Obesity in Young Adulthood: The Role of Physical Activity Level, Musculoskeletal Pain, and Psychological Distress in Adolescence (The HUNT-Study)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
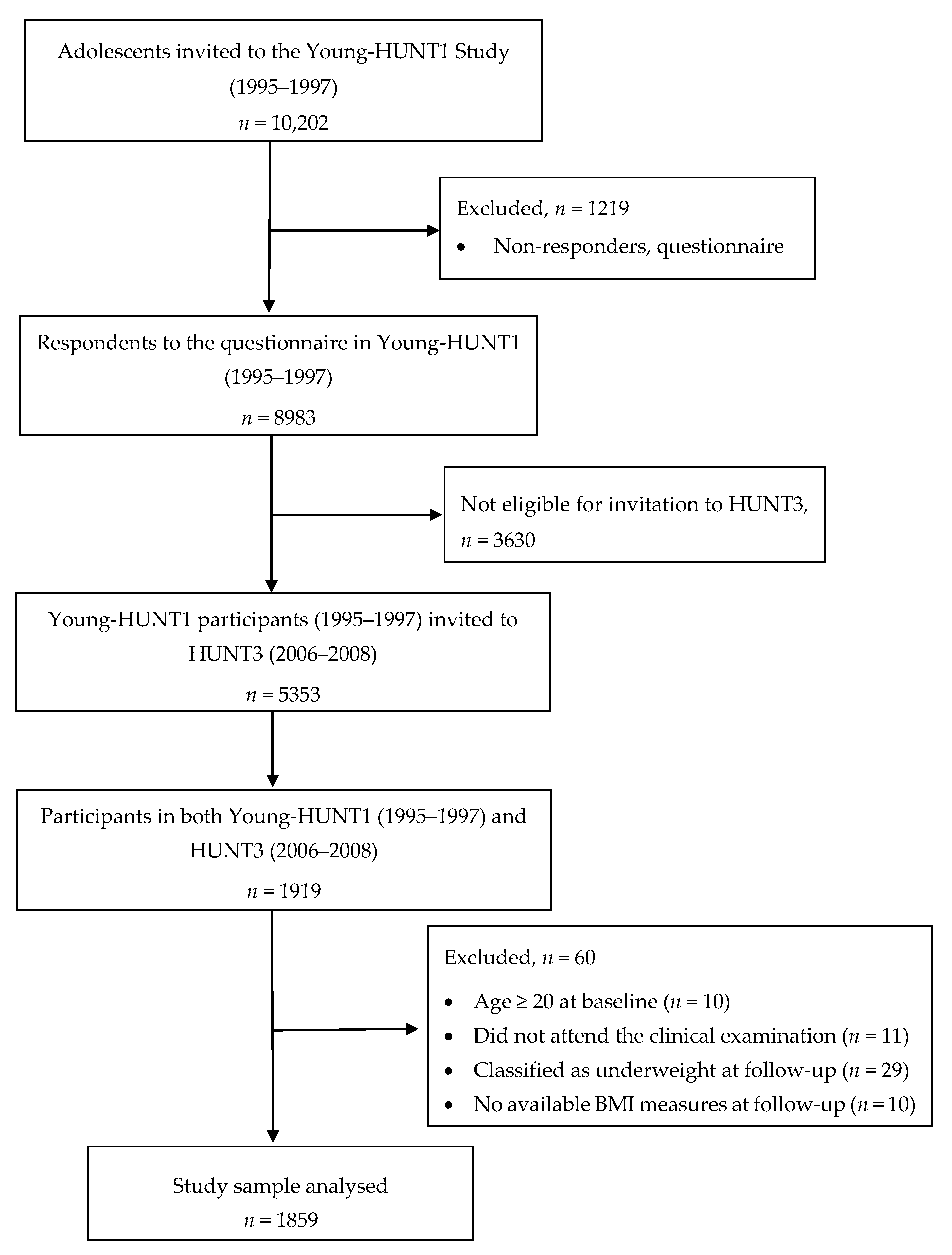
2.1. Study Sample
2.2. Variables
2.3. Exposures
2.3.1. Physical Activity Level (Young-HUNT1)
2.3.2. Musculoskeletal Pain (Young-HUNT1)
2.3.3. Psychological Distress (Young-HUNT1)
2.4. Outcome
Obesity (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) in Young Adulthood (at 11 Years Follow-Up, HUNT3)
2.5. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Sample
3.2. Probability of Obesity in Young Adulthood
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Girls | ||||||
| PA level | ||||||
| Low PA | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Moderate PA | 0.69 | 0.46–1.02 | 0.06 | 0.68 | 0.45–1.03 | 0.07 |
| High PA | 0.63 | 0.39–1.01 | 0.05 | 0.59 | 0.36–0.97 | 0.04 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.56 | 1.09–2.22 | 0.02 | 1.58 | 1.08–2.31 | 0.02 |
| Psychological distress * | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.46 | 0.88–2.42 | 0.15 | 1.11 | 0.65–1.90 | 0.71 |
| Boys | ||||||
| PA level | ||||||
| Low PA | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Moderate PA | 0.66 | 0.41–1.04 | 0.07 | 0.61 | 0.38–0.97 | 0.04 |
| High PA | 0∙45 | 0.27–0.75 | <0.01 | 0.43 | 0.26–0.72 | <0.01 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.26 | 0.82–0.93 | 0.28 | 1.28 | 0.83–1.97 | 0.27 |
| Psychological distress * | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.33 | 0.58–3.07 | 0.50 | - | - | |
| PA Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low PA | Moderate PA | High PA | ||
| MS pain | Psychol. distress | 35% | 27% | 24% |
| (20–50%) | (10–44%) | (5–43%) | ||
| No psychol. distress | 32% | 25% | 22% | |
| (23–41%) | (17–33%) | (12–32%) | ||
| No MS pain | Psychol. distress | 25% | 19% | 17% |
| (6–44%) | (0–41%) | (0–43%) | ||
| No psychol. distress | 23% | 17% | 15% | |
| (17–29%) | (13–21%) | (9–21%) | ||
| PA Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low PA | Moderate PA | High PA | |
| MS pain | 43% | 32% | 25% |
| (31–55%) | (22–42%) | (14–36%) | |
| No MS pain | 37% | 27% | 20% |
| (30–44%) | (21–33%) | (14–26%) | |
References
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swinburn, B.A.; Kraak, V.I.; Allender, S.; Atkins, V.J.; Baker, P.I.; Bogard, J.R.; Brinsden, H.; Calvillo, A.; De Schutter, O.; Devarajan, R.; et al. The Global Syndemic of Obesity, Undernutrition, and Climate Change: The Lancet Commission report. Lancet 2019, 393, 791–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberga, A.S.; Sigal, R.J.; Goldfield, G.; Prud’homme, D.; Kenny, G.P. Overweight and obese teenagers: Why is adolescence a critical period? Pediatric. Obes. 2012, 7, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, M.C.; Story, M.; Larson, N.I.; Neumark-Sztainer, D.; Lytle, L.A. Emerging adulthood and college-aged youth: An overlooked age for weight-related behavior change. Obesity (Silver Spring Md.) 2008, 16, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global trends in insufficient physical activity among adolescents: A pooled analysis of 298 population-based surveys with 1.6 million participants. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamper, S.J.; Henschke, N.; Hestbaek, L.; Dunn, K.M.; Williams, C.M. Musculoskeletal pain in children and adolescents. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2016, 20, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieling, C.; Baker-Henningham, H.; Belfer, M.; Conti, G.; Ertem, I.; Omigbodun, O.; Rohde, L.A.; Srinath, S.; Ulkuer, N.; Rahman, A. Child and adolescent mental health worldwide: Evidence for action. Lancet 2011, 378, 1515–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertha, E.A.; Balazs, J. Subthreshold depression in adolescence: A systematic review. Eur. Child. Adolesc. Psychiatry 2013, 22, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokdad, A.H.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Daoud, F.; Mokdad, A.A.; El Bcheraoui, C.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Kyu, H.H.; Barber, R.M.; Wagner, J.; Cercy, K.; et al. Global burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors for young people’s health during 1990-2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2016, 387, 2383–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, A.P.; Andersen, L.B.; Byrne, N.M. Physical activity and obesity in children. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 866–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnussen, C.G.; Smith, K.J.; Juonala, M. When to prevent cardiovascular disease? As early as possible: Lessons from prospective cohorts beginning in childhood. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2013, 28, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumith, S.C.; Gigante, D.P.; Domingues, M.R.; Kohl, H.W., 3rd. Physical activity change during adolescence: A systematic review and a pooled analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 40, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareham, N.J.; van Sluijs, E.M.; Ekelund, U. Physical activity and obesity prevention: A review of the current evidence. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2005, 64, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilks, D.C.; Besson, H.; Lindroos, A.K.; Ekelund, U. Objectively measured physical activity and obesity prevention in children, adolescents and adults: A systematic review of prospective studies. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2011, 12, e119–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narciso, J.; Silva, A.J.; Rodrigues, V.; Monteiro, M.J.; Almeida, A.; Saavedra, R.; Costa, A.M. Behavioral, contextual and biological factors associated with obesity during adolescence: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, R.C.; Angermeyer, M.; Anthony, J.C.; Graaf, R.D.E.; Demyttenaere, K.; Gasquet, I.; Girolamo, D.E.G.; Gluzman, S.; Gureje, O.; Haro, J.M.; et al. Lifetime prevalence and age-of-onset distributions of mental disorders in the World Health Organization’s World Mental Health Survey Initiative. World Psychiatry Off. J. World Psychiatr. Assoc. (WPA) 2007, 6, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Belfer, M.L. Child and adolescent mental disorders: The magnitude of the problem across the globe. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2008, 49, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, S.; Kopala-Sibley, D.C.; Noel, M. The Co-occurrence of Pediatric Chronic Pain and Depression: A Narrative Review and Conceptualization of Mutual Maintenance. Clin. J. Pain 2019, 35, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen, J.; Hancock, M.J.; Kongsted, A.; Louw, Q.; Ferreira, M.L.; Genevay, S.; Hoy, D.; Karppinen, J.; Pransky, G.; Sieper, J.; et al. What low back pain is and why we need to pay attention. Lancet 2018, 391, 2356–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegethoff, M.; Belardi, A.; Stalujanis, E.; Meinlschmidt, G. Comorbidity of Mental Disorders and Chronic Pain: Chronology of Onset in Adolescents of a National Representative Cohort. J. Pain Off. J. Am. Pain Soc. 2015, 16, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. GBD Compare. Available online: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/ (accessed on 29 October 2019).
