Rowing Training in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Longitudinal Study of Physical Fitness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Breast Cancer: Prevention and Control. Available online: https://www.who.int/topics/cancer/breastcancer/en (accessed on 11 April 2020).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Today. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. Cancer Tomorrow. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/home (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Cantarero-Villanueva, I.; Fernández-Lao, C.; Del Moral-Avila, R.; Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Feriche-Fernández-Castanys, M.B.; Arroyo-Morales, M. Effectiveness of core stability exercises and recovery myofascial release massage on fatigue in breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 620619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Anthis, N.J.; Kavanaugh-Lynch, M.H.E. The Global Challenge to Prevent Breast Cancer: Surfacing New Ideas to Accelerate Prevention Research. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.M.; Montgomery, D. Follow-up after breast cancer. BMJ 2008, 336, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Maldonado, A.; Carrera-Ruiz, Á.; Díez-Fernández, D.M.; Esteban-Simón, A.; Maldonado-Quesada, M.; Moreno-Poza, N.; del Mar García-Martínez, M.; Alcaraz-García, C.; Vázquez-Sousa, R.; Moreno-Martos, H.; et al. Effects of a 12-week resistance and aerobic exercise program on muscular strength and quality of life in breast cancer survivors: Study protocol for the EFICAN randomized controlled trial. Medicine 2019, 98, e17625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Barquero, C. Actividad física en el tiempo libre previene enfermedades cardiacas/cardiovasculares: Una revisión sistemática. Rev. Iberoam. Cienc. Act. Física y Deporte 2020, 9, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez Rigueira, P.; Pedrero Chamizo, R.; Aparicio Ugarriza, R.; Santiago Dorrego, C.; Calonge, S.; Gómez, F.; Le Ble, G.P.; Manjón, R.D.; Meléndez, A.; Barrios, L.; et al. Efectos de un programa de ejercicio intradiálisis en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica. Rev. Iberoam. Cienc. Act. Física y Deporte 2019, 8, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moros, M.T.; Ruidiaz, M.; Caballero, A.; Serrano, E.; Martínez, V.; Tres, A. Effects of an exercise training program on the quality of life of women with breast cancer on chemotherapy. Rev. Médica de Chile 2010, 138, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mascherini, G.; Tosi, B.; Giannelli, C.; Grifoni, E.; Degl’innocenti, S.; Galanti, G. Breast cancer: Effectiveness of a one-year unsupervised exercise program. