Spatio-Temporal Prediction for the Monitoring-Blind Area of Industrial Atmosphere Based on the Fusion Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Time Series Prediction Methods
2.2. Spatial Analysis of Atmospheric Environment
3. Fusion Network of Spatio-Temporal Prediction
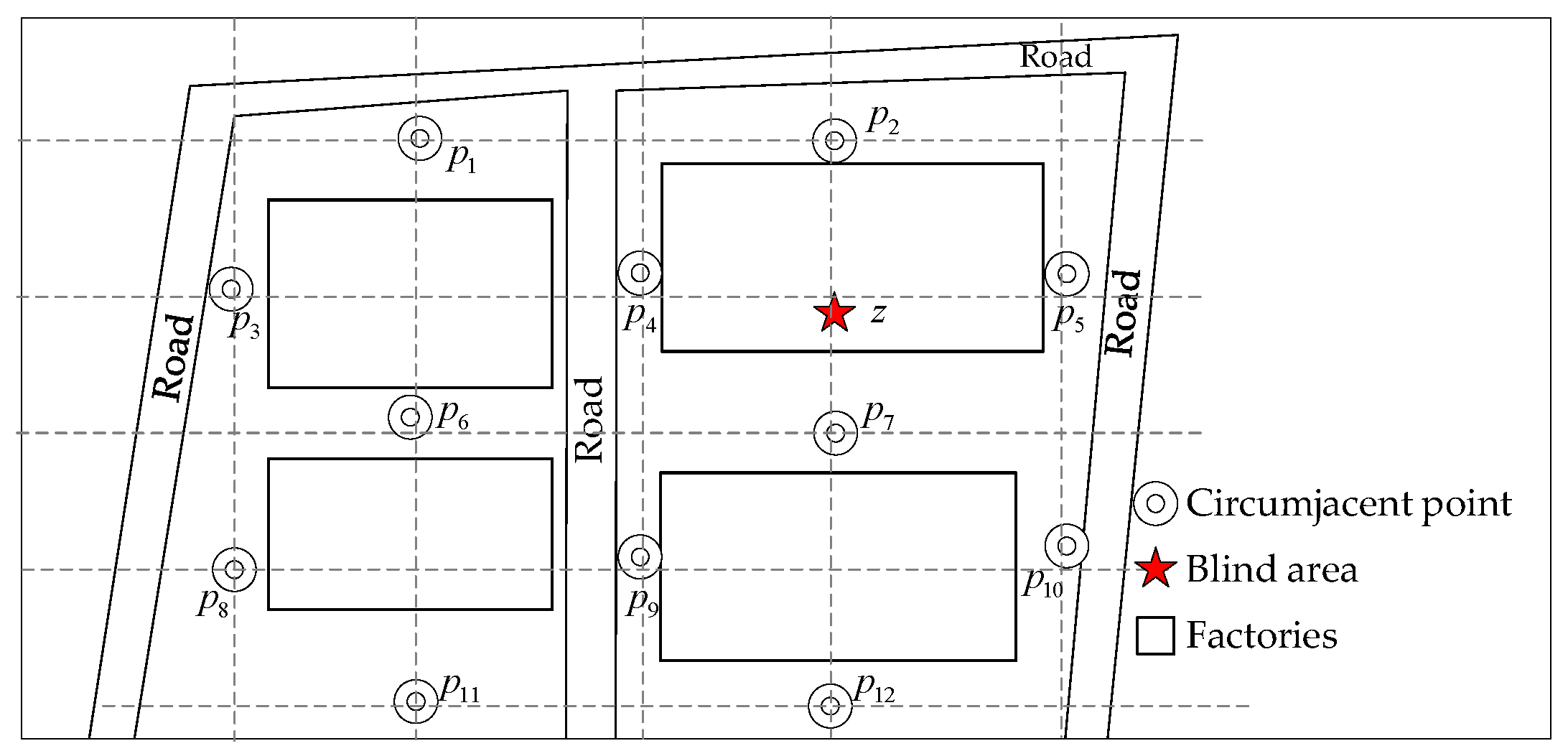
3.1. Problem Description
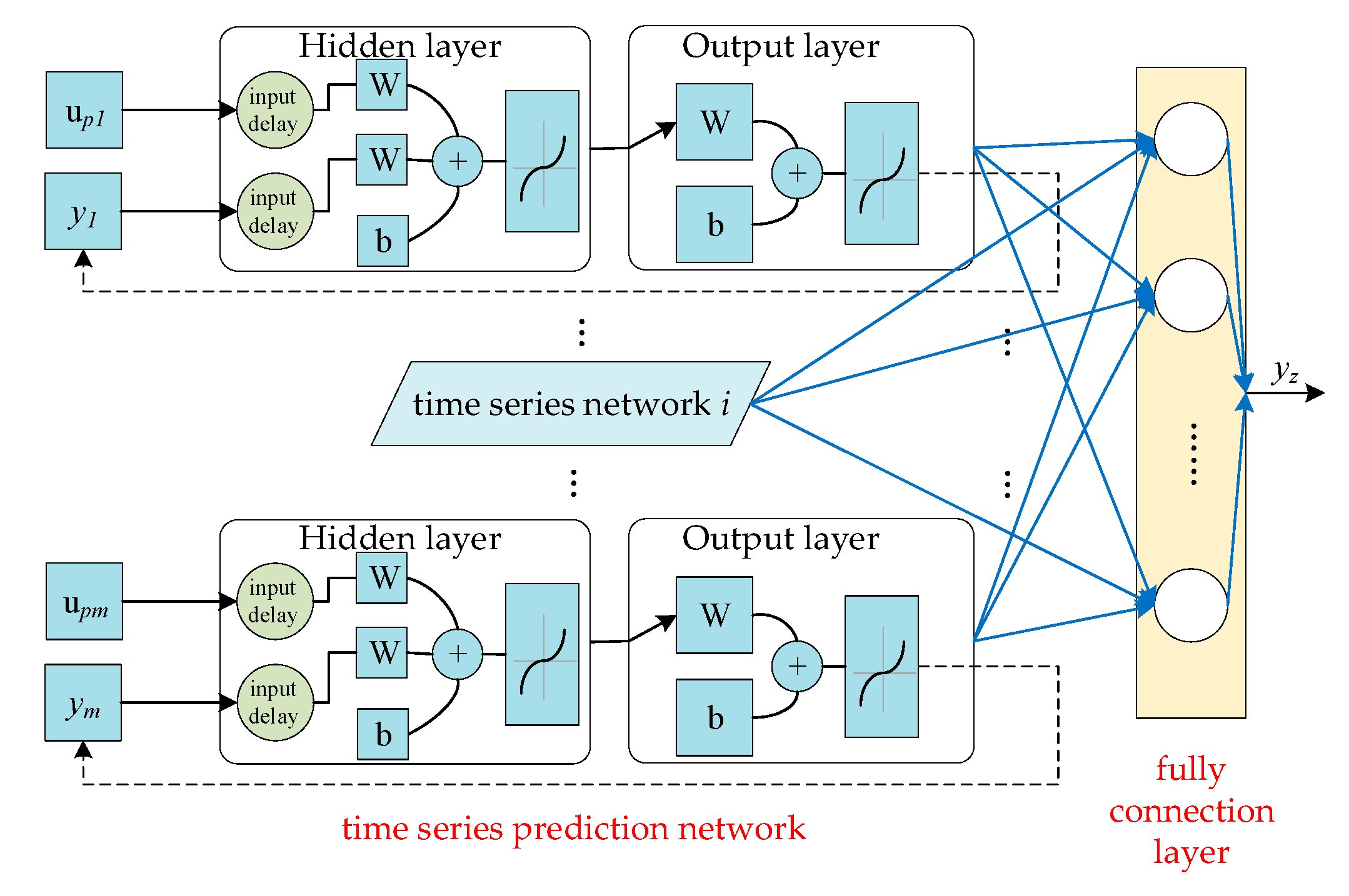
3.2. Fusion Network Framework
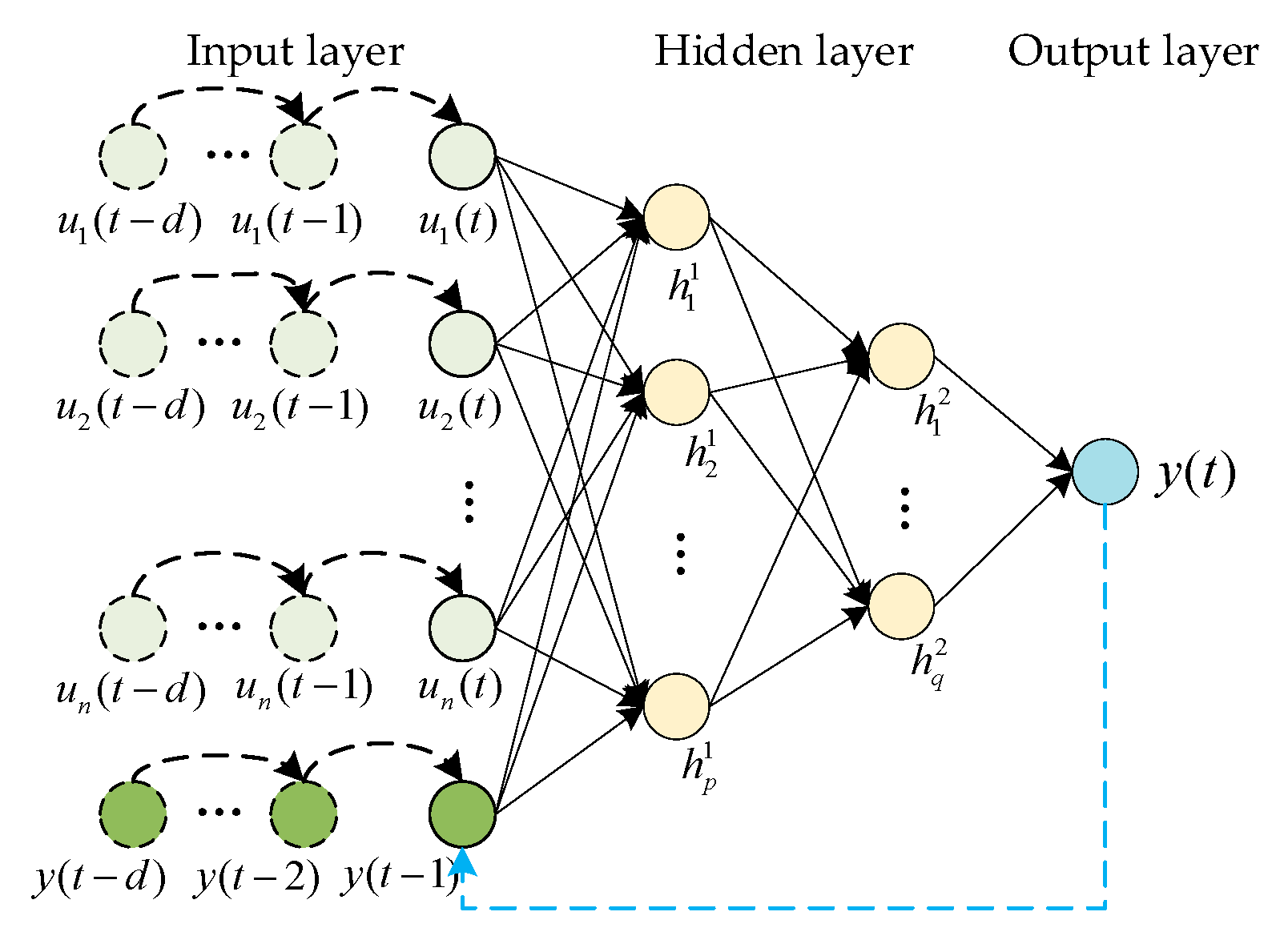
3.3. Time Series Prediction Model Based on NARX
3.4. Spatial Inference Model
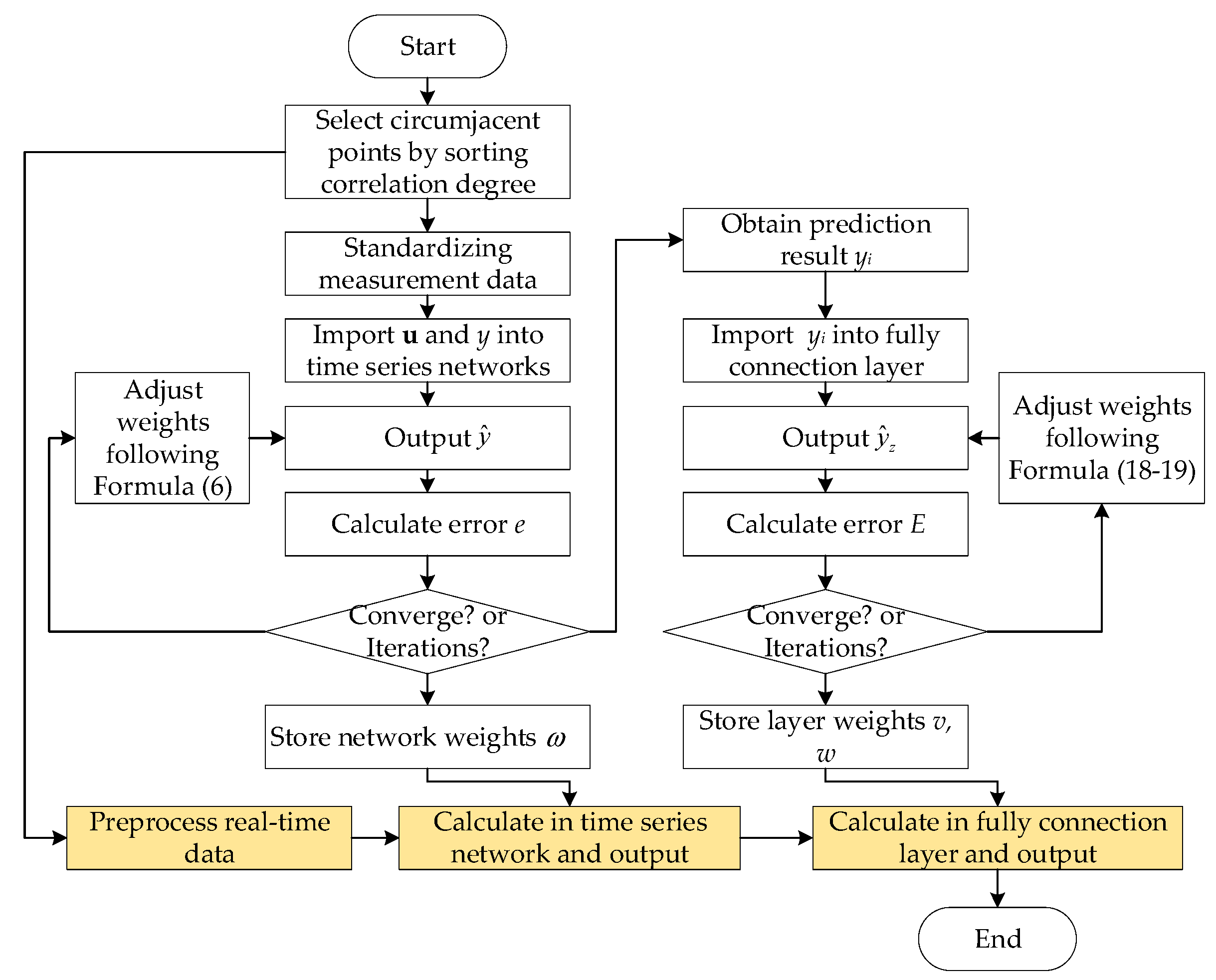
3.5. Spatio-Temporal Prediction Algorithm
4. Experiment and Result
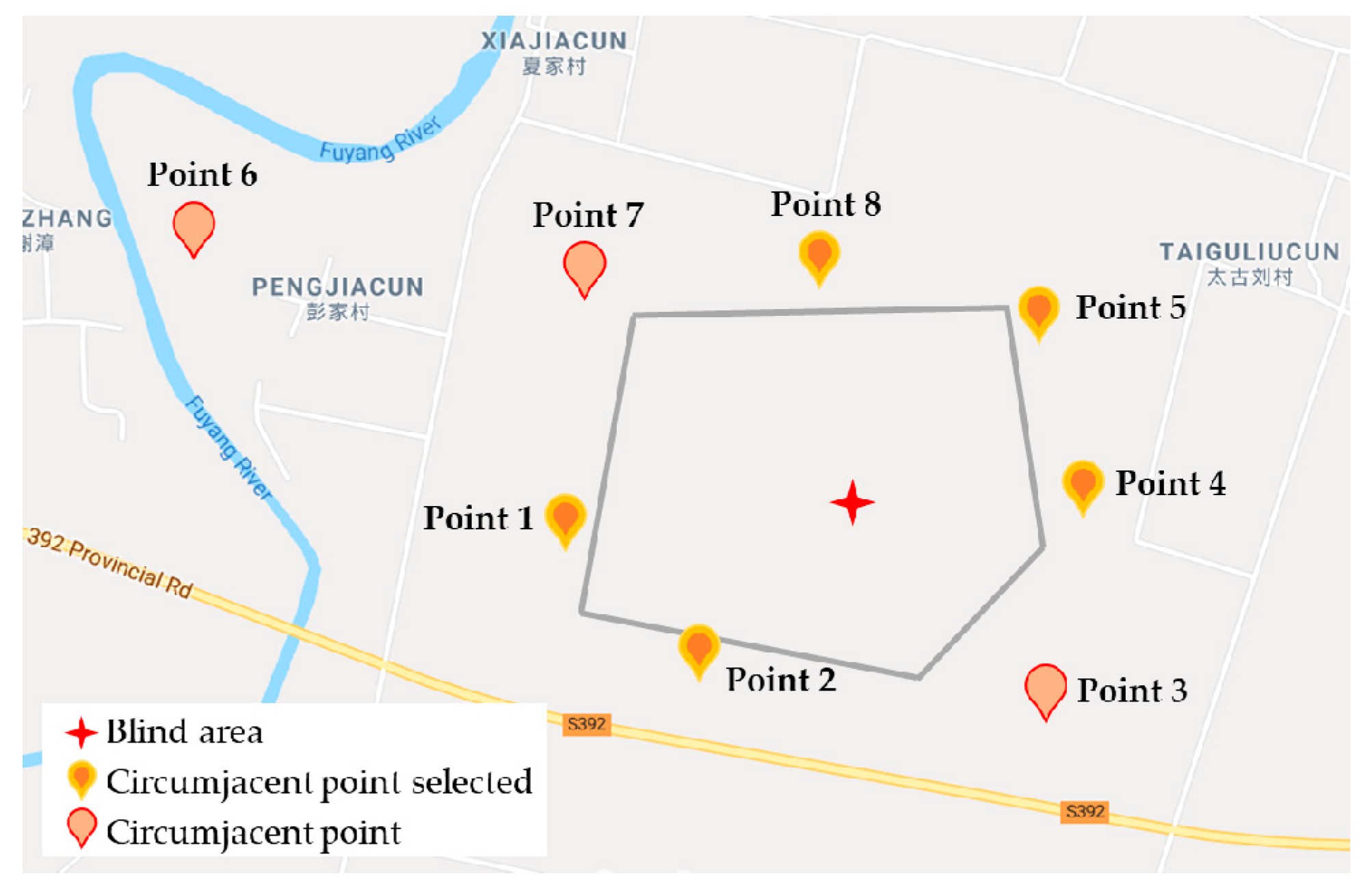
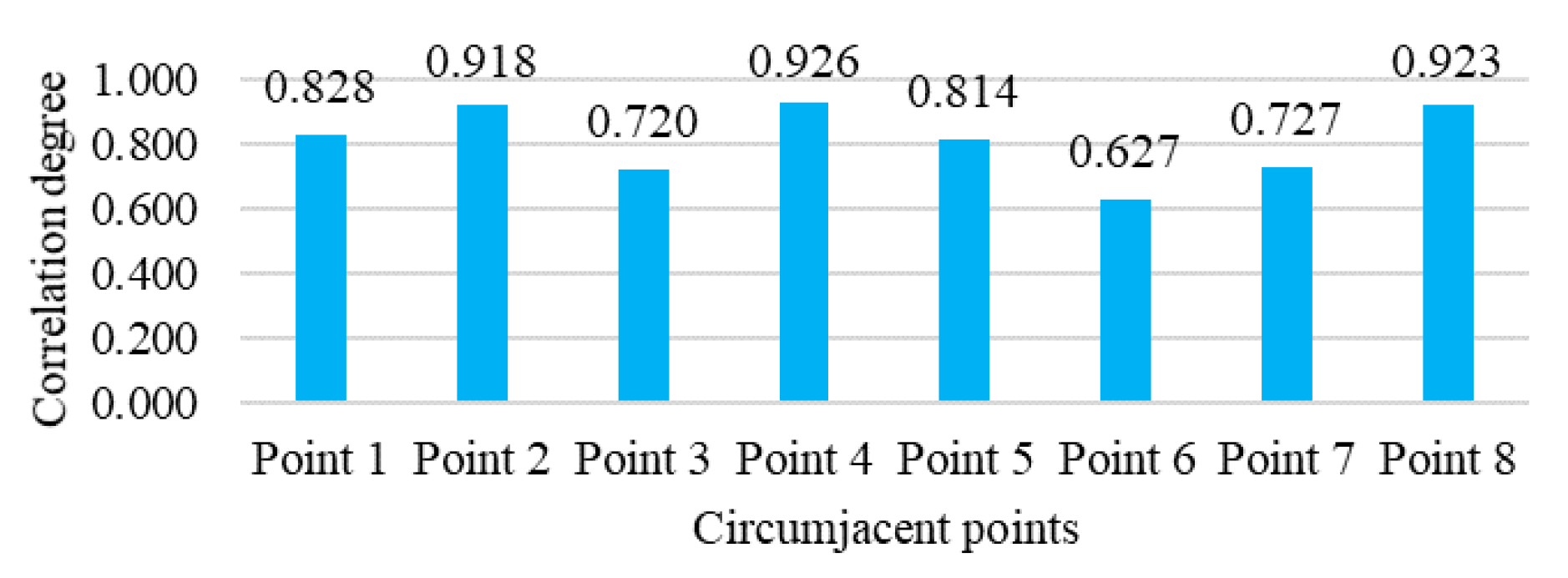
4.1. Experiment Data and Setting
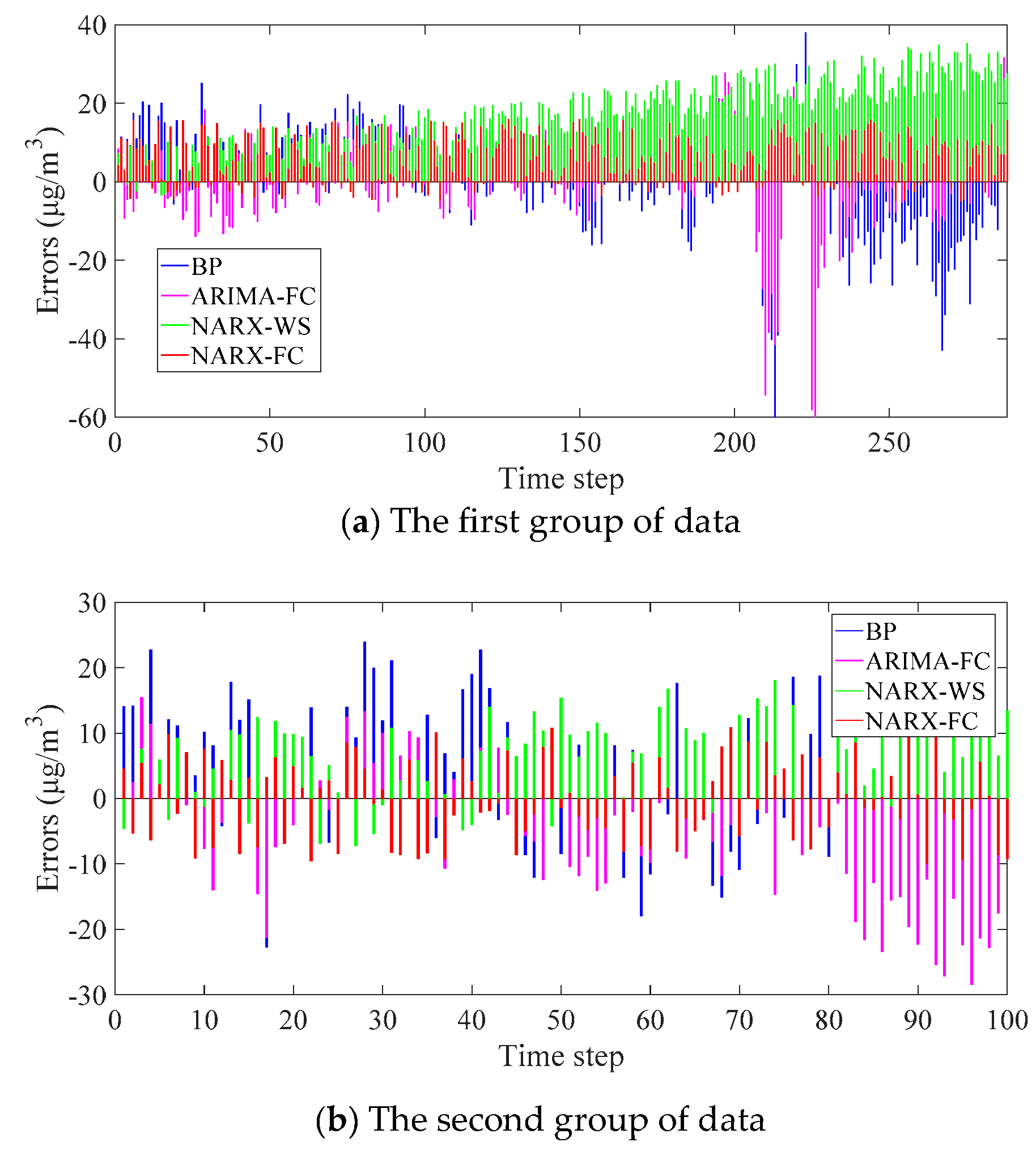
4.2. Experiment Result
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J. Study on VOCs in atmosphere and their sources of atypical industrial park in Shanghai. J. Shanghai Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2017, 46, 298–303. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Roy, G.; Hurley, W.J.; Andrews, W.S. Dispersion coefficients for Gaussian puff models. Bound. Layer Meteor. 