The Effects of Need Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Flourishing among Young Chinese Gamers: The Mediating Role of Internet Gaming Disorder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
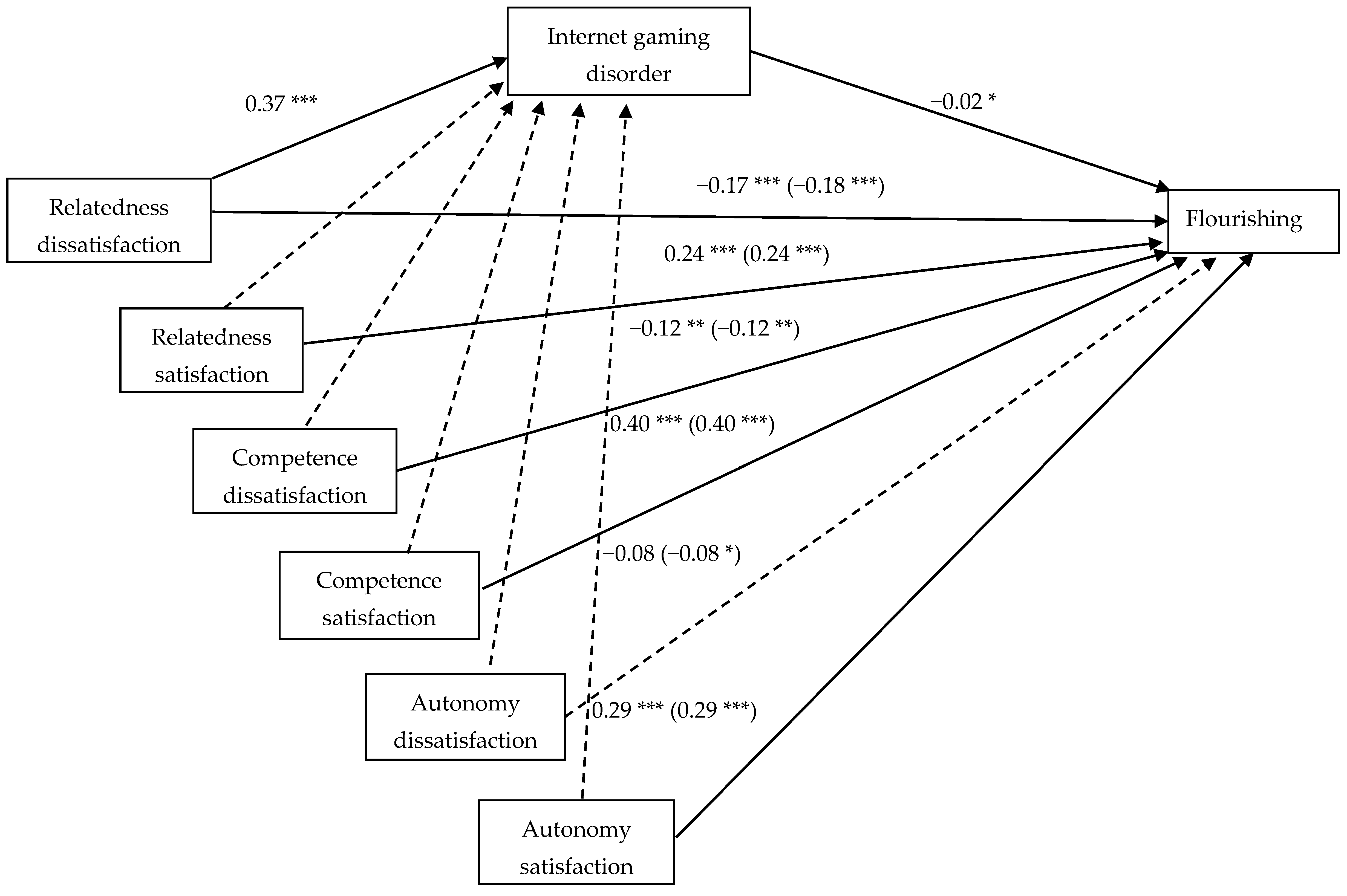
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Mediation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Intrinsic Motivation and Self-Determination in Human Behaviour; Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. The Darker and Brighter Sides of Human Existence: Basic Psychological Needs as a Unifying Concept. Psychol. Inq. 2000, 11, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.P.H.; Kogan, A. Daily Ups and Downs: An Event-Sampling Study of the Mediated Moderation of Prosocial Engagement on Well-Being. Soc. Psychol. Personal. Sci. 2018, 9, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, K.M.; Ryan, R.; Reis, H.T. What Makes for a Good Day? Competence and Autonomy in the Day and in the Person. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 1996, 22, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.S.; Lei, L.L.M.; Ku, L. Psychological Needs, Purpose in Life, and Problem Video Game Playing among Chinese Young Adults. Int. J. Psychol. 2013, 48, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldon, K.M.; Gunz, A. Psychological Needs as Basic Motives, Not Just Experiential Requirements. J. Pers. 2009, 77, 1467–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, K.M.; Hilpert, J.C. The Balanced Measure of Psychological Needs (BMPN) Scale: An Alternative Domain General Measure of Need Satisfaction. Motiv. Emot. 2012, 36, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, Y.; Gunz, A.; Curtis, G.J.; Farsides, T. Measuring Need Satisfaction and Frustration in Educational and Work Contexts: The Need Satisfaction and Frustration Scale (NSFS). J. Happiness Stud. 2016, 17, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.; Margolis, S.; Revord, J.; Lyubomirsky, S. Comparing the Effects of Performing and Recalling Acts of Kindness. J. Posit. Psychol. 