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, K.P.; McTiernan, A. The role of physical activity in breast and gynecologic cancer survivorship. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 149, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda-Malavés, R.; Tudela-Desantes, A.; González-Ródenas, J. Academic and athletic performance in young athletes from the Sports Technification Centre in Cheste. Educ. Sport Health Phys. Act. 2019, 3, 86–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lope, V.; Martín, M.; Castelló, A.; Casla, S.; Ruiz, A.; Baena-Cañada, J.M.; Casas, A.; Calvo, L.; Bermejo, B.; Muñoz, M.; et al. Physical activity and breast cancer risk by pathological subtype. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 144, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyne, D.J.; O’Sullivan, D.E.; Olij, B.F.; King, W.D.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Brenner, D.R. Physical Activity, Global DNA Methylation, and Breast Cancer Risk: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 1320–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, T.; van Mackelenbergh, M.; Wesch, D.; Mundhenke, C. Physical activity influences the immune system of breast cancer patients. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spei, M.E.; Samoli, E.; Bravi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Bamia, C.; Benetou, V. Physical activity in breast cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis on overall and breast cancer survival. Breast 2019, 44, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. A meta-analysis of the association between physical activity and breast cancer mortality. Cancer Nurs. 2019, 42, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahart, I.M.; Metsios, G.S.; Nevill, A.M.; Carmichael, A.R. Physical activity for women with breast cancer after adjuvant therapy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD011292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsou, E.D.; Alexias, G.D.; Anagnostopoulos, F.