Daily Physical Activity Among Toddlers: Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Assessments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Accelerometer Data Processing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
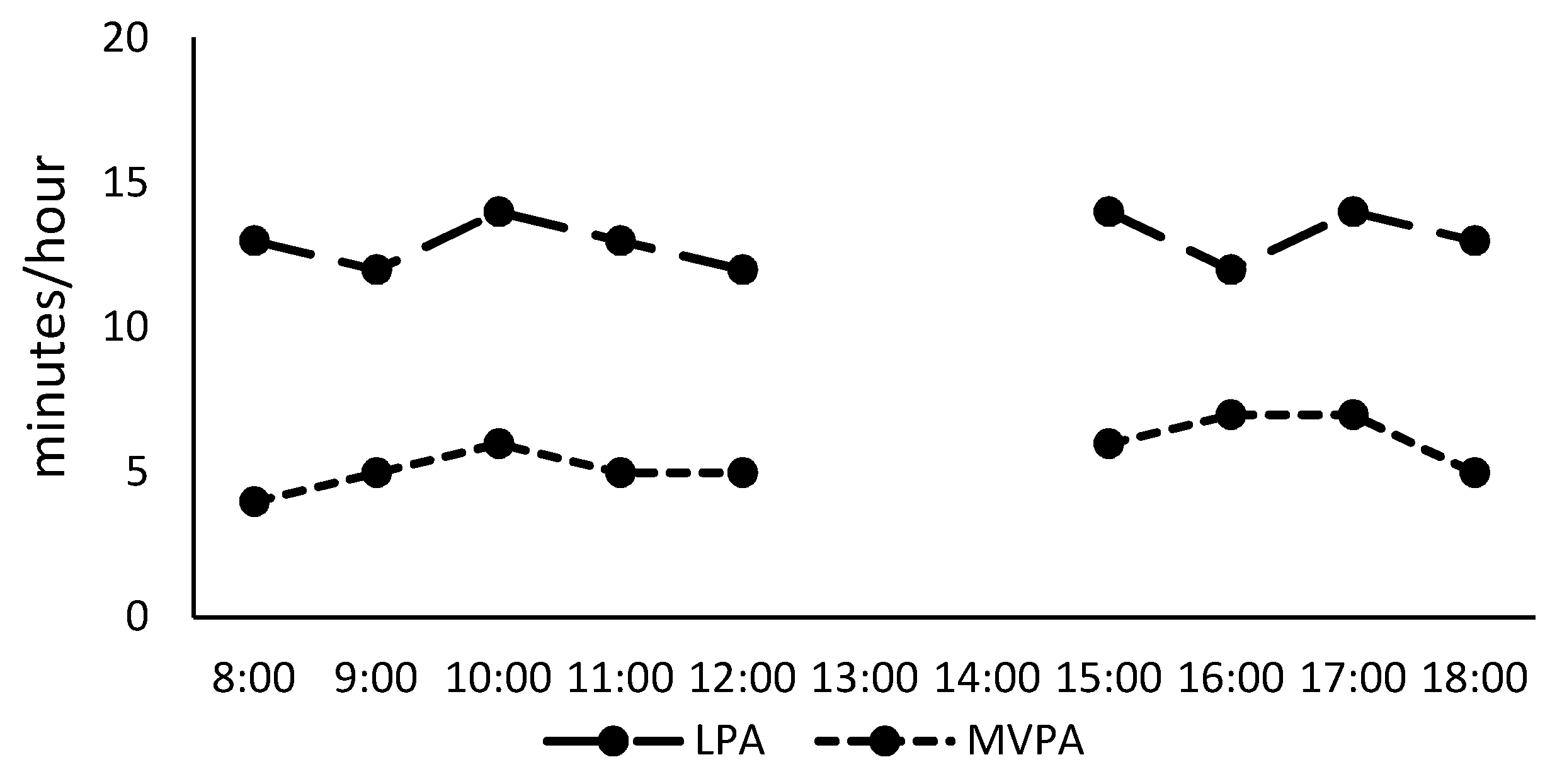
3. Results
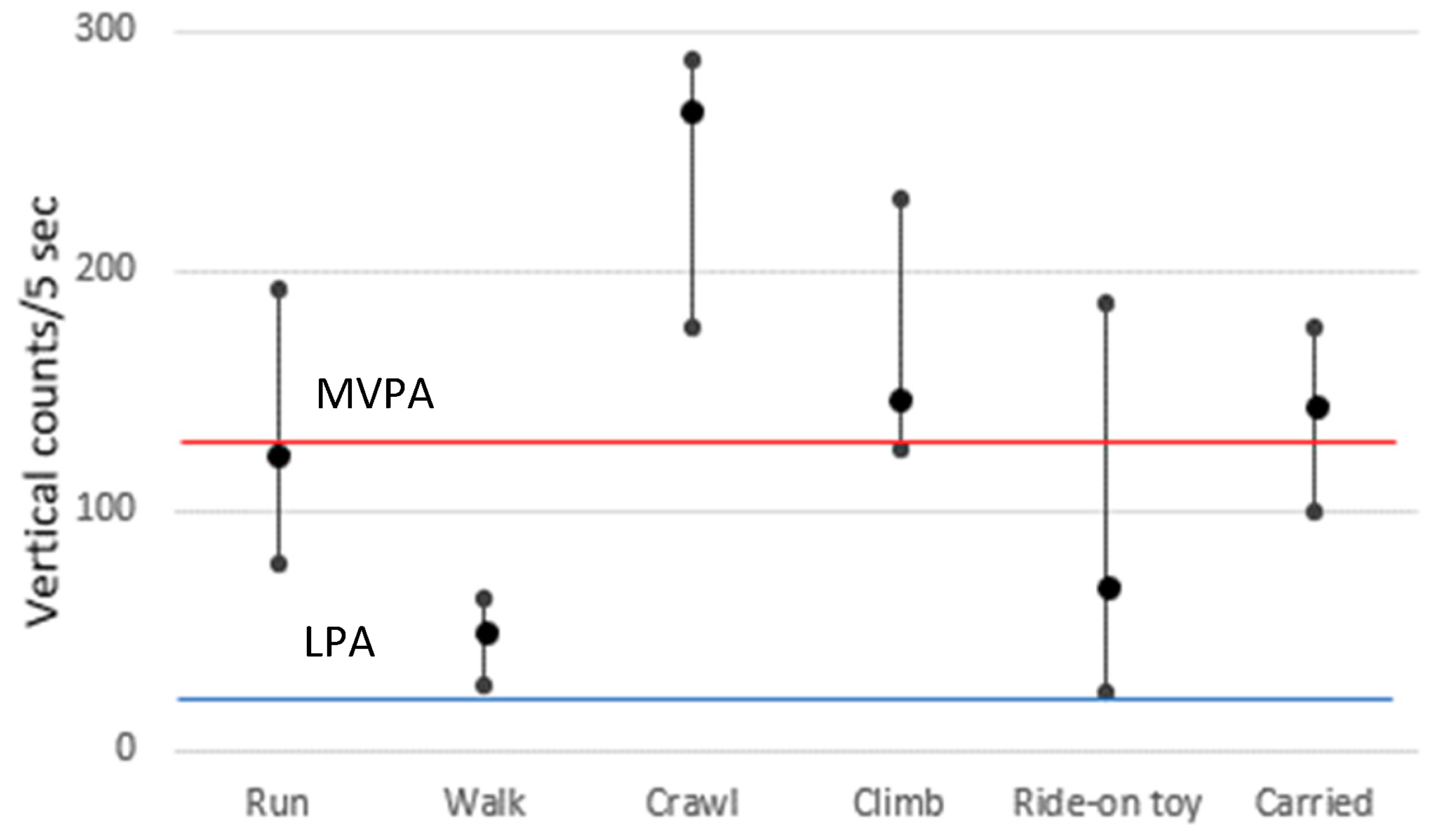
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Physical Activity Guidelies for Americans Committee. 2018 Physical Activity Guidelines Advisory Committee Scientific Report; Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- National Physical Activity Plan Alliance. The 2018 United States Report Card on Physical. Activity for Children and Youth; SHAPE America: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.; Janz, K.; Letuchy, E.; Trudy, B.; Steven, L. Developmental trajectories of physical activity, sports, and television viewing during childhood to young adulthood. Pediatrics 2015, 169, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, V.; Lee, E.Y.; Hesketh, K.D. Physical activity and sedentary behavior across three time-points and associations with social skills in early childhood. BMC Public Health 2019, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meredith-Jones, K.; Haszard, J.; Moir, C. Physical activity and inactivity trajectories associated with body composition in pre-schoolers. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.; Barber, S.E.; Cameron, N.; Clemes, S.A. The objective measurement of physical activity and sedentary behaviour in 2–3 year olds and their parents: A cross-sectional feasibility study in the bi-ethnic Born in Bradford cohort. BMC Public Health 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnatiuk, J.; Ridgers, N.D.; Salmon, J.; Campbell, K.; McCallum, Z.; Hesketh, K. Physical activity levels and patterns of 19-month-old children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1715–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkhoff, C.M.; Heale, L.D.; Anderson, L.N. Objectively measured physical activity of young Canadian children using accelerometry. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 40, 1302–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Hesketh, K.D.; Rhodes, R.E.; Rinaldi, C.M.; Spence, J.C.; Carson, V. Role of parental and environmental characteristics in toddlers’ physical activity and screen time: Bayesian analysis of structural equation models. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2018, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, E.R.; Gormley, C.E.; Latta, L.W.; Treuth, M.S.; Caulfield, L.E.; Black, M.M. Toddler physical activity study: Laboratory and community studies to evaluate accelerometer validity and correlates. BMC Public Health. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzik, N.; Clark, D.; Ogden, N.; Harber, V.; Carson, V. Physical activity and sedentary behaviour of toddlers and preschoolers in child care centres in Alberta, Canada. Can. J. Public Health 2015, 106, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, H.; Zhou, S.M.; Todd, C. Predictors of objectively measured physical activity in 12-month-old infants: A study of linked birth cohort data with electronic health records. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, B.; Covington, L.B.; Hager, E.R.; Black, M.M. Objective sleep and physical activity using 24-h ankle-worn accelerometry among toddlers from low-income families. Sleep Health 2019, 5, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijtzes, A.I.; Kooijman, M.N.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C. Correlates of physical activity in 2-year-old toddlers: The generation R study. J. Pediatr. 2013, 163, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, E.; Hagströmer, M.; Svensson, V. Objectively measured physical activity in two-year-old children-levels, patterns and correlates. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.Y.; Hesketh, K.D.; Hunter, S. Meeting new Canadian 24-Hour Movement Guidelines for the Early Years and associations with adiposity among toddlers living in Edmonton, Canada. BMC Public Health 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hnatiuk, J.; Salmon, J.; Campbell, K.J.; Ridgers, N.D.; Hesketh, K.D. Early childhood predictors of toddlers’ physical activity: Longitudinal findings from the Melbourne InFANT Program. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, S.; Rosu, A.; Hesketh, K.D. Objectively Measured Environmental Correlates of Toddlers’ Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, K.L.; Sallis, J.F.; Conway, T.L.; Van Dyck, D.L. Using accelerometers in youth physical activity studies: A review of methods. J. Phys. Act. Health 2013, 10, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, E.; Gubbels, J.