2011, 139, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, R.; Lai, Y. Modification and application of gaussian plume model for an industrial transfer park. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 785–786, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Huang, L.; Ristic, B. Evaluation of Bayesian source estimation methods with Prairie Grass observations and Gaussian plume model: A comparison of likelihood functions and distance measures. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 152, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overcamp, T.J. An Exact solution for the ground-level gamma dose rate from a spherical Gaussian puff. Health Phys. 2016, 111, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; King, M.; Lu, Z.; Tjøstheim, D. Specification testing in nonlinear and nonstationary time series autoregression. Ann. Stat. 2009, 37, 3893–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chung, E.; Zhai, L. Fusing moving average model and stationary wavelet decomposition for automatic incident detection: Case study of Tokyo Expressway. J. Traff. Transp. Eng. 2014, 1, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Huang, C. Analysis of an adaptive time-series autoregressive moving-average (ARMA) model for short-term load forecasting. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 1995, 34, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, B.K. Statistical methodology: V. Time series analysis using autoregressive integrated moving average (ARIMA) models. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2014, 5, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eknath, K.G.; Muley, A.A.; Deshmukh, N.K.; Bhalchandra, P.U. Autoregressive integrated moving average time series model for forecasting air pollution in Nanded city, Maharashtra, India. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Xiao, B. Short-term cloud coverage prediction using the ARIMA time series model. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Pan, Z.; Bai, W. Review of time series prediction methods. Comput. Sci. 2019, 46, 21–28. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Botvinick, M.M.; Plaut, D.C. Short-term memory for serial order: A recurrent neural network model. Psychol. Rev. 2006, 113, 201–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Multi-dimensional recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Berlin, Germany, 9 September 2007; pp. 549–558. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Paliwal, K.K. Bidirectional recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Han, X.; Li, Q. Research on applied-information technology with PM2.5 generation and evolution model based on BP neural network. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1003, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, D.; Ji, D. Construction of air quality evaluation system based on FCM algorithm and BP neural network. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 7, 279–281. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, F.; Shen, L.; Mao, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Bao, Z. The humidity compensation for measurement systems of aerosol mass concentrations based on the PSO-BP neural network. Chin. J. Sens. Actuators 2017, 30, 360–367. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xin, R. A Study on Application of Neural Network Based on Genetic Optimization and Bayesian Regularization in Air Quality Prediction. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 1 July 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Yuan, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W. Tracking prediction model for PM2.5 hourly concentration based on ARMAX. J. Tianjin Univ. 2017, 50, 105–111. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yan, S.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Forecasting PM2.5 concentration using spatio-temporal extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications, Anaheim, CA, USA, 18 December 2016; pp. 950–953. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, G. A novel hybrid-Garch model based on ARIMA and SVM for PM2.5 concentrations forecasting. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Nieto, P.J.; García-Gonzalo, E.; Bernardo Sánchez, A.; Rodríguez Miranda, A.A. Air quality modeling using the PSO-SVM-based approach, MLP neural network, and M5 model tree in the metropolitan area of Oviedo (Northern Spain). Environ. Model. Assess. 2018, 23, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimpalee, S.U.; Beuscher, J.W.; Van, Z. Investigation of gas diffusion media inside PEMFC using CFD modeling. J. Power Sources 2006, 163, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y. Approach on pollution gases diffusion path of small spacing tunnel entrance based on CFD. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 580–583, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, T.G.; Christophersen, M.; Moldrup, P.; Kjeldsen, P. Relating landfill gas emissions to atmospheric pressure using numerical modelling and state-space analysis. Waste Manag. Res. 2003, 21, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykova, N.A.; Favorov, A.V.; Mironov, A.A. Hidden Markov models for evolution and comparative genomics analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.; Chen, G. Research on air quality of Chengdu city based on Gaussian diffusion model. J. Green Sci. Technol. 2017, 2, 45–47, 49. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Zhu, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, F. Research of air pollution diffusion problem based on Gaussian model. J. Fuyang Teach. Coll. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2016, 33, 12–16. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, J.M.P.; Guilherme, A.B. Long-term time series prediction with the NARX network: An empirical evaluation. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 3335–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Chu, H.J.; Hsiao, C.T. Integration of optimal dynamic control and neural network for groundwater quality management. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 1253–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Network | Time Series Network (for Each) | Full Connection Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Number of training times | 1100 | 1100 |
| Learning rate | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Convergence error | 0.002 | 0.002 |
| Input delay | 1:24 | \ |
| Output delay | 1:6 | \ |
| Number of inputs | 5 | 5 |
| Number of outputs | 1 | 1 |
| Number of first hidden neurons | 8 | 7 |
| Number of second hidden neurons | 4 | \ |
| Error Indicator | Validation Subset 1 | Validation Subset 2 | Validation Subset 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | 4.5683 | 4.9836 | 3.7342 |
| RMSE | 5.9634 | 6.0232 | 5.3427 |
| Data Subsets | Error Indicator | BP | ARIMA-FC | NARX-WS | NARX-FC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First group | MAE | 10.5835 | 9.0415 | 16.9133 | 7.1388 |
| RMSE | 14.5723 | 12.8278 | 18.9587 | 8.6520 | |
| Second group | MAE | 9.2676 | 8.4514 | 7.3071 | 5.3797 |