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. Effects of physical activity on depressive symptoms during breast cancer survivorship: A meta-analysis of randomised control trials. ESMO Open 2017, 2, e000271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Spence, R.R.; Steele, M.L.; Sandler, C.X.; Peake, J.M.; Hayes, S.C. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the safety, feasibility, and effect of exercise in women with stage II+ breast cancer. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 2621–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Ye, W.; Kuo, C.H.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Korivi, M. Exercise intervention improves clinical outcomes, but the “time of session” is crucial for better quality of life in breast cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2019, 11, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchik, D.; Masco, S.; Zinnikas, P.; Hillriegel, B.; Lauder, T.; Suttmann, E.; Chinchilli, V.; Mc Beth, M.; Hermann, W. Effect of exercise on breast cancer-related lymphedema: What the lymphatic surgeon needs to know. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2019, 35, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana López, V.A.; Díaz López, K.J.; Caire Juvera, G. Interventions to improve healthy lifestyles and their effects on psychological variables among breast cancer survivors: A systematic review. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares Falcetta, F.; de Araújo Vianna Trésel, H.; de Almeida, F.K.; Rangel Ribeiro Falcetta, M.; Falavigna, M.; Dornelles Rosa, D. Effects of physical exercise after treatment of early breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardefeldt, P.J.; Penninkilampi, R.; Edirimanne, S.; Eslick, G.D. Physical activity and weight loss reduce the risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 139 prospective and retrospective studies. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e601–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto-Carral, A.; Molina, A.J.; de Pedro, Á.; Ayón, C. Pilates for women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 2018, 41, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Tan, X. Physical activity and risk of breast cancer: A meta-analysis of 38 cohort studies in 45 study reports. Value Heal. 2019, 22, 104–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimley, C.E.; Kato, P.M.; Grunfeld, E.A. Health and health belief factors associated with screening and help-seeking behaviours for breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the european evidence. Br. J. Heal. Psychol. 