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Cardon, G. Feasibility and validity of accelerometer measurements to assess physical activity in toddlers. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairclough, S.J.; Noonan, R.; Rowlands, A.V.; Van Hees, V.; Knowles, Z.; Boddy, L.M. Wear Compliance and Activity in Children Wearing Wrist- and Hip-Mounted Accelerometers. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, S.G.; Zheng, Y.; Wong, W.K. Machine learning for activity recognition: Hip versus wrist data. Physiol. Meas. 2014, 35, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, K.; Kerr, J.; Godbole, S.; Staudenmayer, J.; Lanckriet, G. Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Algorithms for Free-Living Behavior Classification. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, M.; Tremblay, F.; Pronovost, E.; Julien, A.S.; Marc, I. Accelerometry to measure physical activity in toddlers: Determination of wear time requirements for a reliable estimate of physical activity. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; Fees, B.S.; Haar, S.J.; Murray, A.D.; Crowe, L.K. Identification and validity of accelerometer cut-points for toddlers. Obesity 2012, 20, 2317–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.; Zavos, P.; Nickele, K.; Sugianto, A.; Albert, M.A. Hip and wrist-worn accelerometer data analysis for toddler activities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkley, T.; O’Connell, E.; Okely, A.D.; Crawford, D.; Hesketh, K.; Salmon, J. Assessing volume of accelerometry data for reliability in preschool children. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Item | Hip | Wrist | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1 Year Old | 2 Years Old | Total | 1 Year Old | 2 Years Old | |
| Participants, n | 22 | 11 | 11 | 22 | 11 | 11 |
| Toddler refusals to wear monitors, n | 1 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| ≥3 days of wear, n | 19 | 10 | 9 | 14 | 6 | 8 |
| Daily wear minutes, median (min, max) | 499 | 491 | 545 | 479 | 440 | 525 |
| (403, 595) | (403, 594) | (416, 595) | (345, 634) | (345, 487) | (417, 634) | |
| Item | Hip | Wrist | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 1 Year Old | 2 Years Old | Total | 1 Year Old | 2 Years Old | |
| Vertical counts, x 103 counts/day | 254 | 257 | 252 | 1069 | 938 | 1163 |
| (226, 283) | (213, 300) | (200, 304) | (875, 1264) | (467, 1409) | (954, 1372) | |
