Relationships between Social Capital, Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression among Elderly Urban Residents: Analysis of Secondary Survey Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Research Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.2.1. Depression
2.2.2. Social Capital
2.2.3. Social Capital Satisfaction
2.2.4. Self-Esteem
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sociodemographic Differences in Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression
3.2. Measurement Model
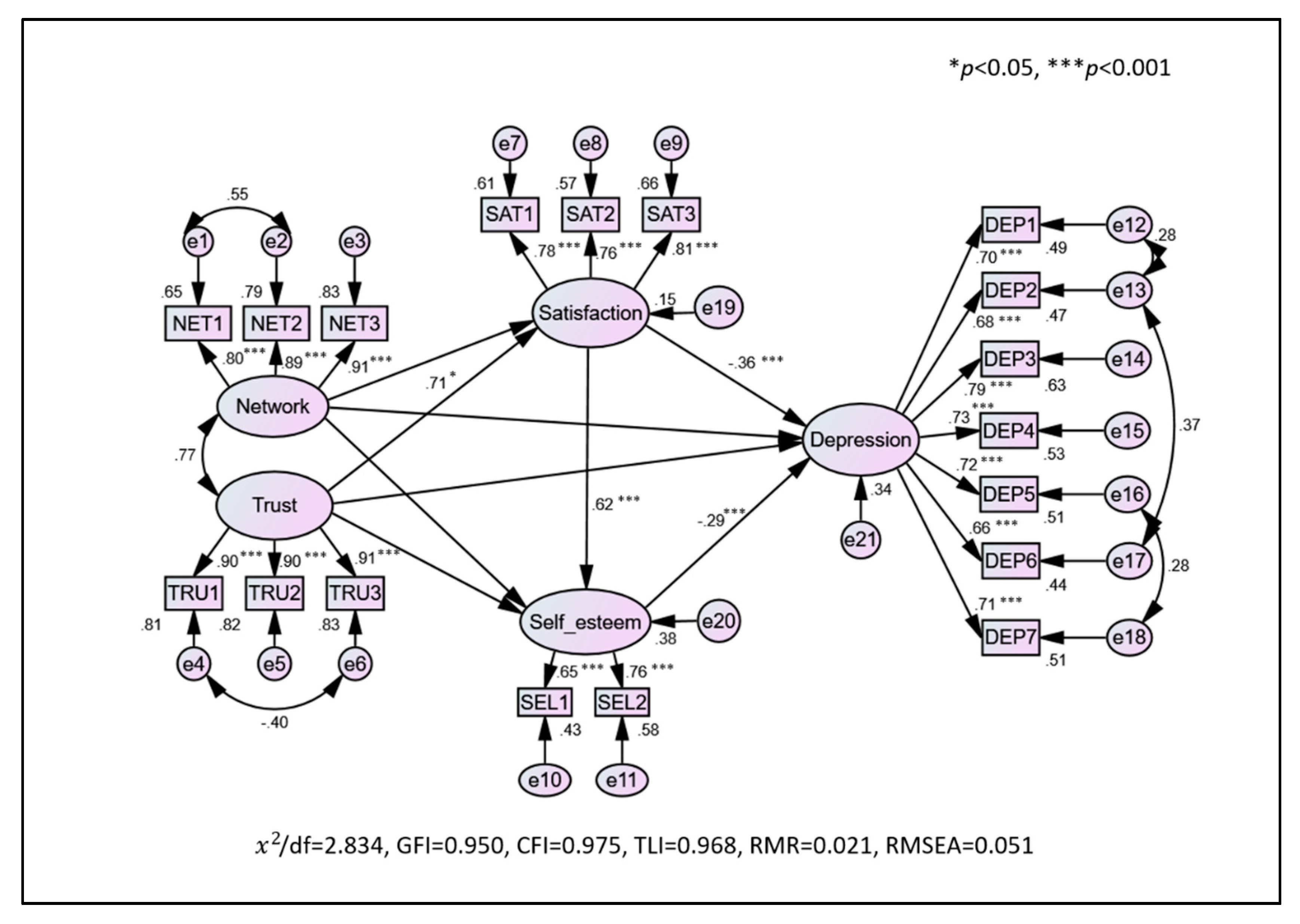
3.3. Structural Model
3.4. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| DEP2 | DEP3 | DEP4 | DEP5 | DEP6 | DEP7 | DEP8 | DEP9 | DEP10 | DEP11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEP1 | −0.629 ** | 0.551 ** | 0.537 ** | 0.486 ** | 0.484 ** | −0.479 ** | 0.376 ** | 0.334 ** | 0.295 ** | 0.296 ** |
| SEL2 | SEL3 | SEL4 | SEL5 | SEL6 | SEL7 | SEL8 | SEL9 | SEL10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SEL1 | 0.496 ** | 0.341 ** | 0.382 ** | 0.310 ** | 0.374 ** | 0.312 ** | 0.219 ** | 0.388 ** | 0.168 ** |
References
- Okkels, N.; Kristiansen, C.B.; Munk-Jørgensen, P.; Sartorius, N. Urban mental health: Challenges and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2018, 31, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Statistical Information Service Urban Population Status. 2017. Available online: http://kosis.kr (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. 2017 Survey of the Elderly; KIHASA: Sejong, Korea, 2017; pp. 29–62. ISBN 1113520000. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemeier, H. Biological risk factors for late life depression. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 18, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Son, S.A. Psychological and Physical Effects of 10 Weeks Urban Forest Therapy Program on Dementia Prevention in Low-Income Elderly Living Alone. J. People Plants Environ. 2018, 21, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deckers, K.; van Boxtel, M.P.J.; Schiepers, O.J.G.; de Vugt, M.; Muñoz Sánchez, J.L.; Anstey, K.J.; Brayne, C.; Dartigues, J.-F.; Engedal, K.; Kivipelto, M.; et al. Target risk factors for dementia prevention: A systematic review and Delphi consensus study on the evidence from observational studies. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langa, K.M. Is the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia declining? Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2015, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, K.B.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Min, J.Y. Parks and green areas and the risk for depression and suicidal indicators. Int. J. Public Health 2017, 62, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wimo, A.; Guerchet, M.; Ali, G.-C.; Wu, Y.-T.; Prina, A.M.; Winblad, B.; Jönsson, L.; Liu, Z.; Prince, M. The worldwide costs of dementia 2015 and comparisons with 2010. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Mental health action and innovation: The evidence-based case for investment. In Investing in Mental Health: Evidence for Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013; pp. 14–22. ISBN 9789241564618. [Google Scholar]
