Assessment of Air Pollution Aggravation during Straw Burning in Hubei, Central China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Straw Burning Information
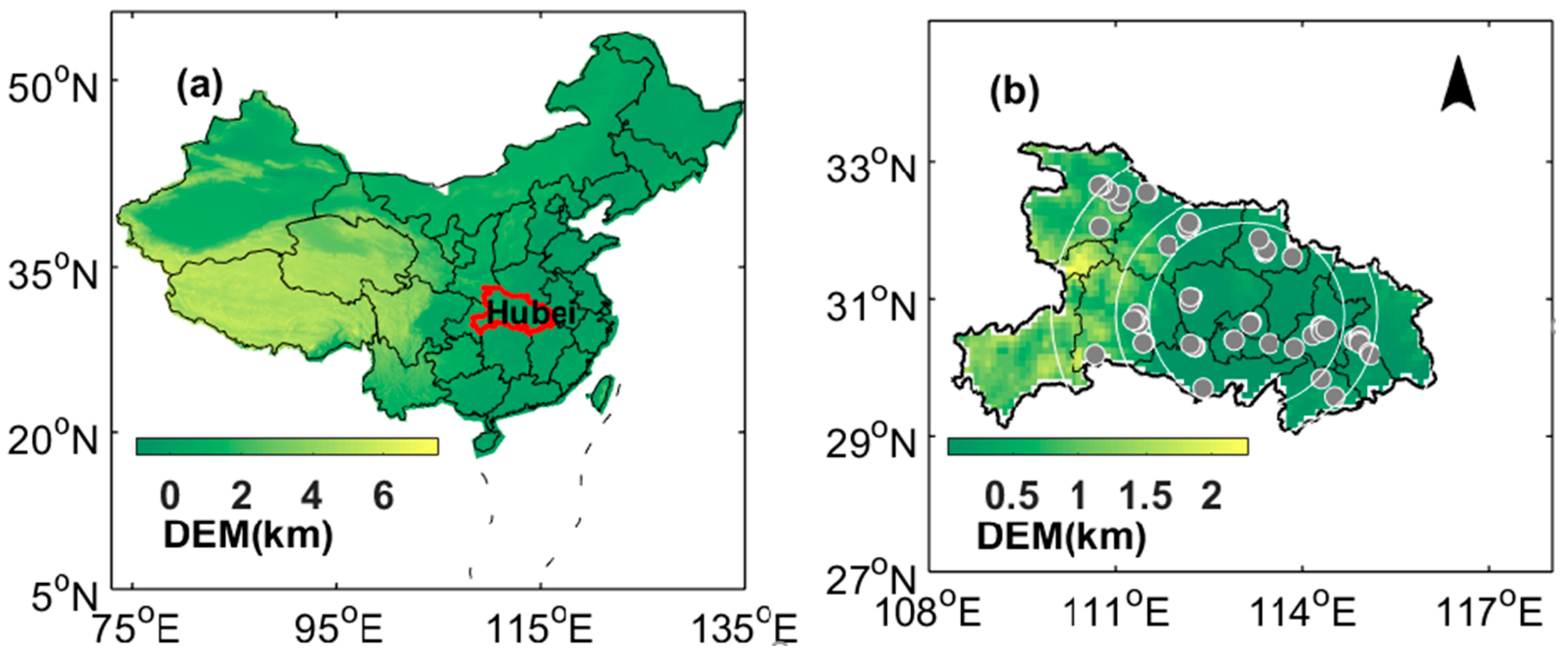
2.1.2. Sampling Site and Ambient Monitoring
2.1.3. Himawari-8 AOD Data
2.2. Methods
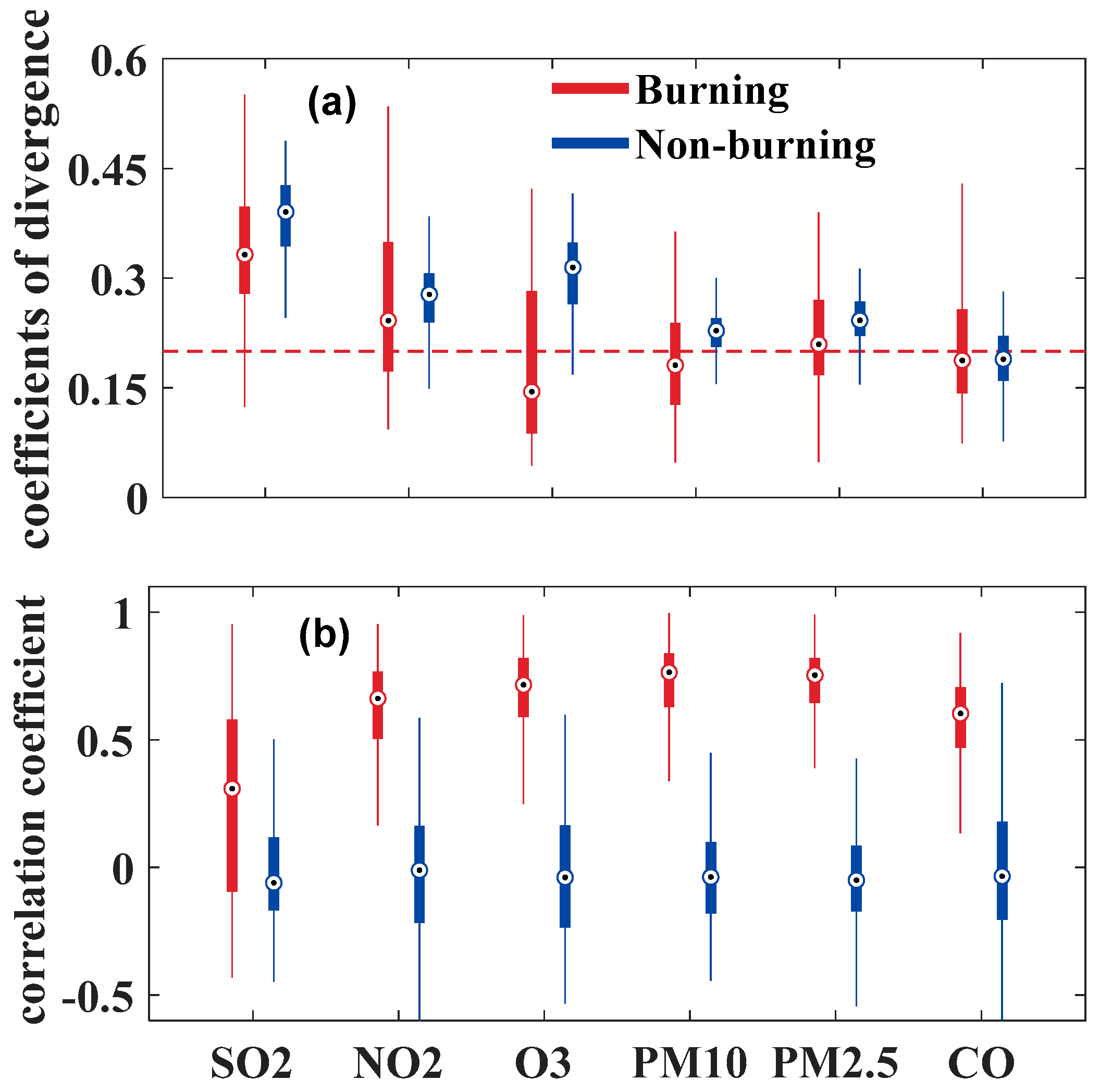
2.2.1. Correlation and Homogeneity Analysis
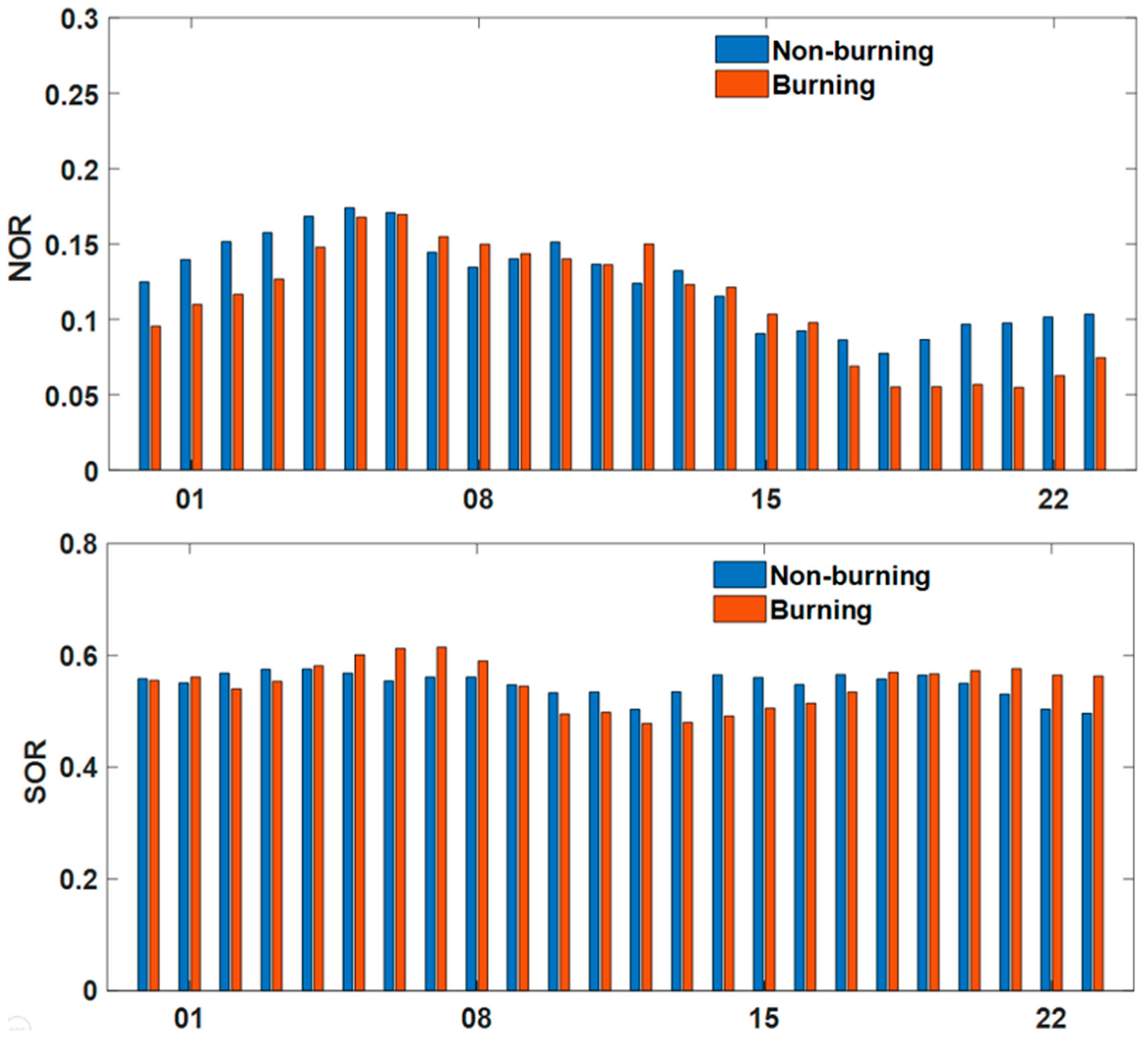
2.2.2. Evaluation of Secondary Aerosols’ Generation
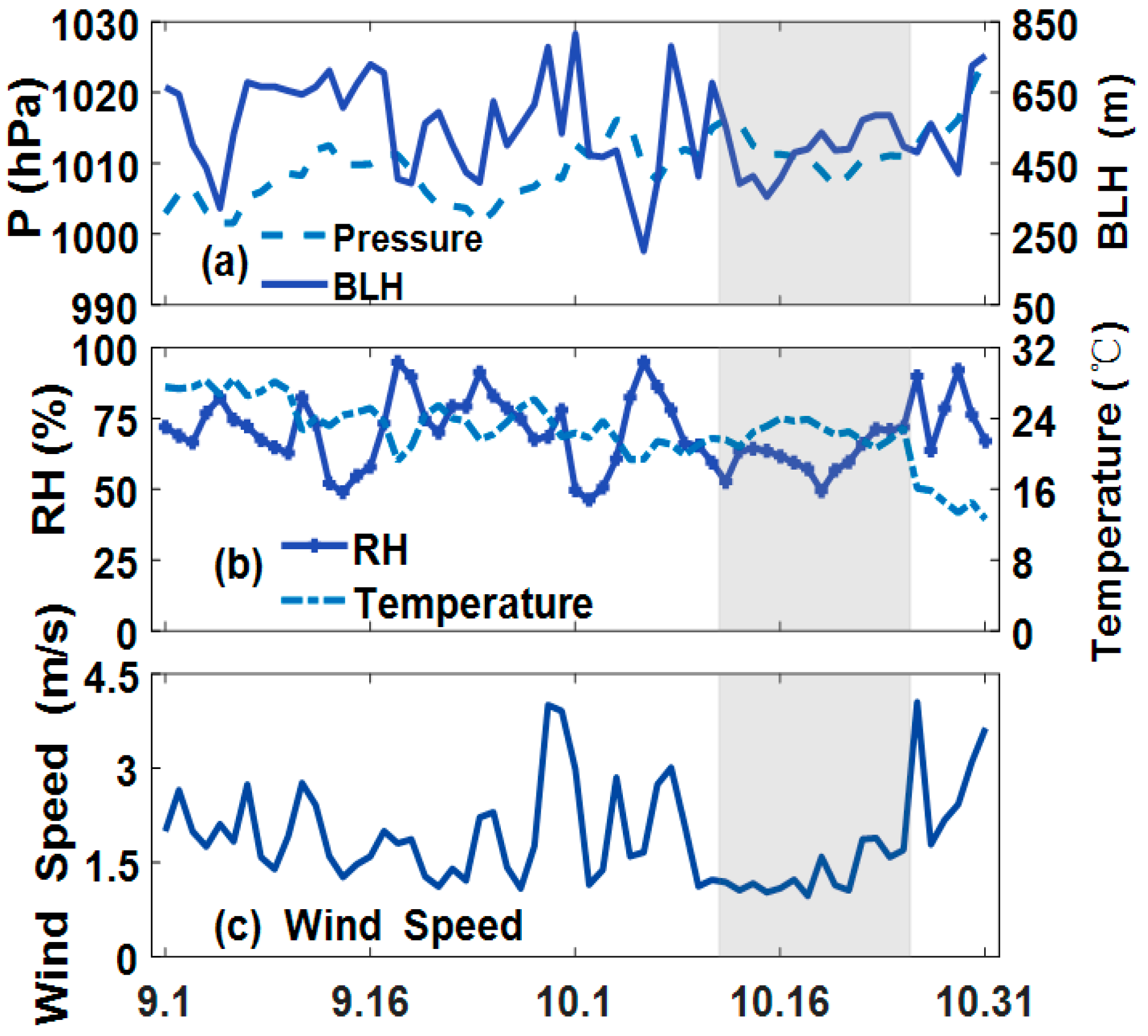
2.2.3. Evaluation of Meteorological Contribution
2.2.4. Pollutant Transport Analysis
3. Results
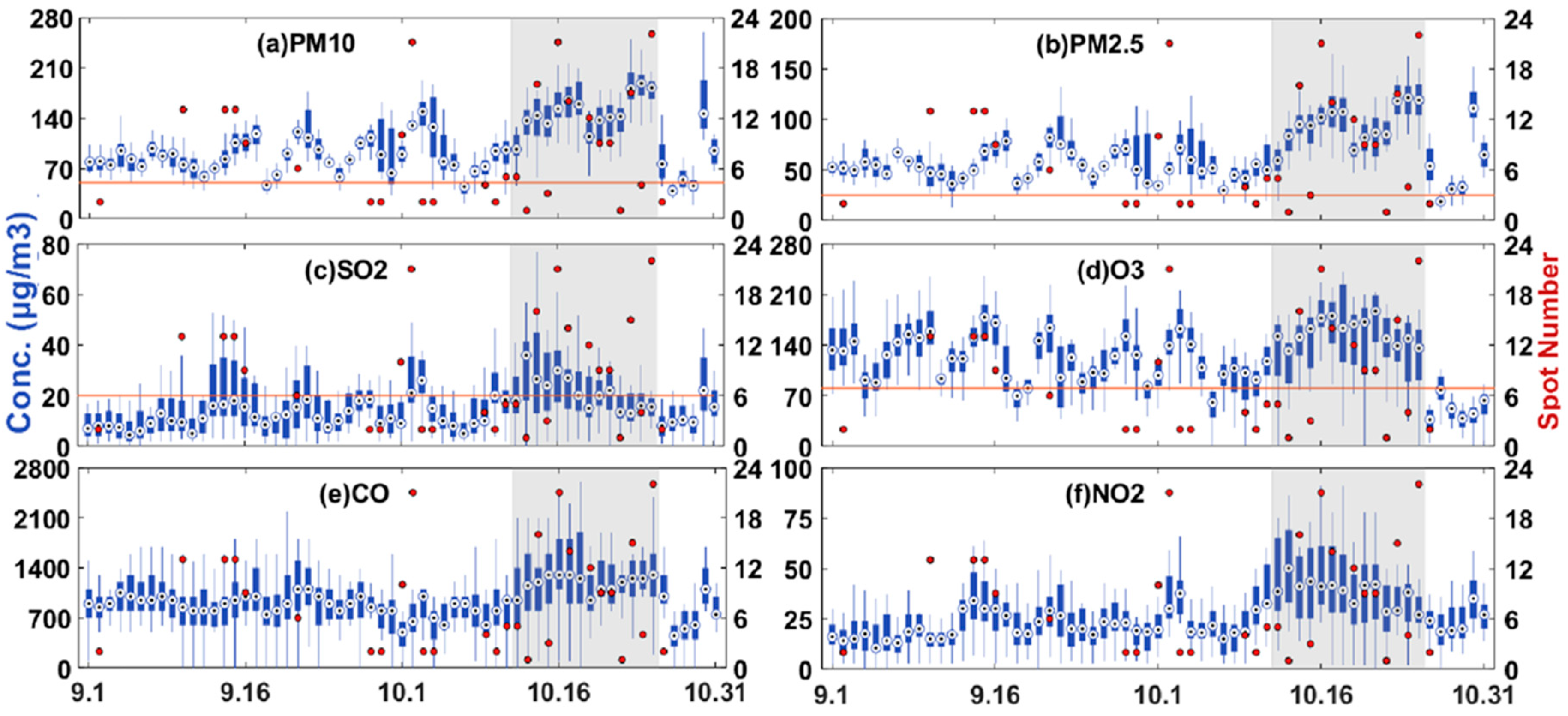
3.1. Daily Variation of Pollutants and Meteorological Conditions
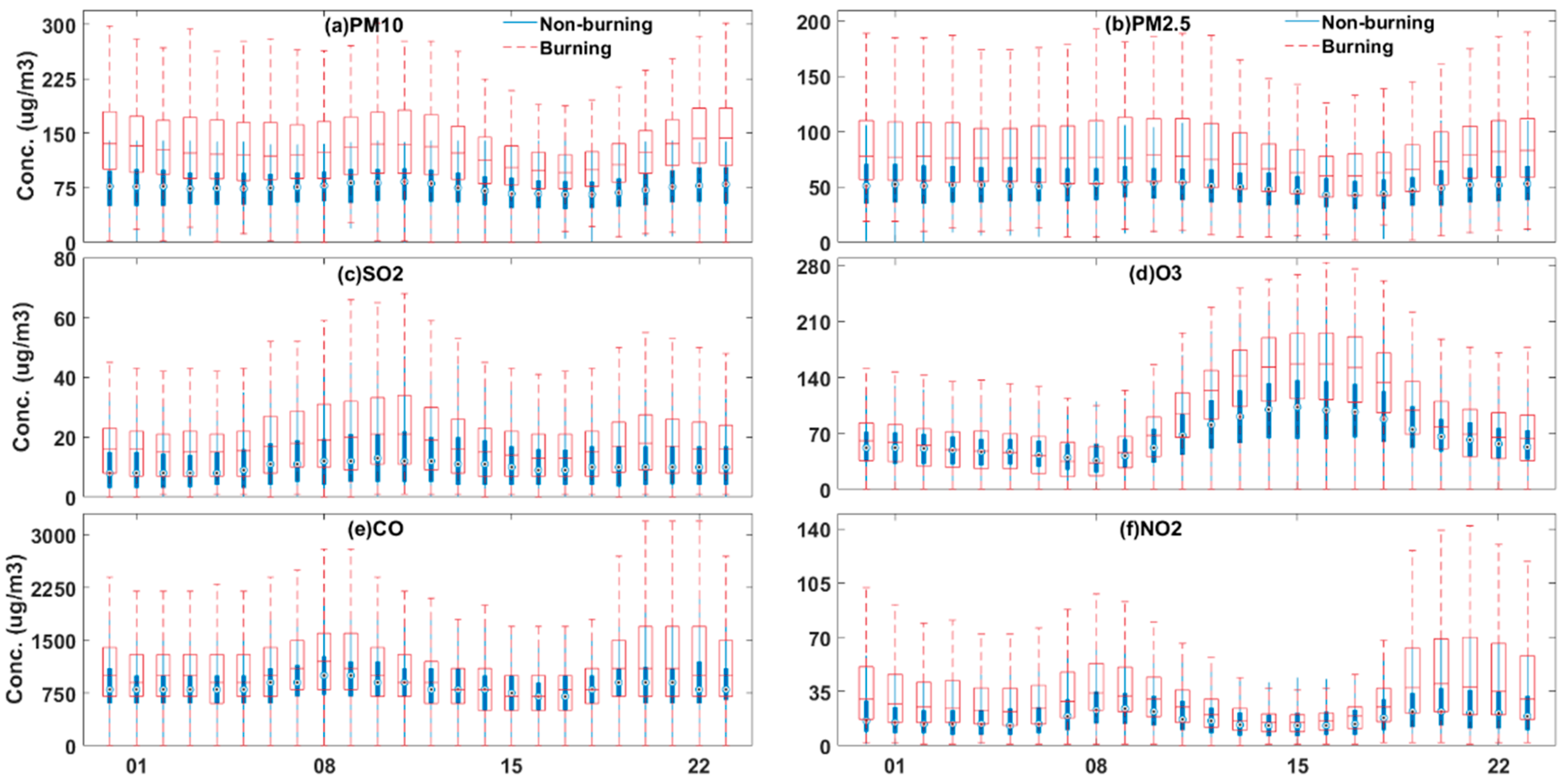
3.2. Diurnal Patterns of Pollutants for Burning and Non-Burning Periods
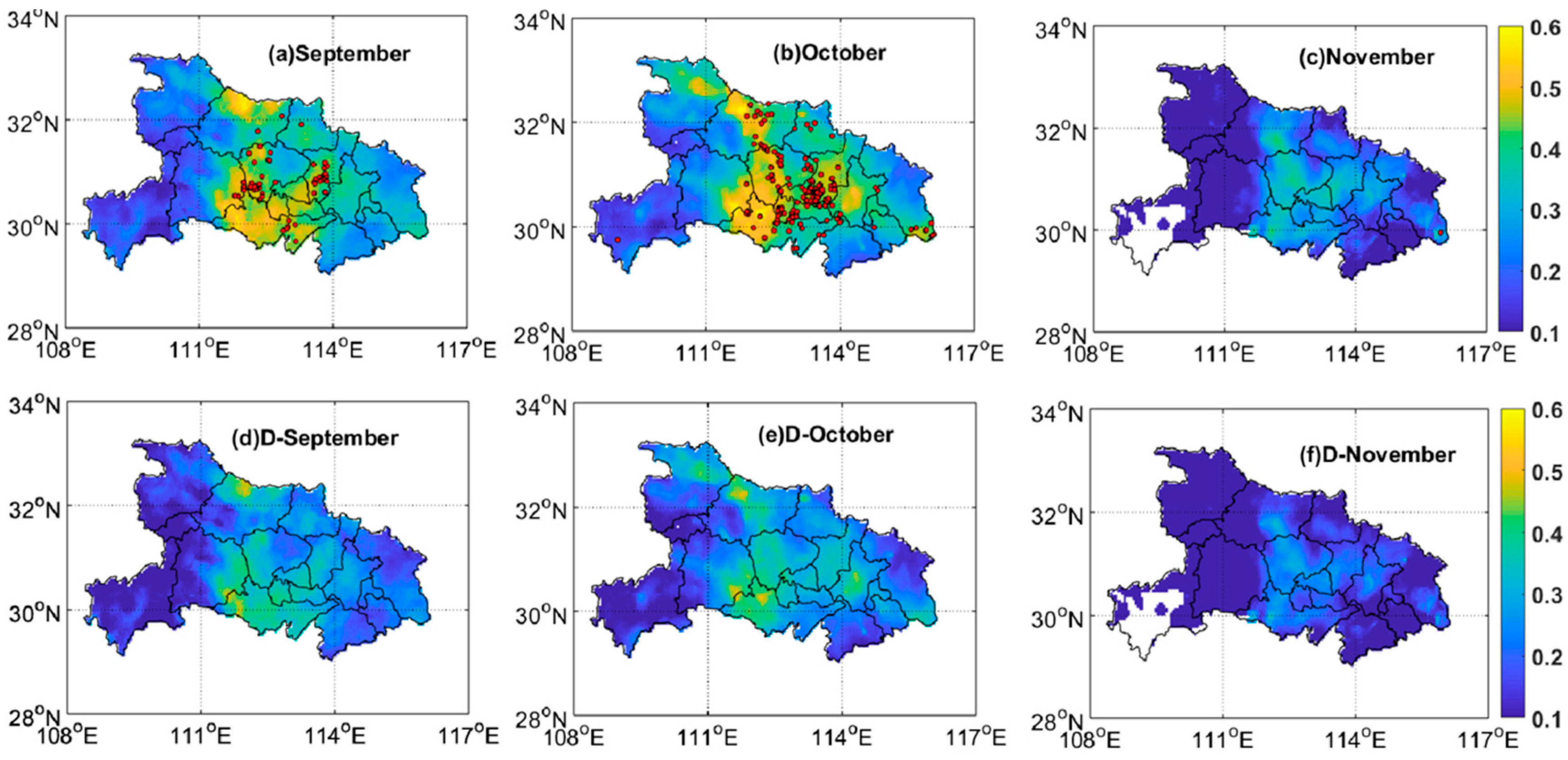
3.3. Spatial Variations of Air Pollutants
3.3.1. Overall Spatial Variations
3.3.2. Spatial Variations along with the Distance Buffer
3.4. Transport of Pollutants and Regional Effects
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1923–1994. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, F.Y.; Pan, Z.X.; Henderson, D.S.; Wang, W.; Gong, W. Vertically resolved physical and radiative response of ice clouds to aerosols during the indian summer monsoon season. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Watson, J.G.