2020, 25, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdin, S.; Lavallée, J.F.; Faulkner, J.; Husted, M. A systematic review of the effectiveness of physical activity interventions in adults with breast cancer by physical activity type and mode of participation. Psycho-Oncology 2019, 28, 1381–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.S.M.; Abar, L.; Cariolou, M.; Nanu, N.; Greenwood, D.C.; Bandera, E.V.; McTiernan, A.; Norat, T. World Cancer Research Fund International: Continuous update project—Systematic literature review and meta-analysis of observational cohort studies on physical activity, sedentary behavior, adiposity, and weight change and breast cancer risk. Cancer Causes Control 2019, 30, 1183–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.M.; Wiskemann, J.; May, A.M.; Schwartz, A.L.; Courneya, K.S.; Zucker, D.S.; Matthews, C.E.; Ligibel, J.A.; Gerber, L.H.; et al. Exercise guidelines for cancer survivors: Consensus statement from international multidisciplinary roundtable. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Blasio, A.; Morano, T.; Cianchetti, E.; Gallina, S.; Bucci, I.; Di Santo, S.; Tinari, C.; Di Donato, F.; Izzicupo, P.; Di Baldassarre, A.; et al. Psychophysical health status of breast cancer survivors and effects of 12 weeks of aerobic training. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2017, 27, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keilani, M.; Hasenoehrl, T.; Neubauer, M.; Crevenna, R. Resistance exercise and secondary lymphedema in breast cancer survivors—A systematic review. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieli-Conwright, C.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Sami, N.; Lee, K.; Sweeney, F.C.; Stewart, C.; A Buchanan, T.; Spicer, D.; Tripathy, D.; et al. Aerobic and resistance exercise improves physical fitness, bone health, and quality of life in overweight and obese breast cancer survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Breast Cancer Res. 2018, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G.A.; Cartmel, B.; Harrigan, M.; Fiellin, M.; Capozza, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ercolano, E.; Gross, C.P.; Hershman, D.; Ligibel, J.; et