Analysis of Sociodemographic and Psychological Variables Involved in Sleep Quality in Nurses
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Factors Influencing Sleep Quality
1.2. Current View of Work
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sleep Quality in Nurses and Sociodemographic Variables
3.2. Factors Associated with Sleep Quality in Nurses
3.3. Related Variables to Sleep Quality in Nurses
3.4. Related Variables to Sleep Quality in Nurses, According to Marital Status
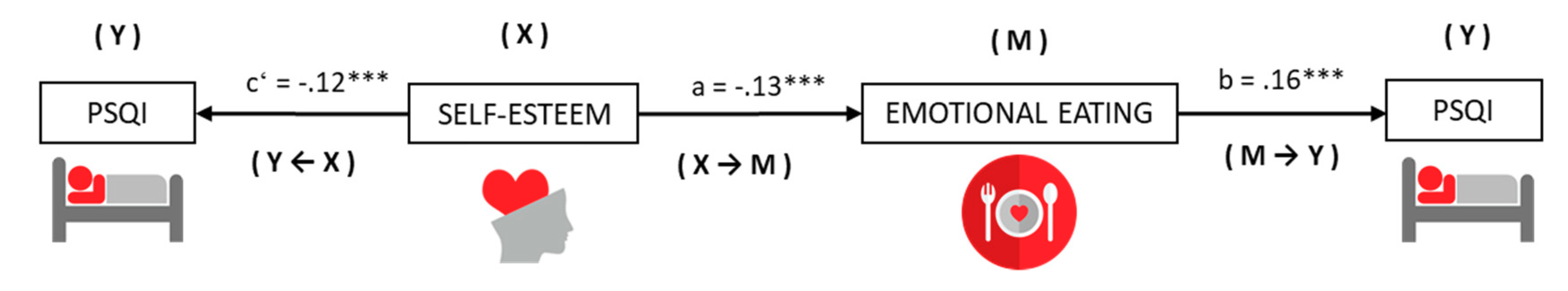
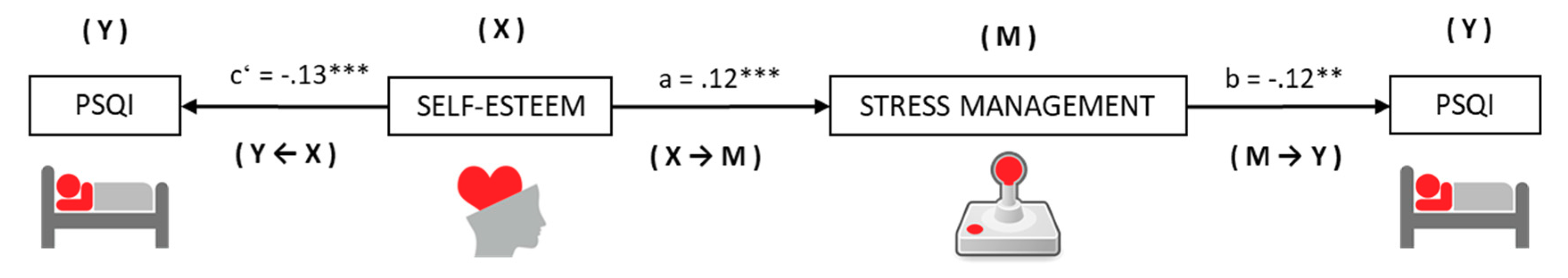
3.5. Effects of Mediation and Moderate Medication on the Relationship between Self-Esteem and Sleep Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madrid-Valero, J.J.; Martínez-Selva, J.M.; Ribeiro do Couto, B.; Sánchez-Romera, J.F.; Ordoñana, J.R. Age and gender effects on the prevalence of poor sleep quality in the adult population. Gac. Sanit. 2017, 31, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguado, T. Sleep quality in hospital, health and non-healthcare professionals. Rev. Enferm. Trab. 2016, 6, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- De Castilho, V.; Corrente, J.E.; Bojikian, B. Association between sleep quality and quality of life in nursing professionals working rotating shifts. Rev. Saúde Pública 2014, 48, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, D.; Gustavsson, P. Declining sleep quality among nurses: A population-based four-year longitudinal study on the transition from nursing education to working life. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zencirci, A.D.; Arslan, S. Morning-evening type and burnout level as factors influencing sleep quality of shift nurses: A questionnaire study. Croat. Med. J. 2011, 52, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaoka, S.; Aritake, S.; Komada, Y.; Ozaki, A.; Odagiri, Y.; Inoue, S.; Shimomitsu, T.; Inoue, Y. Factors associated with shift work disorder in nurses working with rapid-rotation schedules in Japan: The nurses’ sleep health project. Chronobiol. Int. 2013, 30, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, P.L.; Su, H.F.; Hsieh, P.C.; Siao, R.Y.; Ling, P.Y.; Jou, H.J. Sleep quality among female hospital staff nurses. Sleep Disorders 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, B.; De Martino, M.M. Analysis of cognitive function and sleep of nursing staff on different shift work. Rev. Gaúcha Enferm. 2013, 34, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Molero, M.M.; Barragán, A.B.; Martos, A.; Gázquez, J.J. Association with the Quality of Sleep and the Mediating Role of Eating on Self-Esteem in Healthcare Personnel. Nutrients 2019, 11, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiffer, D.; Minonzio, M.; Dipaola, F.; Bertola, M.; Zamuner, A.R.; Vecchia, L.A.; Solbiati, M.; Costantino, G.; Furlan, R.; Barbic, F. Effects of Clockwise and Counterclockwise Job Shift Work Rotation on Sleep and Work-Life Balance on Hospital Nurses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, D.M.; Li, C.B.; Tao, M.F. Influencing Factors for Sleep Quality Among Shift-working Nurses: A Cross-Sectional Study in China Using 3-factor Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. Asian Nurs. Res. 2016, 10, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peter, L.; Reindl, R.; Zauter, S.; Hillemacher, T.; Richter, K. Effectiveness of an Online CBT-I Intervention and a Face-to-Face Treatment for Shift Work Sleep Disorder: A Comparison of Sleep Diary Data. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, G.; Coates, A.; Sargent, C.; Dorrian, J. Sleep Duration and Chronic Fatigue Are Differently Associated with the Dietary Profile of Shift Workers. Nutrients 2016, 8, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Molero, M.M.; Simón, M.M.; Barragán, A.B.; Gázquez, J.J. Emotional Effects of the Duration, Efficiency, and Subjective Quality of Sleep in Healthcare Personnel. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmbach, D.A.; Pillai, V.; Cheng, P.; Arnedt, J.T.; Drake, C.L. Shift Work Disorder, Depression, and Anxiety in the Transition to Rotating Shifts: The Role of Sleep Reactivity. Sleep Med. 2015, 16, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panczyk, M.; Woynarowska-Sołdan, M.; Żmuda-Trzebiatowska, H.; Gotlib, J. Health-enhancing behaviours of nurses in Poland and their association with shift work and age. Collegian 2018, 25, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzweiler, K.; Voigt, K.; Kugler, J.; Hirsch, K.; Bergmann, A.; Riemenschneider, H. Factors influencing sleep quality among nursing staff: Results of a cross sectional study. Appl. Nurs. Res. 2016, 32, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antúnez, J.M.; Navarro, J.F.; Adan, A. Circadian typology and problems in mental health. An. Psicol. 2014, 30, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadie, A.; Shafto, M.; Leng, Y.; Kievit, R.A.; Cam-CAN. How are age-related differences in sleep quality associated with health outcomes? An epidemiological investigation in a UK cohort of 2406 adults. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e014920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandolim, N.; Neves, S.; Viseu, J.N.; Dieter, C.; Guerreiro, M.; Domingues, R.B. Depression and quality of life in older adults: Mediation effect of sleep quality. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2018, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putilov, A.A. Age-related changes in the association of sleep satisfaction with sleep quality and sleep-wake pattern. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 2018, 16, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, B.O.C.L.; Li, L.; Meng, L.R.; Ungvari, G.S.; Forester, B.P.; Chiu, H.F.K.; Kuok, K.C.F.; Tran, L.; Liu, Z.M.; Xiang, Y.T. Prevalence of sleep disturbances and their associations with demographic and clinical characteristics and quality of life in older adults in Macao. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 2016, 54, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, A.; Lim, M.L.; Gwee, X.; Ho, R.C.M.; Collinson, S.L.; y Ng, T.P. Insomnia and daytime neuropsychological test performancein older adults. Sleep Med. 2016, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Sang, F.; Xu, Y. Sleep disturbances among Chinese clinical nurses in general hospitals and its influencing factors. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koikawa, N.; Shimada, S.; Suda, S.; Murata, A.; Kasai, T. Sex differences in subjective sleep quality, sleepiness, and health-related quality of life among collegiate soccer players. Sleep Biol. Rhythms 2016, 14, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, J.R.; Vafa, F.; Pejman, M. Factors affecting quality of life and marital satisfaction among married nurses and nursing assistants. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2017, 10, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.C.; Suh, S.; Kim, H.; Cho, E.; Lee, S.K.; Shin, C. Testing bidirectional relationships between marital quality and sleep disturbances: A 4-year follow-up study in a Korean cohort. J. Psychosomat. Res. 2013, 74, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Grey, M.; Whittemore, R.; Reuning-Scherer, J.; Grilo, C.M.; Sinha, R. Examining the mediating roles of binge eating and emotional eating in the relationships between stress and metabolic abnormalities. J. Behav. Med. 2016, 39, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dweck, J.S.; Jenkins, S.M.; Nolan, L.J. El papel de la alimentación emocional y el estrés en la influencia del sueño corto en el consumo de alimentos. Apetito 2014, 72, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, H.; Stanulewicz, N.; McGill, F. Predictors of physical activity and barriers to exercise in nursing and medical students. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 73, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reche, C.; De Francisco, C.; Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Ros-Martínez, A. Relationship among sociodemographic and sport variables, exercise dependence, and burnout: A preliminary study in athletes. An. Psicol. 2018, 34, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janurek, J.; Hadi, S.A.; Mojzisch, A.; Häusser, J.A. The Association of the 24 Hour Distribution of Time Spent in Physical Activity, Work, and Sleep with Emotional Exhaustion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prado, V.; Villanueva, L.; Górriz, A. Trait emotional intelligence and subjective well-being in adolescents: The moderating role of feelings. Psicothema 2018, 30, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azpiazu, L.; Esnaola, I.; Sarasa, M. Capacidad predictiva del apoyo social en la inteligencia emocional de adolescentes. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 2015, 8, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, A.M.; Méndez, I.; García-Munuera, I. Emotional intelligence, quality of life and alexithymia in elders of an institutionalizazed center. Eur. J. Health Res. 2017, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, R. The Emotional Quotient Inventory (EQ-I): Techical Manual; Multi-Health Systems: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, F.M. Relationships between coping with daily stress, self-concept, social skills and emotional intelligence. Eur. J. Educ. Psychol. 2017, 10, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.M.; Morales, F.M.; Pérez, J.M.; García, B. Differences in empathy and emotional intelligence in relation to academic performance. Eur. J. Develop. Educ. Psychop. 2017, 5, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devonport, T.J.; Nicholls, W.; Fullerton, C. A systematic review of the association between emotions and eating behaviour in normal and overweight adult populations. J. Health Psychol. 2019, 24, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emert, S.E.; Tutek, J.; Lichstein, K.L. Associations between sleep disturbances, personality, and trait emotional intelligence. Pers. Individ. Differ. 2017, 107, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, A.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Molero, M.M.; Gázquez, J.J.; Simón, M.M.; Barragán, A.B. Burnout and engagement in students of health sciences. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2018, 8, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairholme, C.P.; Nosen, E.L.; Nillni, Y.I.; Schumacher, J.A.; Tull, M.T.; Coffey, S.F. Sleep disturbance and emotion dysregulation as transdiagnostic processes in a comorbid sample. Behav. Res. Ther. 2013, 51, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Meg, M.C.; Lee, H.C.; Huang, L.H. The relationships among sleep quality and chronotype, emotional disturbance, and insomnia vulnerability in shift Nurses. J. Nurs. Res. 2015, 23, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herr, R.M.; Barrech, A.; Riedel, N.; Riedel, N.; Gündel, H.; Angerer, P.; Li, J. Long-Term Effectiveness of Stress Management at Work: Effects of the Changes in Perceived Stress Reactivity on Mental Health and Sleep Problems Seven Years Later. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, S.; Michael, H.; Antoni, M.H.; Carver, C.H.; Lechner, S.C.; Wohlgemuth, W.; Llabre, M.; Blomberg, B.B.; Glück, S.; DerHagopian, R.P. Sleep Quality and Fatigue After A Stress Management Intervention For Women With Early-Stage Breast Cancer in Southern Florida. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2014, 21, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phana, T.X.; Malkani, R.G. Sleep and circadian rhythm disruption and stress intersect in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Stress 2019, 10, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molero, M.M.