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Chow, J.C.; et al. Impact of biomass burning on haze pollution in the yangtze river delta, China: A case study in summer 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4573–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.X.; Mao, F.Y.; Wang, W.; Logan, T.; Hong, J. Examining intrinsic aerosol-cloud interactions in South Asia through multiple satellite observations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 11210–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Mao, F.Y.; Guo, J.P.; Gong, W.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z.X. Estimating hourly pm1 concentrations from himawari-8 aerosol optical depth in China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Mao, F.Y.; Pan, Z.X.; Gong, W.; Wang, W.; Tian, L.Q.; Fang, S.H. Three-dimensional physical and optical characteristics of aerosols over central china from long-term calipso and hysplit data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.X.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, W.; Li, C.; Min, Q.L. Macrophysical and optical properties of clouds over East Asia measured by calipso. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.M.; Li, C.L.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.T.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.X.; Hao, J.M.; Zhang, H.F.; He, C.R.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Fu, J.S.; Hsu, N.C.; Gao, Y.; Dong, X.Y.; Tsay, S.C.; Lam, Y.F. Impact assessment of biomass burning on air quality in Southeast and East Asia during Base-Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 78, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegesser, T.C.; Pinkerton, K.E.; Last, J.A. California wildfires of 2008: Coarse and fine particulate matter toxicity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeher, L.P.; Brauer, M.; Lipsett, M.; Zelikoff, J.T.; Simpson, C.D.; Koenig, J.Q.; Smith, K.R. Woodsmoke health effects: A review. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 67–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, C.E.; Brauer, M.; Johnston, F.H.; Jerrett, M.; Balmes, J.R.; Elliott, C.T. Critical review of health impacts of wildfire smoke exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Zerefos, C.; Kazadzis, S.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Eleftheratos, K.; Vrekoussis, M.; Stohl, A.; Mamouri, R.E.; Kokkalis, P.; Papayannis, A.; et al. Impact of the 2009 attica wild fires on the air quality in urban athens. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portin, H.; Mielonen, T.; Leskinen, A.; Arola, A.; Parjala, E.; Romakkaniemi, S.; Laaksonen, A.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Komppula, M. Biomass burning aerosols observed in Eastern finland during the russian wildfires in summer 2010-part 1: In-Situ aerosol characterization. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 47, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phairuang, W.; Hata, M.; Furuuchi, M. Influence of agricultural activities, forest fires and agro-industries on air quality in Thailand. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 52, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.R.; Miljevic, B.; Crilley, L.R.; Surawski, N.C.; Bartsch, J.; Salimi, F.; Uhde, E.; Schnelle-Kreis, J.; Orasche, J.; Ristovski, Z.; et al. Characterisation of the impact of open biomass burning on urban air quality in Brisbane, Australia. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S.D. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a heavy air pollution episode caused by biomass burning in Chengdu, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Hopke, P.K.; Pinto, J.P.; Wilson, W.E. Spatial variability of fine particle mass, components, and source contributions during the regional air pollution study in St. Louis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 4172–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Xu, H.; Guang, J.; Mei, L.; Guo, J.; Li, C.; Mikusauskas, R.; He, X. Observation of an agricultural biomass burning in Central and East China using merged aerosol optical depth data from multiple satellite missions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 5971–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Han, Y.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wang, T.J.; Li, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhuang, B.L.; Li, S. An agricultural biomass burning episode in Eastern China: Transport, optical properties, and impacts on regional air quality. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 2304–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Zhang, J. Long-term measurement for low-tropospheric water vapor and aerosol by raman lidar in Wuhan. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Gong, W.; Mao, F.; Pan, Z.; Liu, B. Measurement and study of lidar ratio by using a raman lidar in Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Li, R.Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, D.L.; Chen, Z.Y.; Gao, B.B.; He, B. Understanding temporal and spatial distribution of crop residue burning in China from 2003 to 2017 using modis data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Yin, S.S.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.Q. Analyses of biomass burning contribution to aerosol in zhengzhou during wheat harvest season in 2015. Atmos. Res. 2018, 207, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Mao, F.Y.; Guo, J.P.; Wang, W.; Pan, Z.X.; Shen, H.F.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Z.M. Estimation of spatiotemporal pm1.0 distributions in China by combining pm2.5 observations with satellite aerosol optical depth. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.J. Characterization of water-soluble ion species in urban ambient particles. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Tang, A.H.; Yuan, H.; Sun, Y.L.; Chen, S.A.; Zheng, A.H. The ion chemistry and the source of pm2.5 aerosol in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 3771–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Hou, B.; Lu, T.; Streets, D.G. Mechanism of formation of the heaviest pollution episode ever recorded in the Yangtze river delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Wang, L.L.; Ji, D.S.; Wen, T.X.; Pan, Y.P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.S. Characterization of the size-segregated water-soluble inorganic ions in the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration: Spatial/Temporal variability, size distribution and sources. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, C.C.; Shu, H.L.; Ying, Y.; Dai, Z.P.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.Y.; Liang, A.M.; et al. The impact of circulation patterns on regional transport pathways and air quality over Beijing and its surroundings. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 5031–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L. Biomass burning sources and their contributions to the local air quality in Hong Kong. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 596, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.L.; Xin, J.Y.; Li, X.R.; Wang, Y.S. The variability of biomass burning and its influence on regional aerosol properties during the wheat harvest season in North China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 157, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, H.T.; Sorooshian, A.; Craven, J.S.; Hersey, S.P.; Metcalf, A.R.; Zhang, X.L.; Weber, R.J.; Jonsson, H.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Water-soluble organic aerosol in the los angeles basin and outflow regions: Airborne and ground measurements during the 2010 calnex field campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonaschutz, A.; Hersey, S.P.; Sorooshian, A.; Craven, J.S.; Metcalf, A.R.; Flagan, R.C.; Seinfeld, J.H. Impact of a large wildfire on water-soluble organic aerosol in a major urban area: The 2009 station fire in Los Angeles County. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 8257–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krudysz, M.A.; Froines, J.R.; Fine, P.M.; Sioutas, C. Intra-community spatial variation of size-fractionated pm mass, oc, ec, and trace elements in the long beach, ca area. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5374–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; van Eyk, P.J.; Medwell, P.R.; Birzer, C.H.; Tian, Z.F.; Possell, M. Identification and quantitative analysis of smoldering and flaming combustion of radiata pine. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 7666–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, W.R.; Brachaczek, W.W.; McKee, D.E. Sulfate emissions from catalyst-equipped automobiles on the highway. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1979, 29, 255–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truex, T.J.; Pierson, W.R.; McKee, D.E. Sulfate in diesel exhaust. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1980, 14, 1118–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S.; Okita, T. A chemical characterization of atmospheric aerosol in Sapporo. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Top. 1990, 24, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Deviations between UAV and MODIS | ≤1 km | 1–2 km | 2–3 km | >3 km |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion | 39.1% | 32.6% | 10.9% | 17.4% |
| Pollutant | Instrument | Method | Sampling Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | TH-2000PM | β Ray absorption | 5 min |
| PM10 | TH-2000PM | β Ray absorption | 5 min |
| SO2 | MODEL 43i | Pulsed fluorescence | 5 min |
| O3 | MODEL 49i | Ultraviolet photometry | 5 min |
| NO2 | MODEL 42i | Chemiluminescence | 5 min |
| CO | MODEL 48i | Gas photometry | 5 min |
| Meteorological Parameters | Non-Burning Period | Burning Period | Intensive Burning Period |
|---|---|---|---|
| RH (%) | 78.3 | 61.8 | 62.5 |
| PBL (m) | 535.4 | 557.7 | 491.6 |
| Pressure (hPa) | 1008.7 | 1010.5 | 1010.5 |
| Temperature (°C) | 22.2 | 22.9 | 22.5 |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.3 |
| Burning Period | Non-Burning Period | Increase | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM10 | 122.72 | 74.89 | 63.49% |
| PM2.5 | 73.52 | 50.18 | 46.29% |
| SO2 | 16.56 | 10.08 | 65.56% |
| NO2 | 26.29 | 17.10 | 64.40% |
| O3 | 84.66 | 64.60 | 48.57% |
| CO | 950 | 830 | 13.49% |
| AQI | 114.1 | 80.4 | 41.9% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N.; Quan, J. Assessment of Air Pollution Aggravation during Straw Burning in Hubei, Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081446
Zhu B, Zhang Y, Chen N, Quan J. Assessment of Air Pollution Aggravation during Straw Burning in Hubei, Central China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(8):1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081446
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Bo, Yu Zhang, Nan Chen, and Jihong Quan. 2019. "Assessment of Air Pollution Aggravation during Straw Burning in Hubei, Central China" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 8: 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081446
APA StyleZhu, B., Zhang, Y., Chen, N., & Quan, J. (2019). Assessment of Air Pollution Aggravation during Straw Burning in Hubei, Central China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(8), 1446. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081446