al. The effect of exercise on body composition and bone mineral density in breast cancer survivors taking aromatase inhibitors. Obesity 2017, 25, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, F.T.; Reike, A.; Reimer, V.; Schumann, M.; Hallek, M.; Taaffe, D.R.; Newton, R.U.; Galvao, D.A. Effects of physical exercise on breast cancer-related secondary lymphedema: A systematic review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, A.J.; Saxton, H.R.; Kauffeldt, K.D.; Sabiston, C.M.; Tomasone, J.R. “We’re all in the same boat together”: Exploring quality participation strategies in dragon boat teams for breast cancer survivors. Disabil. Rehabil. 2020, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giganti, M.G.; Tresoldi, I.; Sorge, R.; Melchiorri, G.; Triossi, T.; Masuelli, L.; Lido, P.; Albonici, L.; Foti, C.; Modesti, A.; et al. Physical exercise modulates the level of serum MMP-2 and MMP-9 in patients with breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchiorri, G.; Viero, V.; Triossi, T.; Sorge, R.; Tancredi, V.; Cafaro, D.; Andretis, C.; Vulpialni, M.C.; Saraceni, V.M. New approach to evaluate late arm impairment and effects of dragon boat activity in breast cancer survivors. Medicine 2017, 96, e8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.L.; Yakiwchuk, C.V.; Griffin, K.L.; Gray, R.E.; Fitch, M.I. Survivor dragon boating: A vehicle to reclaim and enhance life after treatment for breast cancer. Health Care Women Int. 2007, 28, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonough, M.H.; Patterson, M.C.; Weisenbach, B.B.; Ullrich-French, S.; Sabiston, C.M. The difference is more than floating: Factors affecting breast cancer survivors´ decisions to join and maintain participation in dragon boat teams and support groups. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 41, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DAS, A.; Mandal, M.; Syamal, A.K.; Majumdar, P. Monitoring changes of cardio-respiratory parameters during 2000 m rowing performance. Int. J. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 12, 483–490. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshiga, C.C.; Higuchi, M. Rowing performance of female and male rowers. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2003, 13, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aramendi, J.M. Remo olímpico y remo tradicional: Aspectos biomecánicos, fisiológicos y nutricionales. Arch. Med. Deporte 2014, 159, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, S.R. “We’re all in the same boat”: A review of the benefits of dragon boat racing for women living with breast cancer. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 167651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unruh, A.M.; Elvin, N. In the eye of the dragon: Women’s experience of breast cancer and the occupation of dragon boat racing. Can. J. Occup. Ther. 2004, 71, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabiston, C.M.; McDonough, M.H.; Crocker, P.R. Psychosocial experiences of breast cancer survivors involved in a dragon boat program: Exploring links to positive psychological growth. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2007, 29, 419–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, J.C.; Gálvez-Fernández, I.; Gavala-González, J. Estudio longitudinal sobre la pérdida de peso en mujeres jóvenes. J. Sport Health Res. 2019, 11 (Suppl. 1), 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Harriss, D.; Macsween, A.; Atkinson, G. Standards for Ethics in Sport and Exercise Science Research: 2018 Update. Int. J. Sports Med. 2017, 38, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191. [CrossRef]
- Lemmink, K.A.; Kemper, H.C.; de Greef, M.H.; Rispens, P.; Stevens, M. The validity of the sit-and-reach test and the modified sit-and-reach test in middle-aged to older men and women. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2003, 74, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, L.H.; Rask, I.K.; Kondrup, J. Validation of handgrip strength and endurance as a measure of physical function and quality of life in healthy subjects and patients. Nutrition 2010, 26, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, S.P.; Harackiewicz, D.V.; Harman, E.A.; Frykman, P.N.; Rosenstein, M.T. Cross-validation of three jump power equations. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1999, 31, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, T.; Bishop, C.; Antrobus, M.; Brazier, J. The validity and reliability of the My Jump 2 app for measuring the reactive strength index and drop jump performance. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, C.G.; Casanova, C.; Marín, J.M.; Lopez, M.V.; Pinto-Plata, V.; de Oca, M.M.; Dordetlly, L.J.; Nekach, H.; Celli, B.R. Validation and comparison of reference equations for the 6-min walk distance test. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.J.; Rikli, R.E.; Beam, W.C. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 1999, 70, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rikli, R.E.; Jones, C.J. Development and validation of criterion-referenced clinically relevant fitness standards for maintaining physical independence in later years. Gerontol. 2013, 53, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börg, G. Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 1982, 14, 337–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age (Years) | Years from Diagnosis | Breast (%) | Stage (%) | Surgery (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 53.70 ± 7.88 | 6.57 ± 5.02 | Right | 26.09 | I | 4.35 | Preservation | 53.52 |
| II | 30.43 | Total Mastectomy | 39.13 | ||||
| Left | 73.91 | III | 52.17 | ||||
| IV | 8.7 | Double Mastectomy | 4.35 | ||||
| Stage | Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | Initial phase with mobility exercises, proprioceptive exercises and postural control exercises. Main phase with rowing training. Final phase with stretching. Börg scale 5–6. |
| 2 | Initial phase with mobility exercises, proprioceptive exercises and postural control exercises. Main phase with rowing training. Final phase with stretching. Börg scale 6–7. |
| 3 | Initial phase with mobility exercises, proprioceptive exercises and postural control exercises. Main phase with rowing training. Final phase with stretching. Börg scale 7–8. |
| Variables | Pretest | Post-test | Diff Post-Pre | t-Student | Effect Size | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight (kg) | 68.67 ± 10.98 | 68.29 ± 10.79 | −0.37 ± 2.58 | −0.798 | 0.14 | 0.431 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.34 ± 3.78 | 26.19 ± 3.67 | −0.14 ± 1.02 | −0.786 | 0.14 | 0.438 |
| Total body fat (kg) | 27.62 ± 6.79 | 25.85 ± 6.29 | −1.77 ± 7.60 | −1.28 | 0.23 | 0.211 |
| Total lean mass (kg) | 40.43 ± 4.61 | 42.61 ± 3.45 | 2.18 ± 4.81 | 2.486 | 0.45 | 0.019 * |
| Percentage of total body fat (%) | 40.07 ± 4.84 | 37.44 ± 4.88 | −2.63 ± 5.43 | −2.657 | 0.48 | 0.013 * |
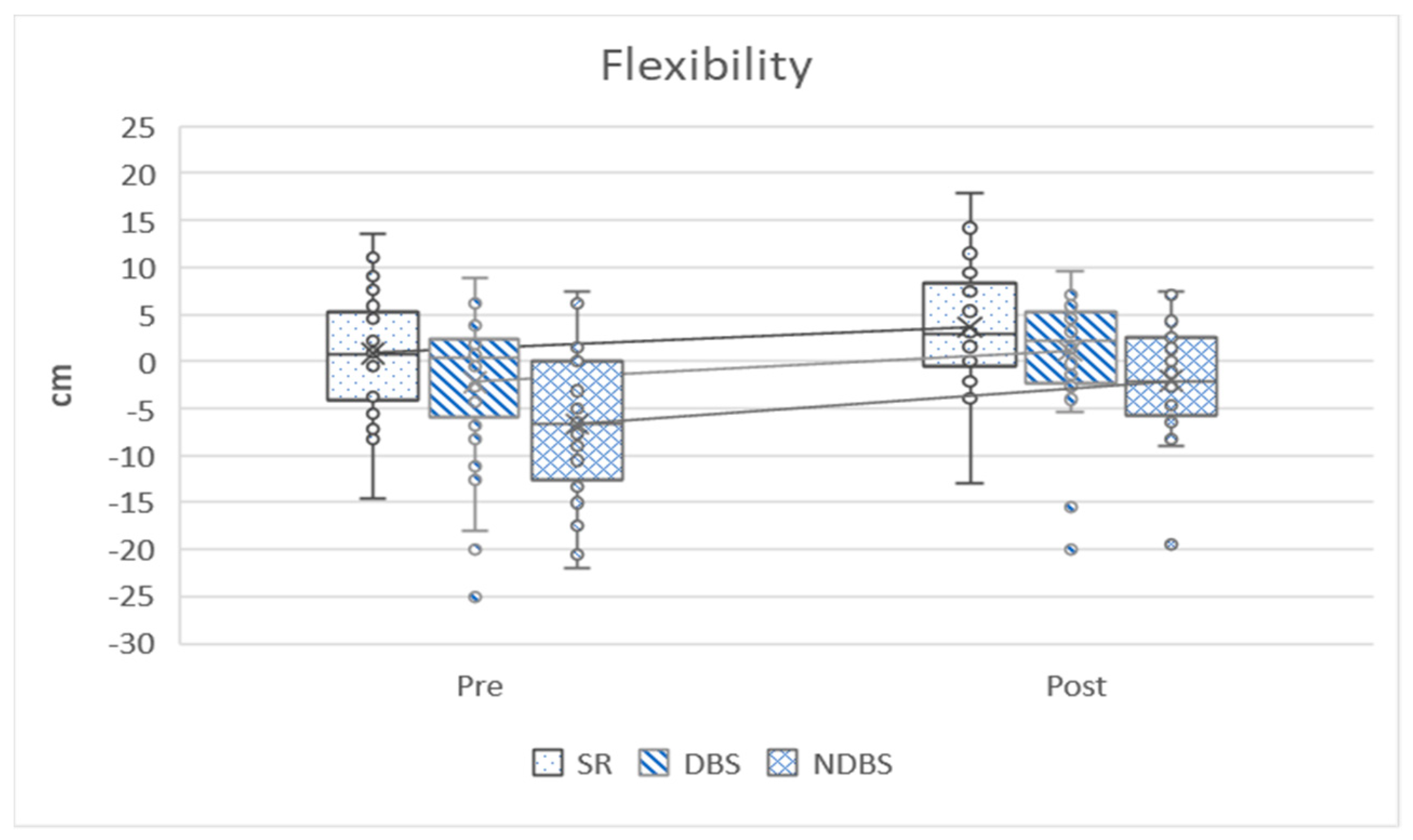
| Sit and reach test (cm) | 0.87 ± 6.61 | 3.69 ± 6.57 | 2.82 ± 1.87 | 8.242 | 1.51 | 0.000 ** |