- Girardi, P.; Pompili, M.; Innamorati, M.; Mancini, M.; Serafini, G.; Mazzarini, L.; Del Casale, A.; Tatarelli, R.; Baldessarini, R.J. Duloxetine in acute major depression: Review of comparisons to placebo and standard antidepressants using dissimilar methods. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2009, 24, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Pompili, M.; Belvederi Murri, M.; Respino, M.; Ghio, L.; Girardi, P.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Amore, M. The effects of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on cognitive performance in treatment-resistant depression. A systematic review. Neuropsychobiology 2015, 71, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerling, A.; Tegtbur, U.; Gützlaff, E.; Kück, M.; Borchert, L.; Ates, Z.; von Bohlen, A.; Frieling, H.; Hüper, K.; Hartung, D.; et al. Effects of adjunctive exercise on physiological and psychological parameters in depression: A randomized pilot trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 177, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiai, H.; Ikei, H.; Song, C.; Kobayashi, M.; Takamatsu, A.; Miura, T.; Kagawa, T.; Li, Q.; Kumeda, S.; Imai, M.; et al. Physiological and psychological effects of forest therapy on middle-aged males with high-normal blood pressure. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingo, C.A.; Martin, K.R.; Shreffler, J.; Schoster, B.; Callahan, L.F. Individual and community socioeconomic status: Impact on mental health in individuals with arthritis. Arthritis 2014, 2014, 256498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, C.; Saito, T.; Saito, M.; Kondo, K.; Murata, C.; Saito, T.; Saito, M.; Kondo, K. The Association between Social Support and Incident Dementia: A 10-Year Follow-Up Study in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padayachey, U.; Ramlall, S.; Chipps, J. Depression in older adults: Prevalence and risk factors in a primary health care sample. South Afr. Fam. Pract. 2017, 59, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.K. Do Sociodemographic Factors and Urban Green Space Affect Mental Health Outcomes Among the Urban Elderly Population? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Xu, L.; Kong, M.; Li, S.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Qin, W.; Kong, F.; Xu, L.; et al. The Relationship between Socioeconomic Status, Mental Health, and Need for Long-Term Services and Supports among the Chinese Elderly in Shandong Province—A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Yu, C.-P.; Wu, C.-D.; Pan, W.-C.; Lee, H.-Y.; Yu, C.-P.; Wu, C.-D.; Pan, W.-C. The Effect of Leisure Activity Diversity and Exercise Time on the Prevention of Depression in the Middle-Aged and Elderly Residents of Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Cline, H.; Turkheimer, E.; Duncan, G.E. Access to green space, physical activity and mental health: A twin study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2015, 69, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orstad, S.L.; McDonough, M.H.; James, P.; Klenosky, D.B.; Laden, F.; Mattson, M.; Troped, P.J. Neighborhood walkability and physical activity among older women: Tests of mediation by perceptions and moderation by depressive symptoms. Prev. Med. (Baltim) 2018, 116, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadvand, P.; Bartoll, X.; Basagaña, X.; Dalmau-Bueno, A.; Martinez, D.; Ambros, A.; Cirach, M.; Triguero-Mas, M.; Gascon, M.; Borrell, C.; et al. Green spaces and General Health: Roles of mental health status, social support, and physical activity. Environ. Int. 2016, 91, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, Y.-L.-A. Social Support: An Effective Resource for Reducing the Disparities in Depression across Socioeconomic Strata. Korean J. Sociol. 