Abstract
Background and Objectives: This study developed a support vector machine (SVM) algorithm-based prediction model with considering influence factors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life as the predictor variables and provided baseline information for enhancing the swallowing quality of elderly people’s lives in the future. Methods and Material: This study sampled 142 elderly people equal to or older than 65 years old who were using a senior welfare center. The swallowing problem associated quality of life was defined by the swallowing quality-of-life (SWAL-QOL). In order to verify the predictive power of the model, this study compared the predictive power of the Gaussian function with that of a linear algorithm, polynomial algorithm, and a sigmoid algorithm. Results: A total of 33.9% of the subjects decreased in swallowing quality-of-life. The swallowing quality-of-life prediction model for the elderly, based on the SVM, showed both preventive factors and risk factors. Risk factors were denture use, experience of using aspiration in the past one month, being economically inactive, having a mean monthly household income <2 million KRW, being an elementary school graduate or below, female, 75 years old or older, living alone, requiring time for finishing one meal on average ≤15 min or ≥40 min, having depression, stress, and cognitive impairment. Conclusions: It is necessary to monitor the high-risk group constantly in order to maintain the swallowing quality-of-life in the elderly based on the prevention and risk factors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life derived from this prediction model.
1. Introduction
A swallowing problem is one of the frailty symptoms caused by aging and it can occur in healthy elderly people due to a missing tooth, esophageal weakness, and decreased cognitive function [1,2]. A nationwide survey of South Korea [3] reported that, as of 2014, 54.6% of the elderly population had difficulties in conducting daily activities due to a swallowing problem caused by the decrease in chewing ability. If a swallowing problem persists, it is highly likely to cause dysphagia. Therefore, it may decrease the ability to eat and drink efficiently and result in secondary problems such as lack of nutrient intake, dehydration, and deteriorated body functions. In severe cases, it can lead to death due to aspiration pneumonia [4]. Additionally, since dysphagia is known to decrease the quality of elderly people’s lives [5], identifying factors affecting the swallowing quality-of-life in rehabilitation science is an important topic.
Previous studies have identified old age, gender, cognitive level, stress, number of missing teeth, resilience, and social confidence as factors affecting the swallowing quality-of-life [2,6]. Roy et al. [7] reported that “taking a longer time to eat”, “a sensation of food stuck in the throat”, and “coughing, throat clearing, or choking before, during, or after eating” were major risk factors of swallowing disorders. Byeon [8] also showed that older adults using dentures had a 1.6-fold higher risk of a swallowing disorder and those accompanied by physical dysfunction had a 4.3-fold higher risk of a swallowing disorder than healthy elderly people.
However, these studies only identified individual risk factors because (1) they only focused on dysphagia-induced physical problems in patients with the damaged central nervous system such as stroke [9], and (2) they mainly used either a regression model or general linear model to evaluate factors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life [2,6,7,8]. Therefore, it is very meaningful to identify multiple risk factors influencing the swallowing quality-of-life, such as sociodemographic factors, and establishing measures to enhance the swallowing quality-of-life based on the findings.
Recent medical and public health studies have utilized data mining techniques, such as support vector machine (SVM), to explore complex risk factors of diseases [10]. SVM is less likely to cause an over-fitting problem than decision trees and it is also possible to classify non-linear data when using a kernel method, which is an advantage [11]. This study developed an SVM algorithm-based prediction model with considering various influence factors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life (e.g., sociodemographic variables, cognitive function, stress, and depression) as the predictor variables and provided baseline information for enhancing the swallowing quality of elderly people’s lives in the future.