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Gaming Disorder. Available online: https://www.who.int/features/qa/gaming-disorder/en/ (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- China Internet Network Information Center. Statistical Report on Internet Development in China (January 2018). Available online: http://www.cac.gov.cn/2018-01/31/c_1122347026.htm (accessed on 30 August 2019). (In Chinese)
- Demetrovics, Z.; Urbán, R.; Nagygyörgy, K.; Farkas, J.; Zilahy, D.; Mervó, B.; Reindl, A.; Ágoston, C.; Kertész, A.; Harmath, E. Why Do You Play? The Development of the Motives for Online Gaming Questionnaire (MOGQ). Behav. Res. Methods 2011, 43, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.M.S.; Lai, M.H.C.; Yu, S.; Lau, J.T.F.; Lei, M. Motives for Online Gaming Questionnaire: Its Psychometric Properties and Correlation with Internet Gaming Disorder Symptoms among Chinese People. J. Behav. Addict. 2017, 6, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiot, C.E.; de la Sablonnière, R.; Terry, D.J.; Smith, J.R. Integration of Social Identities in the Self: Toward a Cognitive-Developmental Model. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2007, 11, 364–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmens, J.S.; Valkenburg, P.M.; Peter, J. Psychosocial Causes and Consequences of Pathological Gaming. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.E.; Von Wahlde, L.; Shockley, T.; Gabbard, G.O. The Development of the Self in the Era of the Internet and Role-Playing Fantasy Games. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics. 6C51 Gaming Disorder. Available online: https://icd.who.int/browse11/l-m/en#/http://id.who.int/icd/entity/1448597234 (accessed on 30 August 2019).
- China Internet Network Information Center. 2014–2015 China Mobile Gaming Users Research Report. Available online: http://www.cnnic.cn/hlwfzyj/hlwxzbg/wybg/201601/P020160105430794926978.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2019). (In Chinese).
