The Synergistic Effects of Organizational Justice and Trust to Supervisor on Vagal Tone: Preliminary Findings of an Empirical Investigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Methods
2.3. Statistical Analyses
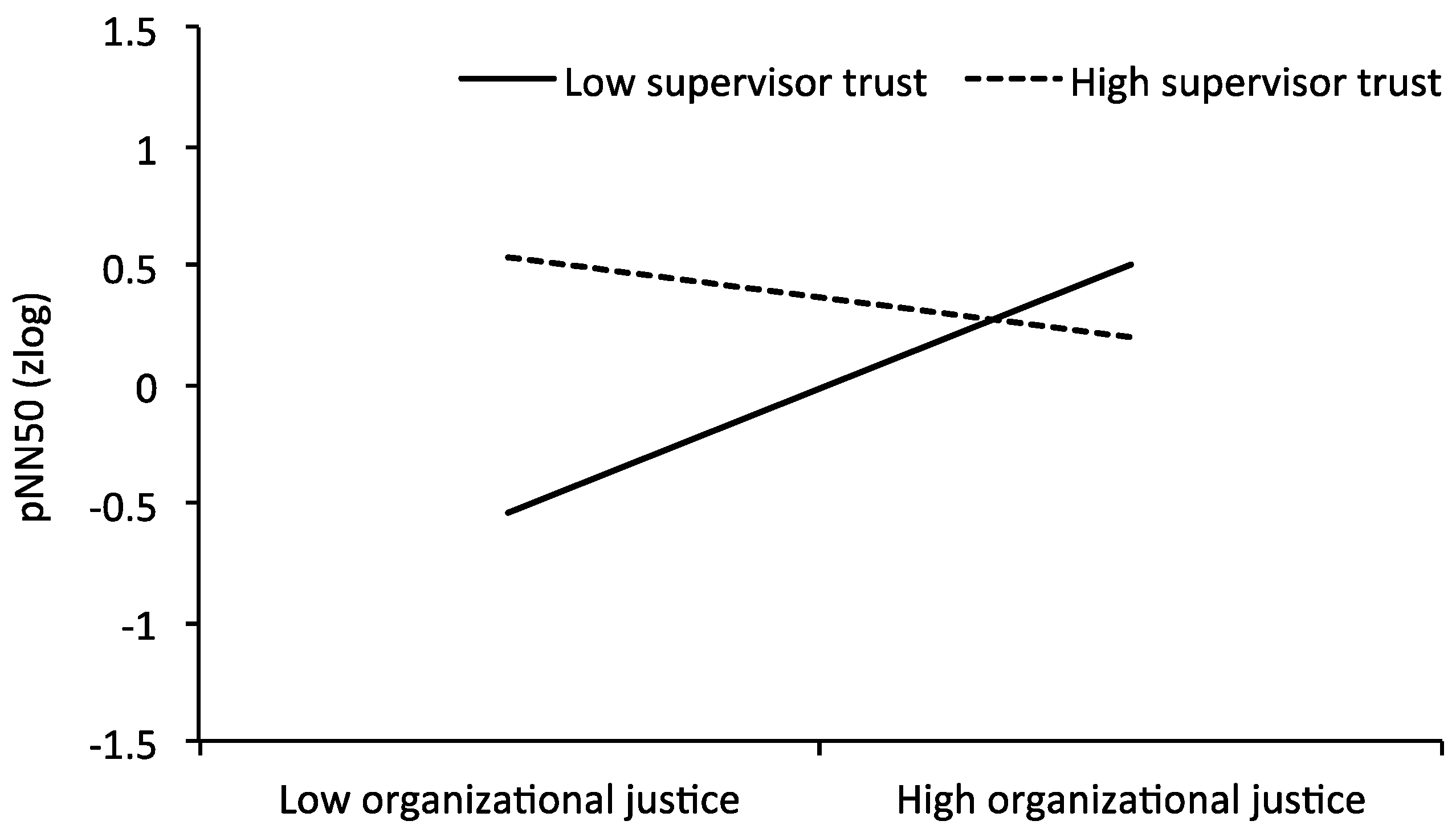
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen-Charash, Y.; Spector, P.E. The Role of Justice in Organizations: A Meta-Analysis. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2001, 86, 278–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquitt, J.A.; Conlon, D.E.; Wesson, M.J.; Porter, C.O.; Ng, K.Y. Justice at the millennium: A meta-analytic review of 25 years of organizational justice research. J. Appl. Psychol. 2001, 86, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J. Organizational Injustice as an Occupational Health Risk. Acad. Manag. Ann. 2010, 4, 205–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndjaboue, R.; Brisson, C.; Vezina, M. Organisational justice and mental health: A systematic review of prospective studies. Occup. Environ. Med. 2012, 69, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elovainio, M.; Heponiemi, T.; Sinervo, T.; Magnavita, N. Organizational justice and health; Review of evidence. G. Ital. Med. Lav. Ergon. 2010, 32, B5–B9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lind, E.A. Fairness heuristic theory: Justice judgments as pivotal cognitions in organizational relations. Adv. Organ. Justice 2001, 56, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Lind, E.A.; Kulik, C.T.; Ambrose, M.; de Vera Park, M.V. Individual and corporate dispute resolution: Using procedural fairness as a decision heuristic. Adm. Sci. Q. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquitt, J.A.; Scott, B.A.; Judge, T.A.; Shaw, J.C. Justice and personality: Using integrative theories to derive moderators of justice effects. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 2006, 100, 110–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, E.A.; van den Bos, K. When fairness works: Toward a general theory of uncertainty management. Res. Organ. Behav. 2002, 24, 181–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colquitt, J.A.; LePine, J.A.; Piccolo, R.F.; Zapata, C.P.; Rich, B.L. Explaining the justice–performance relationship: Trust as exchange deepener or trust as uncertainty reducer? J. Appl. Psychol. 2012, 97, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colquitt, J.A.; Scott, B.A.; Rodell, J.B.; Long, D.M.; Zapata, C.P.; Conlon, D.E.; Wesson, M.J. Justice at the millennium, a decade later: A meta-analytic test of social exchange and affect-based perspectives. J. Appl. Psychol. 2013, 98, 199–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, M.; Elovainio, M. Justice at the Workplace: A Review. Camb. Q. Healthc. Eth. Int. J. Healthc. Eth. Comm. 2018, 27, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cropanzano, R.; Mitchell, M.S. Social exchange theory: An interdisciplinary review. J. Manag. 2005, 31, 874–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, S.; Pawan, S.B.; Zhen Xiong, C. Trust as a Mediator of the Relationship between Organizational Justice and Work Outcomes: Test of a Social Exchange Model. J. Organ. Behav. 2002, 23, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, P.M. Exchange and Power in Social Life; J. Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Herr, R.M.; Bosch, J.A.; Van Vianen, A.E.; Jarczok, M.N.; Thayer, J.F.; Li, J.; Schmidt, B.; Fischer, J.E.; Loerbroks, A. Organizational justice is related to heart rate variability in white-collar workers, but not in blue-collar workers-findings from a cross-sectional study. Ann. Behav. Med. Publ. Soc. Behav. Med. 2015, 49, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, M.N.; Thornhill, A. Organisational justice, trust and the management of change: An exploration. Pers. Rev. 2003, 32, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, M.L.; Johnson, P.D.; Gavin, M.; Gooty, J.; Snow, D.B. Organizational justice, trustworthiness, and trust: A multifoci examination. Gr. Organ. Manag. 2010, 35, 39–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koolhaas, J.M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Buwalda, B.; De Boer, S.F.; Flugge, G.; Korte, S.M.; Meerlo, P.; Murison, R.; Olivier, B.; Palanza, P. Stress revisited: A critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, R.M.; Loerbroks, A.; Van Vianen, A.; Hoffmann, K.; Fischer, J.E.; Bosch, J.A. Injustice at work and leukocyte glucocorticoid sensitivity: Findings from a cross-sectional study. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillebrand, S.; Gast, K.B.; De Mutsert, R.; Swenne, C.A.; Jukema, J.W.; Middeldorp, S.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Dekkers, O.M. Heart rate variability and first cardiovascular event in populations without known cardiovascular disease: Meta-analysis and dose–response meta-regression. EP Eur. 2013, 15, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimaki, M.; Steptoe, A. Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccelletti, E.; Gilardi, E.; Scaini, E.; Galiuto, L.; Persiani, R.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Silveri, N.G. Heart rate variability and myocardial infarction: Systematic literature review and metanalysis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 13, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, C.; Shu, M. Prediction of heart rate variability on cardiac sudden death in heart failure patients: A systematic review. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 174, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laborde, S.; Mosley, E.; Thayer, J.F. Heart Rate Variability and Cardiac Vagal Tone in Psychophysiological Research—Recommendations for Experiment Planning, Data Analysis, and Data Reporting. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarczok, M.N.; Jarczok, M.; Mauss, D.; Koenig, J.; Li, J.; Herr, R.M.; Thayer, J.F. Autonomic nervous system activity and workplace stressors—A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2013, 37, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elovainio, M.; Kivimaki, M.; Puttonen, S.; Lindholm, H.; Pohjonen, T.; Sinervo, T. Organisational injustice and impaired cardiovascular regulation among female employees. Occup. Environ. Med. 2006, 63, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limm, H.; Gundel, H.; Heinmuller, M.; Marten-Mittag, B.; Nater, U.M.; Siegrist, J.; Angerer, P. Stress management interventions in the workplace improve stress reactivity: A randomised controlled trial. Occup. Environ. Med. 2011, 68, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, R.M.; Li, J.; Bosch, J.A.; Schmidt, B.; Dejoy, D.M.; Fischer, J.E.; Loerbroks, A. Psychometric properties of a German organizational justice questionnaire (G-OJQ) and its association with self-rated health: Findings from the Mannheim Industrial Cohort Studies (MICS). Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health. 2012, 87, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prümper, J.; Hartmannsgruber, K.; Frese, M. KFZA. Kurz-Fragebogen zur Arbeitsanalyse [Short-questionnaire for Work Analysis]. Zeitschrift Arbeits-Organisationspsychologie 1995, 39, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Ahonen, L.; Cowley, B.; Torniainen, J.; Ukkonen, A.; Vihavainen, A.; Puolamaki, K. Cognitive Collaboration Found in Cardiac Physiology: Study in Classroom Environment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecasteele, K.; De Cooman, T.; Gu, Y.; Cleeren, E.; Claes, K.; Paesschen, W.V.; Huffel, S.V.; Hunyadi, B. Automated Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on Wearable ECG and PPG in a Hospital Environment. Sensors 2017, 17, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotoia, A.; Dibello, F.; Moscatelli, F.; Sciusco, A.; Polito, P.; Modolo, A.; Gallo, C.; Cibelli, G.; Cinnella, G. Effects of Tibetan Music on Neuroendocrine and Autonomic Functions in Patients Waiting for Surgery: A Randomized, Controlled Study. Anesthesiology Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9683780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konovsky, M.A.; Pugh, S.D. Citizenship Behavior and Social Exchange. Aca. Manag. J. 1994, 37, 656–669. [Google Scholar]
- Pillai, R.; Schriesheim, C.A.; Williams, E.S. Fairness perceptions and trust as mediators for transformational and transactional leadership: A two-sample study. J. Manag. 1999, 25, 897–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J. Stress Fairness to Fare No Stress: Managing Workplace Stress by Promoting Organizational Justice. Organ. Dyn. 2004, 33, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, J. Everybody talks about organizational justice, but nobody does anything about it. Ind. Organ. Psychol. 2009, 2, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, G.S. What should be done with equity theory? New approaches to the study of fairness in social relationship. In Social Exchange: Advances in Theory and Research; Gergen, K.J., Greenberg, M.S., Willis, R.H., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1980; pp. 27–55. [Google Scholar]
- Robbins, J.M.; Ford, M.T.; Tetrick, L.E. Perceived unfairness and employee health: A meta-analytic integration. J. Appl. Psychol. 2012, 97, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicki, R.J.; Wiethoff, C.; Tomlinson, E.C. What is the role of trust in organizational justice. In Handbook of Organizational Justice; Colquitt, J., Greenberg, J., Eds.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 247–270. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, P.D.; McFarlin, D.B. Process and Outcome: Gender Differences in the Assessment of Justice. J. Organ. Behav. 1997, 18, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.P. Multiple hypothesis testing. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 1995, 46, 561–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Domain | Abbreviation | Measurement Unit | Description | ANS Reflection |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | ||||
| pNN50 | % | Percentage of successive RR intervals that deviate more than 50 ms | PNS | |
| RMSSD | ms | Root mean sum of squares of successive differences | PNS | |
| SDNN | ms | Standard deviation of all N-N intervals | SNS and PNS | |