2. Subjects and Methods
This was a cross-sectional study to identify factors affecting the swallowing quality-of-life and it targeted elderly people aged 65 years or over. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Honam University (No.1041223-201812-HR-26) and was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki. This study sampled elderly people who were using a senior welfare center located in Seoul, Incheon, or Suwon using a convenience sampling method. Sample selection criteria were (1) those who did not have a history of a neurological disease (e.g., stroke or Parkinson’s disease) that could affect swallowing; (2) those who scored at least 20 points in the Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE-K), indicating no dementia; and (3) those who agreed to participate in the study. This study estimated the required number of subjects using G*Power ver. 3.1.9.3 at effect size = 0.15, significance level = 0.05, power = 0.95, and number of predictors = 12. It was estimated that the study would need at least 132 subjects. This study recruited 150 subjects on the assumption of a 10% dropout rate, and analyzed data from 142 subjects after excluding subjects who requested to drop out during the questionnaire.
The swallowing problem associated with quality-of-life was defined by the swallowing quality-of-life (SWAL-QOL) [12]. The SWAL-QOL is composed of 44 items under eleven sub-divisions: Two items of ‘pressure’, two items of ‘eating time’, three items of ‘appetite’, 14 items of ‘frequency of symptoms’, two items of ‘food choice’, two items of ‘communication’, four items of ‘fear’, five items of ‘mental health’, five items of ‘social functions’, three items of ‘fatigue’, and two items of ‘sleep’. Each item was measured by the five-point Likert scale (strongly agree = 1, and strongly disagree = 5). The total score ranges from 44 to 220 points and a higher score indicates better swallowing quality-of-life. This study used 111 points as a cut-off score referring to previous studies [13,14] on South Korean elderly people. Cronbach’s α, indicating the internal consistency, was 0.93.
The cognitive level was defined by MMSE-K [15]. MMSK-K is composed of 30 points, and ≤23 was classified as cognitive impairment. Cronbach’s α was 0.88. Depression was measured by the geriatric depression scale short form Korea version (GDSSF-K) [16]. The total score of it is 15 points, and a higher score means a severe depression level. Depression was defined as a score ≥ 5. Cronbach’s α was 0.89. Life stress was measured using Seo’s elderly stress scale (SESS) [17]. SESS consists of 23 items: ‘economic stress (6 items)’, ‘health stress (8 items)’, ‘family stress (9 items)’. Each item is measured by a 5-point Likert scale (strongly disagree = 1, and strongly agree = 5). A higher score indicates more severe life stress, and this study defined ≥70 as the presence of stress. Cronbach’s α was 0.85.