- Przybylski, A.K.; Weinstein, N.; Ryan, R.M.; Rigby, C.S. Having to versus Wanting to Play: Background and Consequences of Harmonious versus Obsessive Engagement in Video Games. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2009, 12, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth-Király, I.; Bőthe, B.; Márki, A.N.; Rigó, A.; Orosz, G. Two Sides of the Same Coin: The Differentiating Role of Need Satisfaction and Frustration in Passion for Screen-Based Activities. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Chiou, W. Psychological Motives and Online Games Addiction: ATest of Flow Theory and Humanistic Needs Theory for Taiwanese Adolescents. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2006, 9, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D.J.; Milyavskaya, M.; Heath, N.L.; Derevensky, J.L. Gaming Motivation and Problematic Video Gaming: The Role of Needs Frustration. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 2018, 48, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D.J.; Milyavskaya, M.; Mettler, J.; Heath, N.L. Personality and Individual Di Ff Erences Exploring the Pull and Push Underlying Problem Video Game Use: A Self- Determination Theory Approach. Pers. Individ. Dif. 2018, 135, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being. Am. Psychol. 2000, 55, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenkiste, M.; Ryan, R.M. On Psychological Growth and Vulnerability: Basic Psychological Need Satisfaction and Need Frustration as a Unifying Principle. J. Psychother. Integr. 2013, 23, 263–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, R.M.; Deci, E.L. On Happiness and Human Potentials: A Review of Research on Hedonic and Eudaimonic Well-Being. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2001, 52, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahneman, D.; Diener, E.; Schwarz, N. Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Deci, E.L.; Ryan, R.M. Hedonia, Eudaimonia, and Well-Being: An Introduction. J. Happiness Stud. 2008, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Jiang, J.; Du, X.; Gu, D.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. Striving and Happiness: Between- and within-Person-Level Associations among Grit, Needs Satisfaction and Subjective Well-Being. J. Posit. Psychol. 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, K.M.; Elliot, A.J. Goal Striving, Need Satisfaction, and Longitudinal Well-Being: The Self-Concordance Model. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 1999, 76, 482–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnell, K.E.; Crocker, P.R.E.; Mack, D.E.; Wilson, P.M.; Zumbo, B.D. Goal Contents, Motivation, Psychological Need Satisfaction, Well-Being and Physical Activity: A Test of Self-Determination Theory over 6 Months. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2014, 15, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, A.J.; Buro, K. Measuring and Predicting Student Well-Being: Further Evidence in Support of the Flourishing Scale and the Scale of Positive and Negative Experiences. Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 121, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Duan, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T. Psychometric Evaluation of the Simplified Chinese Version of Flourishing Scale. Res. Soc. Work Pract. 2016, 26, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, E.; Wirtz, D.; Biswas-Diener, R.; Tov, W.; Kim-Prieto, C.; Choi, D.; Oishi, S. New Measures of Well-Being. In Assessing Well-Being: The Collected Works of Ed Diener; Diener, E., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppert, F.A.; So, T.T.C. Flourishing Across Europe: Application of a New Conceptual Framework for Defining Well-Being. Soc. Indic. Res. 2013, 110, 837–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, E.; Wirtz, D.; Tov, W.; Kim-Prieto, C.; Choi, D.; Oishi, S.; Biswas-Diener, R. New Well-Being Measures: Short Scales to Assess Flourishing and Positive and Negative Feelings. Soc. Indic. Res. 2010, 97, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, D.A.; Choo, H.; Liau, A.; Sim, T.; Li, D.; Fung, D.; Khoo, A. Pathological Video Game Use among Youths: A Two-Year Longitudinal Study. Pediatrics 2011, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.T.F.; Walden, D.L.; Wu, A.M.S.; Cheng, K.M.; Lau, M.C.M.; Mo, P.K.H. Bidirectional Predictions between Internet Addiction and Probable Depression among Chinese Adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.B.; Mo, P.K.H.; Lau, J.T.F.; Su, X.F.; Zhang, X.; Wu, A.M.S.; Mai, J.C.; Chen, Y.X. Online Social Networking Addiction and Depression: The Results from a Large-Scale Prospective Cohort Study in Chinese Adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, B.P.H.; Ngai, P.; Qiu, J.L.; Koo, A. Having Less But Giving More: Work Experience and Prosocial Behavior of Chinese Working-Class Youth. Youth Soc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, B.P.H.; S. Wu, A.M.; Pun, N. Disentangling the Effects of Empathy Components on Internet Gaming Disorder: A Study of Vulnerable Youth in China. J. Behav. Addict. 