| Vector magnitude, x 103 counts/day | 590 | 599 | 581 | 1814 | 1559 | 1996 |
| (535, 645) | (512, 685) | (486, 675) | (1492, 2135) | (835, 2282) | (1638, 2354) | |
| LPA, mins/day | 161 (147, 176) | 156 (133, 178) | 168 (144, 192) | NA | NA | NA |
| MVPA, mins/day | 47 (39, 56) | 50 (38, 62) | 44 (29, 60) | NA | NA | NA |
| Study | Sample | MVPA Definition | MVPA, Mins/Day |
|---|---|---|---|
| InFANT study [7] | 295 children aged 18–19 months | >1672 Hip-worn ActiGraph counts/min | 48 |
| TARGet Kids! Study [8] | 28 children aged < 18 months | ≥2860 hip-worn Actical counts/min | 4 |
| TARGet Kids! Study [8] | 45 children aged 18–59 months old | ≥2860 hip-worn Actical counts/min | 29 |
| Hager et al. [10] | 191 children aged 12–36 months | ≥2201 ankle-worn Actical counts/min | 54 |
| Alberta childcare study [11] | 114 children aged 19–60 months | ≥287.5 hip-worn Actical counts/15 s | 4 |
| Generation R study [14] | 347 children aged 2 years | ≥615 hip-worn ActiGraph accelerometer counts/15 s | 25 |
| Early STOPP study [15] | 123 children aged 2 years | >440 wrist-worn ActiGraph accelerometer counts/5 s * | 84 |
| PREPS study [18] | 149 children aged 19 months on average (12–23 months) | >420 Hip-worn ActiGraph counts/15 s | 58 |
| The current study | 19 children aged 13–35 months | ≥420 Hip-worn ActiGraph counts/15 s | 47 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, S.; Honegger, K.; Mason, M. Daily Physical Activity Among Toddlers: Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Assessments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214244
Kwon S, Honegger K, Mason M. Daily Physical Activity Among Toddlers: Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Assessments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(21):4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214244
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Soyang, Kyle Honegger, and Maryann Mason. 2019. "Daily Physical Activity Among Toddlers: Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Assessments" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 21: 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214244
APA StyleKwon, S., Honegger, K., & Mason, M. (2019). Daily Physical Activity Among Toddlers: Hip and Wrist Accelerometer Assessments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(21), 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16214244