The sociodemographic factors of this study included age (65–74 years old or ≥75 years old), gender, education level (elementary school graduate and below, middle school graduate, or high school graduate or above), living with a family (living with a spouse and a child, living only with a spouse, living only with a child, and living alone), economy activity (yes or no), mean monthly household income (<2 million KRW, 2–4 million KRW, or >4 million KRW), experience of aspiration in the past 1 month (yes or no), mean required time to finish a meal (≤15 min, 16–39 min, or ≥40 min), and denture use (yes or no).
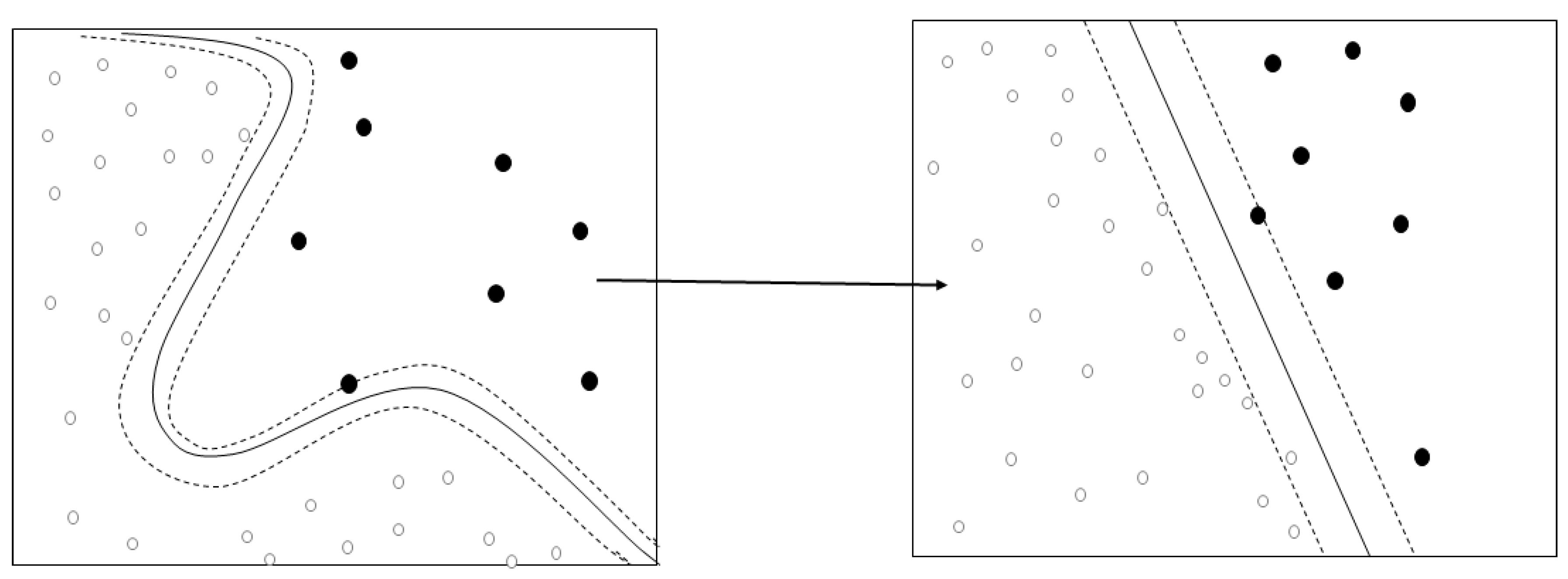
The SVM was used to develop a model to predict the swallowing quality-of-life of the elderly living in a local community (Figure 1). The SVM is a machine-learning algorithm searching for the optimal decision boundary [18]. In other words, it is a linear discriminant function that transforms learning data to a higher dimension through non-linear mapping and optimally separates hyperplane. For example, if A = (a, d) and B = (b, c) are non-linearly separable in the two-dimension, they can have linearly separable characteristics when they are mapped in three-dimensions. Therefore, when appropriate nonlinear mapping is used in a sufficiently large dimension, data containing two classes can always be separated in hyperplanes [19].
Figure 1.
Concepts of kernel algorithm.
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of Subjects
The general characteristics of 142 subjects were analyzed and summarized (Table 1). The majority of the subjects was equal to or older than 75 years old (79.2%). In total, 78.3% of the subjects were female and 21.7% were male. A total of 59.0% of the subjects were elementary school graduate level or below, 42.2% lived alone, 10.1% of the subjects were economically inactive, 72.8% of households had less than 2 million KRW monthly, 62.2% of the subjects swallowed the wrong way in the past one month, 63.7% used dentures, and 66.5% of the subjects spent 16–39 min for a meal on average. A total of 17.7% of subjects had depression, 20.5% of the subjects recognized stress, 28.0% of the subjects had a cognitive impairment, and 33.9% of the subjects decreased in swallowing quality-of-life.

Table 1.
General characteristics of subjects, n (%).
3.2. The General Characteristics of Subjects According to the Level of the Swallowing Quality-of-Life
The general characteristics of subjects according to the level of the swallowing quality-of-life and the factors potentially related to the swallowing quality-of-life are shown in Table 2. The results of the Chi-square test showed that the swallowing quality-of-life was significantly affected by age, gender, education level, living with a family or not, mean required time for completing a meal, aspiration experience in the past one month, denture use, and cognitive level. The proportion of the elderly with a low swallowing quality-of-life was significantly higher when the subjects were equal to or older than 75 years old (38.4%), were female (44.6%), were elementary school graduate or below (35.7%), were living alone (31.7%), experienced aspiration in the past one month (39.8), took 40 min or more to finish one meal on average (40.0%), used dentures (40.0%), and had cognitive impairment (45.0%).

Table 2.
