Assessment of Noise Exposure and Its Characteristics in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
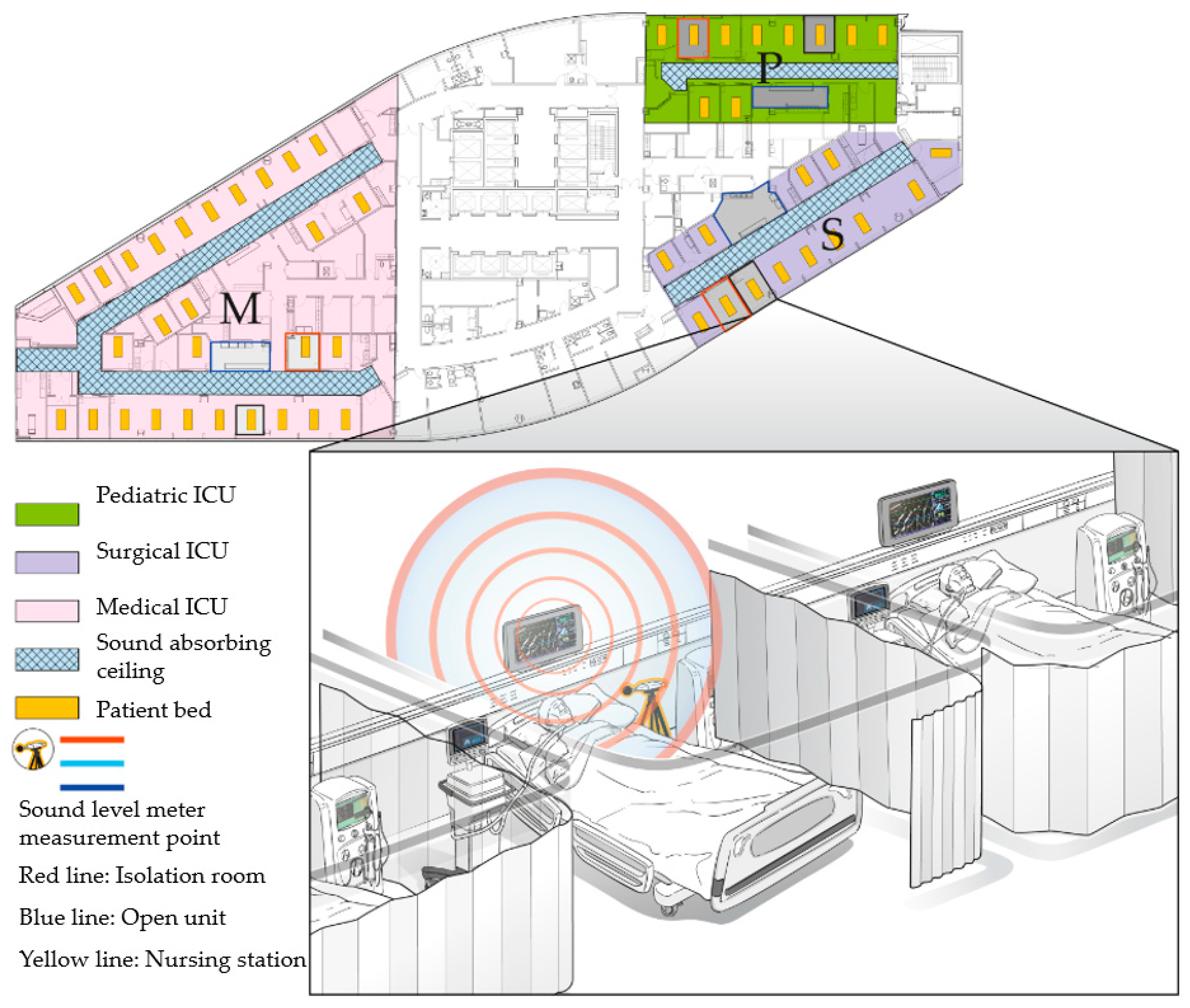
2.1. SPL Measurements
2.2. SPL Analysis and Evaluation Method
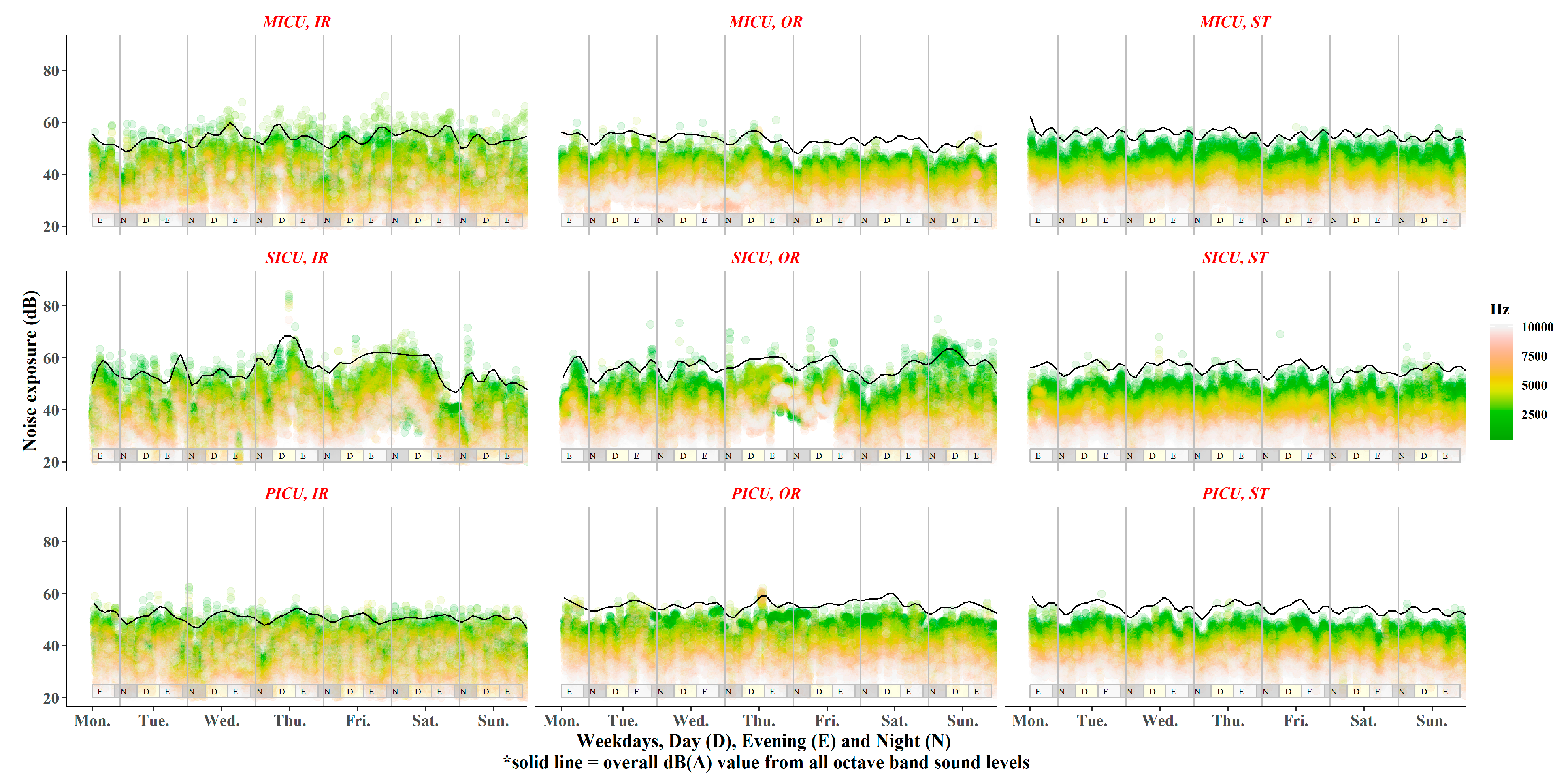
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konkani, A.; Oakley, B. Noise in hospital intensive care units––A critical review of a critical topic. J. Crit. Care 2012, 27, 522-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basner, M.; Babisch, W.; Davis, A.; Brink, M.; Clark, C.; Janssen, S.; Stansfeld, S. Auditory and non–auditory effects of noise on health. Lancet 2014, 383, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwela, D. World Health Organization Guidelines on Community Noise; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, J.H.; Roh, J.; Kim, C.N.; Won, J.U. The risk of occupational injury increased according to severity of noise exposure after controlling for occupational environment status in Korea. Noise Health 2016, 18, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Barach, P.; Dwaihy, M.; Kamat, D.; Shankaran, S.; Panaitescu, B.; Wang, B.; Natarajan, G. A targeted noise reduction observational study for reducing noise in a neonatal intensive unit. J. Perinatol. 2017, 37, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGough, N.N.H.; Keane, T.; Uppal, A.; Dumlao, M.; Rutherford, W.; Kellogg, K.; Ward, E.; Kendal, C.; Fields, W. Noise reduction in progressive care units. J. Nurs. Care Qual. 2018, 33, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tainter, C.R.; Levine, A.R.; Quraishi, S.A.; Butterly, A.D.; Stahl, D.L.; Eikermann, M.; Kaafarani, H.M.; Lee, J. Noise levels in surgical icus are consistently above recommended standards. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 44, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbyshire, J.L.; Muller–Trapet, M.; Cheer, J.; Fazi, F.M.; Young, J.D. Mapping sources of noise in an intensive care unit. Anaesthesia 2019, 74, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.; Dudaryk, R.; Crenshaw, N.; Edworthy, J.; McNeer, R. Recommendation of new medical alarms based on audibility, identifiability, and detectability in a randomized, simulation–based study. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 47, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardsson, L.; Nilsson, E. Noise disturbances in daycare centers before and after acoustical treatment. J. Environ. Health 2013, 75, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guisasola–Rabes, M.; Solà–Enriquez, B.; Vélez–Pereira, A.M.; de Nadal, M. Effectiveness of a visual noise warning system on noise levels in a surgical icu: A quality improvement programme. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2019, 36, 857–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumey, F.; Benarrous, E.; Souquet, L.; Rousset, B.; Soares, J.; Oltra–Gay, C.; Laville, M. Effets du traitement acoustique d’une salle de dialyse sur la qualité de vie des patients. Néphrol. Thér. 2019, 15, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lira Lixandrão, K.C.; Ferreira, F.F. Polypropylene and tire powder composite for use in automotive industry. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.W.; Skrobik, Y.; Gelinas, C.; Needham, D.M.; Slooter, A.J.C.; Pandharipande, P.P.; Watson, P.L.; Weinhouse, G.L.; Nunnally, M.E.; Rochwerg, B.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of pain, agitation/sedation, delirium, immobility, and sleep disruption in adult patients in the icu. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, e825–e873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czaplik, M.; Rossaint, R.; Kaliciak, J.; Follmann, A.; Kirfel, S.; Scharrer, R.; Guski, M.; Vorlander, M.; Marx, G.; Coburn, M. Psychoacoustic analysis of noise and the application of earplugs in an icu: A randomised controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2016, 33, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konkani, A.; Oakley, B.; Penprase, B. Reducing hospital icu noise: A behavior–based approach. J. Healthcare Eng. 2014, 5, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luetz, A.; Weiss, B.; Penzel, T.; Fietze, I.; Glos, M.; Wernecke, K.D.; Bluemke, B.; Dehn, A.M.; Willemeit, T.; Finke, A.; et al. Feasibility of noise reduction by a modification in icu environment. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| 24 h | Day | Evening | Night | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MICU | IR | 51.6 (48.5–58.9) | 53.2 (49.5–59.1) | 52.5 (48.9–59.8) | 49.3 (47.8–56.9) |
| OU | 53.2 (51.0–55.4) | 53.8 (51.8–55.9) | 53.8 (51.9–55.9) | 51.5 (49.7–53.8) | |
| NS | 55.4 (52.9–57.7) | 56.0 (53.5–58.1) | 55.6 (53.6–57.8) | 54.4 (51.6–57.0) | |
| Total | 53.8 (50.6–57.0) | 54.6 (51.6–57.4) | 54.3 (51.5–57.4) | 52.0 (49.2–55.9) | |
| SICU | IR | 51.9 (47.5–58.0) | 53.4 (48.6–61.9) | 51.3 (47.4–56.6) | 51.2 (47.1–56.1) |
| OU | 56.5 (53.9–59.9) | 57.6 (55.0–61.1) | 57.3 (54.7–60.2) | 54.4 (51.7–57.1) | |
| NS | 56.0 (53.8–58.4) | 56.9 (55.2–59.2) | 56.6 (54.6–58.8) | 53.9 (52.0–56.3) | |
| Total | 55.4 (52.0–58.8) | 56.7 (53.6–60.2) | 55.9 (52.8–59.0) | 53.4 (50.5–56.6) | |
| PICU | IR | 49.7 (47.1–54.3) | 50.5 (48.0–55.3) | 50.5 (47.8–55.2) | 47.8 (45.5–52.0) |
| OU | 55.4 (53.6–57.4) | 56.0 (54.0–58.1) | 55.9 (54.3–57.6) | 54.2 (52.3–56.4) | |
| NS | 54.6 (52.2–56.6) | 55.5 (53.8–57.3) | 54.7 (52.3–56.9) | 53.0 (50.9–55.2) | |
| Total | 54.1 (50.7–56.7) | 54.9 (52.1–57.2) | 54.5 (51.2–57.0) | 52.6 (49.1–55.3) | |
| Total | IR | 51.0 (47.8–57.1) | 52.4 (48.7–58.2) | 51.2 (48.2–57.4) | 49.4 (47.0–54.6) |
| OU | 54.9 (52.6–57.5) | 55.8 (53.5–58.3) | 55.6 (53.5–57.9) | 53.5 (51.0–56.0) | |
| NS | 55.3 (52.9–57.6) | 56.1 (54.2–58.2) | 55.7 (53.5–57.9) | 53.7 (51.5–56.2) | |
| Total | 54.4 (51.1–57.5) | 55.4 (52.3–58.2) | 54.9 (51.7–57.8) | 52.7 (49.6–56.0) |
| Noise Exposure (Unit: dB) | MICU | SICU | PICU | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 h | Day | Evening | Night | 24 h | Day | Evening | Night | 24 h | Day | Evening | Night | ||