2006, 45, 175–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.B.; Sohn, U.S. A Meta-analysis of the Variables Related to Depression in Elderly. J. Korean Gerontol. Soc. 2005, 25, 167–187. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanzadeh, J.; Asadi-lari, M.; Baghbanian, A.; Ghaem, H. Association between social capital, health-related quality of life, and mental health: A structural-equation modeling approach. Croat. Med. J. 2016, 57, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.; Lee, S. Neighborhood Built Environments Affecting Social Capital and Social Sustainability in Seoul, Korea. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.S. Social Capital in the Creation of Human Capital. Am. J. Sociol. 1988, 94, S95–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, R.D.; Leonardi, R.; Nanetti, R. Social capital and institutional success. In Making Democracy Work: Civic Traditions in Modern Italy; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1993; pp. 167–170. ISBN 140082074X. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, C. Social capital and depression: Evidence from urban elderly in China. Aging Ment. Health 2015, 19, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, C.E.; von dem Knesebeck, O. Social capital and health among the aged: Comparisons between the United States and Germany. Health Place 2004, 10, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, J.S.; Landis, K.R.; Umberson, D. Social relationships and health. Science 1988, 241, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, A.R.; Choi, H.; Valenstein, M. Social Relationships and Depression: Ten-Year Follow-Up from a Nationally Representative Study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenson, K.R.; Jones, S.A.; Holliday, K.M.; Cohen, D.A.; McKenzie, T.L. Park characteristics, use, and physical activity: A review of studies using SOPARC (System for Observing Play and Recreation in Communities). Prev. Med. (Baltim) 2016, 86, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gou, Z.; Zuo, J. Social support mediates loneliness and depression in elderly people. J. Health Psychol. 2016, 21, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.; Heim, D.; Hunter, S.; Ellaway, A. Health & Place The relative infl uence of neighbourhood incivilities, cognitive social capital, club membership and individual characteristics on positive mental health. Health Place 2014, 28, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. Social capital and perceived stress: The role of social context. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 250, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Linton, K.F.; Lum, W. Social capital and life satisfaction among Chinese and Korean elderly immigrants. J. Soc. Work 2015, 15, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørnskov, C. The happy few: Cross-country evidence on social capital and life satisfaction. Kyklos 2003, 56, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavot, W.; Diener, E.; Colvin, C.R.; Sandvik, E. Further validation of satesfaction with life scale.pdf. J. Personal. Assess. 1991, 57, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, J.-H. The effects of elderly depression on life satisfaction. Fam. Cult. 2008, 20, 95–116. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs (KIHASA) 12th Korea Welfare Panel Study: User’s Guide. Available online: https://www.koweps.re.kr:442/eng/data/guide/list.do (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs (KIHASA) 12th Korea Welfare Panel Study. Available online: https://www.koweps.re.kr:442/eng/main.do (accessed on 25 February 2019).