The factors potentially related to the swallowing quality-of-life, %.
3.3. The Function Weights of Gaussian Kernel Algorithm-Based SVM
The function weights of the Gaussian kernel algorithm-based SVM are shown in Table 3. Although function weights of the SVM are not for simply comparing the sizes of variables or the importance of variables, it is possible to identify whether the relationship between a predictor and an outcome variable is risk or prevention. The swallowing quality-of-life prediction model for the elderly based on the SVM showed both preventive factors and risk factors. Risk factors were denture use, experience of using aspiration in the past one month, being economically inactive, having a mean monthly household income <2 million KRW, being an elementary school graduate or below, female, 75 years old or older, living alone, requiring time for finishing one meal on average ≤15 min or ≥40 min, suffering depression, stress, and cognitive impairment. On the other hand, preventive factors for those aged between 65 and 74 years old included being a middle school graduate or above, having a mean monthly household income ≥2 million KRW, no experience of aspiration in the past one month, requiring time for finishing one meal on average between 16 and 30 min, not using dentures, being economically active, not suffering depression or stress, and having a normal cognitive level. The final prediction rate of the SVM using 435 support vectors was 91.08.

Table 3.
The function weights of Gaussian kernel algorithm.
3.4. The Prediction Accuracy of the SVM-Based Swallowing Quality-of-Life
The prediction accuracy of the SVM-based swallowing quality-of-life classification algorithm is shown in Table 4. In the SVM, the fitness of a model varies by the type of a kernel. Therefore, this study compared the prediction accuracy of the linear, polynomial, and sigmoid algorithms and the Gaussian Kernel in order to compare the performance of a model depending on various kernel types. Moreover, the SVM types of the four algorithms were divided into C-SVM and Nu-SVM SVM types to compare their prediction accuracies. The fitness results showed that the accuracy of C-SVM and that of Nu-SVM did not differ much in this swallowing quality-of-life prediction model. Moreover, it was found that the accuracy of the Gaussian kernel was highest, while that of the sigmoid kernel was lowest.

Table 4.
The prediction accuracy of the SVM-based swallowing quality-of-life, %.
4. Discussion
This study developed an SVM-based swallowing quality-of-life prediction model for elderly people living in a local community. The results of this study showed that 33.9% of the elderly had low swallowing quality-of-life. Although it is not possible to compare directly, the results are similar to the results of the previous studies [7,8,20,21] conducted in the US and Japan, which reported that the proportion of dysphagia risk group ranged from 33% to 52.6% when they stayed at home. In many cases, the elderly living at home tended to consider the symptoms related to swallowing as inevitable symptoms in the process of aging, although they experienced and were aware of these symptoms, and they mostly did not even perceive that they needed to receive appropriate evaluation or treatment [8]. Particularly, the results of this study revealed that one of three elderly people living at home had low swallowing quality-of-life even though they could live independently without physical limitations. The results implied that it would be necessary to monitor the swallowing function of elderly people living in a local community continuously.
In this study, denture use, aspiration experience in the past one month, being economically inactive, having a mean monthly household income <2 million KRW, being an elementary school graduate or below, female, 75 years old or older, living alone, requiring time for finishing one meal on average ≤15 min or ≥40 min, having depression, stress, and cognitive impairment were predictors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life. A number of studies explored the risk factors of dysphagia and reported that sociodemographic factors (e.g., gender, age, and education level), denture use, and mean required time to finish a meal on average were factors influencing the swallowing quality-of-life [2,6,7], and it supported the results of this study.
In particular, the cognitive level is known to be closely associated with dysphagia. Elderly people with a decreased cognitive function cannot maintain a normal harmony among oral, pharyngeal, and laryngeal movements due to the changes in tongue movements, the rise or contraction of the hyoid bone and upper esophageal sphincter, or decreased sensory functions [22]. Consequently, the swallowing problem occurs due to decreased coordination [22,23]. Chouinard (2000) also reported that the quality of dementia patients’ lives was affected by a swallowing problem. For example, it was reported that dementia elderly had a swallowing problem due to the characteristic of delaying swallowing in the pharynx in the early stage, and it became more difficult to swallow food in the mouth as dementia became more severe [22]. Since a swallowing program can cause serious complications such as aspiration pneumonia or malnutrition when it persists for a long time, it is required to monitor a high-risk group continuously and develop a systematic guideline associated with dysphagia in order to prevent the risk of complications and maintain good swallowing quality-of-life.