| Dominant back scratch test (cm) | −2.19 ± 8.22 | 1.10 ± 6.54 | 3.29 ± 3.15 | 5.726 | 1.04 | 0.000 ** |
| Non-dominant back scratch test (cm) | −6.64 ± 7.47 | −2.05 ± 5.72 | 4.59 ± 3.90 | 6.44 | 1.18 | 0.000 ** |
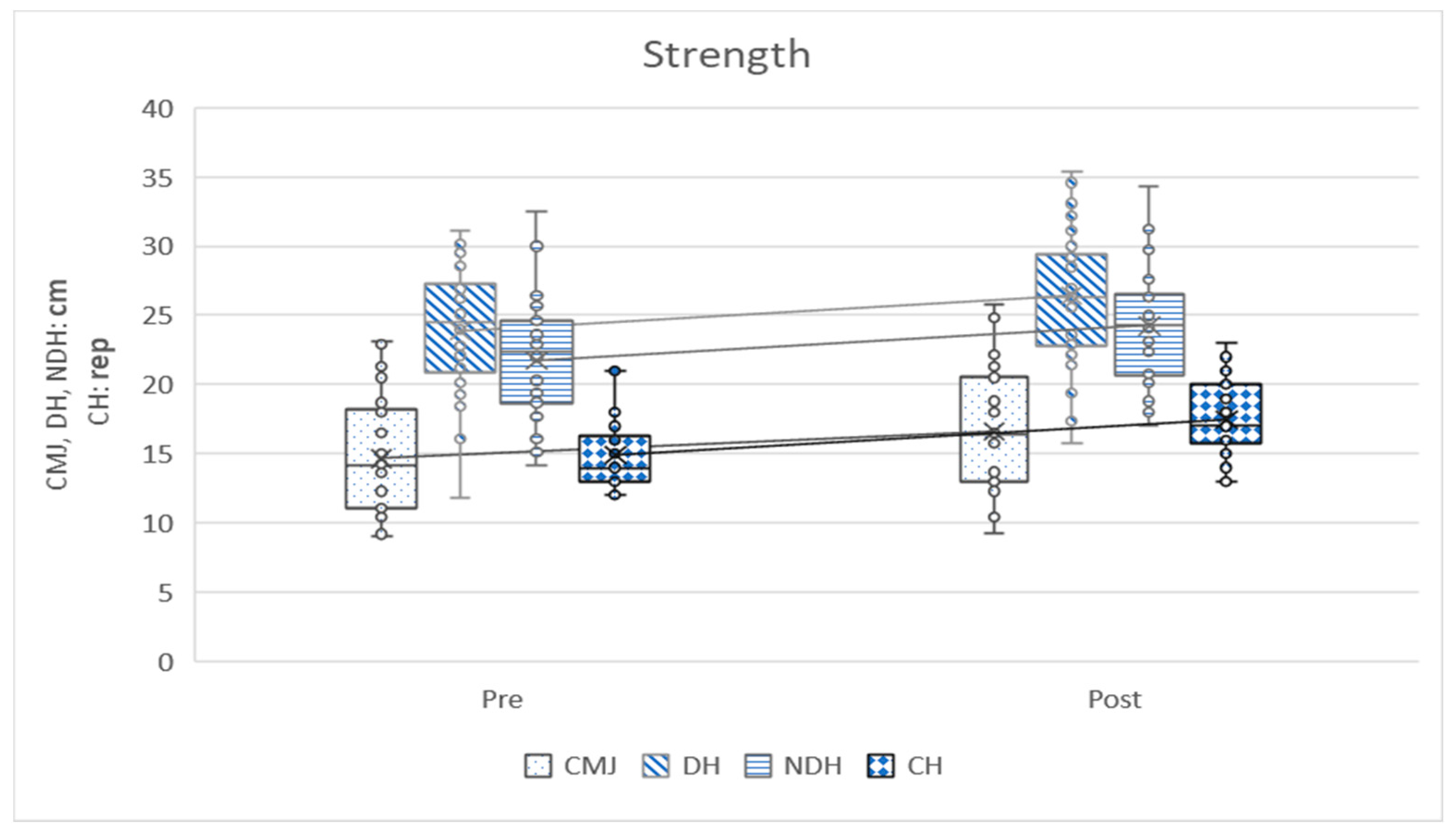
| Counter movement jump test (cm) | 14.67 ± 4.30 | 16.58 ± 4.28 | 1.91 ± 1.71 | 6.128 | 1.12 | 0.000 ** |
| Dominant hand grip test (kgf) | 23.89 ± 4.56 | 26.44 ± 5.00 | 2.54 ± 1.56 | 8.933 | 1.63 | 0.000 ** |
| Non-dominant hand grip test (kgf) | 21.73 ± 4.37 | 24.26 ± 4.06 | 2.53 ± 1.91 | 7.229 | 1.32 | 0.000 ** |
| Chair stand test (rep) | 14.90 ± 2.41 | 17.46 ± 2.75 | 2.56 ± 1.71 | 8.194 | 1.50 | 0.000 ** |
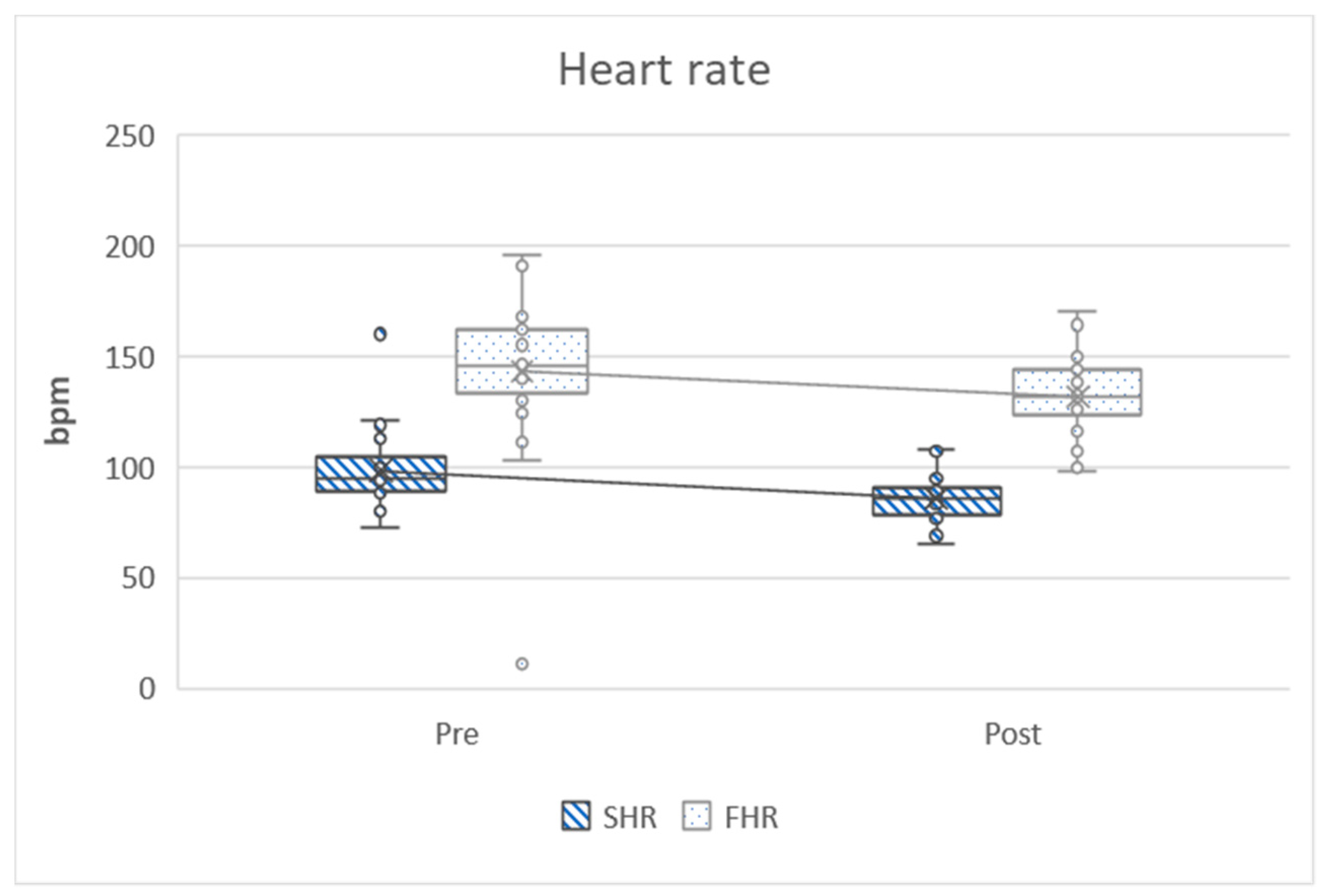
| Starting heart rate at six-minute walking test (bpm) | 98.43 ± 16.72 | 85.80 ± 9.79 | −12.63 ± 14.68 | −4.712 | 0.86 | 0.000 ** |
| Final heart rate at six-minute walking test (bpm) | 143.26 ± 32.64 | 131.80 ± 18.62 | −11.46 ± 28.39 | −2.212 | 0.40 | 0.000 ** |
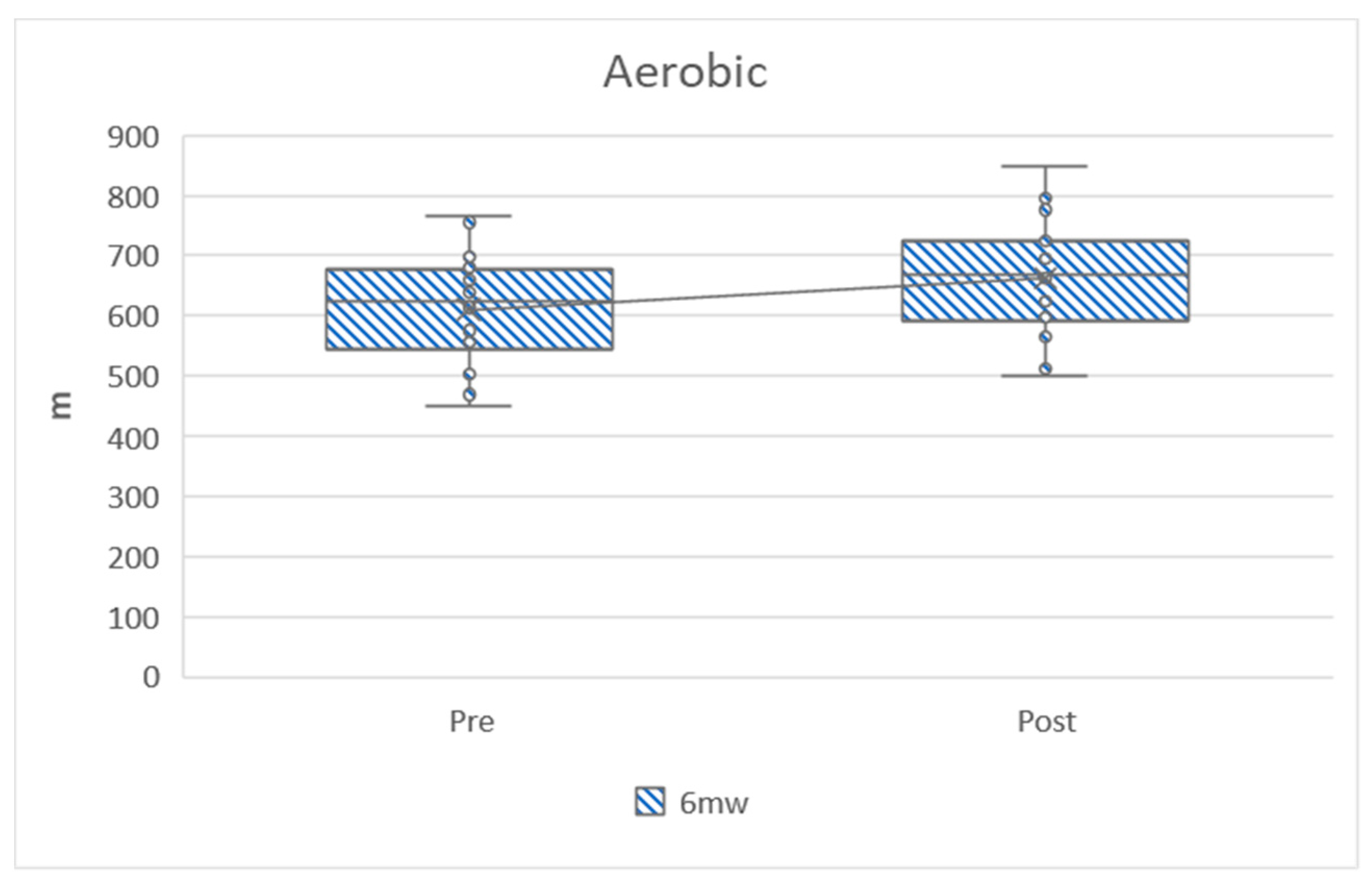
| Distance in six-minute walking test (m) | 611.23 ± 87.01 | 662.80 ± 85.82 | 51.56 ± 48.26 | 5.852 | 1.07 | 0.000 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gavala-González, J.; Gálvez-Fernández, I.; Mercadé-Melé, P.; Fernández-García, J.C. Rowing Training in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Longitudinal Study of Physical Fitness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144938
Gavala-González J, Gálvez-Fernández I, Mercadé-Melé P, Fernández-García JC. Rowing Training in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Longitudinal Study of Physical Fitness. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(14):4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144938
Chicago/Turabian StyleGavala-González, Juan, Ismael Gálvez-Fernández, Pere Mercadé-Melé, and José Carlos Fernández-García. 2020. "Rowing Training in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Longitudinal Study of Physical Fitness" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 14: 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144938
APA StyleGavala-González, J., Gálvez-Fernández, I., Mercadé-Melé, P., & Fernández-García, J. C. (2020). Rowing Training in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Longitudinal Study of Physical Fitness. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(14), 4938. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144938