- Radloff, L.S. The CES-D Scale: A Self-Report Depression Scale for Research in the General Population. Appl. Psychol. Meas. 1977, 1, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellis, Z.D. Assessment of a brief CES-D measure for depression in homebound medically ill older adults. J. Gerontol. Soc. Work 2010, 53, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chon, K.K.; Rhee, M.K. Preliminary Development of Korean Version of CES-D. Korean J. Clin. Psychol. 1992, 11, 65–76. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.-Y.; Kwak, H.-K.; Park, H.-S. The Effect of Community Social Capital on the Elderly’s Subjective Quality of Life: Focusing on the Mediating Effect of the Elderly Depression Mi-Young. J. Welf. Aged Vol. 2014, 66, 307–328. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, D.-H.; Yeo, C.-W.; Seo, Y.-H. Estimation of Life Satisfaction and Development of Welfare Policy using Welfare Panel Data. J. Korean Political Sci. Assoc. 2018, 26, 177–195. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, M. The measurment of self-esteem. In Society and the Adolescent Self-Image; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1965; pp. 16–36. ISBN 1400876133. [Google Scholar]
- Medsker, G.J.; Williams, L.J.; Holahan, P.J. A Review of Current Practices for Evaluating Causal Models in Organizational Behavior and Human Resources Management Research. J. Manage. 1994, 20, 439–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Bolger, N. Mediation in experimental and nonexperimental studies: New procedures and recommendations. Psychol. Methods 2002, 7, 422–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.W.; Cudeck, R. Alternative Ways of Assessing Model Fit. In Testing Structural Equation Models; Bollen, K.A., Long, J.S., Eds.; Sage Publications: Newbury Park, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 136–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. SEM: An Introduction. In Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective; Pearson Prentice Hall: Upper New Jersey River, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, D.B.; Singh, J.; Svensson, G.; Mysen, T. Towards a model of conscientious corporate brands: A Canadian study. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2013, 28, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.P.; Lockwood, C.M.; Williams, J. Confidence Limits for the Indirect Effect: Distribution of the Product and Resampling Methods. Multivar. Behav. Res. 2004, 39, 99–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borge, L.-E.; Rattsø, J. Understanding generational conflict. In Young and Old Competing for Public Welfare Services; CESifo Working Paper Series No. 2223. CESifo Group: Munich, Germany, 2008; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, A.; Martimo, K. Ageing and intergenerational relations in Britain. In Comparing Social Policies: Exploring New Perspectives in Britain and Japan; The Policy Press: Bristol, UK, 2003; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, R. Building Intergenerational Bonds Through the Arts. Generations 2006, 30, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Pinquart, M.; Sörensen, S. Influences of socioeconomic status, social network, and competence on subjective well-being in later life: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Aging 2000, 15, 187–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, M.S. School-Based Intergenerational Programs; UNESCO Institute for Education: Hamburg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mannion, G. Intergenerational Education and Learning: We Are in a New Place. In Families, Intergenerationality, and Peer Group Relations; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 307–327. [Google Scholar]