| IR | <30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| <40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| <50 | 69.00 | 60.70 | 67.70 | 78.90 | 68.10 | 66.20 | 73.40 | 75.80 | 76.50 | 73.00 | 75.40 | 84.90 | |
| <60 | 23.60 | 30.80 | 24.20 | 14.70 | 20.60 | 23.90 | 19.30 | 18.50 | 19.80 | 23.00 | 20.70 | 12.40 | |
| ≥60 | 7.40 | 8.50 | 8.20 | 6.40 | 10.70 | 7.90 | 7.20 | 4.90 | 3.70 | 4.10 | 3.90 | 2.70 | |
| OU | <30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| <40 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| <50 | 45.50 | 40.90 | 49.10 | 61.90 | 27.90 | 19.90 | 21.00 | 41.60 | 13.50 | 9.80 | 11.10 | 24.00 | |
| <60 | 49.50 | 54.20 | 46.50 | 35.20 | 56.90 | 59.90 | 59.90 | 50.20 | 77.30 | 79.30 | 81.20 | 70.70 | |
| ≥60 | 4.90 | 4.90 | 4.40 | 2.70 | 15.20 | 20.20 | 19.10 | 8.30 | 9.30 | 10.90 | 7.70 | 5.30 | |
| NS | <30 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| <40 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| <50 | 41.40 | 34.70 | 44.60 | 53.10 | 36.80 | 22.50 | 31.80 | 53.10 | 44.30 | 32.60 | 49.50 | 59.90 | |
| <60 | 50.10 | 54.80 | 46.80 | 39.80 | 53.80 | 63.30 | 58.90 | 40.90 | 49.40 | 59.50 | 45.40 | 36.10 | |
| ≥60 | 8.60 | 10.40 | 8.10 | 7.20 | 9.40 | 14.10 | 9.30 | 6.00 | 6.30 | 7.80 | 5.10 | 4.00 | |
| Medical Device | Type of Noise | Peak Hz | SPL Range (Min–Max) | SPL Average (Leq) | Pattern Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient monitor (Philips IntelliVue) | INOP alarm | 160 | 42.9 67.5 | 62.8 | 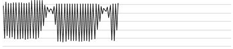 |
| Yellow alarm | 160 | 45.5 69.3 | 63.5 |  | |
| Red alarm | 630 | 76.0 84.9 | 80.7 |  | |
| Oxygen supply via facial tent mask | Low flow (60%, 5 L/min) | 400 | 63.2 66.0 | 64.3 |  |
| High flow (80%, 10 L/min) | 500 | 69.3 71.4 | 70.4 | 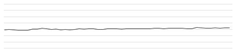 | |
| Syringe pump (Terumo®) | INOP alarm | 250 | 60.8 68.7 | 66.8 | 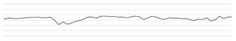 |