2019, 8, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, M.R.; Rogge, R.D. Caring about Carelessness: Participant Inattention and Its Effects on Research. J. Res. Pers. 2014, 48, 61–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, A.W.; Craig, S.B. Identifying Careless Responses in Survey Data. Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 437–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.H.; Yen, J.Y.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, P.W.; Chen, C.S.; Yen, C.F. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Criteria of Internet Gaming Disorder in the DSM-5 among Young Adults in Taiwan. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2014, 53, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guildford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Toral, S.L.; Rocío Martínez-Torres, M.; Barrero, F.; Cortés, F. An Empirical Study of the Driving Forces behind Online Communities. Internet Res. 2009, 19, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T. Understanding Online Community User Participation: A Social Influence Perspective. Internet Res. 2011, 21, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Griffiths, M.D. The Attitudes, Feelings, and Experiences of Online Gamers: A Qualitative Analysis. CyberPsychol. Behav. 2009, 12, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Liu, M. Online Gaming Dependency: A Preliminary Study in China. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2010, 13, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W.; Maurage, P.; Billieux, J. Prevalence and Correlates of Problematic Online Gaming: A Systematic Review of the Evidence Published in Chinese. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2018, 5, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.X.; Wang, X.; Yu, S.M.; Wu, A.M.S. Purpose in Life, Social Support, and Internet Gaming Disorder among Chinese University Students: A 1-Year Follow-up Study. Addict. Behav. 2019, 99, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, D.; Eatough, V.; Davies, M.N.O.; Griffiths, M. EverQuest—It’s Just a Computer Game Right? An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis of Online Gaming Addiction. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2006, 4, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.; Wang, C.; Fang, W. Physical Interpersonal Relationships and Social Anxiety among Online Game Players. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2005, 8, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuss, D.J.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet Gaming Addiction: A Systematic Review of Empirical Research. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2012, 10, 278–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, A.M.S.; Pesigan, I.J.A. Cognitive and Psychosocial Health Risk Factors of Social Networking Addiction. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2016, 14, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Bian, Y.; Han, P.; Gao, F.; Wang, P. Associations between Psychosocial Factors and Generalized Pathological Internet Use in Chinese University Students: A Longitudinal Cross-Lagged Analysis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 72, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Kim, J. Cross-Validation of Reliability, Convergent and Discriminant Validity for the Problematic Online Game Use Scale. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2010, 26, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, F.; Kong, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, D.; Liu, J. Unsatisfied Relatedness, Not Competence or Autonomy, Increases Trait Anger through the Right Amygdala. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehroof, M.; Griffiths, M.D. Online Gaming Addiction: The Role of Sensation Seeking, Self-Control, Neuroticism, Aggression, State Anxiety, and Trait Anxiety. Cyberpsychol. Behav. Soc. Netw. 2010, 13, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.H.; Yen, J.Y.; Liu, S.C.; Huang, C.F.; Yen, C.F. The Associations Between Aggressive Behaviors and Internet Addiction and Online Activities in Adolescents. J. Adolesc. Health 2009, 44, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.P.; Kuperminc, G.; Philliber, S.; Herre, K. Programmatic Prevention of Adolescent Problem Behaviors: The Role of Autonomy, Relatedness, and Volunteer Service in the Teen Outreach Program. Am. J. Community Psychol. 1994, 22, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Tsai, W.; Yen, J.-Y. The Clinical Utility of the Chen Internet Addiction Scale—Gaming Version, for Internet Gaming Disorder in the DSM-5 among Young Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| M (SD) | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex a | — | −0.03 | −0.08 ** | −0.34 *** | −0.15 *** | −0.08 ** | −0.04 | −0.15 *** | −0.04 | −0.02 | −0.00 | −0.06 * |