| RMSE | 11.2321 | 10.9401 | 8.9681 | 6.1651 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.-t.; Wang, X.-y.; Sun, Q.; Jin, X.-b.; Wang, X.-k.; Su, T.-l.; Kong, J.-l. Spatio-Temporal Prediction for the Monitoring-Blind Area of Industrial Atmosphere Based on the Fusion Network. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203788
Bai Y-t, Wang X-y, Sun Q, Jin X-b, Wang X-k, Su T-l, Kong J-l. Spatio-Temporal Prediction for the Monitoring-Blind Area of Industrial Atmosphere Based on the Fusion Network. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2019; 16(20):3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203788
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yu-ting, Xiao-yi Wang, Qian Sun, Xue-bo Jin, Xiao-kai Wang, Ting-li Su, and Jian-lei Kong. 2019. "Spatio-Temporal Prediction for the Monitoring-Blind Area of Industrial Atmosphere Based on the Fusion Network" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 16, no. 20: 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203788
APA StyleBai, Y.-t., Wang, X.-y., Sun, Q., Jin, X.-b., Wang, X.-k., Su, T.-l., & Kong, J.-l. (2019). Spatio-Temporal Prediction for the Monitoring-Blind Area of Industrial Atmosphere Based on the Fusion Network. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(20), 3788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16203788