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Gázquez, J.J.; Barragán, A.B. Burnout in health professionals according to their self-esteem, social support and empathy profile. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simón, M.M.; Molero, M.M.; Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Gázquez, J.J.; Barragán, A.B.; Martos, A. Analysis of the relationship between perceived social support, global self-esteem and general self-efficacy. Eur. J. Health Res. 2017, 3, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemola, S.; Räikkönen, K.; Gomez, V.; Allemand, M. Optimism and self-esteem are related to sleep. Results from a large community-based sample. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2013, 20, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnama, F.; Mardani-Hamooleh, M.; Kouhnavard, M. Correlation between moral sensitivity and self-esteem in nursing personnel. J. Med. Ethics Hist. Med. 2017, 10, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.; Burnard, P.; Bennett, K.; Hebden, U. Un estudio longitudinal del estrés y la autoestima en estudiantes de enfermería. Enfermera Educ. Hoy 2010, 30, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- İlhan, N.; Sukut, O.; Akhan, L.U.; Batmaz, M. The effect of nurse education on the self-esteem and assertiveness of nursing students: A four-year longitudinal study. Nurse Educ. Today 2016, 39, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemola, S.; Räikkönen, K.; Scheier, M.F.; Matthews, K.A.; Pesonen, A.K.; Heinonen, K.; Lahti, J.; Komsi, N.; Paavonen, J.E.; Kajantie, E. Sleep quantity, quality and optimism in children. J. Sleep Res. 2011, 20, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, E.; Reis, D.; Barqueiro de Oliveira, R.; Ingrid Ribeiro, I.; da Silva, E.; Lacerda, R.; Benvenuto, C.; Finotti, V.; Coelho de Oliveira, R.; Friedlander, R.; et al. Stress, self-esteem and well-being among female health professionals: A randomized clinical trial on the impact of a self-care intervention mediated by the senses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, C.; Ruiz-Hernández, J.A.; Llor-Zaragoza, L.; Llor-Zaragoza, P.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.A. User Violence and Psychological Well-being in Primary Health-Care Professionals. Eur. J. Psychol. Appl. Legal Context 2018, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi-Jung, T.; Kenneth, K.H.; Roger, C.M.; Wai San Wilson, T. Prevalence of depression among nursing students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nurse Educ. Today 2018, 63, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royuela, A.; Macías, J.A. Clinimetric properties of the Spanish version of the Pittsburgh questionnaire. Vigilia-Sueño 1997, 9, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza, F.L.; Moreno, Y.; Balaguer, I. An Analysis of the Dimensionality of the Rosenberg Self-Esteem Scale in a sample of Valencian Adolescents. Revista de Psicología Universitas Tarraconensis 2000, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg, M. Society and Adolescent Self-Image; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Sebire, S.J.; Standage, M.; Vansteenkiste, M. Development and validation of the Goal Content for Exercise Questionnaire. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2008, 30, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Gázquez, J.J.; Mercader, I.; Molero, M.M. Brief Emotional Intelligence Inventory for Senior Citizens (EQ-i-M20). Psicothema 2014, 26, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Fuentes, M.C.; Molero, M.M.; Gázquez, J.J.; Oropesa, N.F. Propiedades psicométricas del Three Factor Eating Questionnaire en personal sanitario. Nutrición Hospitalaria 2019, 36, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Jang, S.I.; Jun, Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, H.J.; Park, E.C. Relationship between Mobile Phone Addiction and the Incidence of Poor and Short Sleep among Korean Adolescents: A Longitudinal Study of the Korean Children & Youth Panel Survey. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2017, 32, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean | SD | Correlation PSQI | CI 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Factor Eating Questionnaire (R18) | Uncontrolled eating | 17.34 | 5.86 | 0.17 *** | 0.112, 0.227 |
| Emotional eating | 5.74 | 2.49 | 0.19 *** | 0.132, 0.246 | |
| Restricted eating | 16.04 | 4.56 | 0.04 | −0.019, 0.099 | |
| Goal Content for Exercise Questionnaire (GCEQ) | Social affiliation | 13.96 | 5.60 | −0.01 | −0.069, 0.049 |
| Image | 17.76 | 4.86 | 0.06 * | 0.001, 0.119 | |
| Management of health | 21.72 | 4.47 | −0.00 | −0.059, 0.059 | |
| Social recognition | 10.91 | 5.33 | 0.03 | −0.029, 0.089 | |
| Skill development | 17.93 | 5.23 | −0.03 | −0.089, 0.029 | |
| Brief Emotional Intelligence Inventory (EQ–i–M20) | Intrapersonal | 9.86 | 2.87 | −0.05 | −0.109, 0.009 |
| Interpersonal | 11.65 | 2.04 | −0.01 | −0.069, 0.049 | |
| Stress management | 12.48 | 2.23 | −0.14 *** | −0.198, −0.081 | |
| Adaptability | 11.11 | 2.13 | −0.06 * | −0.119, −0.001 | |
| Mood | 11.75 | 2.33 | −0.20 *** | −0.256, −0.142 | |
| Rosenberg Self-esteem Questionnaire | Self-esteem | 32.45 | 4.53 | −0.23 *** | −0.285, −0.173 |
| Model | R | R2 | Corrected R2 | Change statistics | Durbin Watson | |||||||||
| Std error of estimation | Change in R2 | Change in F | Sig. of change in F | |||||||||||
| 1 (a) | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 2.82 | 0.05 | 62.29 | 0.000 | 1.91 | ||||||
| 2 (b) | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 0.01 | 21.90 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 3 (c) | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 2.77 | 0.01 | 18.97 | 0.000 | |||||||
| 4 (d) | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 2.76 | 0.00 | 7.70 | 0.005 | |||||||
| Model 4 | Non-standardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t | Sig. | CI 95% | Collinearity | ||||||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower limit | Upper limit | Tol. | VIF | ||||||||
| (Constant) | 8.89 | 0.88 | 10.06 | 0.000 | 7.059 | 10.561 | ||||||||
| Self-esteem | −0.11 | 0.02 | −0.17 | −5.73 | 0.000 | −0.153 | −0.076 | 0.89 | 1.11 | |||||
| Emotional eating | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 4.21 | 0.000 | 0.079 | 0.217 | 0.91 | 1.08 | |||||
| Age | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 4.53 | 0.000 | 0.033 | 0.083 | 0.99 | 1.00 | |||||
| Stress management | −0.11 | 0.04 | −0.08 | −2.77 | 0.005 | −0.188 | −0.033 | 0.91 | 1.09 | |||||
| DIVORCED/SEPARATED | Model | R | R2 | Corrected R2 | Change statistics | Durbin Watson | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Std error of estimation | Change in R2 | Change in F | Sig. of change in F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.65 | 0.43 | 0.40 | 2.64 | 0.43 | 16.69 | 0.000 | 2.34 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 0.73 | 0.53 | 0.49 | 2.44 | 0.10 | 4.84 | 0.039 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 0.80 | 0.64 | 0.58 | 2.20 | 0.10 | 5.77 | 0.026 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model 1 | Non-standardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t | Sig. | CI 95% | Collinearity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower limit | Upper limit | Tol. | VIF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Constant) | 18.00 | 4.37 | 4.11 | 0.001 | 8.882 | 27.137 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Emotional eating | 0.49 | 0.17 | 0.43 | 2.88 | 0.009 | 0.136 | 0.847 | 0.77 | 1.28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image | −0.42 | 0.14 | −0.39 | −2.86 | 0.010 | −0.727 | −0.114 | 0.93 | 1.