Another finding of this study was that denture use was associated with low swallowing quality-of-life for the elderly. Byeon [8] identified the risk factors of the dysphagia for the elderly living in a local community using a cross-sectional approach and reported that elderly people using dentures had a 1.6-times higher risk of experiencing dysphagia than those not using dentures. It is believed that elderly people using dentures have a low swallowing quality-of-life because the dentures decrease the secretion of saliva and interfere with the formation of the bolus to adversely affect food intake [24]. Although it is highly possible that elderly people using dentures experience a decrease in swallowing quality-of-life, education programs for dysphagia have been conducted mainly for hospitalized patients in a medical institute and programs for the elderly living at home are very rare [25]. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a program customized for the elderly using dentures that can preserve the swallowing function.
This study compared the prediction accuracy of eight SVM classification algorithms (four algorithms—Gaussian kernel, linear kernel, polynomial kernel, and sigmoid, and two SVMs—C-SVM and Nu-SVM) in order to compare the performance of the SVM according to algorithms. It was found that the prediction accuracy of the C-SVM Gaussian kernel was the highest. The performance of the non-linear SVM largely depends on the kernel function and its parameters [19]. The Gaussian kernel is an algorithm that maps something in a specific space with infinite dimensions and previous studies [26,27] reported that it is an algorithm with high prediction accuracy. The results of this study suggested that using Gaussian kernel-based C-SVM is effective in predicting binary disease/impairment data.
The importance of this study is that it identified factors influencing the swallowing quality-of-life of the elderly living in a local community; these included cognitive function, depression, stress, demographic variables, and physical problems. The limitations of the study are as follows. First, this study did not examine the swallowing function levels of the subjects, which are related to the swallowing quality-of-life. It is necessary to develop a swallowing quality-of-life prediction model by conducting a standardized dysphagia risk assessment, such as the modified dysphagia risk assessment scale for an elderly person (DRACE) [24]. Second, it is not possible to generalize the results of this study because the study subjects were recruited by a convenience sampling method. Future studies are needed to conduct a survey by using a systematic sampling, such as a random sampling. Third, the results of this study cannot be interpreted as a causal relationship because this study analyzed cross-sectional data. A longitudinal study is necessary to demonstrate the causality of the risk factors identified in this study in the future.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study can be used as a basis to establish strategies for preventing and managing the swallowing problem of the elderly living in the community. It is necessary to monitor the high-risk group constantly in order to maintain the swallowing quality-of-life in the old age, based on the prevention and risk factors associated with the swallowing quality-of-life derived from this prediction model. Furthermore, it is needed to develop a customized education program for the elderly living in a local community to prevent dysphagia.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2018R1D1A1B07041091, NRF-2018S1A5A8028249, and NRF-2019S1A5A8034211).