- Daatland, S.O.; Lowenstein, A. Intergenerational solidarity and the family-welfare state balance. Eur. J. Ageing 2005, 2, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowenstein, A. Intergenerational family relations and social support. Z. Gerontol. Geriatr. 1999, 32, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropf, N.P.; Burnette, D. Grandparents as family caregivers: Lessons for intergenerational education. Educ. Gerontol. 2003, 29, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamplekou, E.; Bountziouka, V.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Zeimbekis, A.; Tsakoundakis, N.; Papaerakleous, N.; Gotsis, E.; Metallinos, G.; Pounis, G.; Polychronopoulos, E.; et al. Urban environment, physical inactivity and unhealthy dietary habits correlate to depression among elderly living in eastern Mediterranean islands: The MEDIS (MEDiterranean ISlands elderly) study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.M.; Mak, K.K.; Watanabe, H.; Jeong, J.; Kim, D.; Bahar, N.; Ramos, M.; Chen, S.H.; Cheng, C. The mediating role of Internet addiction in depression, social anxiety, and psychosocial well-being among adolescents in six Asian countries: A structural equation modelling approach. Public Health 2015, 129, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Paik, J. The Effects of Family Conflict, Social Support and Self-Esteem on Life Satisfaction of the Aged. J. Digit. Converg. 2016, 14, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, K.R. The influence of physical activity on mental well-being. Public Health Nutr. 1999, 2, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.A. Psychological foundations of trust. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 2007, 16, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fung, H.H. Age Differences in Trust: An Investigation Across 38 Countries. J. Gerontol. Ser. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2013, 68, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, J.K.; Holmes, J.G.; Zanna, M.P. Trust in Close Relationships. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1985, 49, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.S.; Chan, L.S. Social network, social trust and shared goals in organizational knowledge sharing. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.S.; Tak, Y.R. Effects of Social Capital on Subjective Health in the Community Indwelling Elderly. J. Korean Acad. Community Health Nurs. 2018, 29, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, J.B. Social Capital in the Aged’s Life Long Education; Gacheon University: Seongnam, Korea, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.-H. Social Bonds and the Migration Intentions of Elderly Urban Residents: The Mediating Effect of Residential Satisfaction. Popul. Res. Policy Rev. 2003, 22, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Son, S.A. Qualitative Assessment of Experience on Urban Forest Therapy Program for Preventing Dementia of the Elderly Living Alone in Low-Income Class. J. People Plants Environ. 2018, 21, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Latent Variable | Definition | Observed Variables | Categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| Depression | Depressive symptomatology felt in daily life during the past week | Poor appetite | (1) Extremely rarely (2) Rarely (3) Sometimes (4) Most of the time |
| Doing well | |||
| Depressed | |||
| Burden | |||
| Lonely | |||
| Happiness | |||
| Sadness | |||
| Network | Subjective recognition of the quantitative social network | Who can help in an emergency | |
| Who can make one comfortable | |||
| Who can share in joy and sorrow | |||
| Trust | Confidence in social relationships | Can get help | (1) Strongly disagree (2) Disagree (3) Neither (4) Agree (5) Strongly agree |
| Can depend on others when in trouble | |||
| Can talk about problems | |||
| Satisfaction | The extent to which an individual feels satisfaction | Satisfaction with social relationships | |
| Satisfaction with leisure | |||
| Satisfaction as a whole | |||
| Self-esteem | The extent to which an individual’s respects and approves of himself/herself | Positive attitude toward oneself | (1) Strongly disagree (2) Disagree (3) Agree (4) Strongly agree |
| Satisfaction with oneself |
| Sociodemographic Group | N | % | Satisfaction | Self-Esteem | Depression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M ± SD | M ± SD | M ± SD | |||
| Sex | |||||
| Men | 295 | 42.1 | 9.98 ± 1.87 | 4.90 ± 1.24 | 15.82 ± 5.98 |
| Women | 406 | 57.9 | 9.98 ± 1.92 | 4.78 ± 1.24 | 18.59 ± 6.79 |
| χ2 (p) | 0.13 (0.99) | 7.61 (0.27) | 31.35 (0.051) | ||
| Age group | |||||
| 65–70 | 206 | 29.4 | 9.93 ± 1.83 | 4.74 ± 1.21 | 10.76 ± 3.84 |