| Yellow alarm | 250 | 55.7 67.8 | 63.4 | 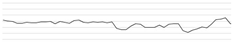 | |
| Pneumatic compression device | Normal operation | 250 | 43.9 51.6 | 46.9 |  |
| Nebulizer | Ventilator connection | 200 | 48.5 70.9 | 58.1 | 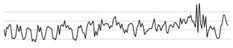 |
| Endotracheal suction | Preparation & procedure | 200 | 57.2 67.2 | 59.5 | 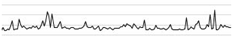 |
| Wall suction | Normal operation | 500 | 58.1 59.9 | 58.7 |  |
| Obstruction | 500 | 78.2 91.6 | 86.4 |  | |
| Warmer | Bair warmer | 200 | 55.1 61.5 | 57.0 | 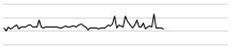 |
| Ventilator | Alarm | 500 | 78.6 82.7 | 80.7 | 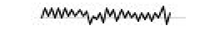 |
| Normal operation | 160 | 48.0 53.3 | 50.2 |  | |
| Respiratory physiotherapy | Normal operation | 200 | 64.9 67.5 | 67.1 |  |
| Continuous renal replacement therapy | INOP alarm | 400 | 49.1 63.0 | 58.3 |  |
| Yellow alarm | 315 | 47.9 62.4 | 58.0 |  |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Rhee, C.; Na, S.; Yoon, J.-H. Assessment of Noise Exposure and Its Characteristics in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134670
Jung S, Kim J, Lee J, Rhee C, Na S, Yoon J-H. Assessment of Noise Exposure and Its Characteristics in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(13):4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134670
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Seungho, Jeongmin Kim, Jiho Lee, Chooljae Rhee, Sungwon Na, and Jin-Ha Yoon. 2020. "Assessment of Noise Exposure and Its Characteristics in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 13: 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134670
APA StyleJung, S., Kim, J., Lee, J., Rhee, C., Na, S., & Yoon, J.-H. (2020). Assessment of Noise Exposure and Its Characteristics in the Intensive Care Unit of a Tertiary Hospital. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(13), 4670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17134670