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Clark, H.M.; Solomon, N.P. Age and sex differences in orofacial strength. Dysphagia 2011, 27, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinari, I.; Ippei, T.; Sizuka, K.; Yuki, S.; Toshiaki, O.; Yoshihiro, T.; Takao, N.; Kouichi, M.; Shigeyuki, N.; Wataru, K. Oral conditions and dysphagia in Japanese, communitydwelling middle-and older-aged adults, independent in daily living. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs. Report on the Korean National Older Adults Life Survey 2014; Ministry of Health Welfare: Seoul, Korea, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sura, L.; Madhavan, A.; Carnaby, G.; Crary, M.A. Dysphagia in the elderly: Management and nutritional considerations. Clin. Interv. Aging 2012, 7, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eslick, G.D.; Talley, N.J. Dysphagia: Epidemiology, risk factors and impact on quality of life—A population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.J.; Lee, E.; Youm, Y.S.; Kim, H.C.; Jung, E.K.; Kim, J.K.; Song, K.B.; Choi, Y.H. Relationship between stress and subjective oral dryness in the elderly in a rural region: A pilot study. J. Korean Acad. Oral Health 2017, 41, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Stemple, J.; Merrill, R.M.; Thomas, L. Dysphagia in the elderly: Preliminary evidence of prevalence, risk factors, and socioemotional effects. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2007, 116, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, H. Analysis of dysphagia risk using the modified dysphagia risk assessment for the community-dwelling elderly. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2016, 28, 2507–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.P.; Brown, S.E.; Folker, J.E.; Corben, L.A.; Delatycki, M.B. Dysphagia and swallowing-related quality of life in Friedreich ataxia. J. Neurol. 2014, 26, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozden, F.O.; Ozgonenel, O.; Ozden, B.; Aydogdu, A. Diagnosis of periodontal diseases using different classification algorithms: A preliminary study. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 18, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.T.; Lin, C.J. A study on sigmoid kernels for SVM and the training of non-PSD kernels by SMO-type methods. Submitt. Neural Comput. 2003, 3, 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mchorney, C.A.; Robbins, J.; Lomax, K.; Rosenbek, J.C.; Chignell, K.; Kramer, A.E.; Bricker, D.E. The SWAL-QOL and SWAL-CARE outcomes tool for oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: III. documentation of reliability and validity. Dysphagia 2002, 17, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cha, Y.J. Reliability and validity of Korean version of the SWAL-QOL. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Cooper. Soc. 2014, 15, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D.G.; Yoo, D.H. A comparison of the swallowing function and quality of life by oral intake level in stroke patients with dysphagia. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2017, 29, 1552–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Na, D.L.; Hahn, S. A validity study on the Korean Mini-Mental State Examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J. Korean Neurol. Assoc. 1997, 15, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, B.S. A preliminary study for the standardization of geriatric depression scale short form-Korea version. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 1996, 131, 298–307. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y. Effect Factors on Psychological Well-Being in Elderly Women; Catholic University: Daegu, Korea, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Raho, G.; Al-Shalabi, R.; Kanaan, G.; Nassar, A. Different classification algorithms based on Arabic text classification: Feature selection comparative study. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2015, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinwart, I.; Christmann, A. Support Vector Machines; Springer Science & Business Media: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Furey, T.S.; Cristianini, N.; Duffy, N.; Bednarski, D.W.; Schummer, M.; Haussler, D. Support vector machine classification and validation of cancer tissue samples using microarray expression data. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukada, J.; Kamakura, Y.; Manzai, T.; Kitaike, T. Development of dysphagia risk screening system for elderly persons. Jpn. J. Dysphagia Rehabilit. 2006, 10, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Chouinard, J. Dysphagia in Alzheimer disease: A review. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2000, 4, 214–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wieseke, A.; Bantz, D.; Siktberg, L.; Dillard, N. Assessment and Early Diagnosis of Dysphagia. Geriatr. Nurs. 2008, 29, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, S.A. Prevalence and influencing factors of dysphagia risk in the community-dwelling elderly. J. Kor. Gerontol. Soc. 2014, 34, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, G.; Jayasekeran, V.; Pendleton, N.; Horan, M.; Jones, M.; Hamdy, S. Prevalence and symptom profiling of oropharyngeal dysphagia in a community dwelling of an elderly population: A self-reporting questionnaire survey. Dis. Esophagus 2011, 24, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, B.C.; Ho, H.H.; Li, C.H.; Hung, C.C.; Taur, J.S. A kernel-based feature selection method for SVM with RBF kernel for hyperspectral image classification. J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- Byeon, H. Model Development for Predicting the Occurrence of Benign Laryngeal Lesions using Support Vector Machine: Focusing on South Korean Adults Living in Local Communities. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).