| 71–75 | 198 | 28.2 | 10.22 ± 1.85 | 4.96 ± 1.29 | 11.59 ± 4.77 |
| 76–80 | 198 | 28.2 | 9.92 ± 1.97 | 4.78 ± 1.27 | 11.46 ± 4.28 |
| >80 | 99 | 14.1 | 9.72 ± 1.95 | 4.83 ± 1.13 | 12.61 ± 4.39 |
| χ2 (p) | 45.47 (0.13) | 11.15 (0.89) | 64.68 (0.32) | ||
| Educational level | |||||
| <Primary school | 494 | 70.5 | 9.92 ± 1.91 | 4.78 ± 1.24 | 11.69 ± 4.32 |
| Middle or high school | 181 | 25.8 | 10.03 ± 1.91 | 4.91 ± 1.25 | 11.08 ± 4.50 |
| >College | 26 | 3.7 | 10.73 ± 1.40 | 5.23 ± 1.18 | 9.58 ± 3.00 |
| χ2 (p) | 20.46 (0.67) | 17.00 (0.15) | 28.12 (0.92) | ||
| Household type | |||||
| Solitary | 245 | 35 | 9.76 ± 1.92 | 4.71 ± 1.18 | 12.58 ± 4.62 |
| Elderly spouse | 453 | 64.6 | 10.12 ± 1.85 | 4.89 ± 1.27 | 10.81 ± 4.00 |
| Multi-generation | 3 | 0.4 | 7.33 ± 3.21 | 4.33 ± 1.53 | 17.00 ± 9.85 |
| χ2 (p) | 100.78 (0.00 **) | 9.38 (0.67) | 176.13 (0.00 **) | ||
| Health status | |||||
| Good | 289 | 41.2 | 10.45 ± 1.65 | 5.16 ± 1.24 | 10.32 ± 3.71 |
| Bad | 412 | 58.8 | 9.65 ± 1.99 | 4.60 ± 1.19 | 12.25 ± 4.59 |
| χ2 (p) | 42.38 (0.00 **) | 41.00 (0.00 **) | 51.34 (0.00 **) | ||
| Income status | |||||
| Low-income class | 509 | 72.6 | 9.78 ± 1.95 | 4.72 ± 1.24 | 11.88 ± 4.59 |
| Middle class | 192 | 27.4 | 10.50 ± 1.63 | 5.11 ± 1.21 | 10.32 ± 3.38 |
| χ2 (p) | 27.15 (0.01 *) | 20.68 (0.00 **) | 39.59 (0.01 *) | ||
| Latent Variable | Item | Convergent Validity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ | OE. | CR | AVE | |||
| Social Capital | Network | NET1 | 0.80 | 0.38 | 0.90 | 0.75 |
| NET2 | 0.89 | 0.22 | ||||
| NET3 | 0.91 | 0.17 | ||||
| Trust | TRU1 | 0.90 | 0.18 | 0.93 | 0.82 | |
| TRU2 | 0.90 | 0.18 | ||||
| TRU3 | 0.91 | 0.17 | ||||
| Satisfaction | SAT1 | 0.78 | 0.21 | 0.90 | 0.75 | |
| SAT2 | 0.76 | 0.27 | ||||
| SAT3 | 0.82 | 0.16 | ||||
| Self-esteem | SEL1 | 0.65 | 0.24 | 0.80 | 0.67 | |
| SEL2 | 0.76 | 0.26 | ||||
| Depression | DEP1 | 0.70 | 0.36 | 0.92 | 0.61 | |
| DEP2 | 0.68 | 0.39 | ||||
| DEP3 | 0.79 | 0.20 | ||||
| DEP4 | 0.73 | 0.38 | ||||
| DEP5 | 0.72 | 0.27 | ||||
| DEP6 | 0.66 | 0.48 | ||||
| DEP7 | 0.71 | 0.20 | ||||
| Variable | Social Capital | Satisfaction | Self-Esteem | Depression | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network | Trust | |||||
| Social capital | Network | 0.75 | ||||
| Trust | 0.59 | 0.82 | ||||
| Social capital satisfaction | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.75 | |||
| Self-esteem | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.39 | 0.67 | ||
| Depression | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.26 | 0.61 | |
| Variable | Total (Direct, Indirect) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trust | Network | Satisfaction | Self-Esteem | |
| Social capital satisfaction | 0.71 * (0.71 *, 0.00) | −0.31 (−0.31, 0.00) | ||
| Self-esteem | 0.80 (0.36, 0.44) | −0.53 (−0.34, −0.19) | 0.62 ** (0.62 **, 0.00) | |
| Depression | −0.44 (0.04, −0.49 *) | 0.22 (−0.04, 0.27) | −0.54 ** (−0.36 **, −0.18 **) | −0.29 ** (−0.29 **, 0.00) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.J.; Lee, D.K.; Song, W. Relationships between Social Capital, Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression among Elderly Urban Residents: Analysis of Secondary Survey Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081445
Lee HJ, Lee DK, Song W. Relationships between Social Capital, Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression among Elderly Urban Residents: Analysis of Secondary Survey Data. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(8):1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081445
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyun Jin, Dong Kun Lee, and Wonkyong Song. 2019. "Relationships between Social Capital, Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression among Elderly Urban Residents: Analysis of Secondary Survey Data" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 8: 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081445
APA StyleLee, H. J., Lee, D. K., & Song, W. (2019). Relationships between Social Capital, Social Capital Satisfaction, Self-Esteem, and Depression among Elderly Urban Residents: Analysis of Secondary Survey Data. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(8), 1445. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16081445