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mood | −0.47 | 0.19 | −0.36 | −2.40 | 0.026 | −0.879 | −0.062 | 0.79 | 1.25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SINGLE | Model | R | R2 | Corrected R2 | Change statistics | Durbin Watson | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Std error of estimation | Change in R2 | Change in F | Sig. of change in F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 2.76 | 0.05 | 32.90 | 0.000 | 1.98 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 0.26 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 2.75 | 0.01 | 7.59 | 0.006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model 2 | Non-standardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t | Sig. | CI 95% | Collinearity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower limit | Upper limit | Tol. | VIF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Constant) | 9.51 | 1.06 | 8.96 | 0.000 | 6.914 | 11.396 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Self-esteem | −0.14 | 0.02 | −0.22 | −5.50 | 0.000 | −0.203 | −0.098 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Age | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 2.75 | 0.006 | 0.019 | 0.114 | 0.99 | 1.00 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MARRIED/STABLE RELATIONSHIP | Model | R | R2 | Corrected R2 | Change statistics | Durbin Watson | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Std error of estimation | Change in R2 | Change in F | Sig. of change in F | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 2.80 | 0.06 | 35.26 | 0.000 | 1.88 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 2.75 | 0.03 | 19.28 | 0.000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 0.32 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 2.74 | 0.00 | 3.86 | 0.050 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Model 3 | Non-standardized coefficients | Standardized coefficients | t | Sig. | CI 95% | Collinearity | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | Std. Error | Beta | Lower limit | Upper limit | Tol. | VIF | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Constant) | 9.69 | 1.07 | 9.06 | 0.000 | 7.593 | 11.796 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mood | −0.25 | 0.05 | −0.20 | −4.67 | 0.000 | −0.365 | −0.149 | 0.93 | 1.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uncontrolled eating | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 3.83 | 0.000 | 0.040 | 0.123 | 0.90 | 1.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stress management | −0.11 | 0.05 | −0.08 | −1.96 | 0.050 | −0.228 | 0.000 | 0.90 | 1.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Fuentes, M.d.C.; Molero Jurado, M.d.M.; Simón Márquez, M.d.M.; Gázquez Linares, J.J. Analysis of Sociodemographic and Psychological Variables Involved in Sleep Quality in Nurses. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203846
Pérez-Fuentes MdC, Molero Jurado MdM, Simón Márquez MdM, Gázquez Linares JJ. Analysis of Sociodemographic and Psychological Variables Involved in Sleep Quality in Nurses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203846
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Fuentes, María del Carmen, María del Mar Molero Jurado, María del Mar Simón Márquez, and José Jesús Gázquez Linares. 2019. "Analysis of Sociodemographic and Psychological Variables Involved in Sleep Quality in Nurses" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203846
APA StylePérez-Fuentes, M. d. C., Molero Jurado, M. d. M., Simón Márquez, M. d. M., & Gázquez Linares, J. J. (2019). Analysis of Sociodemographic and Psychological Variables Involved in Sleep Quality in Nurses. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203846