| Frequency | ||||
| LF power | Hz | Low-frequency power | SNS and PNS, primarily SNS | |
| HF power | Hz | High-frequency power | PNS |
| Age, Years (Mean, SD) | 40.66 | 6.44 |
|---|---|---|
| Segment leader (n, %) | 28.9% | 11 |
| Body mass index (mean, SD) | 27.4 | 2.60 |
| Non-smoker (mean, SD) | 81.6% | 31 |
| Organizational justice (mean, SD) | 3.69 | 0.64 |
| Trust to supervisor (mean, SD) | 4.11 | 0.83 |
| pNN50 (mean, SD) | 6.81 | 6.51 |
| RMSSD (mean, SD) | 26.41 | 9.98 |
| SDNN (mean, SD) | 147.31 | 34.25 |
| HF power (mean, SD) | 249.98 | 207.74 |
| LF power (mean, SD) | 1044.19 | 625.07 |
| Models | pNN50 | RMSSD | SDNN | HF Power | LF Power | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 1 | Model 2 | |||||||||||
| Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | Beta | S.E. | |
| Step I | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Organizational justice | 0.320 * | 0.154 | 0.251 | 0.156 | 0.277 | 0.159 | 0.209 | 0.161 | 0.06 | 0.169 | 0.036 | 0.18 | 0.259 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.164 | 0.295 | 0.155 | 0.214 | 0.149 |
| Step II | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Organizational justice | 0.098 | 0.164 | 0.046 | 0.167 | 0.122 | 0.178 | 0.074 | 0.182 | −0.102 | 0.19 | −0.124 | 0.203 | 0.142 | 0.183 | 0.08 | 0.187 | 0.089 | 0.167 | 0.04 | 0.163 |
| Trust to supervisor | 0.453 ** | 0.166 | 0.430 * | 0.174 | 0.316 | 0.181 | 0.283 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.193 | 0.335 | 0.212 | 0.239 | 0.186 | 0.23 | 0.195 | 0.418 * | 0.17 | 0.364 * | 0.17 |
| Step III | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Organizational justice | 0.134 | 0.151 | 0.105 | 0.16 | 0.164 | 0.162 | 0.149 | 0.17 | −0.084 | 0.19 | -0.094 | 0.207 | 0.181 | 0.17 | 0.148 | 0.179 | 0.112 | 0.164 | 0.078 | 0.163 |
| Trust to supervisor | 0.215 | 0.177 | 0.205 | 0.193 | 0.043 | 0.19 | 0.002 | 0.206 | 0.214 | 0.223 | 0.221 | 0.251 | −0.022 | 0.198 | −0.026 | 0.217 | 0.268 | 0.192 | 0.221 | 0.197 |
| Interaction justice × trust | −0.412 ** | 0.121 | −0.374 * | 0.134 | −0.473 ** | 0.13 | −0.468 * | 0.143 | −0.201 | 0.152 | −0.190 | 0.173 | −0.451 * | 0.136 | −0.426* | 0.15 | −0.260 | 0.131 | −0.237 | 0.137 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herr, R.M.; Li, J.; Angerer, P. The Synergistic Effects of Organizational Justice and Trust to Supervisor on Vagal Tone: Preliminary Findings of an Empirical Investigation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050790
Herr RM, Li J, Angerer P. The Synergistic Effects of Organizational Justice and Trust to Supervisor on Vagal Tone: Preliminary Findings of an Empirical Investigation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(5):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050790
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerr, Raphael M., Jian Li, and Peter Angerer. 2019. "The Synergistic Effects of Organizational Justice and Trust to Supervisor on Vagal Tone: Preliminary Findings of an Empirical Investigation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 5: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050790
APA StyleHerr, R. M., Li, J., & Angerer, P. (2019). The Synergistic Effects of Organizational Justice and Trust to Supervisor on Vagal Tone: Preliminary Findings of an Empirical Investigation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(5), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050790