- Roth-Isigkeit, A.; Thyen, U.; Stöven, H.; Schwarzenberger, J.; Schmucker, P. Pain among children and adolescents: Restrictions in daily living and triggering factors. Pediatrics 2005, 115, e152–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.C.; Samuelson, B.; Palermo, T.M. Obesity in children and adolescents with chronic pain: Associations with pain and activity limitations. Clin. J. Pain 2010, 26, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Murtaugh, T.; Pantaleao, A.; Zempsky, W.T.; Guite, J.W. Chronic Pain and Obesity Within a Pediatric Interdisciplinary Pain Clinic Setting: A Preliminary Examination of Current Relationships and Future Directions. Clin. J. Pain 2017, 33, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaine, B. Does depression cause obesity?: A meta-analysis of longitudinal studies of depression and weight control. J. Health Psychol. 2008, 13, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luppino, F.S.; de Wit, L.M.; Bouvy, P.F.; Stijnen, T.; Cuijpers, P.; Penninx, B.W.; Zitman, F.G. Overweight, obesity, and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, M.; Mamun, A.; Doi, S.; Clavarino, A. Prospective Associations between Depression and Obesity for Adolescent Males and Females- A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamosi, M.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kyvik, K.O. The relation between an adverse psychological and social environment in childhood and the development of adult obesity: A systematic literature review. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2010, 11, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poobalan, A.; Aucott, L. Obesity Among Young Adults in Developing Countries: A Systematic Overview. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2016, 5, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihrauch-Blüher, S.; Kromeyer-Hauschild, K.; Graf, C.; Widhalm, K.; Korsten-Reck, U.; Jödicke, B.; Markert, J.; Müller, M.J.; Moss, A.; Wabitsch, M.; et al. Current Guidelines for Obesity Prevention in Childhood and Adolescence. Obes. Facts 2018, 11, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pate, R.R.; O’Neill, J.R.; Liese, A.D.; Janz, K.F.; Granberg, E.M.; Colabianchi, N.; Harsha, D.W.; Condrasky, M.M.; O’Neil, P.M.; Lau, E.Y.; et al. Factors associated with development of excessive fatness in children and adolescents: A review of prospective studies. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2013, 14, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Street, S.J.; Wells, J.C.; Hills, A.P. Windows of opportunity for physical activity in the prevention of obesity. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2015, 16, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doak, C.M.; Visscher, T.L.; Renders, C.M.; Seidell, J.C. The prevention of overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: A review of interventions and programmes. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2006, 7, 111–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patton, G.C.; Sawyer, S.M.; Santelli, J.S.; Ross, D.A.; Afifi, R.; Allen, N.B.; Arora, M.; Azzopardi, P.; Baldwin, W.; Bonell, C.; et al. Our future: A Lancet commission on adolescent health and wellbeing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2423–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, T.L.; Bratberg, G.; Krokstad, S.; Langhammer, A.; Hveem, K.; Midthjell, K.; Heggland, J.; Holmen, J. Cohort profile of the Young-HUNT Study, Norway: A population-based study of adolescents. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krokstad, S.; Langhammer, A.; Hveem, K.; Holmen, T.L.; Midthjell, K.; Stene, T.R.; Bratberg, G.; Heggland, J.; Holmen, J. Cohort Profile: The HUNT Study, Norway. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norway, S. Student Life and Economic Conditions. Norwegian Results from Eurostudent V in a European Perspective; Statistics Norway: Oslo, Norway, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J.; Lobstein, T. Extended international (IOTF) body mass index cut-offs for thinness, overweight and obesity. Pediatric Obes. 2012, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangul, V.; Holmen, T.L.; Kurtze, N.; Cuypers, K.; Midthjell, K. Reliability and validity of two frequently used self-administered physical activity questionnaires in adolescents. BMC Med Res. Methodol. 2008, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.H.; Dalgard, O.S.; Tambs, K.; Rognerud, M. Measuring the mental health status of the Norwegian population: A comparison of the instruments SCL-25, SCL-10, SCL-5 and MHI-5 (SF-36). Nordic J. Psychiatry 2003, 57, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietilainen, K.H.; Kaprio, J.; Borg, P.; Plasqui, G.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Kujala, U.M.; Rose, R.J.; Westerterp, K.R.; Rissanen, A. Physical inactivity and obesity: A vicious circle. Obesity (Silver Spring Md.) 2008, 16, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmorstein, N.R.; Iacono, W.G.; Legrand, L. Obesity and depression in adolescence and beyond: Reciprocal risks. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2014, 38, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, S.; Rajendran, S.; Anand, K.; Chockalingam, A. Self-reported depressive symptoms in adolescence increase the risk for obesity and high BP in adulthood. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 269, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eime, R.M.; Young, J.A.; Harvey, J.T.; Charity, M.J.; Payne, W.R. A systematic review of the psychological and social benefits of participation in sport for children and adolescents: Informing development of a conceptual model of health through sport. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.B.; Allan, V.; Erickson, K.; Martin, L.J.; Budziszewski, R.; Cote, J. Are all sport activities equal? A systematic review of how youth psychosocial experiences vary across differing sport activities. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, M.L.; Okely, A.D.; Chey, T.; Bauman, A. The reliability and validity of the physical activity questions in the WHO health behaviour in schoolchildren (HBSC) survey: A population study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2001, 35, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Girls (N = 1049) | Boys (N = 810) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 16.0 (1∙8) | 16.0 (1.8) | |
| Physical activity, N (%) | |||
| High PA | 245 (23.4) | 239 (29.5) | |
| Moderate PA | 449 (42.8) | 321 (39.6) | |
| Low PA | 347 (33.1) | 237 (29.3) | 0.005 * |
| Missing | 8 (0.8) | 13 (1.6) | |
| Musculoskeletal pain, N (%) | |||
| Yes | 379 (36.1) | 213 (26.3) | |
| No | 638 (60.8) | 568 (70.1) | p < 0.001 |
| Missing | 32 (3.1) | 29 (3.6) | |
| Psychological distress, (SCL5), N (%) | |||