| Age | 19.48 (1.21) | — | −0.19 *** | −0.13 *** | −0.05 | 0.07 * | −0.07 * | 0.12 *** | −0.01 | 0.09 ** | −0.05 | 0.13 *** |
| Hukou b | — | — | 0.19 *** | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.07 * | 0.03 | 0.07 * | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.01 | |
| Daily gaming frequency | 2.50 (1.92) | — | 0.26 *** | 0.06 * | 0.06 * | 0.01 | 0.08 ** | −0.02 | 0.04 | −0.06 * | ||
| Internet gaming disorder | 1.14 (1.98) | 0.84 | −0.04 | 0.13 *** | −0.07 * | 0.10 ** | −0.03 | 0.19 *** | −0.14 *** | |||
| Autonomy satisfaction | 3.40 (0.70) | 0.66 | 0.15 *** | 0.55 *** | 0.29 *** | 0.48 *** | 0.05 | 0.43 *** | ||||
| Autonomy dissatisfaction | 2.84 (0.66) | 0.42 | 0.11 *** | 0.48 *** | 0.16 *** | 0.49 *** | −0.08 ** | |||||
| Competence satisfaction | 3.45 (0.73) | 0.80 | 0.23 *** | 0.53 *** | −0.05 | 0.51 *** | ||||||
| Competence dissatisfaction | 3.22 (0.73) | 0.63 | 0.26 *** | 0.46 *** | −0.00 | |||||||
| Relatedness satisfaction | 3.59 (0.80) | 0.77 | 0.04 | 0.43 *** | ||||||||
| Relatedness dissatisfaction | 2.78 (0.79) | 0.61 | −0.22 *** | |||||||||
| Flourishing | 4.72 (0.97) | 0.94 |
| Outcome | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internet Gaming Disorder | Flourishing | ||||||||||||||
| Mediator (Model 1) | Total Effect (Model 2) | Direct Effect (Model 3) | Indirect Effect | ||||||||||||
| B | SE | t | B | SE | t | B | SE | t | B | SE | BootCI | ||||
| Sex a | −0.36 | 0.13 | −2.85 | ** | −0.03 | 0.05 | −0.63 | −0.04 | 0.05 | −0.80 | — | — | — | ||
| Age | −0.00 | 0.05 | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 1.98 | * | 0.04 | 0.02 | 1.98 | * | — | — | — | |
| Hukou b | −0.10 | 0.13 | −0.77 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 1.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 1.02 | — | — | — | |||
| Daily gaming frequency | 0.24 | 0.03 | 7.81 | *** | −0.03 | 0.01 | −2.40 | * | −0.02 | 0.01 | −1.89 | — | — | — | |
| Autonomy satisfaction | −0.13 | 0.10 | −1.38 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 7.33 | *** | 0.29 | 0.04 | 7.26 | *** | 0.003 | 0.003 | [−0.002, 0.011] | |
| Autonomy dissatisfaction | 0.16 | 0.10 | 1.58 | −0.08 | 0.04 | −1.96 | * | −0.08 | 0.04 | −1.87 | −0.004 | 0.003 | [−0.011, 0.001] | ||
| Competence satisfaction | −0.16 | 0.10 | −1.70 | 0.40 | 0.04 | 10.16 | *** | 0.40 | 0.04 | 10.06 | *** | 0.004 | 0.003 | [−0.001, 0.012] | |
| Competence dissatisfaction | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.23 | −0.12 | 0.04 | −3.06 | ** | −0.12 | 0.04 | −3.05 | ** | −0.001 | 0.002 | [−0.001, 0.004] | |
| Relatedness satisfaction | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.03 | 6.91 | *** | 0.24 | 0.03 | 6.94 | *** | −0.000 | 0.002 | [−0.006, 0.004] | |
| Relatedness dissatisfaction | 0.37 | 0.08 | 4.38 | *** | −0.18 | 0.03 | −5.27 | *** | −0.17 | 0.03 | −4.98 | *** | −0.009 | 0.004 | [−0.019, −0.002] |
| Internet gaming disorder | — | — | — | — | — | — | −0.02 | 0.01 | −2.06 | * | — | — | — | ||
| Constant | 0.59 | 1.04 | 0.57 | 1.90 | 0.43 | 4.47 | *** | 1.91 | 0.42 | 4.51 | *** | — | — | — | |
| R2 | 0.11 | 0.37 | 0.38 | — | |||||||||||
| F | 15.30 *** | 72.70 *** | 66.66 *** | — | |||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hui, B.P.H.; Wu, A.M.S.; Siu, N.Y.F.; Chung, M.-L.; Pun, N. The Effects of Need Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Flourishing among Young Chinese Gamers: The Mediating Role of Internet Gaming Disorder. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224367
Hui BPH, Wu AMS, Siu NYF, Chung M-L, Pun N. The Effects of Need Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Flourishing among Young Chinese Gamers: The Mediating Role of Internet Gaming Disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(22):4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224367
Chicago/Turabian StyleHui, Bryant Pui Hung, Anise M. S. Wu, Nicolson Y. F. Siu, Ming-Lun Chung, and Ngai Pun. 2019. "The Effects of Need Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Flourishing among Young Chinese Gamers: The Mediating Role of Internet Gaming Disorder" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 22: 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224367
APA StyleHui, B. P. H., Wu, A. M. S., Siu, N. Y. F., Chung, M.-L., & Pun, N. (2019). The Effects of Need Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction on Flourishing among Young Chinese Gamers: The Mediating Role of Internet Gaming Disorder. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(22), 4367. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16224367