| SCL5 ≥ 2 | 123 (11.7) | 46 (5.7) | |
| SCL5 < 2 | 890 (84.8) | 735 (90.7) | p < 0.001 |
| Missing | 36 (3.4) | 29 (3.6) | |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 21.5 (3.2) | 21.1 (3.2) | 0.012 |
| Obese †, N (%) | 16 (1.5) | 24 (3.0) | 0.027 |
| Variables | Univariate Analysis | Multiple Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Girls | ||||||
| PA level | ||||||
| Low PA | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Moderate PA | 0.67 | 0.46–0.98 | 0.04 | 0.67 | 0.45–0.99 | 0.05 |
| High PA | 0.64 | 0.41–1.00 | 0.05 | 0.61 | 0.38–0.97 | 0.04 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.53 | 1.09–2.16 | 0.02 | 1.55 | 1.08–2.22 | 0.02 |
| Psychological distress * | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.41 | 0.87–2.28 | 0.17 | 1.09 | 0.65–1.82 | 0.76 |
| Boys | ||||||
| PA level | ||||||
| Low PA | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Moderate PA | 0.70 | 0.46–1.07 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 0.44–1.02 | 0.06 |
| High PA | 0.56 | 0.35–0.90 | 0.02 | 0.55 | 0∙35–0.89 | 0.02 |
| Musculoskeletal pain | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.30 | 0.88–1.93 | 0.19 | 1.30 | 0.87–1.93 | 0.20 |
| Psychological distress * | ||||||
| No | 1.0 (Reference) | 1.0 (Reference) | ||||
| Yes | 1.12 | 0.53–2.38 | 0.77 | - | - | |
| PA Level | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low PA | Moderate PA | High PA | ||
| MS pain | Psychol. distress | 25% | 18% | 17% |
| (11–39%) | (3–33%) | (1–33%) | ||
| No psychol. distress | 24% | 17% | 16% | |
| (15–33%) | (10–24%) | (8–24%) | ||
| No MS pain | Psychol. distress | 18% | 13% | 12% |
| (1–35%) | (0–32%) | (0–35%) | ||
| No psychol. distress | 17% | 12% | 11% | |
| (11–23%) | (8–16%) | (6–16%) | ||
| PA Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Low PA | Moderate PA | High PA | |
| MS pain | 27% | 20% | 17% |
| (16–38%) | (12–28%) | (7–27%) | |
| No MS pain | 22% | 16% | 14% |
| (16–28%) | (11–21%) | (9–19%) | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guddal, M.H.; Stensland, S.Ø.; Småstuen, M.C.; Johnsen, M.B.; Heuch, I.; Zwart, J.-A.; Storheim, K. Obesity in Young Adulthood: The Role of Physical Activity Level, Musculoskeletal Pain, and Psychological Distress in Adolescence (The HUNT-Study). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124603
Guddal MH, Stensland SØ, Småstuen MC, Johnsen MB, Heuch I, Zwart J-A, Storheim K. Obesity in Young Adulthood: The Role of Physical Activity Level, Musculoskeletal Pain, and Psychological Distress in Adolescence (The HUNT-Study). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(12):4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124603
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuddal, Maren Hjelle, Synne Øien Stensland, Milada Cvancarova Småstuen, Marianne Bakke Johnsen, Ingrid Heuch, John-Anker Zwart, and Kjersti Storheim. 2020. "Obesity in Young Adulthood: The Role of Physical Activity Level, Musculoskeletal Pain, and Psychological Distress in Adolescence (The HUNT-Study)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 12: 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124603
APA StyleGuddal, M. H., Stensland, S. Ø., Småstuen, M. C., Johnsen, M. B., Heuch, I., Zwart, J.-A., & Storheim, K. (2020). Obesity in Young Adulthood: The Role of Physical Activity Level, Musculoskeletal Pain, and Psychological Distress in Adolescence (The HUNT-Study). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(12), 4603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17124603






